No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 February 2018
The mass of RR Lyrae variables has been a controversial problem for about a decade: while the stellar evolution theory predicts masses ranging between 0.65 and 0.75 M⊙ for Oosterhoff type I and II clusters respectively, the stellar pulsation theory predicts smaller masses (0.55 and 0.65 respectively) using the double-mode pulsators. Simon (1990, M.N.R.A.S. 246, 70), comparing hydrodynamical models with observed stars by means of Fourier parameters, has found relations between the stellar mass and its luminosity, pulsation period, Helium content and Fourier parameter ϕ31. Combining his equations we obtain:
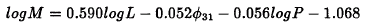 (1)
(1)
from which one can estimate the stellar mass by using the observable quantities P and ϕ31 and a luminosity scale, e.g. the one derived by Cacciari, Clementini and Fernley (1992, Astrophys. J. in press).