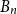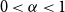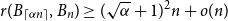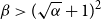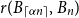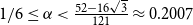207 results
Karenia mikimotoi induced adverse impacts on abalone Haliotis discus hannai in Fujian coastal areas, China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 104 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, e47
-
- Article
- Export citation
Workshop for the protection of Chinese giant salamanders
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Turbulence spreading effects on the ELM size and SOL width
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 90 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2024, 905900117
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On a conjecture of Conlon, Fox, and Wigderson
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2024, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
- Export citation
Synthetic Zeolites Derived from Fly Ash as Effective Mineral Sorbents for Diesel Fuel Spill Remediation
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 64 / Issue 5 / October 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 552-559
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Surface Modification of Zeolite 4A and Its Effect on the Water-Absorption Capability of Starch-G-Poly (Acrylic Acid) Composite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 62 / Issue 3 / June 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 211-223
-
- Article
- Export citation
Brain functional changes across mood states in bipolar disorder: from a large-scale network perspective
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 4 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2023, pp. 763-774
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Changes in the basic structure and strength deterioration of clay minerals with different hydration degrees
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 58 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 October 2023, pp. 324-333
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nanosecond laser conditioning of multilayer dielectric gratings for picosecond–petawatt laser systems
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, e89
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Measurements of plasma density profile evolutions with a channel-guided laser
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2023, e85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Factual and counterfactual learning in major adolescent depressive disorder, evidence from an instrumental learning study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2023, pp. 256-266
-
- Article
- Export citation
Integrating medical rules to assist attention for sleep apnea detection
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
High-power 1560 nm single-frequency erbium fiber amplifier core-pumped at 1480 nm – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2023, e16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Single-frequency upconverted laser generation by phase summation
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2023, e18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
High-energy, hundred-picosecond pulsed 266 nm mid-ultraviolet generation by a barium borate crystal
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2023, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Persistent eutrophication and hypoxia in the coastal ocean
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Coastal Futures / Volume 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2023, e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Is early time to positivity of blood culture associated with clinical prognosis in patients with Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infection?
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2023, e43
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
High-power 1560 nm single-frequency erbium fiber amplifier core-pumped at 1480 nm
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2023, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The effects of visitor density on sika deer (Cervus nippon) behaviour in Zhu-Yu-Wan Park, China
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 19 / Issue 1 / February 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 61-65
-
- Article
- Export citation
Improved modelling of interfacial terms in the second-moment closure for particle-laden flows based on interface-resolved simulation data
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 952 / 10 December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2022, A25
-
- Article
- Export citation