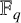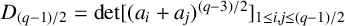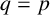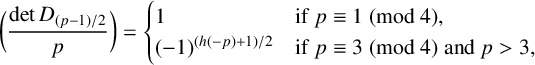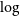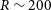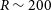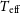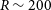333 results
ON GENERALISED LEGENDRE MATRICES INVOLVING ROOTS OF UNITY OVER FINITE FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Macrolide-Resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Several Regions of China from 2013 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The Role of the Cytochrome P450 Superfamily in the Skin
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Trauma diagnostic-related target proteins and their detection techniques
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 26 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Alexithymia and peer victimisation: interconnected pathways to adolescent non-suicidal self-injury – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2024, e65
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fixed-time anti-saturation control with concise system structure for the 6-DOF motion of spacecraft
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2024, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
- Export citation
Alexithymia and peer victimisation: interconnected pathways to adolescent non-suicidal self-injury
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2024, e46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Smoothed particle hydrodynamics modelling of particle-size segregation in granular flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 977 / 25 December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 January 2024, A47
-
- Article
- Export citation
Clinical parameter-based prediction model for neurosyphilis risk stratification
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association between the PLTP rs4810479 SNP and Serum Lipid Traits in the Chinese Maonan and Han Populations
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fabrication and Optimization Design of Multilayer Flyer Plates for Laser-Driven Loading
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Preparation of Organo-Montmorillonites and the Relationship Between Microstructure and Swellability
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 65 / Issue 6 / December 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 417-430
-
- Article
- Export citation
Photo-assisted Catalytic Removal of NOx Over La1–xPrxCoO3/Palygorskite Nanocomposites: Role of Pr Doping
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 348-356
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Compact High-Power Ultra-Wideband Bipolar Pulse Generator
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compact Thomson Scattering Source Based on a Mixed Injection Assisted Laser Wakefield Accelerator
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Model of a 5-MA Linear-Transformer-Driver Accelerator: Comparison of MITL Performance for Bremsstrahlung Electron Beam Diodes and Z-Pinch Loads
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
82 Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback for Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, p. 184
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Strategies and rules for tuning TCR-derived therapy
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 26 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Estimating stellar parameters and identifying very metal-poor stars for low-resolution spectra (R ∼ 200)
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 November 2023, e002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association between micronutrients intake and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: a cross-sectional study based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Nutritional Science / Volume 12 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2023, e117
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation