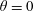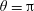38 results
Protective factors for children with autism spectrum disorder during COVID-19-related strict lockdowns: a Shanghai autism early developmental cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 6 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2023, pp. 1102-1112
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Exotic flotation theory with new method for floating stability analysis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 973 / 25 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 October 2023, A25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Static and dynamic stability of pendant drops
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 968 / 10 August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2023, A30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of gravity on natural oscillations of sessile drops
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 962 / 10 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2023, A10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Surface tension force on a partially submerged horizontal concave cylinder
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 950 / 10 November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 October 2022, A15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 13 - The History of Psychological Testing in East Asia
-
-
- Book:
- International Histories of Psychological Assessment
- Published online:
- 28 July 2022
- Print publication:
- 11 August 2022, pp 236-251
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Knowledge Hiding and Hider's Innovative Behavior in Chinese Organizations: The Mediating Role of Silence Behavior and the Moderating Role of Zhongyong Thinking
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review / Volume 18 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2022, pp. 491-518
-
- Article
- Export citation
Perceived Parental Care and Next-Generation Family Members’ Succession Intentions: The Sequential-Mediating Role of General Self-Efficacy and Perceived Person-Job Fit
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review / Volume 18 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 November 2021, pp. 319-357
-
- Article
- Export citation
Schistosomiasis in the People's Republic of China – down but not out
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 149 / Issue 2 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2021, pp. 218-233
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Middle Miocene climate transition in the Tibetan Plateau: identification and significance
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2021, pp. 153-172
-
- Article
- Export citation
Compact multimode-resonator multiplexer with wide upper-stopband and high isolation
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 13 / Issue 2 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2020, pp. 111-118
-
- Article
- Export citation
Corticolimbic brain anomalies are associated with cognitive subtypes in psychosis: A longitudinal study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 63 / Issue 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2020, e40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
General exotic capillary tubes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 885 / 25 February 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 December 2019, A1
-
- Article
- Export citation
Capillary surfaces in and around exotic cylinders with application to stability analysis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 882 / 10 January 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 November 2019, A28
-
- Article
- Export citation
Indentation size effect in aqueous electrophoretic deposition zirconia dental ceramic
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2019, pp. 555-562
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fluorescence and phase transitions of Mg-Al-Eu ternary layered double hydroxides – dependence on annealing
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 46 / Issue 3 / September 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 July 2018, pp. 487-493
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of surface tension on a floating body in two dimensions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 847 / 25 July 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2018, pp. 489-519
-
- Article
- Export citation
Consumption of preserved egg, a high-lead-containing food, is strongly associated with depressive symptoms in Chinese adults
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 118 / Issue 9 / 14 November 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2017, pp. 737-742
- Print publication:
- 14 November 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Differential protein analysis of serum exosomes post-intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in patients with Kawasaki disease
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 27 / Issue 9 / November 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2017, pp. 1786-1796
-
- Article
- Export citation