111 results
The amino acid sensor methionyl-tRNA synthetase is required for methionine-induced milk protein synthesis in a domestic pigeon model
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Imagined China: Research on Chinese Films in the 1980s By Wang Haizhou. Trans by Jin Haina. Abingdon: Routledge. 246 pages. Hardcover, £120.00 GBP, ISBN: 9781032254418. Paperback, £29.59, ISBN: 9781032254449. Ebook, £29.59, ISBN: 9781003283201.
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Asian Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2024, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
An improved wide-lane ambiguity resolution method for kinematic smartphone positioning
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 May 2024, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A comprehensive diagnostic system of ultra-thin liquid sheet targets
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ASYMPTOTICS FOR TIME-VARYING VECTOR MA(
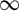 $\infty $) PROCESSES
$\infty $) PROCESSES
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2024, pp. 1-33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Alpha-Particle Generation from H-11B Fusion Initiated by Laser-Accelerated Boron Ions
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Laterite as a Potential Seepage Barrier From a Karst-Depression Tailings Impoundment
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Synthetic Zeolites Derived from Fly Ash as Effective Mineral Sorbents for Diesel Fuel Spill Remediation
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 64 / Issue 5 / October 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 552-559
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Rare Earth and Critical Element Chemistry of the Volcanic Ash-fall Parting in the Fire Clay Coal, Eastern Kentucky, USA
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 71 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 309-339
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Synchronous post-acceleration of laser-driven protons in helical coil targets by controlling the current dispersion
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2023, e51
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
High-energy, hundred-picosecond pulsed 266 nm mid-ultraviolet generation by a barium borate crystal
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2023, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Yellow River: A Natural and Unnatural History By Ruth Mostern. New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Press, 2021. xiii, 326 pp. ISBN: 9780300238334 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Asian Studies / Volume 81 / Issue 4 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 November 2022, pp. 759-761
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Not All Juices are the Same: The Superior Perception of and Preference for Florida Orange Juice
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Agricultural and Applied Economics / Volume 54 / Issue 4 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. 621-633
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Perturbations of graphs for Newton maps I: bounded hyperbolic components
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 43 / Issue 9 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2022, pp. 2997-3025
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association between hyperhomocysteinaemia and the risk of all-cause and cause-specific mortality among adults in the USA
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 July 2022, pp. 1046-1057
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The psychological outcomes of COVID-19 affected the pandemic-after risk perceptions of nurse clinicians: a latent profile analysis
-
- Journal:
- Global Mental Health / Volume 9 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2022, pp. 123-132
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Personal motivation, self-regulation barriers and strategies for weight loss in people with overweight and obesity: a thematic framework analysis
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 25 / Issue 9 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 February 2022, pp. 2426-2435
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dementia literacy and worry among older Chinese Americans in Arizona: a comparison between 2013 and 2017
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2021, pp. 43-53
-
- Article
- Export citation