Article contents
CONSTRUCTIVE REFLECTIVITY PRINCIPLES FOR REGULAR THEORIES
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 September 2019
Abstract
Classically, any structure for a signature  ${\rm{\Sigma }}$ may be completed to a model of a desired regular theory
${\rm{\Sigma }}$ may be completed to a model of a desired regular theory  ${T}}$ by means of the chase construction or small object argument. Moreover, this exhibits
${T}}$ by means of the chase construction or small object argument. Moreover, this exhibits 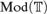 ${\rm{Mod}}\left(T)$ as weakly reflective in
${\rm{Mod}}\left(T)$ as weakly reflective in 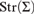 ${\rm{Str}}\left( {\rm{\Sigma }} \right)$.
${\rm{Str}}\left( {\rm{\Sigma }} \right)$.
We investigate this in the constructive setting. The basic construction is unproblematic; however, it is no longer a weak reflection. Indeed, we show that various reflectivity principles for models of regular theories are equivalent to choice principles in the ambient set theory. However, the embedding of a structure into its chase-completion still satisfies a conservativity property, which suffices for applications such as the completeness of regular logic with respect to Tarski (i.e., set) models.
Unlike most constructive developments of predicate logic, we do not assume that equality between symbols in the signature is decidable. While in this setting, we also give a version of one classical lemma which is trivial over discrete signatures but more interesting here: the abstraction of constants in a proof to variables.
Information
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Association for Symbolic Logic 2019
References
REFERENCES
- 1
- Cited by

