No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Steady and Fluctuating Parts of Sun’s Internal Magnetic Field
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 April 2016
Abstract
Core share and HTML view are not available for this content. However, as you have access to this content, a full PDF is available via the ‘Save PDF’ action button.
We have modeled the ‘steady’ part of sun’s internal poloidal magnetic field in the form of a central dipole and a central hexapole with strengths (0.6±0.1)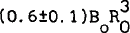 and
and 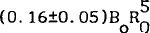 embedded in an asymptotically uniform field Bo. A small deviation from isorotation seems to indicate:(i) a slow build-up of toroidal field near the base of the convection zone and (ii) presence of torsional MHD perturbations in the outer radiative core, with latitudinal structure and time scales which may be similar to those of solar activity.
embedded in an asymptotically uniform field Bo. A small deviation from isorotation seems to indicate:(i) a slow build-up of toroidal field near the base of the convection zone and (ii) presence of torsional MHD perturbations in the outer radiative core, with latitudinal structure and time scales which may be similar to those of solar activity.
Information
- Type
- I. Setting the stage: Sun, Stars Galaxies and the Universe
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Astronomical Society of the Pacific 1993
References
Christensen-Dalsgaard, J., & Schou, J.
1988, in Seismology of the Sun and Sun-like Stars, ed. Domingo, V. and Rolfe, E.J. ESA: SP-286, p. 149.Google Scholar
Gokhale, M.H., Javaraiah, J., Kutty, K.N.. & Varghese, B.A.
1992, Solar Phys, 138, 35.Google Scholar

