No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
On the sign changes of Dirichlet coefficients of triple product L-functions
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 November 2024
Abstract
Let f and g be two distinct normalized primitive holomorphic cusp forms of even integral weight 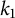 $k_{1}$ and
$k_{1}$ and 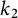 $k_{2}$ for the full modular group
$k_{2}$ for the full modular group 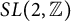 $SL(2,\mathbb {Z})$, respectively. Suppose that
$SL(2,\mathbb {Z})$, respectively. Suppose that 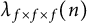 $\lambda _{f\times f\times f}(n)$ and
$\lambda _{f\times f\times f}(n)$ and 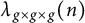 $\lambda _{g\times g\times g}(n)$ are the n-th Dirichlet coefficient of the triple product L-functions
$\lambda _{g\times g\times g}(n)$ are the n-th Dirichlet coefficient of the triple product L-functions 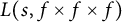 $L(s,f\times f\times f)$ and
$L(s,f\times f\times f)$ and 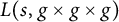 $L(s,g\times g\times g)$. In this paper, we consider the sign changes of the sequence
$L(s,g\times g\times g)$. In this paper, we consider the sign changes of the sequence 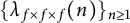 $\{\lambda _{f\times f\times f}(n)\}_{n\geq 1}$ and
$\{\lambda _{f\times f\times f}(n)\}_{n\geq 1}$ and 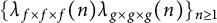 $\{\lambda _{f\times f\times f}(n)\lambda _{g\times g\times g}(n)\}_{n\geq 1}$ in short intervals and establish quantitative results for the number of sign changes for
$\{\lambda _{f\times f\times f}(n)\lambda _{g\times g\times g}(n)\}_{n\geq 1}$ in short intervals and establish quantitative results for the number of sign changes for 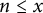 $n \leq x$, which improve the previous results.
$n \leq x$, which improve the previous results.
Information
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of Canadian Mathematical Society


