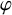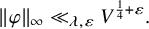2336 results
A governance and legal framework for getting to “yes” with enterprise-level data integration
-
- Journal:
- Data & Policy / Volume 6 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2024, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Suction Responses Due to Homogeneous Shear of Dilute Montmorillonite-Water Pastes
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 14 / February 1966
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2024, pp. 307-316
-
- Article
- Export citation
Theta functions, fourth moments of eigenforms and the sup-norm problem II
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Pi / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2024, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Critical left main coronary artery stenosis presenting as cardiac arrest in coarctation of the aorta patient
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2024, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
P.009 Long-term comparative efficacy of inebilizumab from N-MOmentum participants versus azathioprine and immunosuppressants and placebo in NMOSD patients
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, pp. S16-S17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P.010 Safety and efficacy of inebilizumab in AQP4+ NMOSD participants with history of immunosuppression treatment prior to N-MOmentum study
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P.047 Survey of caregivers of individuals with NBIAs to identify relevant quality of life outcomes
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Sex-dependent differences in vulnerability to early risk factors for posttraumatic stress disorder: results from the AURORA study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The effects of dairy on the gut microbiome and symptoms in gastrointestinal disease cohorts: a systematic review
-
- Journal:
- Gut Microbiome / Volume 5 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2024, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Methylation profiles at birth linked to early childhood obesity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 15 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
21 - Gender–Sexuality Alliances
- from Part VI - Education and Engaged Research
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Community Empowerment
- Published online:
- 18 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 25 April 2024, pp 532-555
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Comment on: Fürsich et al., 2023, Miocene instead of Jurassic: the importance of sound fieldwork for paleontological data analysis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
50 Why are Black and Mexican American children more vulnerable than White children to upper respiratory viral infection?
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Shale Diagenesis in the Bergen High Area, North Sea
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 37 / Issue 2 / April 1989
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 97-112
-
- Article
- Export citation
Head and Neck Cancer: United Kingdom National Multidisciplinary Guidelines, Sixth Edition
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue S1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2024, pp. S1-S224
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Regional impact of multidrug-resistant organism prevention bundles implemented by facility type: A modeling study
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Japan at War in the Pacific: The Rise and Fall of The Japanese Empire in Asia 1868–1945 By Jonathan Clements. 351 pp. Rutland, VT, Tuttle Publishing, 2022.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2024, pp. 477-480
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
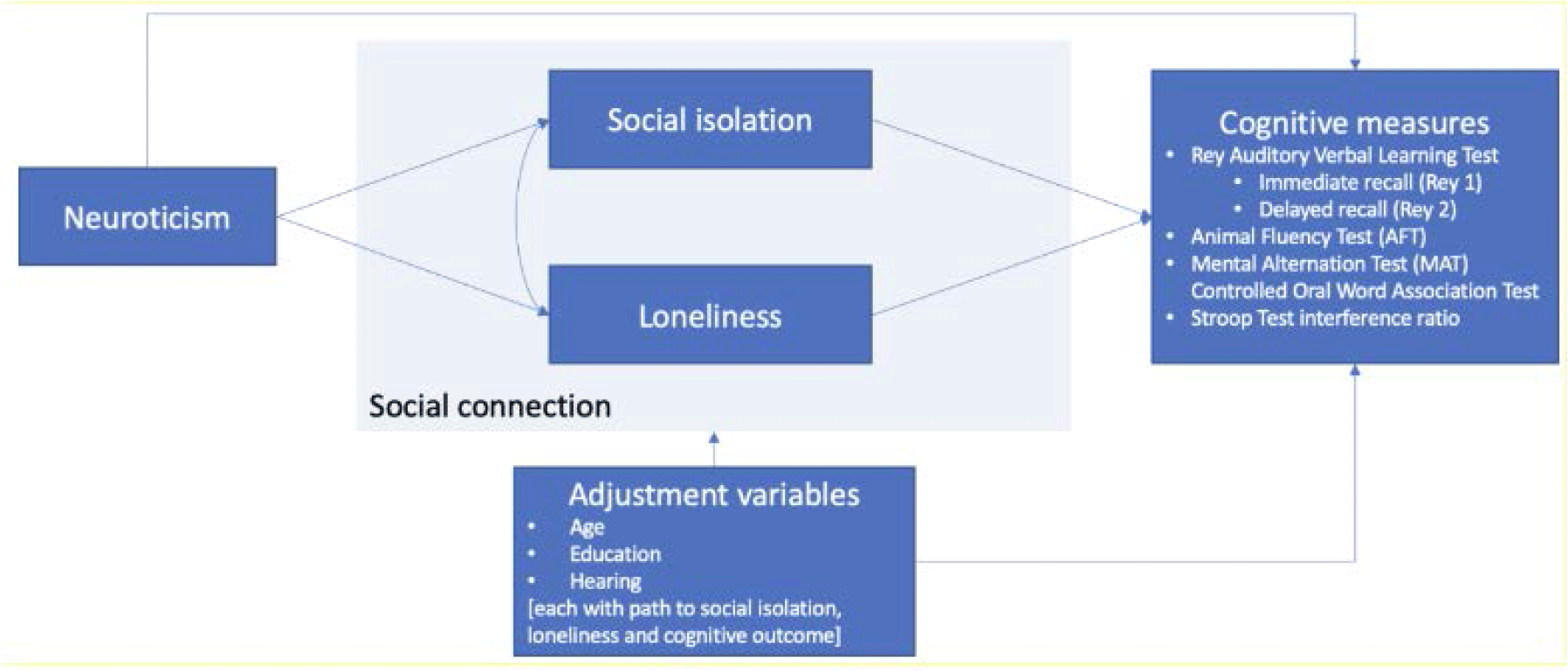
FC30: The relationships between neuroticism, social connection and cognition
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 92-94
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A five-year quasi-experimental study to evaluate the impact of empiric antibiotic order sets on antibiotic use metrics among hospitalized adult patients
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 609-617
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mineralogical and Elemental Trends in Regolith on Historically Managed Sites in the southeastern United States Piedmont
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 539-554
-
- Article
- Export citation