93 results
234 Translation of Community Engagement Studios into Practice: Increased Research Participation and Diversity in a Multicenter Trial
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, pp. 70-71
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Using 4D-STEM to Track Structural Changes Due to Electrochemical Doping in Organic Electrochemical Transistors
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 2256-2257
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Altered neurodevelopmental DNA methylation status after fetal growth restriction with brain-sparing
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 13 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, pp. 378-389
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Modeling spatially distributed snow instability at a regional scale using Alpine3D
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 67 / Issue 266 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2021, pp. 1147-1162
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
How the space environment influences organisms: an astrobiological perspective and review
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Astrobiology / Volume 20 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 March 2021, pp. 159-177
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) cycle threshold and Clostridioides difficile infection outcomes
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 42 / Issue 10 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 February 2021, pp. 1228-1234
- Print publication:
- October 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Toddler milk perceptions and purchases: the role of Latino ethnicity
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 10 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 January 2021, pp. 2911-2919
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation influences mood in healthy male volunteers
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 26 / Issue S2 / March 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. 1155
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
An overlapping pattern of cerebral cortical thinning is associated with both positive symptoms and aggression in schizophrenia via the ENIGMA consortium
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 12 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 October 2019, pp. 2034-2045
-
- Article
- Export citation
Summer ice dynamics during SHEBA and its effect on the ocean heat content
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Glaciology / Volume 33 / 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2017, pp. 201-206
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Drug-related problems in community-dwelling primary care patients screened positive for dementia
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 29 / Issue 11 / November 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 August 2017, pp. 1857-1868
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Restart capability of resting-states of Euglena gracilis after 9 months of dormancy: preparation for autonomous space flight experiments
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Astrobiology / Volume 17 / Issue 2 / April 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 May 2017, pp. 101-111
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prefrontal cortical thinning links to negative symptoms in schizophrenia via the ENIGMA consortium
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 48 / Issue 1 / January 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2017, pp. 82-94
-
- Article
- Export citation
Early life risk exposure and stunting in urban South African 2-year old children
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 8 / Issue 3 / June 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2017, pp. 301-310
-
- Article
- Export citation
Experience With Rapid Microarray-Based Diagnostic Technology and Antimicrobial Stewardship for Patients With Gram-Positive Bacteremia
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 37 / Issue 11 / November 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2016, pp. 1361-1366
- Print publication:
- November 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Genomewide Association Study of Nicotine and Alcohol Dependence in Australian and Dutch Populations
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 13 / Issue 1 / February 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 January 2016, pp. 11-29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Dimensional structure of bodily panic attack symptoms and their specific connections to panic cognitions, anxiety sensitivity and claustrophobic fears
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 45 / Issue 8 / June 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 December 2014, pp. 1675-1685
-
- Article
- Export citation
Adipose-derived stromal cells for osteoarticular repair: trophic function versus stem cell activity
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 16 / 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2014, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Jurassic to Early Cretaceous postaccretional sinistral transpression in north-central Chile (latitudes 31–32°S)
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 149 / Issue 2 / March 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2011, pp. 208-220
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inner composition, defects and morphology of AlGaAs nanowires grown by Au-catalyzed MOVPE
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 1350 / 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 July 2011, mrss11-1350-ee06-02
- Print publication:
- 2011
-
- Article
- Export citation



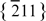 and {110} planes as the slowest to grow. The NWs have free-electron concentrations ∼10
and {110} planes as the slowest to grow. The NWs have free-electron concentrations ∼10