Laetoli footprints: the relationship between the two individuals
For more on this topic, read the full article, Relationship between trackmakers of the Laetoli footprints from gait synchronization, by Wataru Nakahashi.…

For more on this topic, read the full article, Relationship between trackmakers of the Laetoli footprints from gait synchronization, by Wataru Nakahashi.…

Welcome to our “Meet the Editors” series, where we interview the editorial team about their work and their relationship to the journal.…

From 99 faecal samples we identified 21 species of intestinal parasites – everything from common worms to various protozoa and amoebae. Overall, seven in ten monkeys harboured at least one parasite, and Guinea baboons averaged nearly three different species apiece.
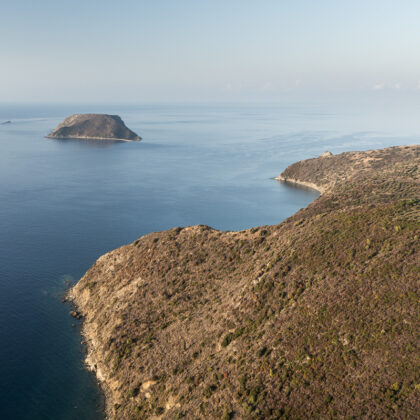

Several new hotspots have been identified in the past three decades, particularly in Italy, but none have approached the numbers observed at those three traditional sites. Up to now, the flyway connecting Greece with North Africa during post-breeding migration has been studied through observations from the island of Antikythira, located between southern Greece and Crete.
This study not only adds valuable information about Brazil’s overlooked parasite diversity but also challenges how we classify one of the most important groups of fish parasites. It’s a reminder that even in familiar waters, there's still a lot left to discover.

Since last year, Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems has published two additional papers related to bees and pollinator health and are celebrating World Bee Day with an update to their World Bee Day Collection.
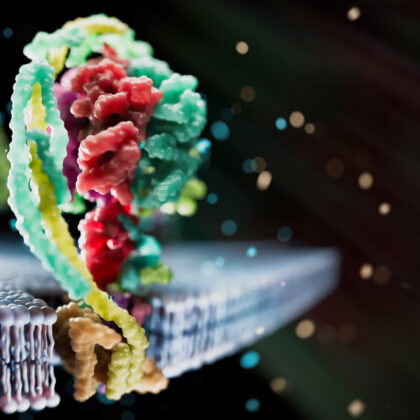

Metabolism, the intricate web of biochemical reactions that sustain life within cells, serves as the powerhouse driving essential cellular functions. At the heart of metabolism lies the provision of energy and building blocks crucial for the synthesis of macromolecules, vital for cellular structures, growth, and proliferation. This complex network comprises thousands of reactions catalysed by enzymes, involving an array of co-factors and metabolites.

Parasitology mark World Malaria Day 2025 and take a moment to reflect upon a few key articles and conference activities that contribute to and support the cause.
The microscopic parasite Strongyloides stercoralis infects millions of humans worldwide, often without symptoms. For years, the treatment of choice has been ivermectin, a drug that has been recognized for its use in combating diseases, such as river blindness. However, what is another option? Our recent study compared ivermectin to its lesser-known antiparasitic, moxidectin, and the results were promising.

The latest Paper of the Month for Bird Conservation International is The impact of storm-induced tree loss on the population of Wilkins’s Finch Nesospiza wilkinsi and is available as open access.…

I am very excited and extremely honoured to be the Joint Editor in Chief of Animal Welfare (AWF). Professor Bas RodenburgUtrecht University, The Netherlands Can you briefly explain the journal’s aims and scope?…

If left unchecked, both overabundant white-tailed deer populations and invasive shrubs like Amur honeysuckle (Lonicera maackii) can devastate deciduous native tree regeneration. Yet, a management strategy focused only on deer, or only on invasive shrubs, results in little or no forest health improvement, according to research from Ohio, spanning more than 10 years.

Beyond just the discovery of this invasive species on New Jersey shores, this study reveals the usefulness of reporting platforms like iNaturalist. Checking kilometers of coastline requires many hours of work – far beyond what is possible for an academic study. But through reporting of sightings, citizen scientists can provide a wealth of useful data. Indeed, since the publication of the paper, the beadlet anemone has now been found to the north in New York State. The colonists are spreading out.
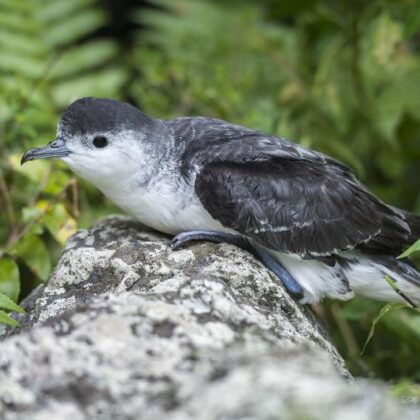

The latest Paper of the Month for Bird Conservation International is Tracking the non-breeding range of Rapa Shearwater Puffinus myrtae, a Critically Endangered seabird of the South Pacific Ocean and is available as open access.…

Until now, not much was known about the influence that nozzle type and application volume have on weed control efficacy with remotely piloted aerial application systems (RPAASs). However, new research shows that RPAAS applications using low-drift nozzles at low spray volumes (1.0–1.5 gallons/acre) can achieve weed control levels comparable to ground sprayer applications at 10 gallons/acre in turf.
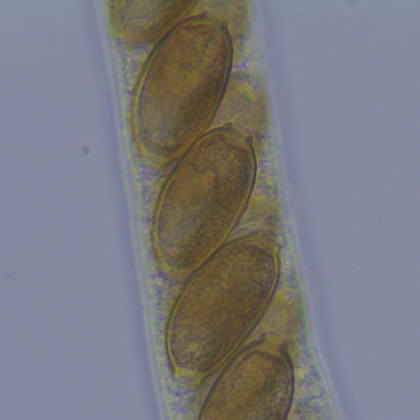
The parasite faunas of wood mice (Apodemus sylvaticus) and bank voles (Myodes glareolus) have often been studied by infectious disease ecologists and parasitologists.…

As World Water Day is celebrated around the globe, Cambridge University Press and its Prisms journals are leading the way in the fight to ensure a sustainable future for the World’s water resources.…
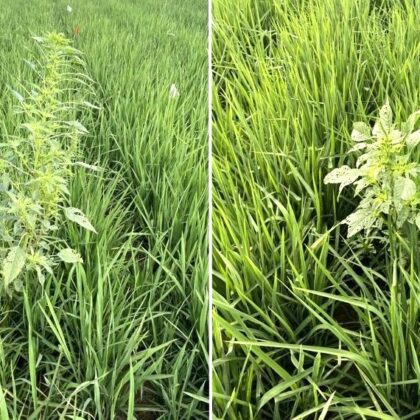

A recently published article in the journal Weed Science shows that successful, in-furrow rice production greatly hinges on Palmer amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri) weed pressure – before, during and after the growing season.

What does it take to make conservation work? If you thought funding and science were sufficient, think again. A new study by Brooks et al.…

The latest Paper of the Month for Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom is The longest documented travel by a West Indian manatee and is freely available for one month. …

Every year, an increasing proportion of scientific articles are published open access, which means they are fully available to all, rather than being hidden behind a subscription paywall. There are various reasons for this trend, but all are underpinned by the fact that publicly available research enables greater impact and visibility, while also increasing the accessibility of scientific knowledge.

A strategy utilizing both preemergence (PRE) and postemergence (POST) herbicide treatments optimized weed control outcomes in early planted soybean. Researchers conducted their study in 2021 at three locations across Central Illinois.

These studies, led or co-authored by women, published in Oryx, reinforce the essential role of female scientists in addressing global conservation challenges. As we celebrate this day, we recognise their dedication to shaping a sustainable future for our planet.

These studies, led or co-authored by women, reflect the vital role of female scientists in addressing pressing conservation challenges. As we celebrate this day, we recognise their commitment to safeguarding bird species and their habitats for future generations.

As we celebrate the incredible contributions of women in science, it’s time to make space for even more voices, ideas, and innovations. We encourage you to share your work by submitting to Quarterly Reviews in Biophysics or QRB Discovery. Your research can inspire others, break down barriers, and shape the future of science.
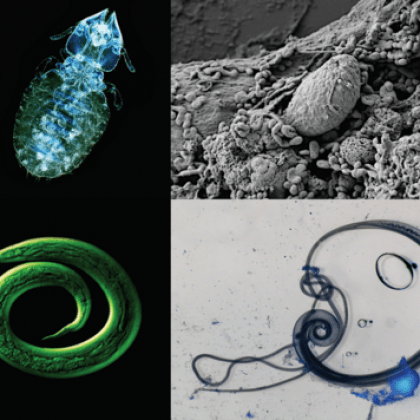
On 30th January, we celebrate World Neglected Tropical Diseases Day. This annual celebration highlights the hard work and achievements of the many researchers, medical workers, NGOs and other committed individuals in this field, and acts as a convenient forum to demand and sustain the necessary concerted actions to #BeatNTDs.…
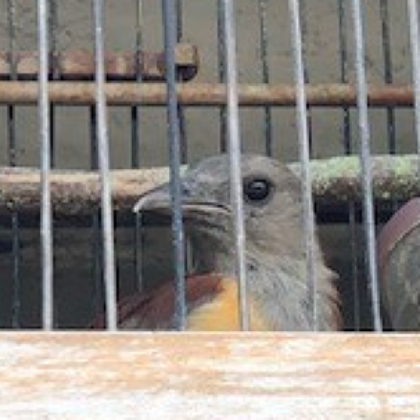

The latest Paper of the Month for Bird Conservation International is Poisonous pitohuis as pets and is available as open access. In our line of work, we come across new trends in the use of wildlife.…

Recent research shows promise for controlling herbicide-resistant weeds, such as waterhemp, in soybean fields by using a seed impact mill at harvest.

Stopping and reversing deforestation is a top priority across the tropics. Numerous policies and programs try to stem forest clearance, encourage tree planting, and restore forest landscapes.…

A recent study published in QRB Discovery sheds light on the impact of humidity on the infectivity of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, responsible for COVID-19 transmission. The study found that there was a notable decrease in the infection rate as the surrounding air's relative humidity increased.

Recently published research in the journal Weed Science shows planting soybean into a green, living cover crop effectively suppresses two problematic Amaranthus weed species – waterhemp and Palmer amaranth – when integrated with pre-emergence (PRE) herbicides.

December 5th is World Soil Day. Recommended by the International Union of Soil Sciences in 2002, the establishment of World Soil Day was led by the Kingdom of Thailand as part of the Global Soil Partnership—it was formally adopted by the UN General Assembly after endorsement by the FAO in December 2013.…
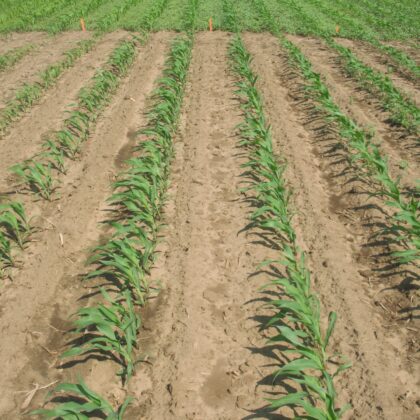

Diflufenican, a new mode of action herbicide for preemergence use in corn, demonstrates effectiveness as an integrated weed management strategy for multiple-herbicide resistant (MHP) waterhemp (Amaranthus tuberculatus) control. That’s the conclusion from a recently published research article in the journal Weed Technology, a journal of the Weed Science Society of America (WSSA)

We are delighted to announce that the new front cover image for Parasitology 2025 features the protist Trypanosoma cruzi, photograph taken by Ramiro Tomasina & Carlos Robello. This parasite is responsible for American trypanosomiasis or Chagas Disease in South America. It infects a wide range of mammalian hosts by stercorarian transmission from contaminated faeces of Reduviid bugs.

The scientific programme was very exciting. It allowed several leaders in this field to share their latest experiences and findings from their laboratories. In total, there were eight speakers representing universities across the UK, Ireland & Europe. With a larger international audience on site, speakers intermingled during lunch and break sessions for discussions and collaborative networking.

Farmers and land-managers looking to reduce their herbicide applications now have another promising option via machine-vision technology. That’s the summary from a recently published research article in Weed Technology, a journal of the Weed Science Society of America (WSSA).

My introduction to the fascinating world of parasites and Fasciola was accidental, or rather, a fluke! I met Professor John Dalton, the lead of the Molecular Parasitology Laboratory while working on a drug metabolism and hepatotoxicity project using HepG2 cell-derived spheroids at the Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics at the University of Galway. After several hours of parasite chat, I was hooked and embarked on a PhD migratory pathway!

To recognize World Toilet Day, Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems is featuring a series of four articles reviewing the use of human waste in agriculture. They investigate what drives growers to use human waste as a fertilizer supplement, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, along with the potential benefits and risks of such use. One study also looks at US growers’ perceptions of recycled water and municipally treated wastewater, including how different understandings impact risk and willingness of use.

Parasitology are Celebrating World Toilet Day 19th November 2024 Those that study parasitic diseases, particularly the soil-transmitted helminthiases and/or giardiasis, know that the enduring theme of the toilet and sanitation typically conjures up serious academic debate.…
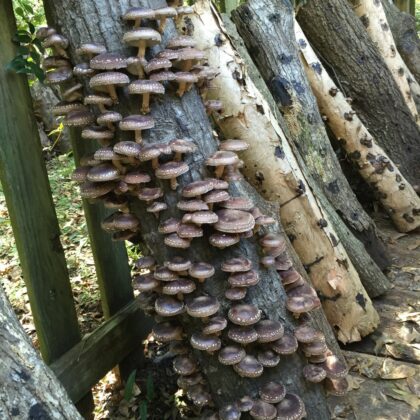

A new Weed Science Society of America research publication provides insights on repurposing an invasive tree species to produce edible mushrooms.

October 16th is World Food Day, commemorating the 1945 founding of the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). The Day also aims to raise awareness around the foundational issues impacting poverty and hunger around the world.…

In our 2024 paper, “Integrative Research of Mediterranean Climate Regions: A Global Call to Action“ we highlight the need for a collaborative, interdisciplinary approach to studying Mediterranean-climate regions.…

Welcome to our “Meet the Editors” series, where we interview the editorial team about their work and their relationship to the journal.…
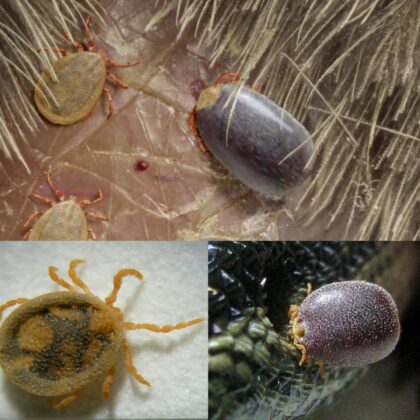

Before 1935, ticks were composed of the hard (Ixodidae) and soft (Argasidae) tick families. In 1931, Gerald Bedford described a peculiar tick species named Nuttalliella namaqua, which he considered a missing link between the two families, since it shared characteristics with both families.

Friday, August 9th was designated as the International Day of the World’s Indigenous Peoples in December of 1994 by the UN General Assembly resolution 49/214.…

Global sea surface temperatures are rising and have hit record high values in recent months. This potentially threatens seabirds, their prey and their habitats, both on land and at sea.

The latest Paper of the Month for Parasitology is First report of apparent praziquantel resistance in Dipylidium caninum in Europe and is freely available for one month. …
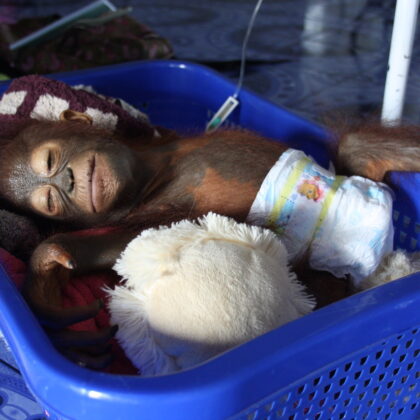

The latest Paper of the Month for Parasitology is ‘Naturally acquired immunity to Plasmodium pitheci in Bornean orangutans (Pongo pygmaeus)‘ and is freely available for one month. …

Considered among the “world’s worst” aquatic weeds, a northern hydrilla subspecies (lithuanica) hinders recreational activities by forming dense canopies.…

Recently published research in the journal Weed Science shows that drill-interseeded cover crops into vegetative growth stage 3 (V3) corn performs well in Northeast U.S. production regions.

Zhejiang University, in collaboration with Cambridge University Press, is launching the new journal - Animal Nutriomics - that covers all novel research on animal nutrition science from the perspective of genomics, especially in the fields of animal molecular nutrition, nutrition in animal health, nutritional regulation of genetics and epigenetics, nutrition-related omics, phenotype and metabolism.
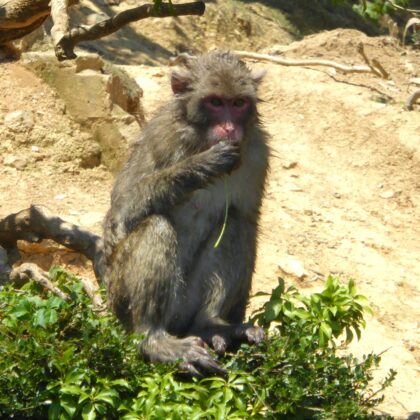

The paper “Novel insight into the genetic diversity of strongylid nematodes infecting South-East and East Asian primates” published in Parasitology is freely available to read online.…

Circadian rhythms are timekeeping mechanisms responsible for the cyclic repetition of metabolic, behavioural and psychological processes in all living organisms, typically over a 24-hour period.

Climate change could shift where invasive plant species establish hotspots, and certain U.S. states could be negatively impacted without a rapid response plan.

We would like to thank all our reviewers for their pro bono services to Parasitology in 2023, to our authors and to science in general.

This paper focuses on the biodiversity and ecology of specific trophically transmitted helminth endoparasites (TTHs) in Mediterranean Sea ecosystems.

Recently published research in the journal Weed Science provides new mechanistic insights into S-metolachlor resistance in waterhemp.

We investigate parasite guilds within and between squid cohorts. 318 squids were examined for metazoan parasites in the Patagonian continental shelf.
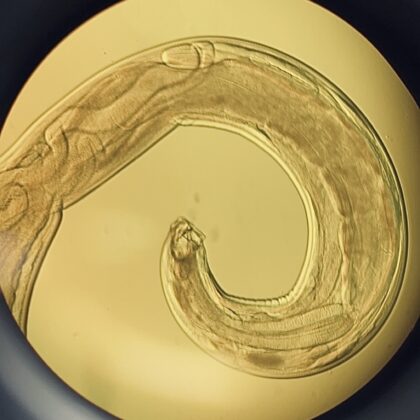
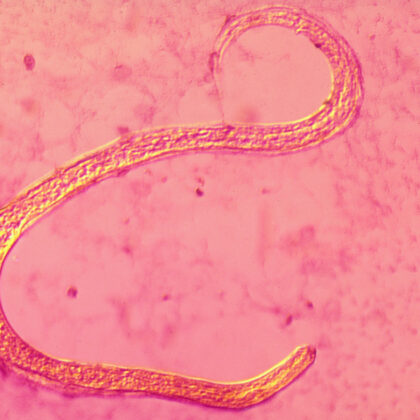
The hookworm A. ceylanicum doesn't infect mice but does to other animals. We hypothesized that the immune system is the deciding factor for hookworm infections.
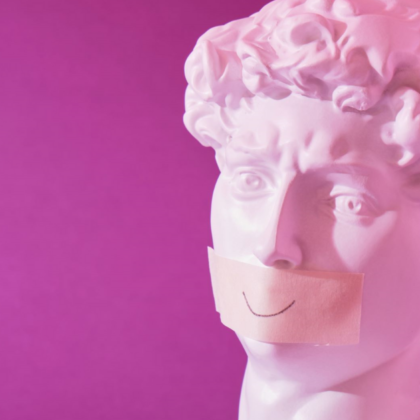

In support of Mariana Carrito and colleague’s article, When he smiles: Attractiveness preferences for male faces expressing emotions. Facial attractiveness has long been a subject of curiosity and study, with scientists attempting to unravel the complex factors that influence our perception of beauty.…

Identifying the factors that drive homicide rates is not only of paramount interest to scholars across the social and behavioral sciences but is necessary to inform policy decisions aimed at reducing lethal aggression. Studies nominate diverse causes of homicide, including ambient temperature, city greenness, firearm ownership, firearm laws, structural racism, income inequality, poverty, and more. However, without general theory scholars struggle to disentangle causal factors from correlated effects. This distinction is vitally important for designing interventions that target underlying causes rather than spurious correlations.
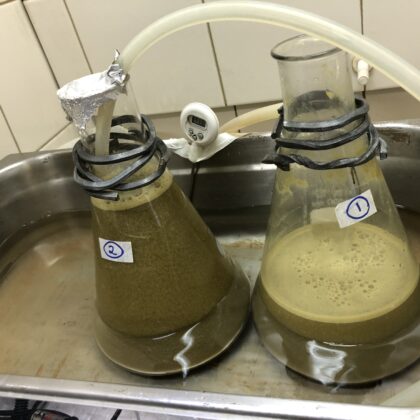

The increasing use of the in vitro gas production technique has created a greater scope for testing animal feeds. The rationale for this paper was the additional requirement of researchers in the field of feed evaluation to compare substrate treatment significance.
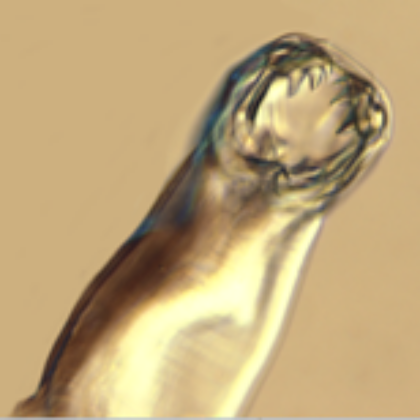

The journal Parasitology is delighted to announce the winner of this year's front cover competition.

Lactation, a minority period (15-19%) of the sow's productive cycle, is a period of maximum digestive and metabolic demand since in a few days (two weeks at most) the sow multiplies its production level by three.

Climate change is a big concern for wheat crop in Australia. We look at the relationship between weather parameters and grain number, yield and protein content.

This systematic review analyzed the diversity of metastrongyles in marine mammals and the host and parasite traits associated with virulence.

Lodgewood pine are weeds that quickly outcompete local flora. New Zealand has launched The National Wilding Conifer Management Programme to manage the problem.
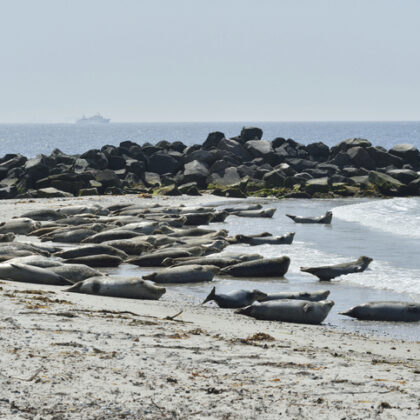

Parasitologists have discovered 2 cases of grey seals infected with heartworms in the North Sea.

In this work we show that LRR17, a secreted Leishmania protein never reported before, facilitates parasite attachment and internalization by the macrophage.

When Richard Burton and John Speke came across Lake Tanganyika in 1858 as the first Europeans, they had no idea what they had just discovered.

Prof Pier Luigi Nimis is an outstanding lichenologist and ecologist. To mark his 70th birthday, The Lichenologist published a Special Issue dedicated to him.

Is human cultural diversity partly shaped by the diversity of environments in which human societies live? Finding that a particular cultural feature is significantly associated with specific environmental variables adds weight to an argument that human diversity is shaped by environment. For example, many aspects of human cultural diversity have been found to correlate with parasite load, and these correlations have been interpreted as support for the hypothesis that cultures with high pathogen load develop features that limit the chance of infection, such as ritualized behaviours, xenophobia, belief in supernatural agents, and inclusion of antimicrobial ingredients in food.

Last month Cambridge University Press & Assessment (CUPA) announced the first sponsorship of a question in its innovative Research Directions: One Health journal.…

Challenging the popular but problematic 'Five Domains model' approach to categorising the experiences of animals in animal welfare science.
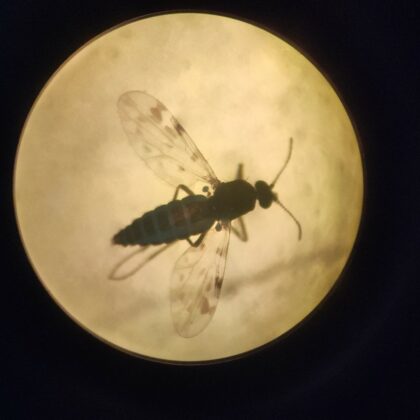

The Irish Society for Parasitology organises a vibrant annual meeting for parasitologists to come together and share their research and build collaborations.…

This research enhances our understanding of the Echinococcus granulosus complex and its impact on human health.

Researchers have developed a tool that can distinguish specimens of common reed reliably in the field, without time-consuming and costly genetic testing.

The latest Paper of the Month for Parasitology is “Rat lungworm (Angiostrongylus cantonensis) active larval emergence from deceased bubble pond snails (Bullastra lessoni) into water” and is freely available. …

As evolutionary human scientists, we care about causality. We usually want to know whether something causes something else, rather than whether things are just correlated. We want to know whether aspects of our culture, social structure or ecology cause a given behaviour, as opposed to being merely associated with it, for instance. Experiments are the gold standard for assessing causality, but for obvious reasons cannot answer everything, especially many of the evolutionary questions we’re interested in – Randomising infants to be raised as religious or not, for instance, would be both impossible and ethically questionable (to put it mildly!).
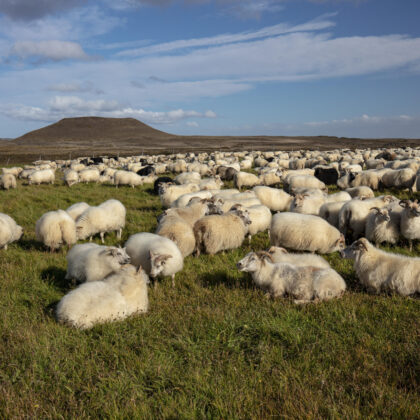

In Parasitology's latest article, we reveal the genetic identity for one of the last Echinococcus isolates in Iceland, obtained from a sheep 46 years ago.
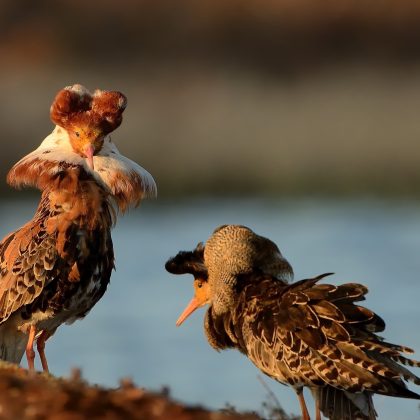

A new paper in BCI reveals that 38% of Europe’s 546 bird species are of conservation concern, including 14% of global concern.…

Professor Richard Kock, Editor-in-Chief of Research Directions: One Health, recently launched by Cambridge University Press, explains why a broad concept of health and well-being is essential.…

What is your current job title within Parasitology and what does it involve? Where are you based in the world? I’m the Publisher at Cambridge University Press for Parasitology.…

The latest Paper of the Month for Parasitology is Comparative transcriptomics from intestinal cells of permissive and non-permissive hosts during Ancylostoma ceylanicum infection reveals unique signatures of protection and host specificity and is freely available. …

Organically produced sweetpotato crops can be significantly more profitable than those grown in conventional production systems. But it’s not all smooth sailing. Growers know it can be tough to manage weed infestations in the absence of synthetic herbicides.

The latest Paper of the Month for Parasitology is “First report of eprinomectin-resistant isolates of Haemonchus contortus in dairy sheep farms in France“ and is freely available for one month. …

Martyn Dade-Robertson, Editor-in-Chief of Research Directions: Biotechnology Design, explains more about this emerging branch of science Can we grow a building?…

Buffelgrass is a highly invasive perennial that reduces the biodiversity of native ecosystems and provides ready fuel for wildfires in the arid regions where it thrives. After examining a decade of data from Arizona’s Saguaro National Park, researchers writing in the journal Invasive Plant Science and Management describe best practices for buffelgrass control.

The latest Paper of the Month for Parasitology is “Immunological mechanisms involved in macrophage activation and polarization in schistosomiasis” and is freely available.…

Professor Tomonori Totani of the University of Tokyo, Japan, answers our questions about his latest research article Solid grains ejected from terrestrial exoplanets as a probe of the abundance of life in the Milky Way in the International Journal of Astrobiology (IJA)

Q&A with Author Kostas Kampourakis about his upcoming Cambridge Festival event

When do parasites infect hosts? And does timing differ between separate host populations? Answers to these questions are fundamental to our understanding of host-parasite interactions and co-evolution. Yet often these aspects of host-parasite interactions are understudied.

Starting my PhD in 2020 on the conservation of Swedish parasitic freshwater mussels (Order: Unionida), I initially noted a lack of effort put into the study of what these mussels actually do to their hosts. If our goal is to increase the number of these mussels in our lakes and rivers, this will inevitably have some downstream impact on their host fishes.
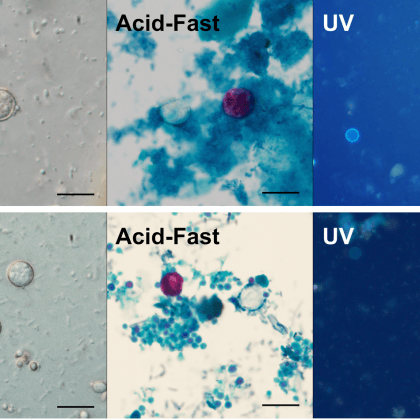
Despite its impact on United States (US) food safety since the 1990’s, efforts to understand Cyclospora cayetanensis genetics only really began within the last 7 years. However, we have learned a great deal over that time; genotyping technologies now exist for Cyclospora, and these are being used routinely to complement cyclosporiasis outbreak investigations performed by US public health agencies

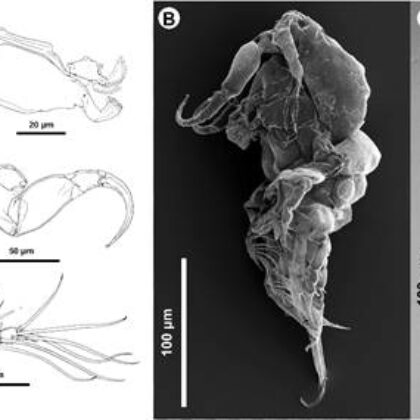
Biting midges (genus Culicoides) are one of the world’s smallest and most abundant blood-sucking flies. Haematophagous females are well-known vectors of several pathogens, including those affecting both livestock and wildlife.

Welcome to our “Meet the Editors” series, where we interview the editorial team about their work and their relationship to the journal. In this post we meet Professor Joseph A. Jackson, Editor for Parasitology.
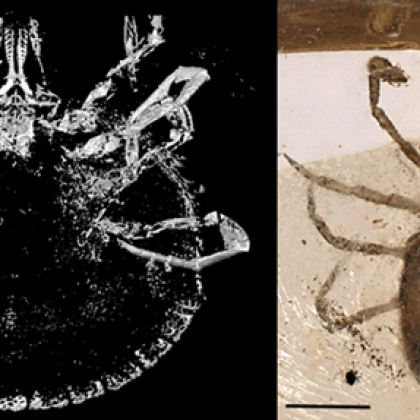

Amber is a rich source of invertebrate fossils that constantly turn up new families, genera, and species. To become an amber fossil, an organism needs to be trapped in tree resin oozing from injured trees, which hardens and gets buried beneath sediment before fossilization at high pressure and temperature.
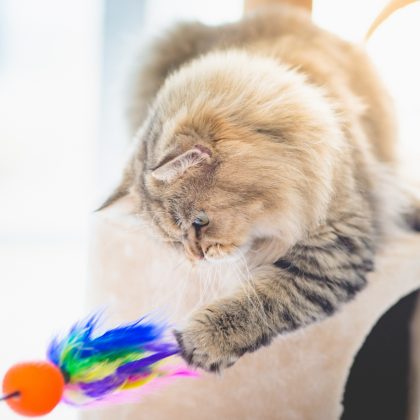

Play is often considered an indicator and promotor of animal welfare. Playing with your cat may also nurture closer cat-human bonds. In a new study, scientists have investigated these links by applying in-depth empirical methods to analyse data gathered from around the world.

Dr. Fay Clarke speaks to us about her career in social and biological science.

Javier González Miguel was one of the winners of the Early Career Researcher Award 2019, awarded each year by Parasitology for first or last authors of outstanding papers published in the journal. Three years later we catch up with him to see how his career has progressed since then.