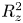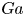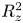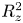376 results
Tunnels of power: The cultural politics of the Beijing subway
-
- Journal:
- Modern Asian Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 September 2024, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Solid bases and functorial constructions for (p-)Banach spaces of analytic functions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2024, pp. 1-32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Spatial–temporal distribution characteristics of pulmonary tuberculosis in eastern China from 2011 to 2021
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2024, e84
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prevalence of nontuberculous mycobacteria and the emergence of rare species in Henan Province, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2024, e92
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investigation of fermentation profiles, bacterial community structure and bacterial β-carotene synthesis of alfalfa silage treated with propionic acid or its combination with squalene
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 162 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, pp. 118-129
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Relationship between syncopal symptoms and head-up tilt test modes
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Lessons learned from implementing a diversity, equity, and inclusion curriculum for health research professionals at a large academic research institution
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2024, e22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Design and construction of the near-earth space plasma simulation system of the Space Plasma Environment Research Facility
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 90 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, 345900101
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Plasma Spectroscopy on Hydrogen-Carbon-Oxygen Foam Targets Driven by Laser-Generated Hohlraum Radiation
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cross-Section Measurements of the 11B(p,α)2α Reaction near the First Resonant Energy
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Alkylammonium-Intercalated Vermiculites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 65 / Issue 6 / December 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 378-386
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Artificial Selection Drives SNPs of Olfactory Receptor Genes into Different Working Traits in Labrador Retrievers
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e77
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Generation of energetic electrons by an electron cyclotron wave through stochastic heating in a spherical tokamak
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 November 2023, 905890603
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Wave statistics and energy dissipation of shallow-water breaking waves in a tank with a level bottom
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2023, A25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the settling of aligned spherical particles in various quiescent media
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, R1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Gray matter atrophy is constrained by normal structural brain network architecture in depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 7 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 1318-1328
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Enhancing bipolar disorder treatment among employed college students through the integration of civic education and lamotrigine: a context of educational psychology
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, p. S38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Three-dimensional wake transitions of steady flow past two side-by-side cylinders
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, A17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Decoding anxiety–impulsivity subtypes in preadolescent internalising disorders: findings from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development study
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 223 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2023, pp. 542-554
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation