Introduction
Numerical mechanical or thermomechanical ice-sheet models (e.g. Reference Hughes, Denton and HughesHughes, 1981; Reference Hindmarsh, Boulton and HutterHindmarsh and others, 1989; Reference Fastook and HolmlundFastook and Holmlund, 1991; Reference Huybrechts and T’siobbelHuybrechts and T’siobbel, 1995) are the main tools for reconstruction of ice-sheet surface topography, a parameter of fundamental importance for climate modelling. The output from numerical ice-sheet models is in calendar-year time-slice format, typically depicting ice-sheet surface topography and hence ice-flow patterns.
The ice-flow directional record in maps of till lineations and striations is the most valuable data record for validating or constraining results from numerical three-dimensional ice-sheet models. However, the actual use of this record has been severly hampered by the fact that glacial landforms are inscribed at the base of ice sheets by processes that are highly variable in time, Space and magnitude, resulting in a heterogeneous record. Moreover, major deglaciation related landform systems are time-transgressive (i.e. they do not reflect true ice-flow lines at a given time, but are the result of an iuward-transgressive formation of landforms near the ice margin) and cannot therefore be directly compared to time-slice results from numerical models. Thus, there is a need for a stricter treatment of the geological and morphological record if comparisons with numerical model output are to be made. We see the development of an inversion model (i.e. a theoretical model that formalises the procedure of using the landform record to reconstruct palaco-ice sheet evolution and flow patterns) as a necessary step towards more strict validation of ice-sheet models. Such a model must take into account the temporal properties within, as well as between, landform systems.
Compilations and interpretation of the geological record in North America and northern Europe form the base of our current understanding of the evolution of the Laurentide and Fennoscandian ice sheets (e.g. Reference PrestPrest, 1970; Reference LundqvistLundqvist, 1989, Reference Lundqvist1992; Reference Anderson and MangerudAndersen and Mangerud, 1989). These works are focused largely on stratigraphical correlations and dating of marginal positions, but do not integrate the flow-trace evidence in any methodically stringent manner. This is a Striking bias, considering the substantial effort that has gone into striation and till-lineation mapping during the past century (e.g. Reference HögbomHögbom, 1906; Reference TannerTanner, 1914; Reference HoppeHoppe, 1948; Reference LjungnerLjungner, 1949: Reference Prest, Grant and RamptonPrest and others, 1968), creating a data base that comprises hundreds of published works and thousands of individual flow-trace observations. In our view, an important reason for this deficit of efficient use of existing flow-directional data, is the vastly increased methodological difficulties involved in analyzing flow-trace information on ice-sheet scale, largely related to the time-transgressive nature of many glacial landscapes.
Two different approaches have dominated the use of lineation information. The first approach (Reference HoppeHoppe, 1948; Reference StrömbergStrömberg, 1981; Reference Boulton, Smith, Jones and NewsomeBoulton and Others, 1985) applies the assumption that most lineations were formed near a retreating ice margin, i.e. emphasises the time-transgressive nature of the flow-trace record. The second approach treats the flow-trace record as a stack of “events” (Reference LjungnerLjungner, 1949; Reference Boulton and ClarkBoulton and Clark, 1990a, Reference Boulton and Clarkb; Reference Klassen and ThompsonKlassen and Thompson, 1993), i.e. the flow-trace record is assumed to represent discrete events that reflect true flow patterns. The first approach works well in areas where the last ice sheet more or less Completely erased older landforms during its waning stages (Reference StrömbergStrömberg, 1981), but fails and creates confused reconstructions if applied to areas with preserved older glacial land-forms. The second model allows recognition of previous flow patterns, for example in core areas of past ice sheets, where palimpsest landscapes displaying several generations of landform systems can be found (Reference Hirvas, Nenonen, Kujansuu and SaarnistoLjungner, 1949; Reference Boulton and ClarkBoulton and Clark 1990a, Reference Boulton and Clarkb). However, it creates erroneous results if applied to time-transgressive deglacial landscapes.
In this paper, we use the inversion model developed by Reference KlemanKleman and Borgström (1996)to reconstruct the evolution of the Fennoscandian ice sheet during the Weichselian glacial cycle. This model makes use of the directional information in the Subglacial lineation record as well as the marginal meltwater landform record. Fundamental in the inversion model is the separation of deglacial landform systems from non-deglacial systems, as well as the recognition of intra-system age gradients (i.e. metachronous vs synchronous landform systems). The inversion model also includes packing of individual landforms into spatially delineated “fans” (map units).
The development of the inversion model draws on recent advances in (i) the identification and use of cross-cutting lineations (Reference LagerbäckLagerbäck, 1988b; Reference Boulton and ClarkBoulton and Clark, 1990a, Reference Boulton and Clarkb; Reference ClarkClark, 1993, Reference Clark1994), (ii) the separation of spatial information provided by marginal meltwater traces from the lineation record (Reference BolducBorgström, 1989; Reference KlemanKleman, 1992), (iii) the development of morphological criteria for identification of frozen-bed zones (Reference SugdenSugden, 1978; Reference KlemanKleman and Borgström, 1990, Reference Kleman1994; Reference DykeDyke, 1993; Reference KlemanKleman, 1994), and (iv) the understanding of the linkage between specific landforms and landform assemblages and glaciological condition (Reference Sollid and SorbelSollid and Sørbel, 1988; Reference Dyke, Morris and EnglandDyke and others, 1992; Reference Kleman, Bongstraöm and HättsetrandKleman and others, 1994).
The actual implementation of the model has been aided by recent advances in mapping of minor and cross-cutting landforms, including glaciofluvial channels (Reference Sollid and KristianssenSollid and Torp, 1984) and the discovery and mapping of pre-late Weichselian glacial landforms in northern Fennoscandia (Reference KujansuuKujansuu, 1975; Nordkalott Project, 1986a, b; Reference LagerbäckLagerbäck, 1988b; Reference Lagerbäck and RobertssonLagerbäck and Robertsson, 1988; Reference RodheRodhe, 1988; Reference KlemanKleman, 1992).
The primary results of the application of the inversion model are reconstructions of ice-sheet evolution and flow patterns, whereas the chronological assignment of the identified configurations rests on correlations with published stratigraphical data and proxy records of climate and global ice volume. The maps conveying our results are in a time-slice calendar-year format and are specifically designed to be used as a boundary condition for numerical models that use bed properties and flow patterns as input data, or for validation of mass-balance driven models that give flow patterns and thermal regime of ice-sheet beds as output. Unless otherwise stated, all ages are given in thousand calendar years (ka) or million calendar years (Ma) BP.
Late Quaternary Climate and Chronology
The Fennoscandian record of glacial landforms reflects two dominant glaciation modes: (i) west-centred Scandinavian ice sheets with a linear ice divide essentially parallel to the elevation axis of the Scandinavian mountain range, reflecting shorter periods of climatic deterioration (Reference Anderson and MangerudAndersen and Mangerud, 1989; Reference KlemanKleman, 1992), and (ii) Fennoscandian ice sheets with a more easterly dispersal centre, independent of the mountain range, reflecting prolonged glacial build-up periods under climatic conditions similar to those during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM). These two configurations are thought to have occurred repeatedly over Fennoscandia throughout the Late Cenozoic (Reference PorterPorter, 1989; Reference MangerudMangerud, 1991; Reference Kleman and StroevenKleman and Stroeven, 1997), during which the time period 2.5–0.8 Ma was dominated by smaller mountain-centred Scandinavian ice sheets, while large east-centred ice sheets only developed after 0.8 Ma.
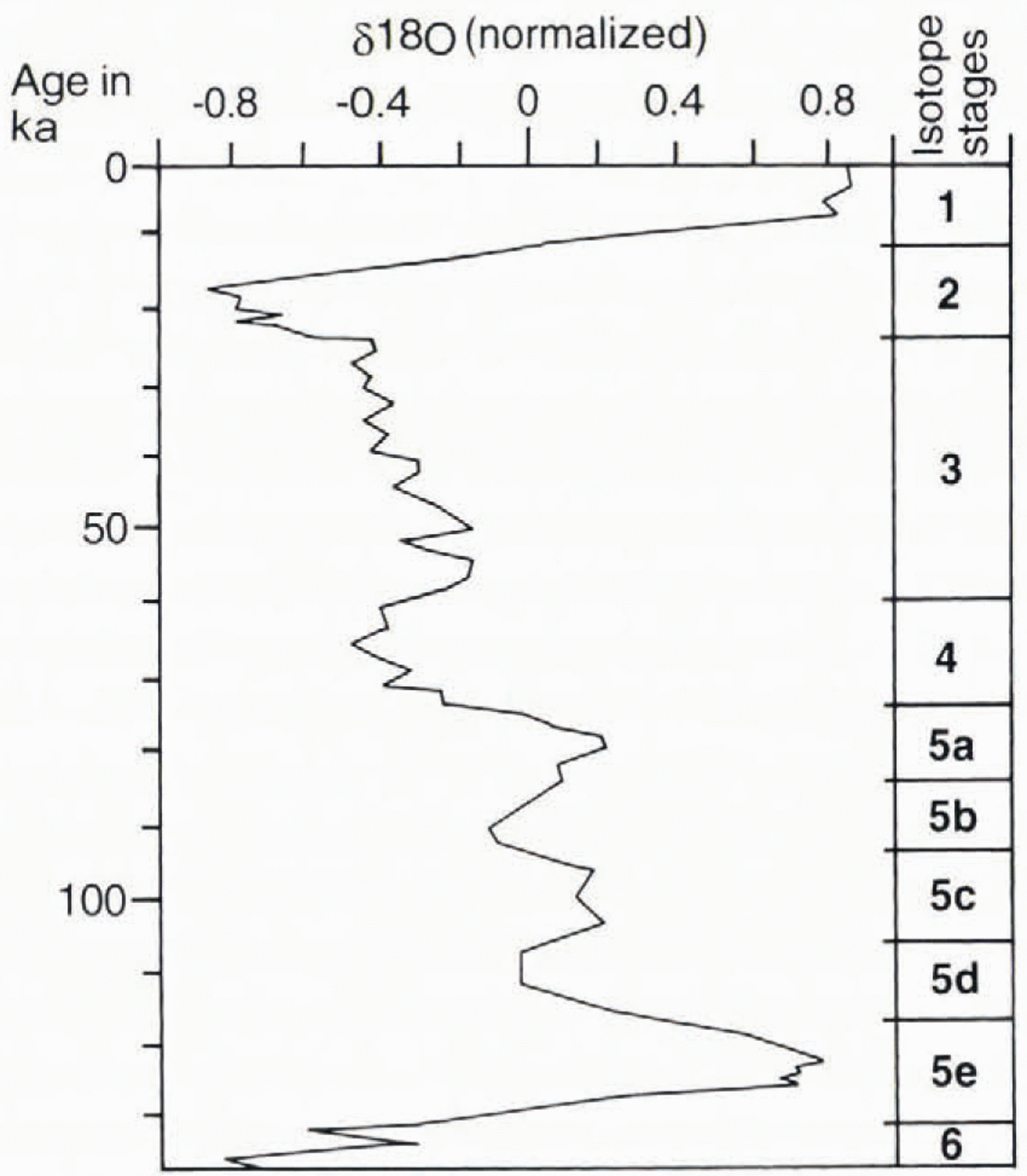
As a chronological framework for the period prior to the LGM we use the marine oxygen-isotope record, which is assumed to reflect largely global ice-volume evolution, i.e. a climatic signal dampened and smoothed through the filter of ice-sheet mass-balance relations. For assigning ages to pre-LGM Configurations and flow patterns we have made correlations to the Reference Martinson, Pisias, Hays, Moore and ShaekletonMartinson and others (1987)record (Fig. 1), which has an orbitally tuned time-scale. We assume that Fennoscandian glaciation varied in approximate concert with global ice-volume changes, as indicated by the Reference Martinson, Pisias, Hays, Moore and ShaekletonMartinson and others (1987)record. The Greenland ice-core record (Reference DansgaardDansgaard and others, 1993) reflects directIy Northern Hemisphere climate, giving information about millennium-scale dynamics. However, such short-time variations in the climatic signal are unlikely to be reflected in the subglacial landform record of the Fennoscandian ice sheet. We have therefore refrained from trying to correlate the climatic signals in the Greenland ice core with variations in the long-term evolution of the Fennoscandian ice sheet.
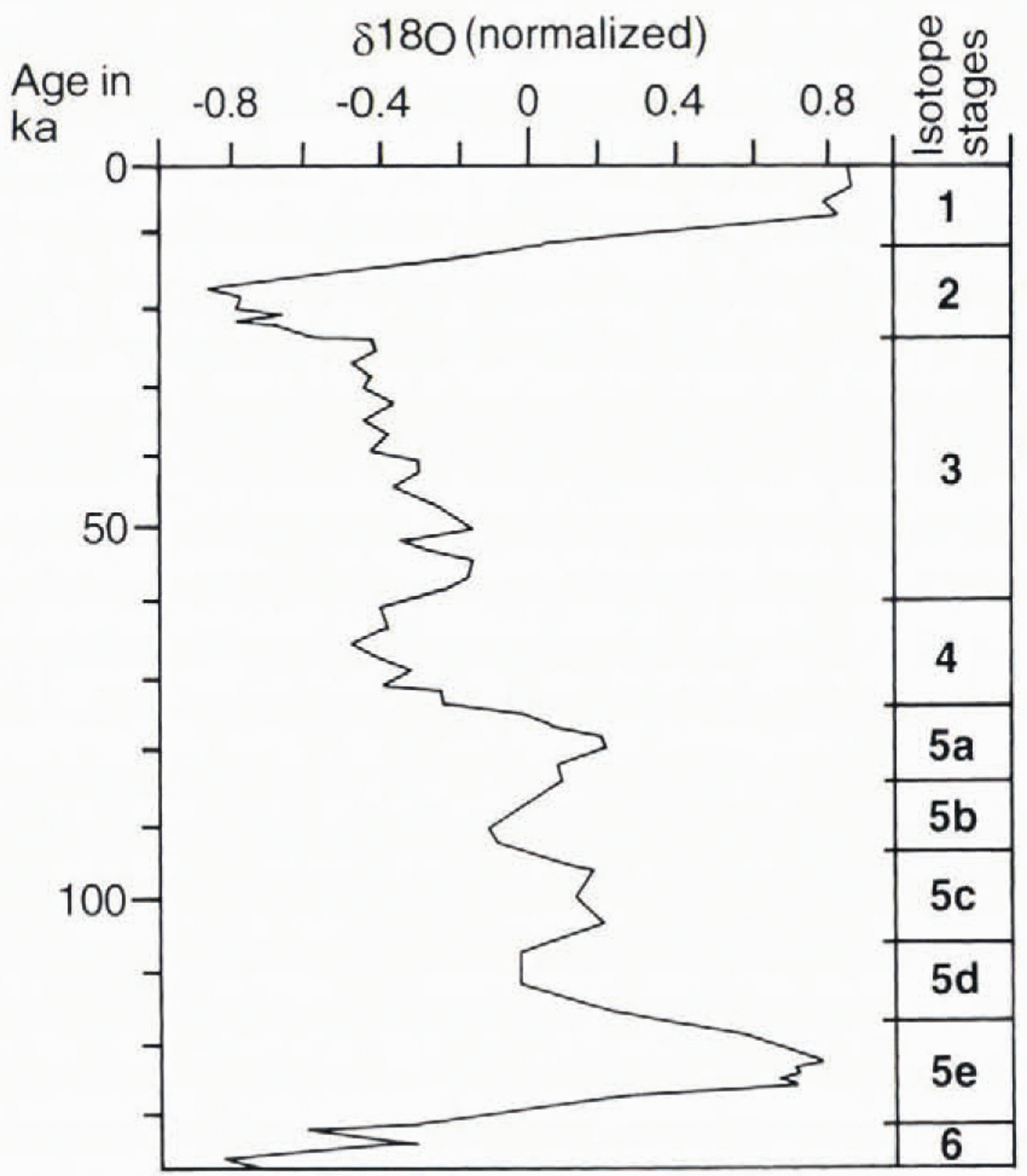
Fig. 1. The stacked oxygen-isotope record of Reference Martinson, Pisias, Hays, Moore and ShaekletonMartinson and others (1987), with a time-scale based on orbital tuning. This is a proxy record for global ice volume during the last glacial cycle.
Method
The inversion model comprises a new classification system for glacial landform assemblagesand a stepwise deciphering procedure. The conceptual framework behind the model is fully described in Reference KlemanKleman and Borgström (1996), as is the rationale behind our basic assumptions. The following assumptions are employed in the model:
(i) The basic control on landform creation, preservation and destruction is the location of the phase boundary water/ice at or under the ice-sheet base (i.e. basal temperature ).
(ii) Basal sliding requires a thawed bed.
(iii) Lineations can only form if basal sliding occurs.
(iv) Lineations (drumlins, flutes, striae) are created in alignment with the local flow and perpendicular to the ice-surface contours at the time of creation.
(v) Frozen-bed conditions inhibit rearrangement of the subglacial landscape.
(vi) Regional deglaciation is always accompanied by the creation of a spatially coherent but metachronous system of melt water features such as channels, eskers and glacial lake shorelines. Iu the case of frozen-bed deglaciation, eskers may be lacking.
(vii) Eskers are formed in an inward-transgressive fashion inside a retreating ice front.
Critical to our model are assumptions (v) and (vii). Assumption (v) is based on evidence for frozen-bed preservation of landforms during prolonged periods of ice cover. For example, it has been shown that whole glacial landscapes, as well as delicate landforms formed during early-Weichselian stadials and interstadials, have been more or less unaltered by subsequent ice-sheet overriding during later stages of the glaciation (Reference Lagerbäck and RobertssonLagerbäck 1988b; Reference KlemanKleman, 1992, Reference Kleman1994; Reference DykeDyke, 1993; Reference KlemanKleman and Borgström, 1994). Assumption (vii) relies on studies showing cyclic sedimentation in eskers and the correlation that can be made between these cyclic sequences and proglacial rhythmic sediments (e.g. varved clays), thereby demonstrating the direct link between surface melting and esker build-up (Reference NormanNorman, 1938: Reference De GeerDc Geer, 1940; Reference HebrandHebrand and Åmark, 1989; Reference BolducBolduc, 1992).
The main components used in the inversion model are called fans.These are temporary tools in the inversion model and are the simplified and spatially delineated map representations of glacial landform swarms thai occur in formerly glaciated areas. The use of fans serves the purpose of data reduction and allows relative chronologies to be applied to a manageable number of cartographic units. A classification in outward-younging, synchronous and inward-younging systems is a necessary first-order approximation to allow reconstruction of time-slice patterns from landforms systems with different temporal properties. Coherent fans are defined on the basis of spatial continuity and the resemblance to a glaciologically plausible pattern, i.e. a minimum-complexity assumption.
The basic criterion of “resemblance to a glaciologically plausible pattern” is similar in that employed by Reference Boulton and ClarkBoulton and Clark (1990a, Reference Boulton and Clarkb)for their delineation of “flow sets". Yet there is a major difference between the Boulton and Clark landscape-level classification (flow sets) and ours (fans) Reference Boulton and ClarkBoulton and Clark (1990a, Reference Boulton and Clarkb)use only one class, defined by lineations alone, whereas our four fan types are defined on the basis of characteristic landform assemblages (including meltwater traces) and temporal gradients within these land-form assemblages.
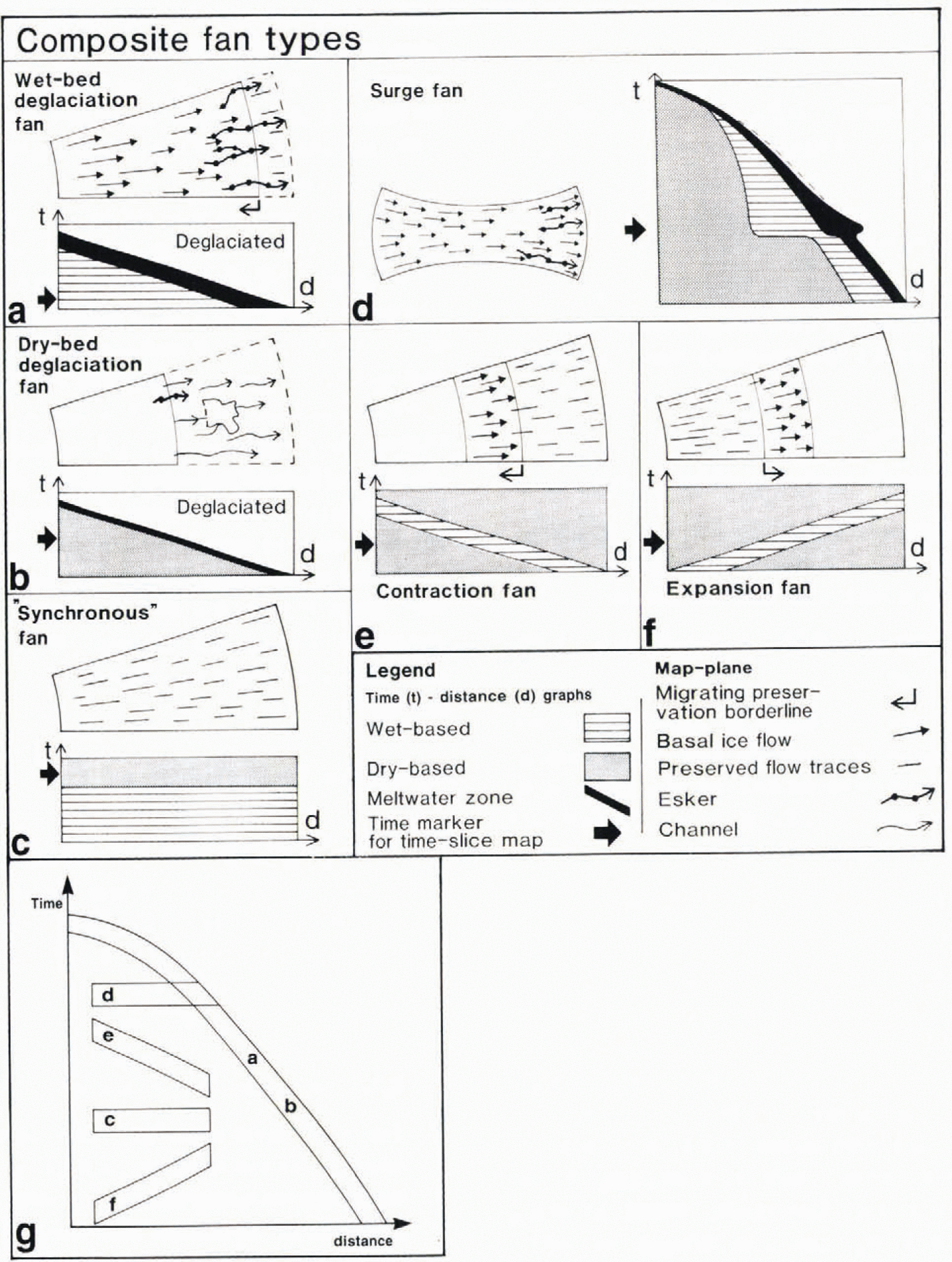
Those elements which allow definition of a fan can be any geological features that reflect ice-flow direction (e.g. striae, flutes, till fabrics, glaciotectonic folds, etc.). Frozenbed deglaciation fans can be defined on the basis of melt-water traces alone. Landform systems may be formed during a single event or formed in a time-transgressive (outward or inward) fashion. A mapped fan is therefore the orthogonal projection of a system that may be sloping in the three-dimensional time-distance domain (Fig. 2) and consequently we classify fans as inward-younging, synchronously formed or outward-younging.
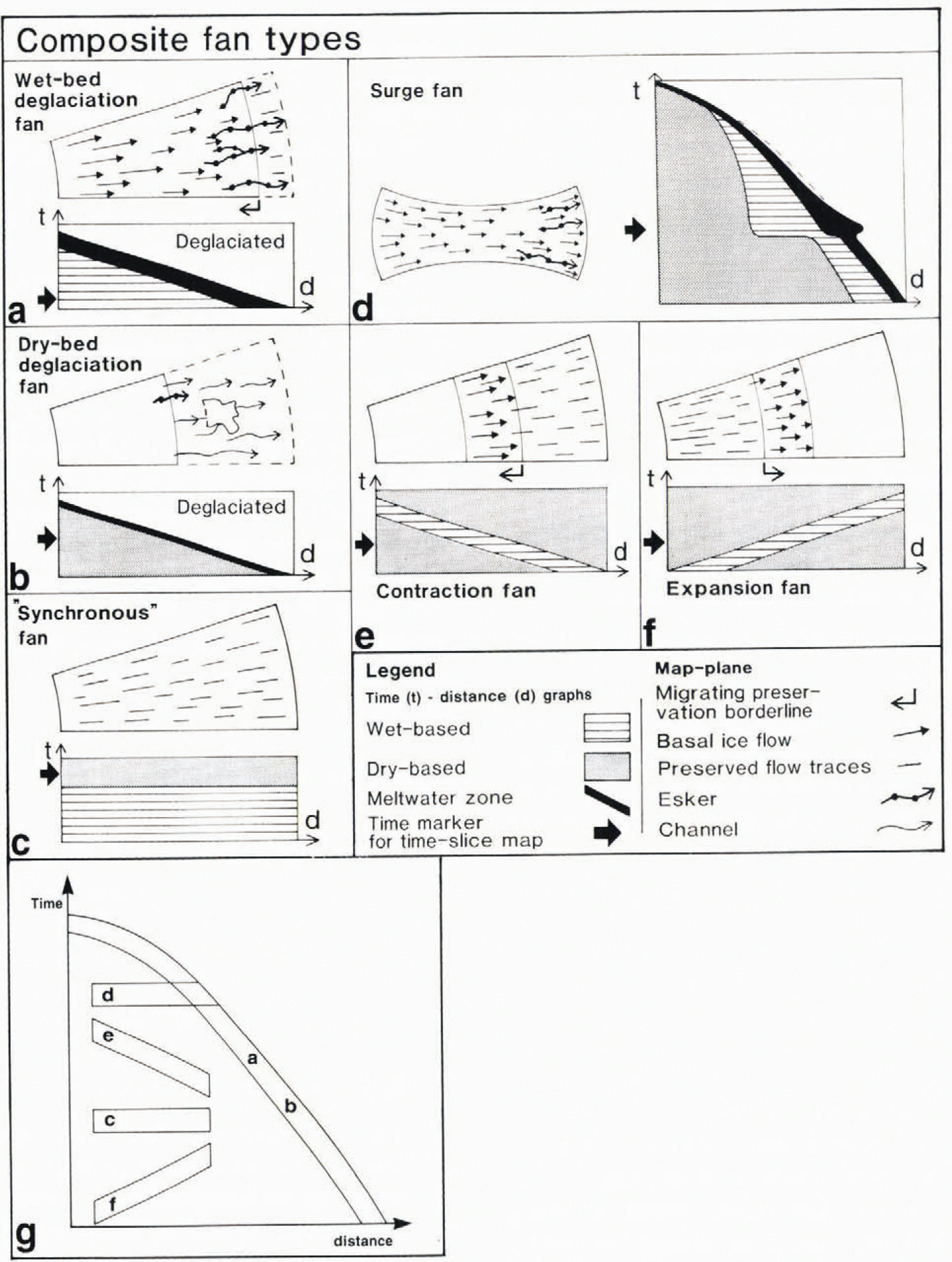
Fig. 2. (a-f) Formative conditions and temporal gradients for glacial landform assemblages, classified into six different fan types. The map plane and time-distance graphs shouw horizontal and vertical cuts, respectively, through the three-dimensional domain of the ice-sheet base (two dimensions) through time (one dimension). For each fan type, the map-plane graph shows characteristic landforms in formation at the times indicated by thick arrows in the corresponding time distance diagrams. Landforms become fossilised behind migrating preservation borderlines (a, e and f). The position of the ice margin is indicated in (a), (b) and (d), while the map-plane graphs in (c),(e) and (f) are fully ice-covered. The width of the meltwater zone in (d) shows a distinct widening because low-gradient surge-ice profiles result in a temporary expansion of the ablation area where meltwater is produced. (g) Time gradients of fan types a-f plotted in a time (t)-distance (d) domain. Fan types d and с are horizontal mid the only ones where the fan patterns directly represent flowines. All other fan types may or may not represent flowlines, depending an whether ice-sheet configuration changes occurred during the formation of the landform system constituting the fan. The figure is modified from Reference KlemanKleman and Borgström (1996).
A fan is spatially defined by longitudinal continuity lines, aligned to a visually coherent system of flow traces, and transverse up- and downstream boundaries. The latter are drawn transverse to continuity lines, in a stepped fashion if necessary.
Landscape-level classification
The fаn types we recognise are classified as follows (Fig. 2.)
(1) Wet-bed deglaciation fan.These fans consist of a flow-trace fan with an overlain and aligned esker fan. These “classic” fans are interpreted as representing inward-transgressive formation of flow traces (Reference Boulton, Smith, Jones and NewsomeBoulton and others, 1985; Reference KlemanKleman, 1990), which become preserved as new areas are successively deglaciated. Such fans are unlikely to represent true flowlines.
(2) Frozen-bed deglaciation fan.In these fans the landform Systems consist solely of a see-through pattern of melt-water traces overprinted on a relict surface. Marginal channels are dominant and eskers are small or lacking. The relict surfaces may be former subaerially developed surfaces or may contain (usually non-aligned) flow traces from an older glacial event.
(3) "synchronous” or event fan.These fans are defined by land-form systems with abundant flow traces but lacking aligned meltwater traces, in some cases they can be interpreted as the sites of former ice streams; in other cases they may have formed by slow sheet flow far inside the margin. If such a fan is defined by till lineations lacking a later overprint, the termination of lineation creation was probably caused by change to a frozen bed (Fig. 2c.) If a fan is defined by a low-frequency but regional occurrence of older striations, no inferences can be made regarding basal temperature during subsequent events. On the Spatial scale of individual roches moutonn´es, lee-side protection and preservation is operational. Hence, old striae can be preserved, despite sustained wet-based ice flow from other directions.
(4) Surge fan.These fans represent events of enhanced ice flow, draining considerable amounts of ice, probably during decay stages. Surge fans often have a distinctive bottleneck pattern, and the flow traces are thought to form nearlt synchronouslt over the whole fan area. Meltwater traces are often aligned in the distal part but not in the up-glacier part. The time-span during which the fan is formed is short, and therefore the patterns probably closely reflect true flowlines.
(5) Contraction fan.These represent the inward migration of a preservation mechanism other than deglaciation. This is likely to occur during an inward expansion of a frozen outer zone in an ice sheet.
(6) Expansion fans.. Such fans represent the outward migration of a preservation borderline, probably by refreezing of the bed during an outward expansion of a frozen core zone in an ice sheet.
The first four fan types (i.e. wet-based deglaciation fans, frozen-bed deglaciation fans, synchronous fans and surge tans) are the ones currently employed in the inversion model.We postulate the existence of contractionand expansion,but do not yet have morphological criteria to discriminate these fan types from synchronous fans on the basis of landforms alone. Consequently, all non-deglacial and non-surge fans are presently classified as synchronous fans. However, as will be elaborated on below, circumstantial or strati-graphical evidence can in some cases permit identification of advance fans.
Deciphering procedure
As a firsi step in the deciphering procedure, fans were spatially delineated and classified according to the morphological criteria described above. At fan intersections, relative chronologies were established, using mainly published striae and till fabric, and in some cases also employing our own air-photo interpretation of cross-cutting landforms. The fans were sorted into relative-age stacks, according to the relative chronologies, the first result being the reconstruction of the inward-transgressive decay pattern. Synchronous fans and deglaciation fans older than the last decay stage were aggregated into groups forming glaciologically plausible, coherent flow patterns.
For the reconstruction of time-slice flow patterns, metachronous (deglaciation) fans in the stack were deciphered in terms of reconstructing the changing ice-sheet configurations during the deglaciation. This was done by going up-fan and relating successively younger parts of the tan to successively younger dispersal-centre locations. The time slices were distributed into stadials on the basis of correlations wilh stratigraphical sequences of regional significance.
In contrast to Reference Boulton and ClarkBoulton and Clark (1990a), we do not claim that this type of reconstruction can be performed strictly objectively. We rather regard it as an iterative process with an output thay is objectively testable. Because of the reliance on spatial continuity assumptions, the inversion model works best in medium- to low-relief topography with dominant sheet-flow conditions. It is less powerful in dissected mountainous relief as in western Norway.
Ice-Flow Directional Record
In this section we give an account of the geomorphological and glacial geological record used and the overall distribution pattern, while specifics are treated in the results section.
Till lineations
The map in Figure 3, showing till lineations in the Fenno-scandian ice-sheet core area, was compiled from existing maps (see sources in the figure caption), as well as from our own mapping. In general, we regard the data as very reliable. In areas where independent source maps overlap there is a good match in till-lineation directions. In areas where only Satellite image interpretation has been used (e.g. in Finland; Reference PunkariPunkari, 1984), there may be small-scale lineation sets that are missing, due to the low spatial resolution of the source material. However, we regard it as highly unlikely that any major lineation sets, which would influence the general interpretation of our results, are missing.

Fig. 3. Till lineation in the Fennoscandian ice-sheet core area. Sources of information: Norway: Reference Sollid and KristianssenSollid and Torp (1984); sweden: Reference Lidmar-Bergstrom, Elvhage and RingbergLidmar-Bergström and others (1991), Reference KlemanKleman (1992)and C. Hättestrand (unpublished glacial geomorphological map of Sweden; scale 1:250 000); Finland and northwestern Russia: Reference Larsen, Gulliksen, Lie, Levlie and MangerudPunkari (1984)and Reference Niemelä, Ekman and LukashovNiemelä and others (1993). For the kola Peninsula we also used our own mapping in stereoscopic satellite images. The map sheets comprising the Nordkalott Project (1986a, b)were used for parts of northern Fennoscandia.
Till lineations occur over the entire Fennoscandian shield area (Fig. 3), except for the central Kola peninsula and minor uplands and summit areas in northern Sweden and Finland. In northern Finland and Sweden, cross-cutting lineations are common and partly date to glacial events before the late Weichselian. In peripheral parts of Norway, the southern third of Sweden, southeastern Finland, as well as all southern and southeastern peripheral areas of LGM ice-sheet extent, most lineations relate to deglacial or near-deglacial flow of the last ice sheet. In those areas, older ice-flow directions an only preserved as older striae or till fabrics in lower strata.
Striae and till fabrics
Striae and till fabrics are excellent data for the establishment of relative chronologies at fan intersections, but being point data they are less reliable than area-covering till lineations for definition of fan patterns. In southern Sweden some fans were defined by regionally persistent older striae patterns alone, as were some minor fans in northern Sweden and Finland. In addition, the two fans in Denmark were defined using till fabrics and glaciotectonie data.
Meltwater landforms
For discrimination of deglacial fans from non-deglacial fans by the criterion of aligned eskers, we have used the esker information present in the source maps listed in the caption of Figure 3. High-quality information regarding glaciofluvial meltwater channels on the regional scale is available only in Reference Sollid and KristianssenSollid and Torp (1984), the Nordkalott Project (1986a)and C. Hättestrand (unpublished manuscript maps). We have found no way of summarising this information (the interpretation of which is dependent on the local topography in a readable map, but point out that we have actually used the melt water landform record in the reconstruction of the deglaciation patterns (cf. Reference LundqvistLundqvist, 1973b; Reference SeppäläSeppälä, 1980; Reference BolducBorgström, 1989; Reference KlemanKleman, 1992).
Results
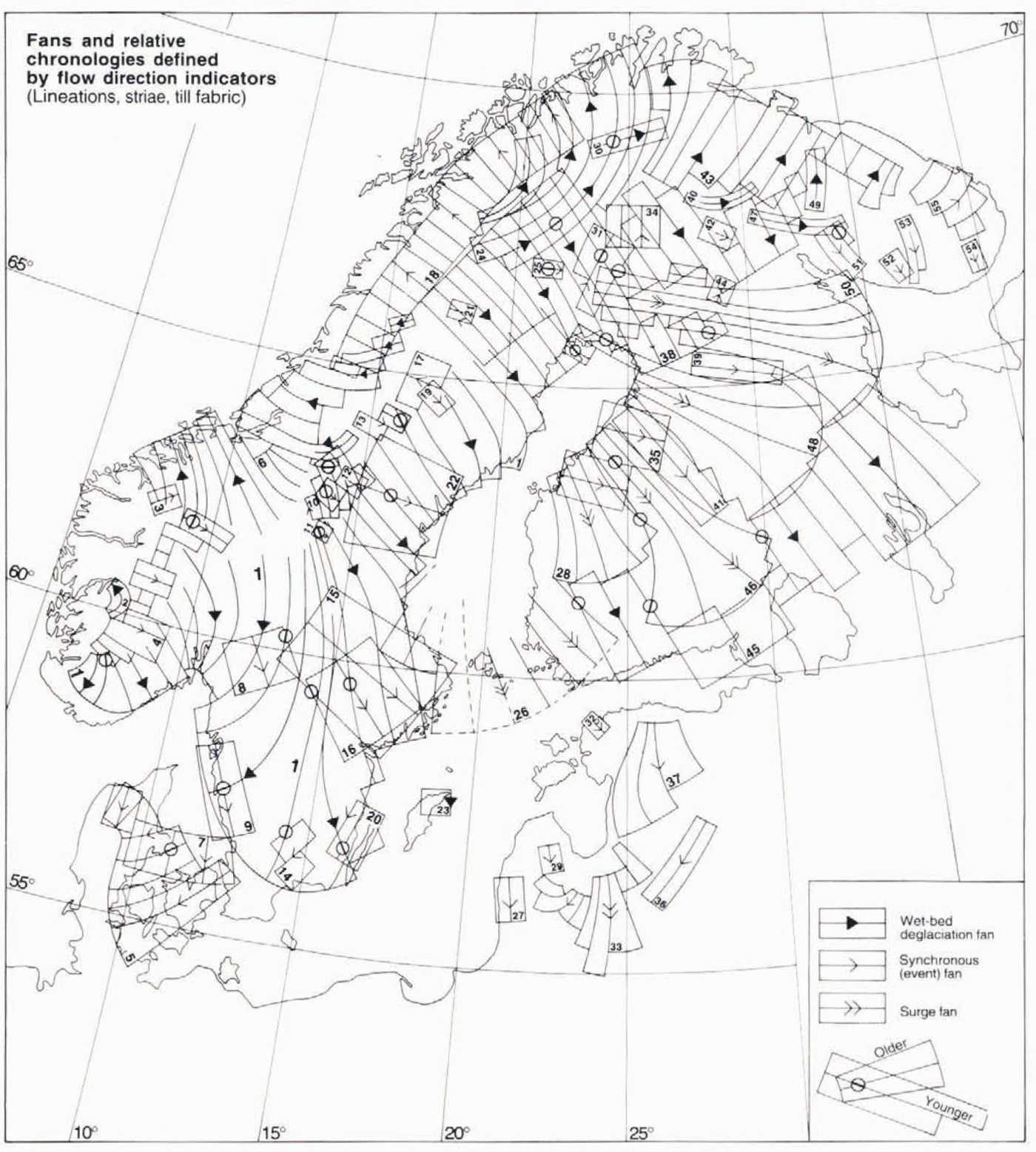
Using the data set described above and in Figure 3we delineated fans according to the principles detailed in the methods section. This resulted in 56 fans, numbered from west to east in Figure 4, and the classification of these is also shown in Table 1. The overall characteristics of the fans are described below, while details are given in connection with the reconstructed time slices.

Fig. 4. Fans defined on the basis of flow-trace swarms shown in Figure 3. and published striae and till-fabric data. Fan classification into deglacial and non-deglacial fans by the presence or absence off aligned glaciofluvial meltwater traces was done using mainly the data sources referred to in the caption of Figure 3. Fans are numbered from west to east. Relative chronologies are shown at intersections of flow-parallel fan lines, and are based on published striae observations, as well as on air-photo interpretation of cross-cutting lineation systems. Sources used are given in the text. Fan 56 in northern Sweden and Finland, which reflects dry-bed deglaciation. is show in Figure 9. together with adjacent fans.
Table 1. Classification of the fans shown in Figure 4

Deglaciation fans
Fans 1, 2, 6, 23, 24, 43 and 45 are all formed by landforms created in a wet-based marginal zone and fossilised by inward transgression of the ice margin during the decay phase. In much of Sweden, southeasternmost Finland and adjacent part of Russia, deviations from this pattern are rare. Eskers are aligned with ice-flow traces. The spatial gaps between fans 1 and 2, 2 and 6, and 6 and 24 do not reflect a lack of deglacial traces in those areas, but rather reflect areas with high-relief topography and thereby deglacial flow traces that follow valleys. To define fans in such areas is not meaningful in an ice-sheet-level reconstruction. The gap between fans 6 and 24 (which is essentially covered by the event fan 18) has, during both near-maximum stages and the decay period, experienced ice flow from the east-southeast. Consequently, directional changes due to increased topographical control during ice-sheet thinning predominate over any shifts related to configuration changes. Thus, for deciphering late-glacial ice-sheet configuration changes, this area is less important.
Most of southern and coastal northern Sweden is covered by fan 1. In eastern Sweden, successive ice margins, reconstructed transverse to fan lines, fit well to ice margins reconstructed by the independent method of clay—varve chronology (Reference StrömbergStrömberg, 1989). We have shown fans 1 and 6 open-ended towards the central part of the Scandinavian peninsula because of weak landform development at late stages in deglaciation of those areas, and consequently the occurrence of windows with older lineations. This weak deglacial imprint is related to the fact that those areas must have deglaciated from the southern tip of an elongated ice-sheet remnant. This divergent-flow tip of the ice sheet persisted during theretreat from roughly 62° to 66° N. For the whole of this inner zone, we have used the spatial constraints provided by the distribution of proglacial lakes and glaciofluvial channels to reconstruct the pattern of the last deglaciation.
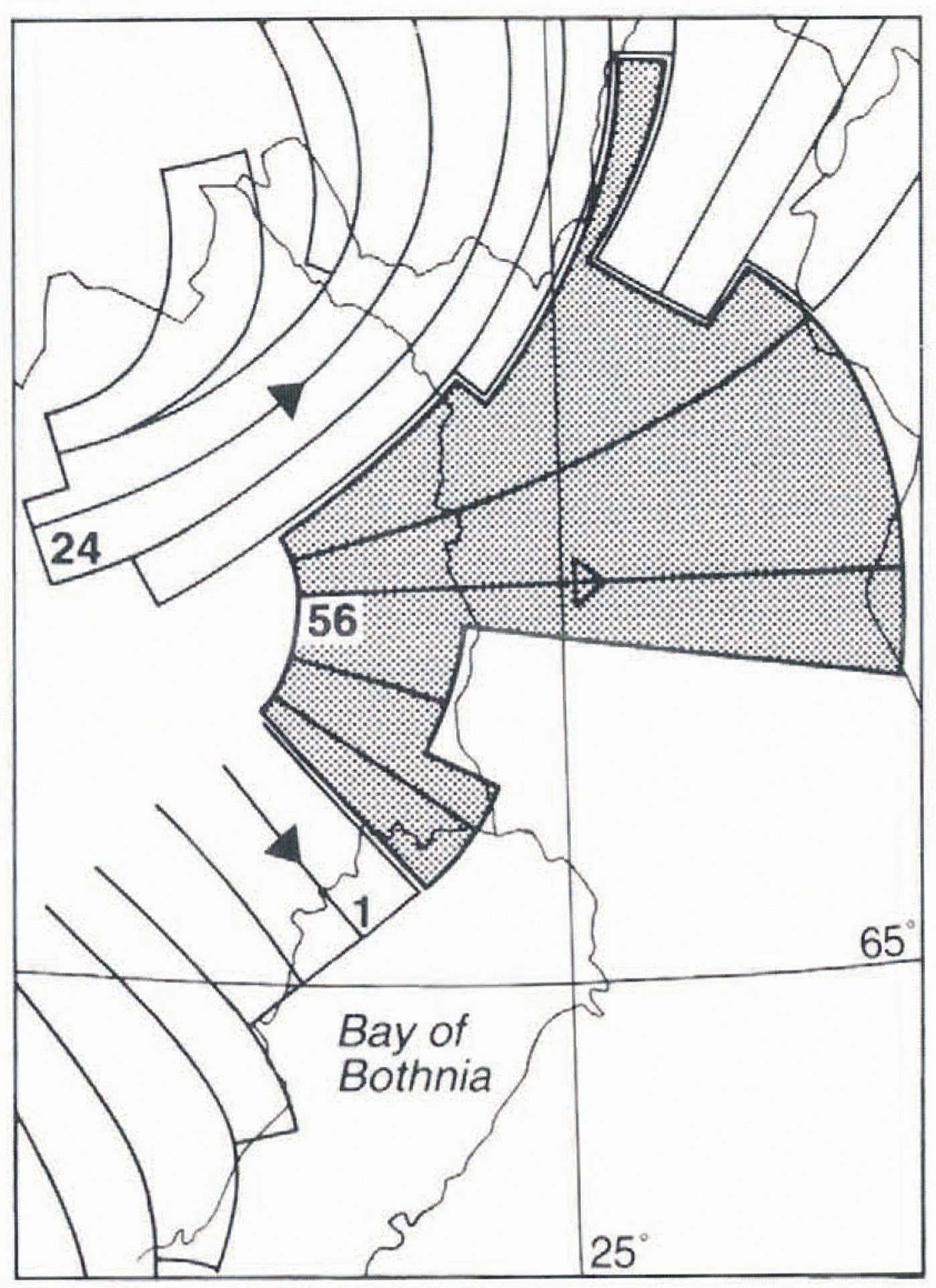
Two major complications in this simple deglacial fan pattern fan pattern occure in Finland and adjacent parts of northern Sweden. First, in southern and central Finland four major divergent fans related to the Salpausselkä zone, as well as the some what smaller (and younger) fan terminating at the central Finnish ice-marginal zone, are classified as surge fans and are considered to be related to short-lived ice streams during decay (fans 26, 28, 46, 48 and 50). Secondly, north and west of fan 50, substantial wet-bed imprints from the last deglaciation are lacking, but instead spatially coherent traces of deglacial meltwater drainage are superimposed across much older glacial landscapes. The local ice-surface slopes inferred from marginal meltwater channels have guided the definition of this frozen-bed deglaciation fan. In the area covered by this fan (No. 56), till lineations are rare, but the scattered striae and flutings that do occur support the deglacial flow direction inferred from meltwater traces.
Fan 38 is defined by abundant lineations in a generally northwest southeast direction. The occurrence of directionally conformable eskers, marginal moraines and marginal meltwater channels indicates that it is a deglacial landform system and shows that the area experienced ice-free conditions before the build-up of the late-Weichselian ice sheet. In the area where fan 38 is cross-cut by fan 24, related to the last deglaciation, mainly larger lineations in the older landscape remain (Reference GoodwillieGoodwillie, 1995). Stratigraphical data, linked to morphology, from Reference KujansuuKujansuu (1975), Reference LagerbäckLagerbäck (1988b)and Reference Lagerbäck and RobertssonLagerbäck and Robertsson (1988)unequivocally permit the assignment of fan 38 to a pre-late-Weichselian ice sheet, as do the stratigraphical data presented by Reference KorpelaKorpela (1969), Reference Hirvas, Nenonen, Kujansuu and SaarnistoHirvas and Nenonen (1987)and Reference HirvasHirvas (1991). Similar conclusions regarding a pre-late-Weichselian age were reached in morphological analyses by Reference RodheRodhe (1988)and Reference KlemanKleman (1992). Because of the regional and integral occurrence of ice-marginallandforms, such as end moraines and marginal channels, in the older overprinted northwesterly system, we refute the suggestion by Reference ForsströmForsström (1995)that this landscape should reflect an older configuration of the late-Weichselian ice sheet.
The areally restricted fans 30, 40 and 47, none of which fit into the last deglaciation pattern defined by fans 24 and 43, are probably remnants from one or more older deglacial events, as indicated by the presence of aligned eskers in fans 30 and 40 and suiu-s of lateral mcUwater channels in fan 47. However, we have been unable to determine ihe age of these fans.
We have abstained from trying to resolve the complex near-marginal ice dynamics during post-LGM stages in Denmark and southern Sweden (Reference LagerlundLagerlund, 1987; Ring-berg. 1989), which most probably involved topographically determined drainage of thin rast-moving lobes. Such near-marginal dynamics have little potential to illuminate the core-area configuration changes that are the focus of this paper.
Synchronous (event) fans
These fans are all defined by flow traces older than the last deglaciation. Except for the near-marginal fan 5, none of these fans contain aligned eskers or Others features indicating close proximity to the ice margin. Fans 4, 8, 10, 19, 25, 31, 34 and 42 are based on till lineations and striae data. Fans 9, 11, 13, 14, 16, 17, 20, 21, 35 and 44 are based on information from Striations alone. Fans 15 and 22 are defined by till fabrics in an old bluish-grey line-grained till that is occasionally found in central Sweden (Reference BjörnbomBjörnbom, 1979). Fans 27, 29 and 32 are based on small lineation patches only, and may well be deglaciation-related. It should be noted that the classification of fans 36 and 37 is uncertain.
For fans 5 and 7 we have accepted Reference Houmark-NielsenHoumark-Nielsen’s (1981)reconstructed “Norwegian advance” and LGM flow patterns, respectively. Both fans are mainly defined on the basis of till fabrics and glaciotectonic deformations.
Fans 51–55 and those on the Kola peninsula were mapped as synchronous (event) fans due to the lack of positive evidence for aligned deglacial meltwater features, but they may well reflect post-Younger Dryas deglacial flow of an ice-sheet sector that was largely cold-based, having insignificant subglacial drainage. This is in agreement with the ubiquitous presence of regolith on the east-central Kola peninsula (Reference Niemelä, Ekman and LukashovNiemelä and others, 1993).
Surge fans
These strongly divergent fans, all terminating in end moraines, are interpreted as representing fast, laterally constrained ice flow (i.e. ice streams separated by sluggish-flow interlobate zones; Reference PunkariPunkari, 1989). As discussed by Reference ClarkClark (1994), these patterns are difficult to explain by time-trans-gressive formation close inside a retreating margin. We do not know if fast flow occurred strictly simultaneously over the whole fan area, but the fan that striae in the proximal part of fan 48 are clearly older than deglacial striae forming part of fan 1 testifies to the strongly reduced slope in the time—space domain in comparison to deglacial fans. Fan 26 in the Gulf of Bothnia covers the area where Reference StrömbergStrömberg (1989)found evidence for a rapid collapse in the marine area, which we consider to be compatible with calving during a low-gradient post-surge situatation, The surges associated with fans 26, 28, 46, 48 and 50 probably resulted in an accelerated westward shift of the ice divide during deglaciation, as they must have drained considerable amounts of ice from the interior of the waning ice sheet. Fan 33 is also most probably a surge fan. Such an extremely divergent fan is unlikely to result from sheet flow, and there are no topographic features constraining the ice flow.
Time-slice outlines
Figures 5, 6and 7show the time slices for which we think enough evidence exists to suggest the outline and age of the ice sheet. For the LGM time slice we have also suggested the surface topography (form lines) which we find most compatible with the geological and geomorphological evidence. For the chronological assignment we have assumed that glaciation in the area has in general followed global ice-volume changes, as inferred from the proxy record in Figure 1.
Marine isotope stages 5d–5a, 115–74ka (Fig. 5)
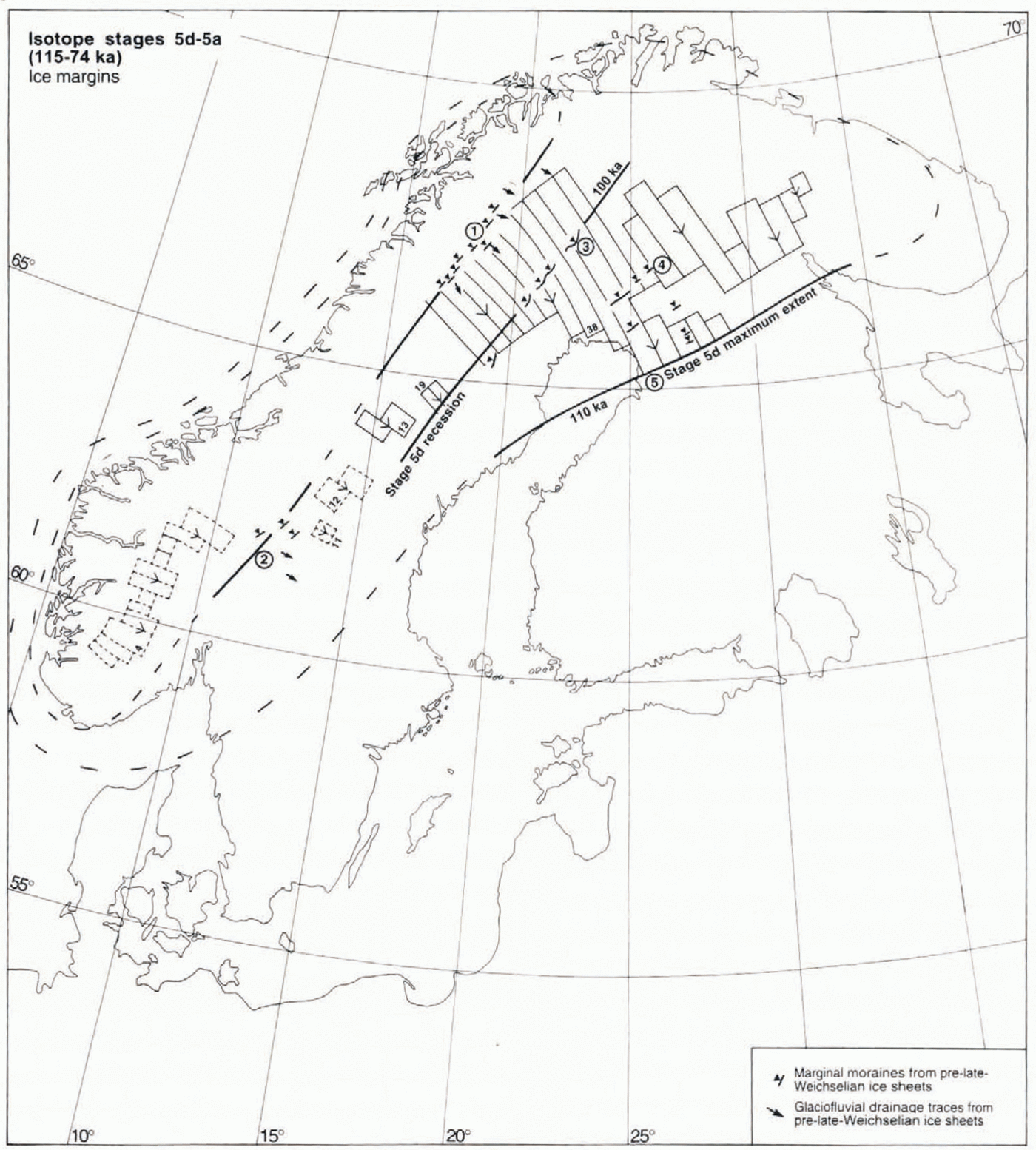
Fig. 5. Fans, ice-marginal landforms and ice-sheet outlines assigned to the 115–74 ka period (early Weichselian). Numbers 1–5 refer to ice-marginal zones discussed in the text. Solid lines represent ice margins inferred from geological and geomorphological evidence. Dashed lines represent suggested ice-sheet outlines.
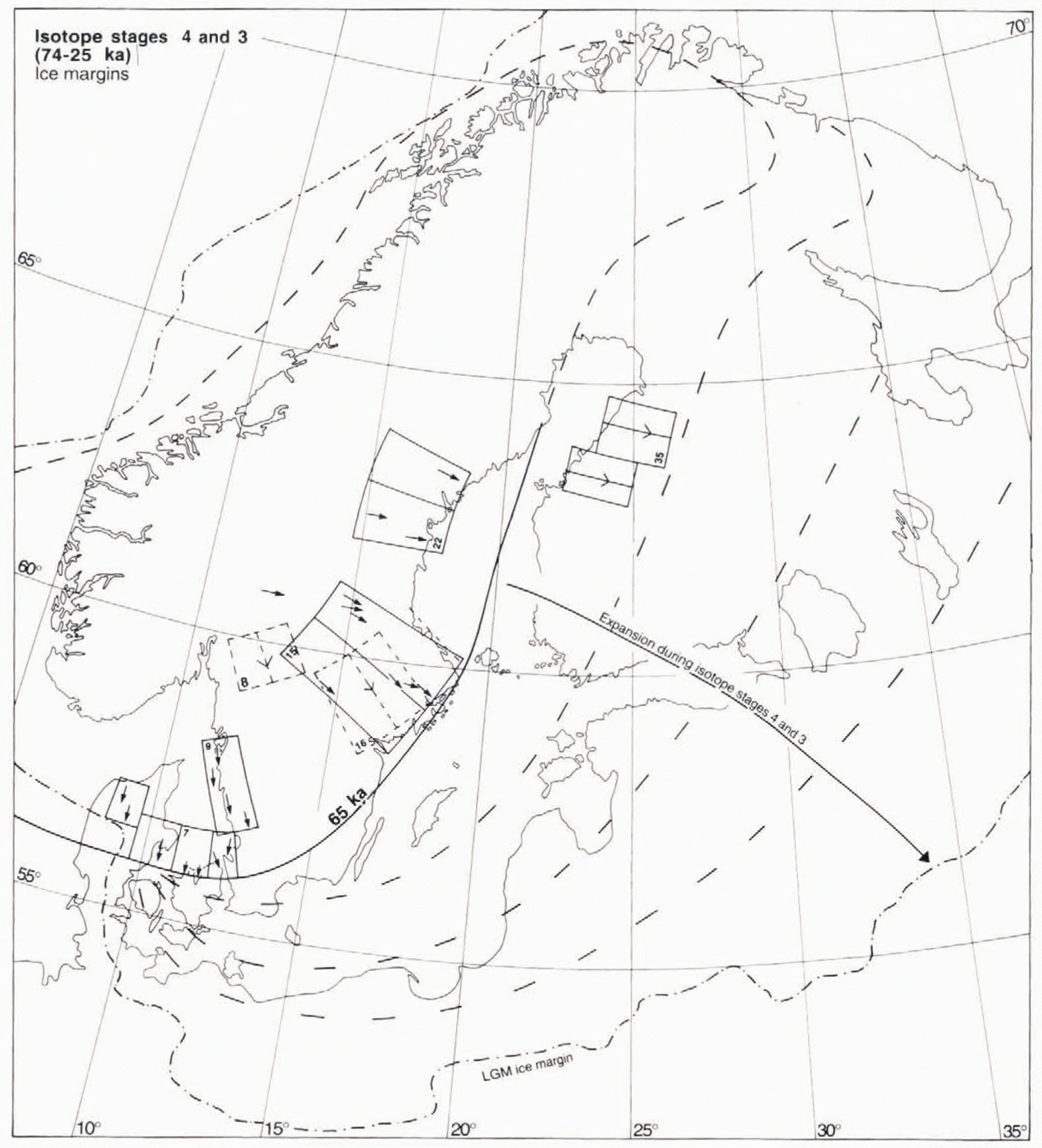
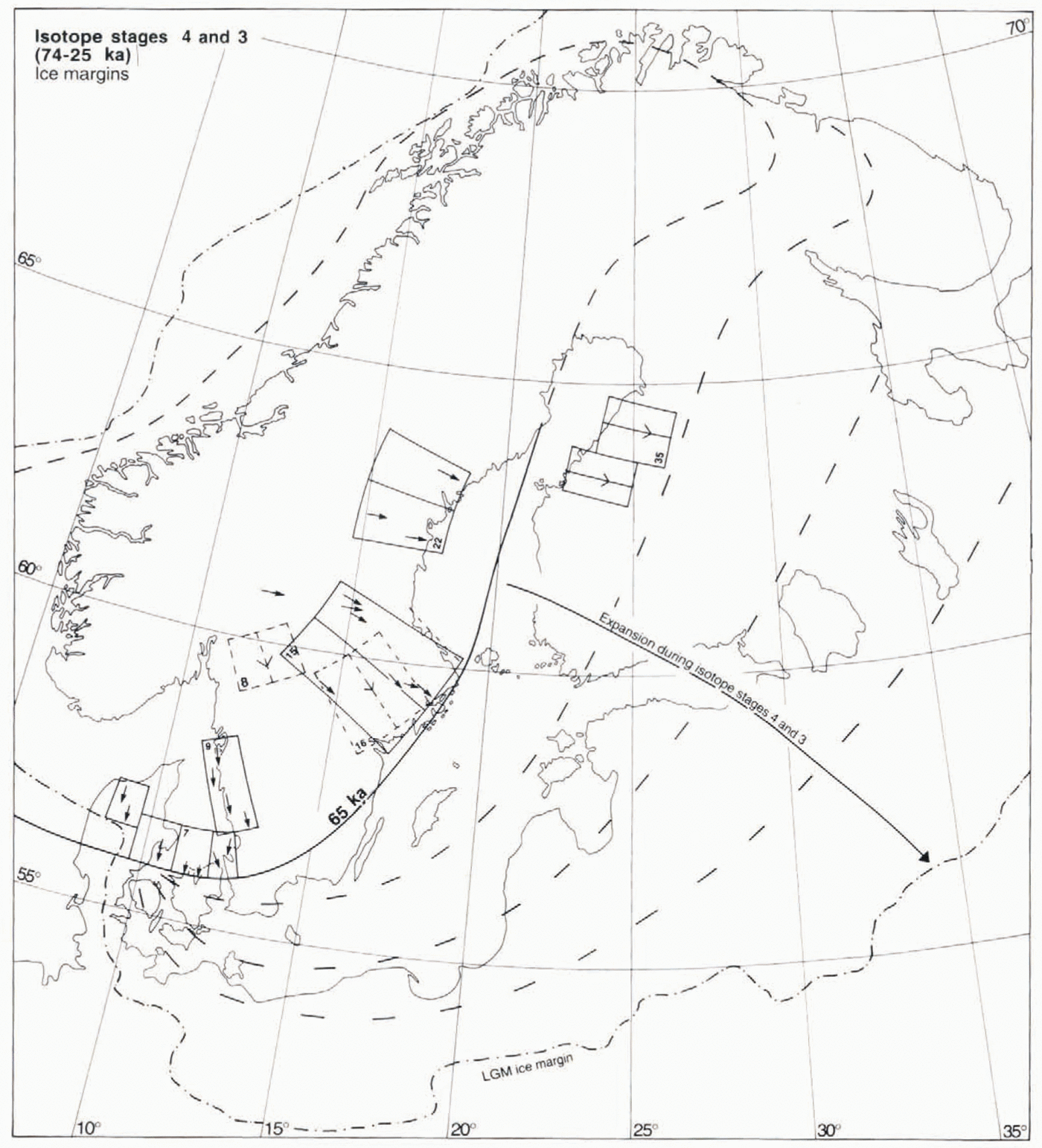
Fig. 6. Fans, and ice-marginal outlines assigned to the 74–25 ka period. Fans 7, 9, 15 and 22 together define an ice sheet with centre of mass located over southern Norway. This cofiguration is interpreted as representing the build-up phase of the mid-Weichselian ice sheet during isotope stage 4. Fan 16 is younger than fan 15 and probably reflects a northeastward migration of the ice-dispersal centre during further expansion of the ice sheet.
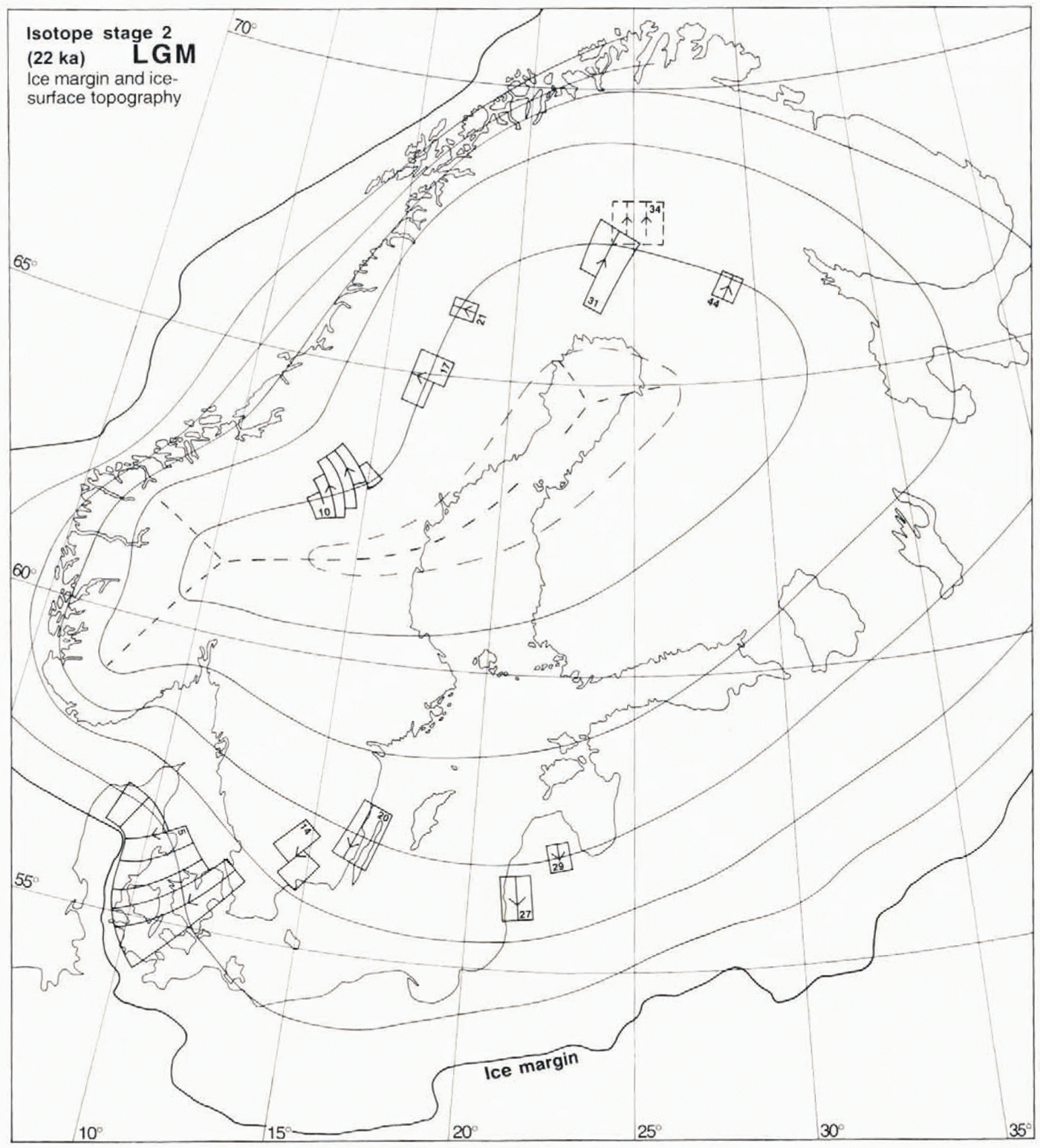
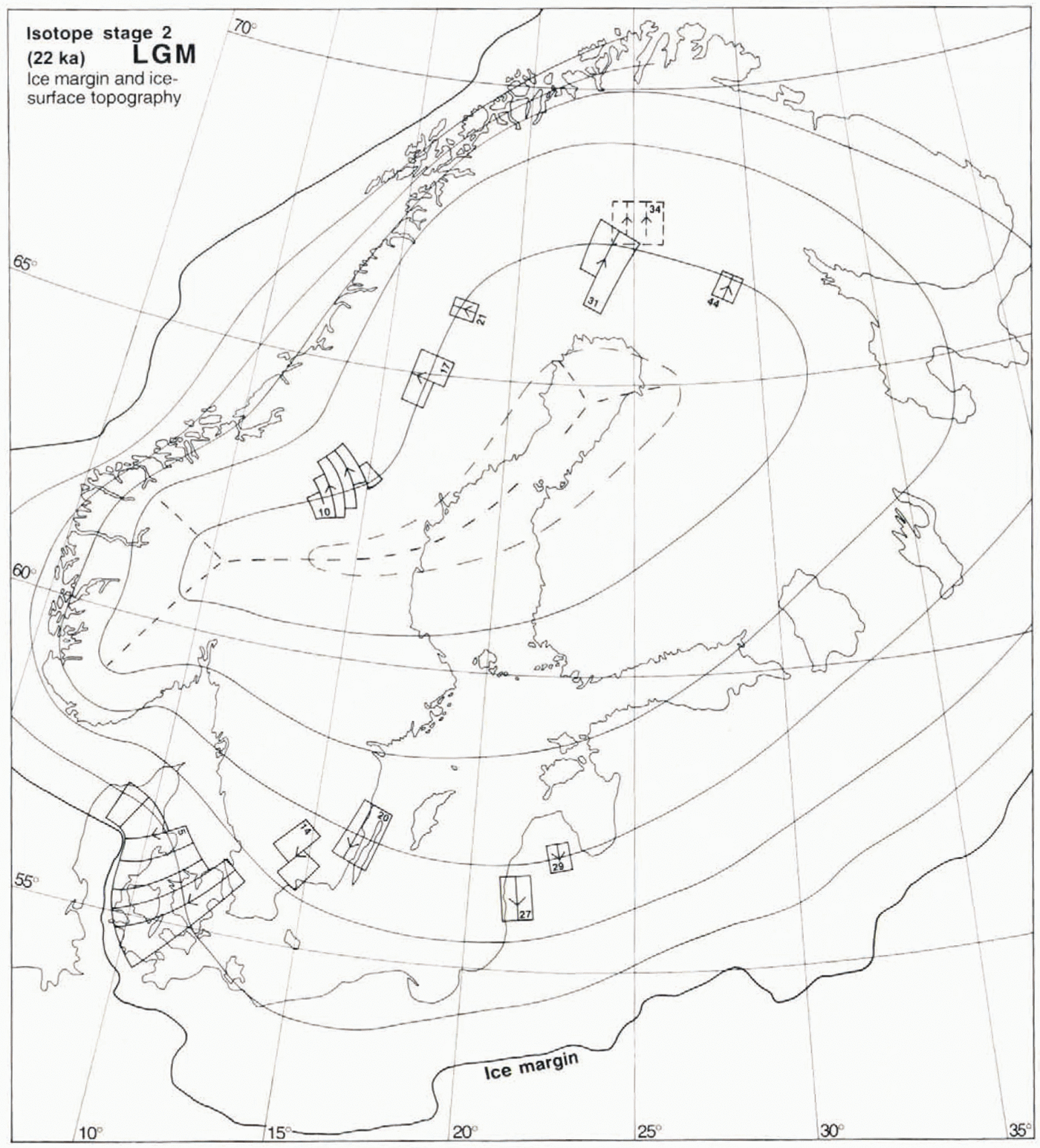
Fig. 7. The suggested ice-surface topography at 22 ka BP (LGM), and the fans which constrain this reconstruction. The ice-surface contours (form lines) define the interpreted shape of the ice surface. The heavy dashed line indicates the position of the LGM ice divide. Fan 31 may be slightly Younger or older than the LGM, as it indicates a somewhat more westerly dispersal centre than fans 34 and 44. Fans 17, 21 and 44 are defined on the basis of striae alone. The scarcity of LGM till lineations in the Fennoscandian shield area is explained as the result of froren-bed conditions under the central parts of the ice sheet (see Fig. 10).
Fan 38 forms a coherent deglacial landform system over much of northern Fennoscandia, reflecting ice flow of an elongated west-centred ice sheet with its elevation axis parallel to the Scandinavian mountain range. Interpretation of Stratigraphical data unequivocally assigns this to an early-Weichselian glaciation beyond the radiocarbon-dating range, separated from the late Weichselian In one (Reference Hirvas, Nenonen, Kujansuu and SaarnistoHirvas, 1991), or two (Reference Lagerbäck and RobertssonLagerbäck and Robertsson, 1988) interstadials. Reference LagerbäckLagerbäck (1988a, Reference Lagerbäckb)suggested a stage 5d age for this ice sheet, as did Manugerud (1991) and Reference LundqvistLundqvist (1992). The apparent discrepancy between the Finnish and Swedish data may reflect a restricted areal extent of the stage 5b ice sheet inferred to have existed by Reference Lagerbäck and RobertssonLagerbäck and Robertsson (1988). Five ice-marginal zones pertaining to one or both of the early-Weichselian ice sheets are defined by landforms or buried glaciofluvial outwash. These zones are detailed below and are marked in Figure 5.
Zone 1: The Hornavan-Torneträsk marginal zone, defined by lateral moraines in major valleys (Reference KlemanKleman, 1992) and degraded marginal channels (Reference RodheRodhe, 1988; Reference KlemanKleman, 1992) cross-cut by glaciofluvial channels from the last deglaciation.Both glaciofluvial systems cover vast areas and reflect incompatible ice configurations.
Zone 2: The Transtrand-Idre-Femunden area, where several of the low-mountain groups display glaciofluvial channels reflecting one or more deglaciations older than the last one (Reference KlemanKleman and others, 1992), and also scattered “old” marginal moraines (Reference Sollid and TorpSollid and Kristianssen, 1982; Borgström. 1989). Both zones 1 and 2 contain abundant relict periglacial surfaces (Reference KlemanKleman and Borgström, (1990, Reference Kleman1994), reflecting permafrost processes during inierstadials and preservation in frozen-bed zones of the late-Weichselian ice sheet.
Zone 3: The Veiki moraine zone, comprising hummocky moraine reflecting supraglacial sinkhole deposition, eskers and end moraines. Reference LagerbäckLagerbäck (1988b)interpreted these landforms as having formed during the areal stagnation of a debris-loaded sluggish stage 5d ice sheet. Detailed mapping (C. Hättestrand, manuscript map) reveals that the Veiki moranines appear mainly in approximately 10 km wide bands immediately inside each end-moraine zone. We therefore interpret this landform assemblage as representing repeated halts in the decay of an active ice sheet. Thus, we accept Lager-bäck’s age assignment but not the concept of areal stagnation.
Zone 4: A series of till-covered glaciofluvial formations in northern Finland, at right angles to the stage 5d flow pattern (Nordkalott Project, 1986a, b).
Zone 5: Buried end morains in the Pudasjärvi area (Reference Sutinensutinen, 1984), probably reflecting the maximum extent of the stage 5d ice sheet.
No unequivocal evidence exists for the extern of the southern and western parts of the stage 5d ice sheet. Although the striae in the synchronous fans 4 (Reference VorrenVorren, 1977, Reference Vorren1979), 11 and 12 (Reference LundqvistLundqvist, 1969) define westerly ice divides of a probable early-Weichselian age, they cannot be linked to any specific ice-marginal position. In the northeast we have placed the ice margin at the above zone 5, where also the coherent flow traces defining fan 38 terminate. Such an ice margin could possibly explain a zone of sandy sediments on the Gulfof Bothnia sea-floor (Reference FredénFredén, 1994), which forms a direct southwesterly extension of the suggested ice margin. We have assigned the stage 5d maximum configuration an age of 110 ka, by correlation with the marine oxygen-isoiope record. The configuration where the ice margin is defined by zone 3 is assigned an age of 100 ka. In its overall outline, our reconstructed stage 5d ice sheet is similar to the outline suggested by Reference LundqvistLundqvist (1992), the only important difference being that we infer a complete ice cover over coastal Norway. We do this on the basis of the morphological evidence for extremely west-centred configurations during early parts of the last glaciation (Reference LjungnerLjungner, 1949; Reference KlemanKleman, 1992).
For ice-marginal zones 1 and 2 no accurate age constraints exist; we only know that the zones recflect the occurrence of small-sized ice sheets prior to the build-up of the late Weichselian ice sheet (i.e. they can have formed any time during the early Weichselian, or even during the Saalian glaciation). Regarding the stage 5b ice sheet, inferred to have existed on the basis of thin till beds separating the Peräpohjola and Tärendö interstadial deposits (Lager-bäck and Robertsson, 1988), we have found no coherent system of flow-direction indicators directly supporting its existence. As a completely cold-based ice cover need not leave any flow traces, the lack of such traces leaves open the alternatives of (1) no ice sheet, or (2) an almost entirely cold-based ice sheet. If a stage 5b ice sheet existed, meltwater landforms must have formed during decay (Borgström, 1989), but it is conceivable that they are directionally compatible with the meltwater pattern laid down during the stage 5d decay and therefore cannot be distinguished, Our preferred interpretation is that stage 5b in northern Fenno-scandia was characterised by a restricted glaciation, with build-up of a thin, entirely cold-based ice sheet of limited size, not reaching the Swedish Finnish border or the Bothnian coast. This is in agreement with the lack of evidence for a stage 5b ice sheet in northern Finland (Reference HirvasHirvas, 1991).
An alternative, but in our opinion less likely, interpretation is that the ice sheet defined by fan 38 is indeed of 5bage, with the two subsequent interstadials instead representing 5a and a partial deglaciation of northern Fennoscandia in isotope stage 3. around 50 ka (cf. Garcia Ambrosiani, 1991).
Marine isotope stages 4 and 3, 74–25 ka (Fig. 6)
Most of Sweden is generally assumed to have been ice-covered during isotope stage 4 (Reference Anderson and MangerudAndersen and Mangerud, 1989; Reference LundqvistLundqvist, 1992). A key problem in this context is the age and stratigraphic value of a characteristic clayey, bluish grey till with a high content of far-travelled clasts (Reference LundqvistLundqvist, 1973a; Björnbom, 1979), with possible correlatives in Norway (Låg, 1948) and Finland (Reference Rainio and LahermoRainio and Lahermo, 1976; Reference IisaloIisalo, 1992). An earkt-Weichselian age was Suggested by Reference LundqvistLundqvist (1973a)and Reference LundqvistLundqvist anil Miller (1992), whereas an initial phase of the late Weichselian was suggested by Björnbom (1979). Data presented by Reference IisaloIisalo (1992)show that a bluish silty lower till in the area of fan 35 is older than interstadial sediments dated as older than 44 ka. However, it is unknown if the lower till described by Reference IisaloIisalo (1992), which contains abundant reworked marine sediments from the Baltic basin, is a true correlative to the Swedish sites.
Of particular importance are the ice-flow directions, inferred from till fabrics and a few striae observations for the tills described by Björnbom (1979). In central Sweden ice flow was from the west or west-northwest. This indicates an ice sheet with a southern centre of mass, including a dome centre over southern Norway, as opposed to the stage 5d configuration, which had a northerly centre of mass. Fans 15 and 22 are defined by till-fabric data and a few associated striae in Björnbom (1979). Two other fans, 7 and 9, also indicate an ice sheet with a major dome centre over southern Norway, and when grouped with 15 and 22 form a glaciologically plausible ice-sheet configuration.
We note that the pattern of fan 7, which unquestionably is older than the LGM (Reference Houmark-NielsenHoumark-Nielson, 1981). indicates a pre-late-weichselian ice margin in western Denmark southof the LGM position. This indicates an extensive ice sheet covering the North Sea, possibly linked with the British ice sheet, in line with suggestions by Reference Larsen and SejrupLarsen and Sejrup (1990), and very harsh climatic conditions. Fan 9, defined by a regional occurrence of older striae from the north-northwest (Reference Adrielsson and KlingbergAdrielsson and Klingberg, 1989; Påsse, 1990, 1993), lacks any dating constraints. However, Påsse (1993) found westerly and northwesterly orientated glacial tectonic features in Eemian sediments in this area, and considered these flow directions to represent the first post-Eemian ice cover in the area. We consider fans 7, 9, 15 and 22 incompatible with any reasonable LGM or later flow pattern. This also holds true for fan 8, defined on the basis of lineations and an older striae system documented by Reference Ericsson and GrånäsEricsson and Grånäs (1983). In short, we regard the flow-trace evidence for the existence of the southwest-centred Configuration shown in Figure 6as compelling, but acknowledge substantial uncertainty regarding its age.
Our preferred interpretation is that fans 7, 9, 15 and 22 reflect the rapid build-up of a southwest-centred ice sheet during the climatic deterioration at the beginning of isotope stage 4, i.e. that these fans are indeed expansion fans. We suggest further that this configuration reflects ice build-up during extreme cooling, with a seasonally ice-covered Norwegian Sea, severely limiting precipitation supply to the northeastern part of the ice sheet. The stage 4 ice-sheet configuration is distinctly different from the stage 5d ice-sheet outline, which instead indicates a two-domed ice sheet with a northerly centre of mass. We also consider it less likely that fans 7, 9, 15 and 22 represent the Stage 5b ice sheet. This is because the approximately 6 ka duration of the cooling and probable build-up phase during stage 5b is, with realistic precipitation values, too short a time period to build an ice sheet that in this sector is as large as, or larger than, the LGM configuration.
No ice-flow directional evidence bears on the detailed pattern of growth from the 65 ka time-slice configuration to the LGM at 22 ka. Oxygen isotope data (Fig. 1) indicate a decrease in global ice Volume during isotope stage 3 (mid-Weichselian), which is likely to be reflected also in the Fennoscandian ice sheet. Interstadial deposits along the coast of Norway (Reference Anderson, Nydal, Wangen and ØstmoAndersen and others, 1981, Reference Andersen, Serjrup and Kirkhus1983; Reference MangerudMangerud and others, 1981; Reference Larsen, Gulliksen, Lie, Levlie and MangerudLarsen and others, 1987), in southwestern Sweden(Reference HilleforsHillefors, 1974; Reference MillerMiller, 1977) and in the northeastern parts of Denmark (Reference Houmark-Nielsen and KolstrupHoumark-Nielsen and Kolstrup, 1981) have been dated at 28–55 ka and indicate that there was a mid-Weichselian retreat from our reconstructed stage 4 ice-sheet extent. The magnitude of this retreat is debated, and reconstructions range from very limited (Reference DonnerDonner, 1996)
to near-complete (Reference Olsen, Mehdahl and SelvikOlsen and others, 1996) deglaciation during the mid-Weichselian. The oxygen isotope values during stage 15 are slightly more negative than during stage 5d and 5b (Fig. 1). Thus, we argue that the minimum mid Weichselian ice-sheet extent was in the same range as the maximum early-Weichselian ice-sheet configuration, outlined in Figure 5.
We also consider it likely that fans 8 and 16, defined by till lineations and the regional occurrence of northwesterly striae in the Lake Mälaren region, respectively (Reference Möller and StalhosMöller and Stålhös 1965, Reference Möller and Stalhos1969; Björnbom, 1981; Reference MagnussonMagnusson, 1986; Reference EricssonEricsson and Lidén, 1988; Reference GrånäsGrånäs, 1990), belong to this period of ice-sheet growth. This is because fan 16 is younger than fan 15, which we assigned to isotope stage 4 (around 65 ka), but older than the LGM. As fans 8 and 16 indicate a more northerly direction of ice flow than fan 15, they probably represent an eastward migration of the ice-dispersal centre.
Marine isotope stage 2.22 ka, LGM (Fig. 7)
This reconstruction differs from the previous ones in that the LGM ice margin is well documented (Reference Andersen, Denton and HughesAndersen, 1981), except for some problematic areas located in the North Sea and Barents Sea sectors. We have tried to reconstruct a realistic surface topography based on the following lines of reasoning, (i) With a western ice-sheet margin constrained by the Norwegian shelf edge, the most easterly ice-divide position should have occurred when the eastern ice margin of the ice sheet was at its maximum position, i.e. during the LGM. (ii) In northern and southern Fennoscandia the fans related to the most easterly dispersal centre are likely to have formed at near-maximum stages. (iii) The isostatic uplift pattern does not indicate a heavy ice-load in northeasternmost Fenuoscandia (Reference EkmanEkman, 1989).
We have based the suggested ice-surface form lines on the direction of fans 5, 10, 14, 17, 20, 21, 27, 29, 31 and 44. We are uncertain about the chronologic position of fan 34: it may belong to this stage or it may be a much older feature preserved beneath cold-based areas of the ice sheet. Fan 20 is based on older striae in the Kalmar area (Reference RudmarkRudmark, 1980, Reference Rudmark1981, Reference Rudmark1983, Reference Rudmark1984), directionally compatible with a Baltic ice stream. The direction of fan 14, defined by older striae as described by Reference DanielDaniel (1989), matches the direction of fans 5 and 20 very well, defining a flow pattern from an easterly dispersal centre. Fan 31 may not necessarily have formed during the LGM, but nevertheless constrains an ice-dispersal centre, located far to the east of the mountain range. Fan 10, based on striae (Reference LundqvistLundqvist, 1969) and till lineations (Borgström, 1989), is compatible only with a main ice divide trending eastwards from the high ground in southern Norway. The location and shape of this fan indicate that the lower elevation in the central part of the mountain range significantly influenced the ice-drainage pattern, causing a distinct bend in die main ice divide.The form lines of the ice sheet in Figure 7have been drawn at right angles to the ice-flow directions corresponding to the above mentioned fans.
Marine isotope stages 2 and 1, post-LGM decay pattern (Fig. 8)
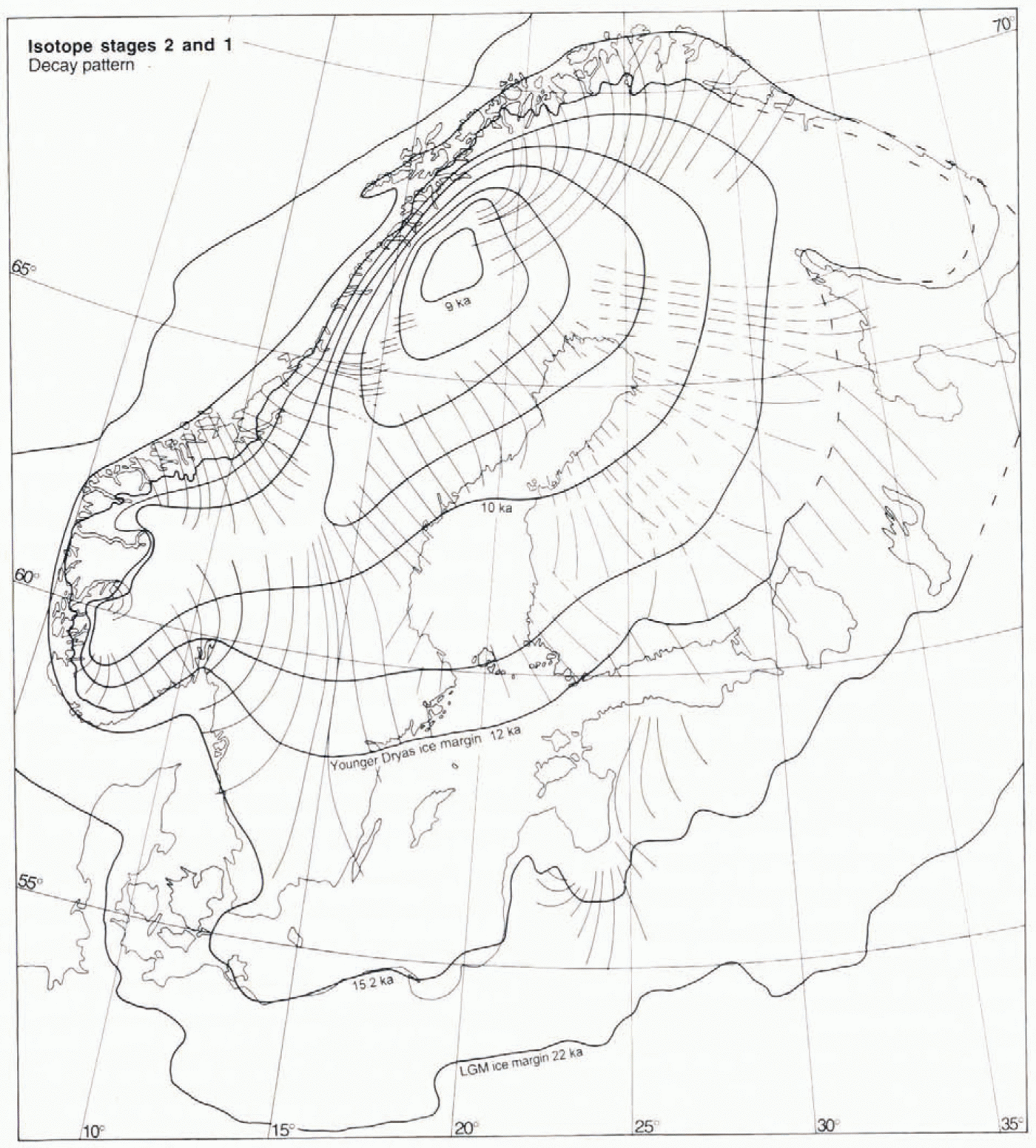
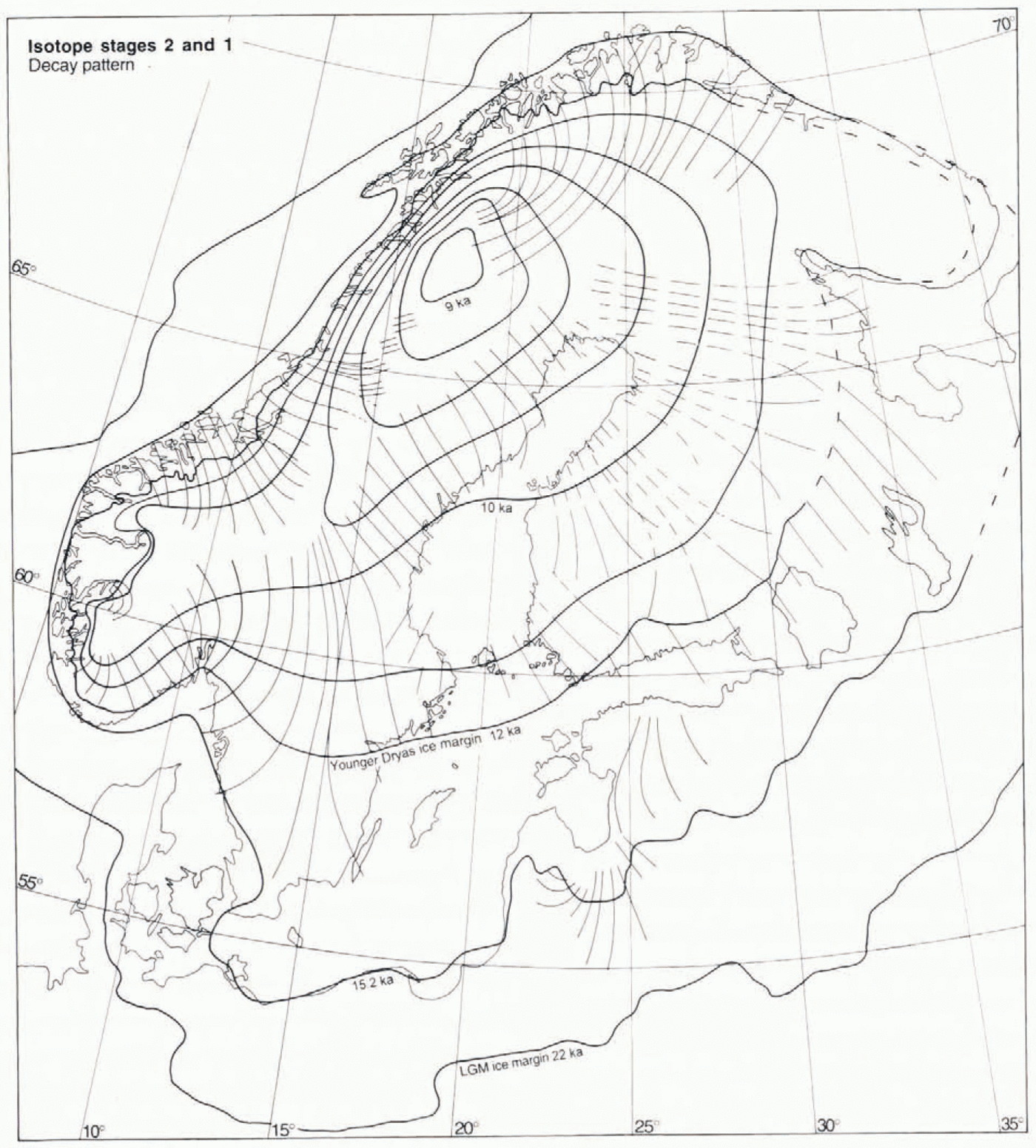
Fig. 8. The decay pattern from 22 ka to approximately 9 ka. Thin lines are the longitudinal continuity lines for deglacial fans 1, 2, 6, 24, 43 and 45, as well as the distal parts of fans 26, 28, 46, 48 and 50, representing time-transgressive formation of flow traces and subsequent preservation by deglaciation. Thin dashed lines represent the near-deglacial flowlines of the proximal parts of fans 28, 46, 48 and 50. Ice-marginal positions at 22 and 15.2 ka are based on Reference Andersen, Denton and HughesAndersen (1981), recalculated from radiocarbon years to calendar years on the basis of Reference Bard, Hamelin, Fairbanks and zindlerBard and others (1990). The 12 ka (Younger Dryas) and 10 ka ice margins are based on the Swedish varve chronology (Reference StrömbergStrömberg, 1989, Reference Strömberg1994), with a 350 a correction based on the age of the Younger Dryas climatic event in the Greenland icе-cоrе record (Reference MayewskiMayewski and others, 1993).
The post-12 ka retreat pattern in Figure 8is based on fans 1, 2, 6, 23, 24, 43 and 45, and the dry-bed fan 56, shown in Figure 9. The ice-sheet outline at 22 and 15.2 ka is based on Reference Andersen, Denton and HughesAndersen (1981). The marginal retreat from the LGM position to the final disappearance of the ice sheet has been extensively studied (e.g. Reference Andersen, Denton and HughesAndersen, 1981; Reference LundqvistLundqvist, 1986). This evolution is within the radiocarbon-dating range and is, in the Baltic area, also dated by varve counting (Reference StrömbergStrömberg, 1989). Hence, different parts of the retreat sequence are dated by different methods and, in the case of radiocarbon dating, different materials involving various time lags and error sources. Gives our ambition to present calendar-year configurations and time-slice flow patterns on ice-sheet scale, these incompatibilities have to be overcome. Our approach involves the following components:
(1) Acceptanee of the calibration of the radiocarbon time-scale by U-Th dating of Barbados corals (Reference Bard, Hamelin, Fairbanks and zindlerBard and others, 1990).
(2) For the area south of the Baltic, where the lineations in Figure 3give poor spatial control, we have accepted Reference Andersen, Denton and HughesAndersen’s (1981)13 ka (14C years) ice margin. For conversion to calendar years, we have used a 2.2 ka correction derived from Reference Bard, Hamelin, Fairbanks and zindlerBard and others (1990).
(3) Acceptance of the Greenland ice-core record (Reference MayewskiMayewski and others, 1993), dated by annual layer counting, as a “true” record giving the absolute age of the Younger Dryas climatic event, an event whose glacial geological effects are well displayed in Fenno-scandia.
(4) We regard the Swedish varve chronology as being accurate for post-Younger Dryas stages. This previously floating chronology has been connected to the present by Reference CatoCato (1987). However, in line with the suggestion put forward by Reference StrömbergStrömberg (1994), we consider that the time lag between the abrupt post-Younger Dryas warming, evident in the Greenland record, and the onset of rapid retreat from then Younger Dryas moraines in central Sweden (Reference StrömbergStrömberg, 1994) is unrealistically large. According to Reference MayewskiMayewski and others (1993), the age of the Younger Dryas climatic event is 12.9–11.5 ka, whereas the clay-varve chronology (Reference StrömbergStrömberg, 1994) dates the corresponding readvance, subsequent haly and moraine-building event at 11.64–10.94 ka. Thus, it appears that varve ages are too young. We regard a substantial time lag between the onset of cooling, readvance and halt of the ice margin as plausible. However, a 550 year time lag between the onset of warming and onset of rapid marginal retreat appears unlikely; a time lag of only 200 years appears more reasonable.We have therefore added 350 years to the clay varve age of the Younger Dryas moraines in Sweden, thus assigning an ageof 12 ka to the Yntnger Dryas margin shown in Figure 8.

Fig. 9. The dry-bed deglaciation fan (56) in northern Fenno-scandia. This fan lacks till lineations and eskers and is instead defined by glaciofluvial channel systems and scattered observations of locally youngest striae. Older glacial and non-glacial landforms were largely preserved in this frozen-bed area.
Basal thermal zonation at the LGM
We interpret preserved pre-late-Weichselian glacial and non-glacial landforms under the central parts of the ice sheetas marking sustained frozen-bed conditions during the last stadial (Reference KlemanKleman and Borgström, 1990; Reference Kleman and StroevenKleman, 1994). Areas with abundant relict landforms are shown in Figure 10. Ii is not implied that marked areas have completely escaped erosion during the late Weichselian; locally within these areas there are zones which have been slightly reshaped during the last stadial. There is commonly an intricate patchwork of fluted and completely preserved areas (Reference KlemanKleman and Borgström, 1994). However, the greater part of the marked areas is unaltered, and we thus interpret them as representing areas where the late-Weichselian Fennoscandian ice sheet was frozen to its bed.
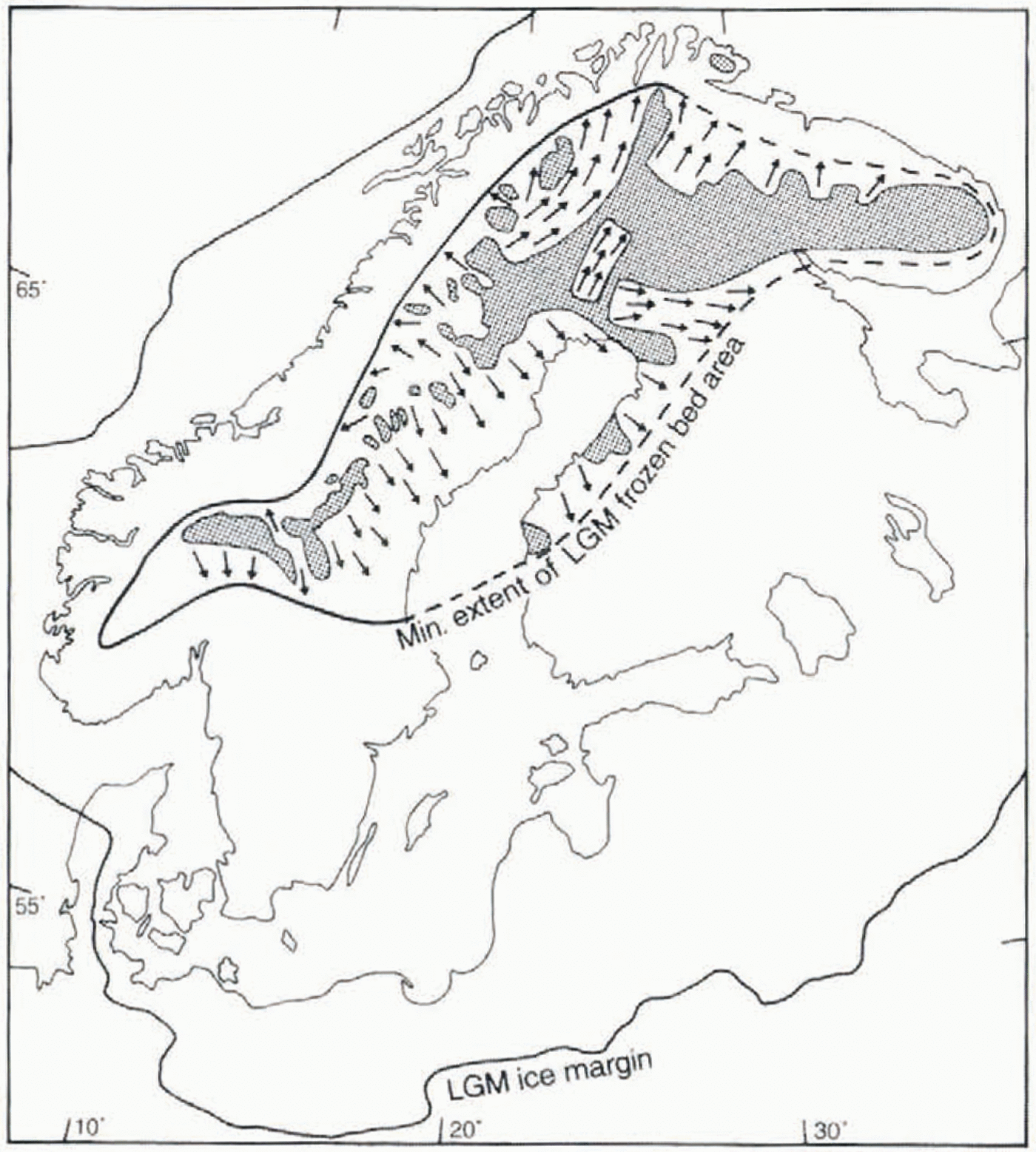
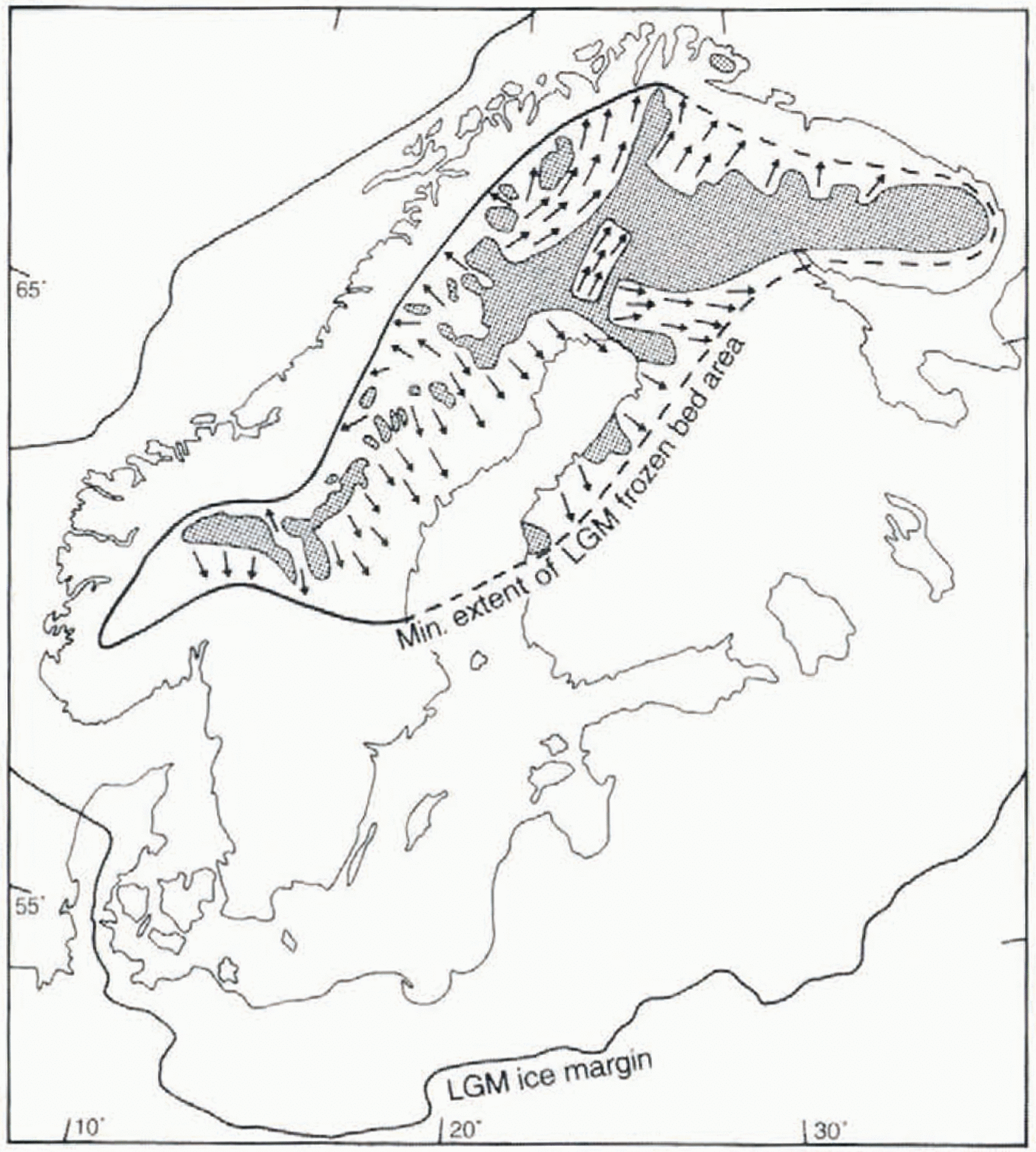
Fig. 10. Frozen-bed distribution at deglaciation (shaded areas) and inferred minimum frozen-bed zone at LGM (enclosed by bold line). Arrows mark ice-flow directions in wet-bed zones cutting into the frozen-bed core area of the ice sheet. The map is based on data presented in this paper as well as from Reference KaitanenKaitanen (1969), Reference KujansuuKujansuu (1975), Nordkalott Project (1986a, b), Reference LagerbäckLagerbäck (1988a, Reference Lagerbäckb). Reference Lagerbäck and RobertssonLagerbäck and Robertsson (1988), Reference RodheRodhe (1988), Bogström (1989), Reference KlemanKleman and Borgström (1990, Reference Kleman1994), Reference KlemanKleman (1992), Reference KlemanKleman and others (1992), Reference LundqvistLundqvist (1992), and Reference HättestrandHättestrand (inpress).
The fragmented nature of the preserved area, which in northern Fennoscandia is clearly dissected by inward-trans-gressive lineation swarms (fans 24 and 43), the surge fan 50 and the non-deglacial fan 31, indicates a larger former extentof the frozen-bed zone. In our view, only the severely restricted erosion associated with a frozen bed can explain theobserved pattern, with sharp lateral boundaries between young lineation zones and relict landscapes. As shown by the inward-transgressive lineation swarms, the frozen-bed area was diminished during the post-LGM stages. We have used thisrelationship to infer what we consider to be the minimum realistic frozen-bed extent at the LGM (heavy line in Fig. 10). As stratigraphical data indicate near-complete deglaciation during isotope stage 5a (Reference Lagerbäck and RobertssonLagerbäck and Robertsson.1988; Reference LundqvistLundqvist, 1992), the cold-based central zone must have developed during the 70–22 ka interval. Reference LagerbäckLagerbäck (1988a)inferred an extremely harsh polar desert climate in northern Fennoscandia during stage 5a, which through the development of deep permafrost may have facilitated the build-up of a largely cold-based ice-sheet sector. The scarcity of flow traces that can be assigned to marine isotope stage 3 is well explained by a frozen bed in the core area of the ice sheet.
In the inversion presented here, there is one group of subglacial landforms which we have not employed, namely, the ribbed moraines. Despite the fact that ribbed moraines are common features in the interior parts of former ice sheets, they cannot at present be used in the reconstruction of ice sheets, as the state of knowledge regarding their genesis is inadequate. However, there appears to be a spatial linkage between the ribbed-moraine distribution and the basal thermal regime of the Fennoscandian ice sheet. The area of frozen bed during the LGM (inside the thick line in Fig. 10) closely follows the distribution pattern of ribbed moraines in Fennoscandia (Reference Sollid and KristianssenSollid and Torp, 1984; Nordkalott Project, 1986a; Reference HättestrandHättestrand, in press). Asimilar correlation of a shrinking frozen-bed zone and the development of ribbed moraines has previously been suggested for the Labrador sector of the Laurentide ice sheet (Reference Kleman, Bongstraöm and HättsetrandKleman and others, 1994). This is in line with the formation hypothesis for ribbed moraines put forward by Reference HättestrandHättestrand (in press), who argues that ribbed moraines form by fracturing and extension of a pre-existing drift sheet, during the transition from frozen to wet-based conditions. Thus, it is possible that the distribution of ribbed moraines may in the future be used as an additional tool in mapping the extent of frozen-bed areas under former ice sheets.
Time-slice flow patterns
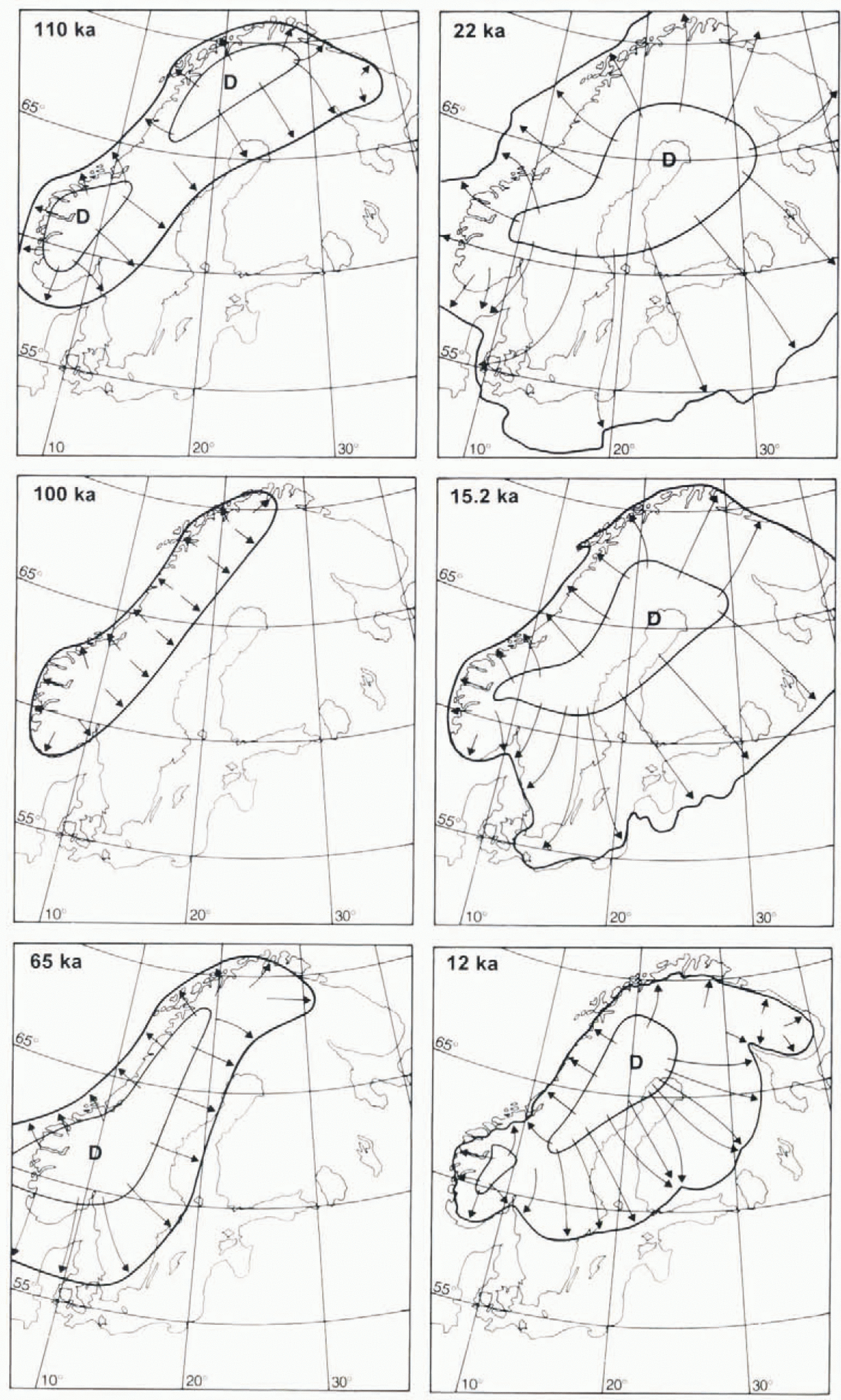
Figure 11summarises, for each time slice, the surface configuration and flow patterns that are most compatible with the evidence previously presented. The configurations during glacial maxima (110 and 22 ka) can be confidently reconstructed, as can the stages during the last deglaciation, whereas ice-marginal positions and configurations during isotope stage 3 remain elusive. The identification of the 65 ka configuration centred In the extreme southwest indicates substantial shifts, not only in the east west balance (Reference LjungnerLjungner, 1919; Reference Anderson and MangerudAndersen and Mangerud, 1989; Reference LundqvistLundqvist, 1992), butalso in the north south balance of the ice sheet.
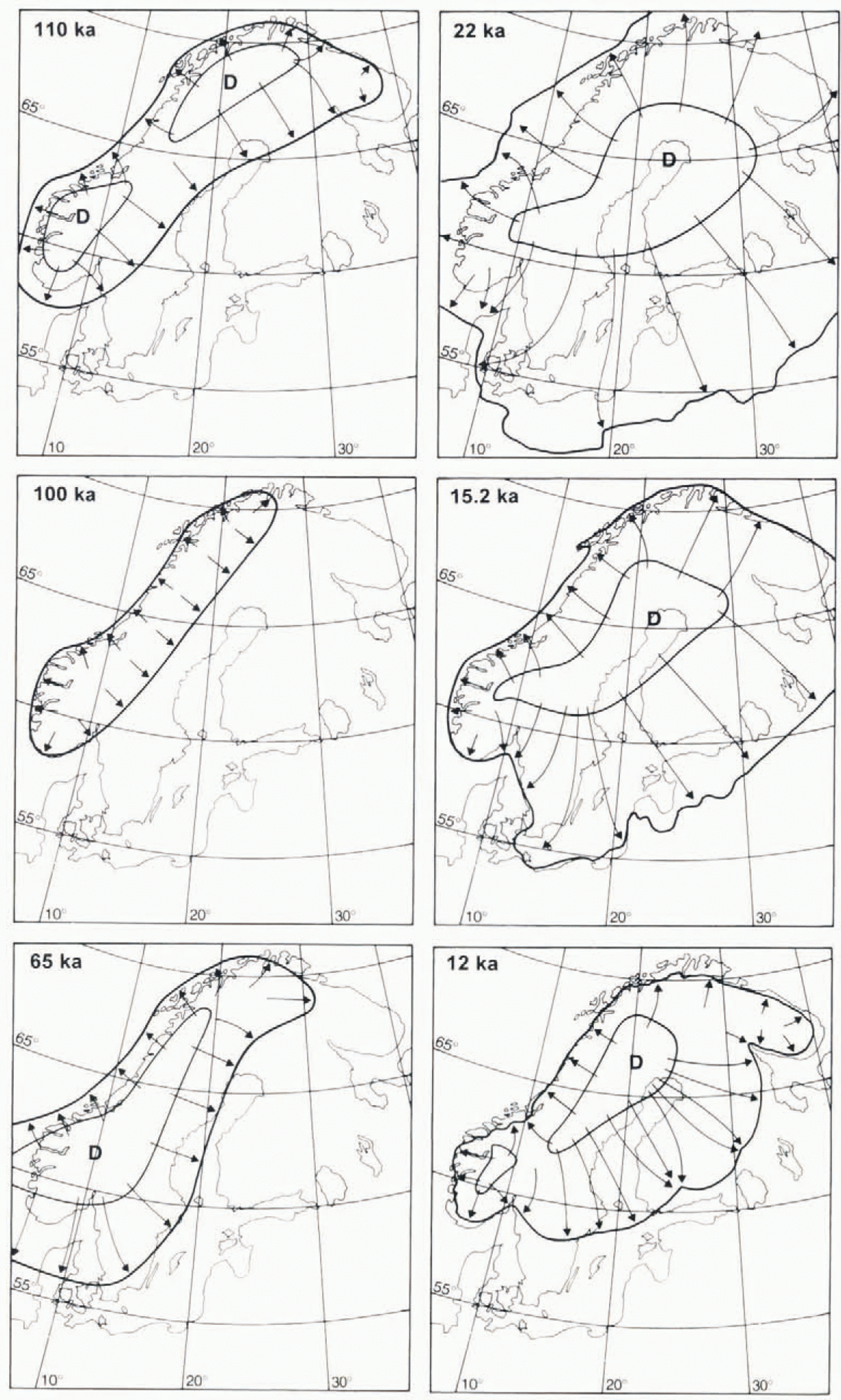
Fig. 11. Synthesis of the favoured interpretations regarding ice-sheet outline, dispersal-centre location (D) and flow pattern (arrows) for six discrete time slices during the last glacial cycle.
Discussion
Glaciological mechanisms
Our results indicate that the configuration changes of the Fennoscandian ice sheet during the last glacial cycle represent a unique, climatically driven evolution. There is no evidence to indicate short-term oscillatory changes in basaltemperature (binge-purge mechanism), as has been suggested for the Laurentide ice sheet (Reference MacAyealMacAyeal, 1993). If such repeated wet-bed events had occurred, we would expect complete erasure of old morphology and evidence for repeated flow events with only slightly differing patterns. The evidence for frozen-bed conditions for more than 50 ka in the early-Weichselian landscape indicates instead that the late-Weichselian ice sheet was a glaciologically Stable feature, with athermal zonation pattern Strongly resembling that proposed by Reference Hughes, Denton and HughesHughes (1981)for terrestrial ice domes. These results are in line with recent modelling experiments by Reference Huybrechts and T’siobbelHuybrechts and T’siobbel (1995)and J. Fastook (personal communication, 1995), which indicate a Stable frozen-bed core area for the Fennoscandia ice sheet. The existence of a frozen-bed core area in Fennoscandia was previously suggested by Sehytt (1974) and Reference Sollid and SorbelSollid and Sorbel (1988). We thus envisage a frozen-bed core area, an intermediate zone with a fractal patchwork of frozen and thawed bed, and an outer wet-bed zone as a normal zonation for terrestrial ice domes, in line with reconstructions for peripheral domes of the Laurentide ice sheet (Reference DykeDyke, 1993), and the Labrador sector of the Laurentide ice sheet (Reference KlemanKleman and others, 1994).
We likewise find another suggested glaciological mechanism, drumlin formation caused by subglacial “megaflood” Outbursts (Reference ShawShaw, 1989), not applicable to the Fennoscandian ice sheet. The major drumlin zones in northern Fennoscandia all terminate proximally in frozen-bed zones, leaving no space for major subglacial water reservoirs. Furthermore, some major lineation swarms are elearly time-transgressive and reflect continuous formation over thousands of years, which is incompatible with the subglacial flood hypothesis, as Hoods cannot be sustained over such long time periods.
Comparison with numerical modelling results
A comparison with recent numerical modelling of the Fennoscandian ice sheet by Reference Holmlund and FastookHolmlund and Fastook (1995)reveals great similarity in pattern for the early-Weichselian interval (their Fig. 4b), although there are differences in the age assignments of the events. However, none of their time slices can explain the flow traces in fans 7, 9, 15 and 22, constituting our 65 ka configuration. This indicates a substantial spatial deficiency of the mass-balance forcing in their model for at least one critical time interval during the last glacial. The same holds true for the model of Reference Huybrechts and T’siobbelHuybrechts and T’siobbel (1995)which, although creating a central frozen-bed zone in reasonable agreement with the geological evidence, initially builds an ice sheet centred over northeastern Fennoscandia, and does not show any potential to explain the flow pattern documented by the above fans. In our view, these discrepancies between geological data and numerical modelling results suggest an inability of present glaciological models to handle adequately the large spatial changes in precipitation pattern that were most likely associated with major changes in the position of the polar water front (McIntyrr and others, 1972) Reference McManus, Bond, Broecker, Johnsen and HigginsMcManus and others, 1994) and sea-ice cover in the North Atlantic.
It should also be noted that while the use of the glacial geological inversion model described in this paper can give information on the evolution of the ice sheet in two dimensions, i.e. the ice-flow patterns and, to some extent, the outline of the ice sheet, very little can be concluded concerning the thickness of the ice. Thus, the results presented in this paper should be used as boundary conditions for numerical ice-sheet models, as only these models can give information on the full three-dimensional evolution of the Fennoscandian ice sheet.
Conclusions
In this paper we have shown that, by employing a glacial geologic inversion model to formalise the use of the glacial landform record, it is possible to reconstruct the evolution of the Fennoscandian ice sheet through the last glacial. The most important conclusions from the investigations are as follows:
The flow traces in both time-transgressive and “event” land-form systems can be used efficiently for reconstruction of flow-pattern evolution through the use of the graphical glacial geological inversion model.
Some time during the early Weichselian, probably during isotope stage 5d, a northwest-centred ice sheet reached just across the Gulf of Bothnia.
The major build-up phase of the Weichselian Fennoscandian ice sheet was characterised by a centre of mass in an extreme southwesterly position during isotope stage 4. It is probable that the British and Fennoscandian ice sheets were confluent at this Stage. Build-up of the northeastern sector of the Fennoscandian ice sheet slowly took place during the 65–22 ka interval.
At the LGM, die Fennoscandian ice Sheet had a main ice divide over the Gulf of Bothnia and a major bend in the ice divide caused by outflow to the northwest over the lowest part of the mountain chain. The ice sheet had a frozen-bed corearea, which was only partly consumed by inward-transgressive wet-bed zones during the decay phase.
The southwest-centered pattern of build-up during isotope stage 4 is poorly reproduced by current numerical glaciological models.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by grants from the Swedish Natural Science Research Council. J. Lundqvist, M. Saarnisto, M. Siegert, В. Strömberg and an anonymous referee have made constructive comments on the manuscript. We also want to thank K.Jansson for figure work.