277 results
Influence of pH on the Hydrothermal Synthesis of Al-Substituted Smectites (Saponite, Beidellite, and Nontronite)
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 71 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2024, pp. 539-558
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluating the Minority Candidate Penalty with a Regression Discontinuity Approach
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Political Science , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
3 Mobile Toolbox: Enrollment of a Large Normative Sample Using the UCSF Brain Health Registry
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 781-782
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
1 - Shock
- from Section 1 - General Critical Care
-
-
- Book:
- Practical Emergency Resuscitation and Critical Care
- Published online:
- 02 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 23 November 2023, pp 3-14
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Development, implementation, and dissemination of operational innovations across the trial innovation network
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2023, e251
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Increasing fibre intake in the UK: lessons from the Danish Whole Grain Partnership
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 672-685
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Decentralized clinical trials in the trial innovation network: Value, strategies, and lessons learned
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2023, e170
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Empower: Design of a digital intervention for workplace stress and mental health. A European study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S160-S161
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
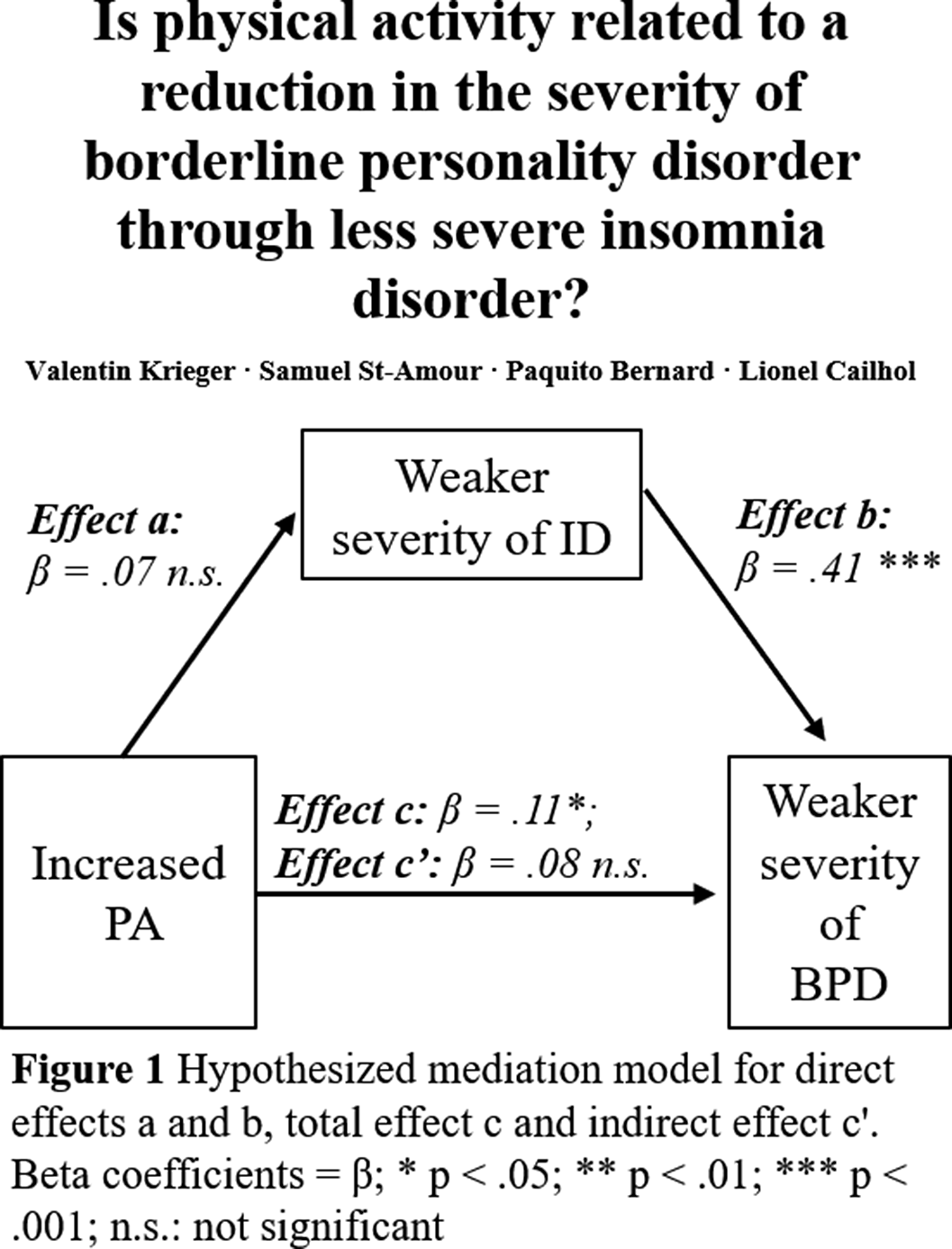
Is physical activity related to a reduction in the severity of borderline personality disorder through less severe insomnia disorder?
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S1002-S1003
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Picking up the pieces: Lessons learned about optimal public health and acute-care hospital collaboration during pandemics
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2023, e125
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Psychopathology as dynamic markers of alcohol initiation across development: A three-year longitudinal examination
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 March 2023, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Blue justice: A review of emerging scholarship and resistance movements
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Coastal Futures / Volume 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2023, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Second Nutrition and Cancer Networking Meeting Nutrition and Breast Cancer: Translating Evidence into Practice
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2022, pp. 58-62
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON THE NUMBER OF NEARLY SELF-CONJUGATE PARTITIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 108 / Issue 1 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 November 2022, pp. 114-119
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
9 - Considerations for First-Generation Students in Graduate School
- from Part II - Beginning your Career
-
-
- Book:
- The Portable Mentor
- Published online:
- 21 July 2022
- Print publication:
- 04 August 2022, pp 166-178
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
5 - Impostor Syndrome in Graduate School
- from Part II - Beginning your Career
-
-
- Book:
- The Portable Mentor
- Published online:
- 21 July 2022
- Print publication:
- 04 August 2022, pp 102-118
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Securely sharing DSMB reports to speed decision making from multiple, concurrent, independent studies of similar treatments in COVID-19
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 6 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2022, e49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Here Comes Everybody: Using a Data Cooperative to Understand the New Dynamics of Representation
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 55 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2022, pp. 300-302
- Print publication:
- April 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Significance of application timing, formulation, and cytochrome P450 genotypic class on sweet corn response to dicamba
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 70 / Issue 2 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 January 2022, pp. 167-173
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mars: new insights and unresolved questions – Corrigendum
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Astrobiology / Volume 21 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2022, p. 46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation