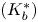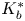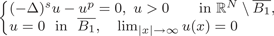31 results
Buckled elastic sheet as a vortex generator in dual channels
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 985 / 25 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, A39
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comprehensive psychological crisis intervention of college students with anxiety disorder
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, p. S2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
8 - Causation in the Chinese Civil Code
-
-
- Book:
- The Making of the Chinese Civil Code
- Published online:
- 31 August 2023
- Print publication:
- 14 September 2023, pp 179-196
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
On axisymmetric dynamic spin coating with a single drop of ethanol
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 951 / 25 November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2022, A30
-
- Article
- Export citation
A blood digestion scoring method for poultry red mites, Dermanyssus gallinae
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 149 / Issue 12 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2022, pp. 1623-1630
-
- Article
- Export citation
Offsetting the cost of community-supported agriculture (CSA) for low-income families: perceptions and experiences of CSA farmers and members
-
- Journal:
- Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems / Volume 37 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 November 2021, pp. 206-216
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dynamics of an infection age-space structured cholera model with Neumann boundary condition
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 33 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2021, pp. 393-422
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rural consumer response to a food distribution innovation that connects farmers, retailers, and buyers
-
- Journal:
- Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems / Volume 36 / Issue 5 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 March 2021, pp. 457-464
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fast and slow decay solutions for supercritical fractional elliptic problems in exterior domains
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2021, pp. 28-53
- Print publication:
- February 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Spatially Mediated Peer Effects in the Adoption of Conservation Agriculture Practices
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Agricultural and Applied Economics / Volume 53 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Perceptions of nutrition education classes offered in conjunction with a community-supported agriculture intervention among low-income families
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 10 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2020, pp. 3028-3036
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Modulation of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration using Programmable Polymer Sheet Actuators
-
- Journal:
- MRS Advances / Volume 5 / Issue 46-47 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2020, pp. 2381-2390
- Print publication:
- 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fine-tuning of Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Senescence via Microtopography of Polymeric Substrates
-
- Journal:
- MRS Advances / Volume 5 / Issue 12-13 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2019, pp. 643-653
- Print publication:
- 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
AFM Assessment of the Mechanical Properties of Stem Cells During Differentiation
-
- Journal:
- MRS Advances / Volume 5 / Issue 12-13 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2019, pp. 601-607
- Print publication:
- 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Polydopamine-mediated Surface Modification Promotes the Adhesion and Proliferation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
-
- Journal:
- MRS Advances / Volume 5 / Issue 12-13 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2019, pp. 591-599
- Print publication:
- 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
The association between gut microbiota composition and BMI in Chinese male college students, as analysed by next-generation sequencing
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 122 / Issue 9 / 14 November 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2019, pp. 986-995
- Print publication:
- 14 November 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Noble surface molecularly imprinted polymer modified titanium dioxide toward solanesol adsorption selectivity study
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 19 / 14 October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2019, pp. 3271-3287
- Print publication:
- 14 October 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation