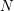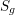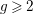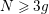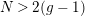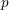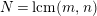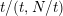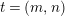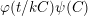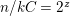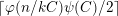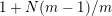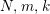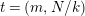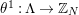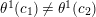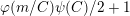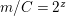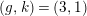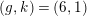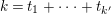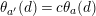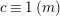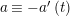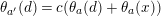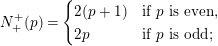1 Introduction
By an action of a group
![]() $G$
on a surface
$G$
on a surface
![]() $S$
we understand an embedding of
$S$
we understand an embedding of
![]() $G$
into the group
$G$
into the group
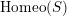 $\text{Homeo}(S)$
of homeomorphisms of
$\text{Homeo}(S)$
of homeomorphisms of
![]() $S$
. Two such actions are topologically conjugate, or of the same topological type, if the images of
$S$
. Two such actions are topologically conjugate, or of the same topological type, if the images of
![]() $G$
are conjugate in
$G$
are conjugate in
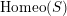 $\text{Homeo}(S)$
.
$\text{Homeo}(S)$
.
In [Reference Hirose10], it was shown that, except for a few cases, the order
![]() $N$
of the finite cyclic group
$N$
of the finite cyclic group
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
acting on a closed orientable topological surface
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
acting on a closed orientable topological surface
![]() $S_{g}$
of genus
$S_{g}$
of genus
![]() $g\geqslant 2$
determines the topological type of the action, provided that
$g\geqslant 2$
determines the topological type of the action, provided that
![]() $N\geqslant 3g$
. In [Reference Bagiński, Carvacho, Gromadzki and Hidalgo2], Grzegorz Gromadzki et al. undertook a more general problem of topological classification of such actions for
$N\geqslant 3g$
. In [Reference Bagiński, Carvacho, Gromadzki and Hidalgo2], Grzegorz Gromadzki et al. undertook a more general problem of topological classification of such actions for
 $N>2(g-1)$
. This is an essential extension, because between
$N>2(g-1)$
. This is an essential extension, because between
![]() $3g$
and
$3g$
and
![]() $4g+2$
only
$4g+2$
only
![]() $3g+1$
,
$3g+1$
,
![]() $3g+2$
,
$3g+2$
,
![]() $3g+4$
and
$3g+4$
and
![]() $4g$
can stand as the period of a single self-homeomorphism of
$4g$
can stand as the period of a single self-homeomorphism of
![]() $S_{g}$
, whereas there are infinitely many rational values of
$S_{g}$
, whereas there are infinitely many rational values of
![]() $a,b$
such that for
$a,b$
such that for
 $N=ag+b$
we have
$N=ag+b$
we have
 $N>2g-2$
and
$N>2g-2$
and
![]() $N$
is the period of a self-homeomorphisms of
$N$
is the period of a self-homeomorphisms of
![]() $S_{g}$
for infinitely many
$S_{g}$
for infinitely many
![]() $g$
. In [Reference Gromadzki, Szepietowski and Zhao7], we considered analogous problem for cyclic actions generated by an orientation-reversing self-homeomorphism, while in [Reference Gromadzki and Szepietowski6] – a similar problem for closed nonorientable surfaces, obtaining a classification of topological types of action of
$g$
. In [Reference Gromadzki, Szepietowski and Zhao7], we considered analogous problem for cyclic actions generated by an orientation-reversing self-homeomorphism, while in [Reference Gromadzki and Szepietowski6] – a similar problem for closed nonorientable surfaces, obtaining a classification of topological types of action of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
on a surface
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
on a surface
![]() $S$
in function of a possible type of the quotient orbifold
$S$
in function of a possible type of the quotient orbifold
![]() $S/\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
, provided that
$S/\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
, provided that
![]() $N$
is sufficiently big.
$N$
is sufficiently big.
The present paper, in which we deal with topological classification of actions of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
on a bordered surface of algebraic genus
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
on a bordered surface of algebraic genus
![]() $p$
, where
$p$
, where
 $N>p-1$
, completes our project of topological classification of big cyclic actions on compact surfaces. The lower bound
$N>p-1$
, completes our project of topological classification of big cyclic actions on compact surfaces. The lower bound
![]() $p-1$
for the order of an action is essential for two reasons. The first is that we again cover a quite large class of actions, since there are infinitely many rational values of
$p-1$
for the order of an action is essential for two reasons. The first is that we again cover a quite large class of actions, since there are infinitely many rational values of
![]() $a,b$
, for which there are infinitely many values of
$a,b$
, for which there are infinitely many values of
![]() $p$
, such that a bordered surface of algebraic genus
$p$
, such that a bordered surface of algebraic genus
![]() $p$
admits a cyclic action of order
$p$
admits a cyclic action of order
 $N=ap+b$
and
$N=ap+b$
and
 $N>p-1$
. The second reason for the bound
$N>p-1$
. The second reason for the bound
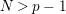 $N>p-1$
is that it is satisfied for all the actions realizing the solutions of the so-called minimum genus and maximum order problems for bordered surfaces found in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4], and the question about their topological rigidity partially motivated the present paper.
$N>p-1$
is that it is satisfied for all the actions realizing the solutions of the so-called minimum genus and maximum order problems for bordered surfaces found in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4], and the question about their topological rigidity partially motivated the present paper.
Our results can be seen as a topological classification of cyclic group actions of order
![]() $N$
on bordered surfaces of algebraic genus
$N$
on bordered surfaces of algebraic genus
![]() $p\leqslant N$
. Another problem, suggested by the referee of this paper, would be to obtain a similar classification for surfaces of large genera that is
$p\leqslant N$
. Another problem, suggested by the referee of this paper, would be to obtain a similar classification for surfaces of large genera that is
![]() $p$
bigger than
$p$
bigger than
![]() $N$
. We remark that there are many results in the literature about the spectrum of genera of surfaces admitting a given finite group as a group of self-homeomorphisms. As an example of such results in the case of closed orientable surfaces let us mention the important paper [Reference Kulkarni14] by Kulkarni. While we believe that it should not be difficult to obtain similar results for bordered surfaces, it seems that it would be a rather difficult problem to classify topologically actions of order
$N$
. We remark that there are many results in the literature about the spectrum of genera of surfaces admitting a given finite group as a group of self-homeomorphisms. As an example of such results in the case of closed orientable surfaces let us mention the important paper [Reference Kulkarni14] by Kulkarni. While we believe that it should not be difficult to obtain similar results for bordered surfaces, it seems that it would be a rather difficult problem to classify topologically actions of order
![]() $N<p$
. The main reason is that the orbit spaces which occur in the case
$N<p$
. The main reason is that the orbit spaces which occur in the case
![]() $N<p$
may have much bigger and much more complicated mapping class groups (see Section 5 for a definition) than for
$N<p$
may have much bigger and much more complicated mapping class groups (see Section 5 for a definition) than for
![]() $p\leqslant N$
, and in such a case our method, based on a good understanding of these mapping class groups, is not effective.
$p\leqslant N$
, and in such a case our method, based on a good understanding of these mapping class groups, is not effective.
There are two more interesting features of the actions considered in this paper. The first is that finite group actions on compact surfaces of negative Euler characteristic may be realized by analytic actions on Riemann surfaces, or dianalytic actions on Klein surfaces, due to the Hurwitz–Nielsen, Kerkjarto and Alling–Greenleaf geometrizations mentioned in Section 3.1. The loci in the moduli spaces of Klein surfaces composed of the points classifying the surfaces dianalytically realizing the actions considered here have dimensions 1, 2 or 3 (this follows from Lemma 4.3, formula (4) and classical formula of Fricke and Klein for dimension of Teichmüller spaces of Fuchsian groups cf. [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4, Theorem 0.3.2]). This is similar as in the case of actions on unbordered nonorientable Klein surfaces [Reference Gromadzki and Szepietowski6], or orientation-reversing automorphisms of classical Riemann surfaces [Reference Gromadzki, Szepietowski and Zhao7], but in contrast to the classical case of orientation-preserving cyclic actions of order
 ${>}2g-2$
described in [Reference Bagiński, Carvacho, Gromadzki and Hidalgo2], where the loci of such structures in the moduli space are 0-dimensional, which means, in particular, that the topological type of an action of an orientation-preserving self-homeomorphism of such order usually uniquely determines the conformal type of a Riemann surface on which it acts as an automorphism. Finally, observe that our results can be stated in terms of birational actions on real algebraic curves due to the functorial equivalence between bordered Klein surfaces and such curves described in [Reference Alling and Greenleaf1].
${>}2g-2$
described in [Reference Bagiński, Carvacho, Gromadzki and Hidalgo2], where the loci of such structures in the moduli space are 0-dimensional, which means, in particular, that the topological type of an action of an orientation-preserving self-homeomorphism of such order usually uniquely determines the conformal type of a Riemann surface on which it acts as an automorphism. Finally, observe that our results can be stated in terms of birational actions on real algebraic curves due to the functorial equivalence between bordered Klein surfaces and such curves described in [Reference Alling and Greenleaf1].
This paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we state our main results. Section 3 contains necessary preliminaries concerning finite topological actions on bordered surfaces from the combinatorial point of view. In particular, we review non-Euclidean crystallographic groups. In Section 4, we determine the possible topological types of the orbit space (orbifold) of a cyclic action of order
![]() $N$
on a bordered surface of algebraic genus
$N$
on a bordered surface of algebraic genus
 $p<N+1$
. We obtain ten different topological types here, all of which are either a disc or an annulus or a Möbius band, with some cone points in the interior and some corner points on the boundary. In Section 5, we review the relationship between the groups of automorphisms of non-Euclidean crystallographic groups and mapping class groups. We also compute the mapping class groups of three surfaces: once-punctured annulus, once-punctured Möbius band and twice-punctured disc, which are needed for Section 6, where we prove our main results. Finally, in Section 7, we apply our results to study topological rigidity of the solutions of the so-called minimum genus and maximum order problems for cyclic actions on bordered surfaces, solved over 30 years ago in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4].
$p<N+1$
. We obtain ten different topological types here, all of which are either a disc or an annulus or a Möbius band, with some cone points in the interior and some corner points on the boundary. In Section 5, we review the relationship between the groups of automorphisms of non-Euclidean crystallographic groups and mapping class groups. We also compute the mapping class groups of three surfaces: once-punctured annulus, once-punctured Möbius band and twice-punctured disc, which are needed for Section 6, where we prove our main results. Finally, in Section 7, we apply our results to study topological rigidity of the solutions of the so-called minimum genus and maximum order problems for cyclic actions on bordered surfaces, solved over 30 years ago in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4].
2 Statement of the main results
Suppose that a cyclic group of order
![]() $N$
acts on a bordered surface
$N$
acts on a bordered surface
![]() $S$
of algebraic genus
$S$
of algebraic genus
![]() $p$
, where
$p$
, where
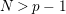 $N>p-1$
. We show in Section 4 that the orbit space
$N>p-1$
. We show in Section 4 that the orbit space
![]() $S/\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is one of the following orbifolds:
$S/\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is one of the following orbifolds:
(1) disc with 6 corner points;
(2) annulus with 2 corner points;
(3) Möbius band with 2 corner points;
(4) 1-punctured disc with 2 corner points;
(5) 1-punctured disc with 4 corner points;
(6) 1-punctured Möbius band;
(7) 2-punctured disc;
(8) 1-punctured annulus;
(9) 3-punctured disc;
(10) 2-punctured disc with 2 corner points.
Our classification of cyclic actions of big order is split into ten cases and the results are presented in ten consecutive subsections. Their proofs are given in Section 6 which is also divided in ten subsections with the same titles for the reader’s convenience. Throughout the whole paper
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}$
will denote the Euler totient function. We also need similar function
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}$
will denote the Euler totient function. We also need similar function
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}$
defined in [Reference Bagiński, Carvacho, Gromadzki and Hidalgo2] as
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}$
defined in [Reference Bagiński, Carvacho, Gromadzki and Hidalgo2] as
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(1)=1$
and given a prime factorization
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(1)=1$
and given a prime factorization
 $C=p_{1}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{1}}\cdots p_{r}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{r}}>1$
$C=p_{1}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{1}}\cdots p_{r}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{r}}>1$
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)=\mathop{\prod }_{i=1}^{r}(p_{i}-2)p_{i}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{i}-1}.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)=\mathop{\prod }_{i=1}^{r}(p_{i}-2)p_{i}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{i}-1}.\end{eqnarray}$$
Observe the analogy with the Euler function
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}$
which is defined for such
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}$
which is defined for such
![]() $C$
as
$C$
as
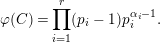 $$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(C)=\mathop{\prod }_{i=1}^{r}(p_{i}-1)p_{i}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{i}-1}.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(C)=\mathop{\prod }_{i=1}^{r}(p_{i}-1)p_{i}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{i}-1}.\end{eqnarray}$$
2.1 Actions with a disc with 6 corner points as the quotient orbifold
Theorem 2.1. There is an action of a cyclic group of order
![]() $N$
on a bordered surface
$N$
on a bordered surface
![]() $S$
with a disc having
$S$
with a disc having
![]() $6$
corner points as the quotient orbifold if and only if
$6$
corner points as the quotient orbifold if and only if
![]() $N=2$
and
$N=2$
and
![]() $S$
is a
$S$
is a
![]() $3$
-holed sphere. Furthermore, such action is unique up to topological conjugation.
$3$
-holed sphere. Furthermore, such action is unique up to topological conjugation.
2.2 Actions with annulus with 2 corner points as the quotient orbifold
Theorem 2.2. There is an action of a cyclic group of order
![]() $N$
on a bordered surface
$N$
on a bordered surface
![]() $S$
with an annulus having two corner points as the quotient orbifold if and only if
$S$
with an annulus having two corner points as the quotient orbifold if and only if
![]() $N$
is even and
$N$
is even and
![]() $S$
is one of the following surfaces:
$S$
is one of the following surfaces:
∙
 $N/2$
-holed Klein bottle;
$N/2$
-holed Klein bottle;∙
 $N/2$
-holed torus, where
$N/2$
-holed torus, where
 $N/2$
is odd;
$N/2$
is odd;∙
 $(N/2+1)$
-holed projective plane;
$(N/2+1)$
-holed projective plane;∙
 $(N/2+2)$
-holed sphere, where
$(N/2+2)$
-holed sphere, where
 $N/2$
is odd.
$N/2$
is odd.
Furthermore, such action is unique up to topological conjugation for each of these surfaces.
2.3 Actions with Möbius band with 2 corner points as the quotient orbifold
Theorem 2.3. There is an action of a cyclic group of order
![]() $N$
on a bordered surface
$N$
on a bordered surface
![]() $S$
having a Möbius band with
$S$
having a Möbius band with
![]() $2$
corner points as the quotient orbifold if and only if
$2$
corner points as the quotient orbifold if and only if
![]() $N$
is even and
$N$
is even and
![]() $S$
is either
$S$
is either
![]() $N/2$
-holed Klein bottle or
$N/2$
-holed Klein bottle or
![]() $N/2$
-holed torus, the latter being possible only for odd
$N/2$
-holed torus, the latter being possible only for odd
![]() $N/2$
. Furthermore, in both cases the action is unique up to topological conjugation.
$N/2$
. Furthermore, in both cases the action is unique up to topological conjugation.
2.4 Actions with a 1-punctured disc with 2 corner points as the quotient orbifold
Theorem 2.4. There is an action of a cyclic group of order
![]() $N$
on a bordered surface
$N$
on a bordered surface
![]() $S$
with a disc having one cone point of order
$S$
with a disc having one cone point of order
![]() $m$
and
$m$
and
![]() $2$
corner points as the quotient orbifold if and only if either
$2$
corner points as the quotient orbifold if and only if either
∙
 $m$
is even,
$m$
is even,
 $N=m$
and
$N=m$
and
 $S$
is
$S$
is
 $N/2$
-holed projective plane; or
$N/2$
-holed projective plane; or∙
 $m$
is odd,
$m$
is odd,
 $N=2m$
and
$N=2m$
and
 $S$
is
$S$
is
 $N/2$
-holed sphere.
$N/2$
-holed sphere.
Furthermore in both cases the action is unique up to topological conjugation.
2.5 Actions with a 1-punctured disc with 4 corner points as the quotient orbifold
Theorem 2.5. There is an action of a cyclic group of order
![]() $N$
on a bordered surface with a disc having one cone point of order
$N$
on a bordered surface with a disc having one cone point of order
![]() $m$
and
$m$
and
![]() $4$
corner points as the quotient orbifold if and only if either
$4$
corner points as the quotient orbifold if and only if either
∙
 $m$
is even,
$m$
is even,
 $N=m$
and
$N=m$
and
 $S$
is
$S$
is
 $N$
-holed projective plane; or
$N$
-holed projective plane; or∙
 $m$
is odd,
$m$
is odd,
 $N=2m$
and
$N=2m$
and
 $S$
is
$S$
is
 $N$
-holed sphere.
$N$
-holed sphere.
Furthermore, in both cases the action is unique up to topological conjugation.
2.6 Actions with 1-punctured Möbius band as the quotient orbifold
We consider the actions on orientable and nonorientable surfaces separately.
Theorem 2.6. There is an action of a cyclic group of order
![]() $N$
on a bordered orientable surface with
$N$
on a bordered orientable surface with
![]() $k$
boundary components, with a Möbius band having
$k$
boundary components, with a Möbius band having
![]() $1$
cone point of order
$1$
cone point of order
![]() $m$
as the quotient orbifold, if and only if
$m$
as the quotient orbifold, if and only if
![]() $k$
divides
$k$
divides
![]() $N$
,
$N$
,
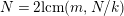 $N=2\text{lcm}(m,N/k)$
, and either
$N=2\text{lcm}(m,N/k)$
, and either
 $t=(m,N/k)$
is odd, or
$t=(m,N/k)$
is odd, or
![]() $N/2t$
is even. Furthermore, in such case the algebraic genus of the surface is equal to
$N/2t$
is even. Furthermore, in such case the algebraic genus of the surface is equal to
 $1+(m-1)N/m$
and there are
$1+(m-1)N/m$
and there are
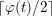 $\lceil \unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)/2\rceil$
conjugacy classes of such actions.
$\lceil \unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)/2\rceil$
conjugacy classes of such actions.
Theorem 2.7. There is an action of a cyclic group of order
![]() $N$
on a bordered nonorientable surface with
$N$
on a bordered nonorientable surface with
![]() $k$
boundary components, with a Möbius band having
$k$
boundary components, with a Möbius band having
![]() $1$
cone point of order
$1$
cone point of order
![]() $m$
as the quotient orbifold, if and only if
$m$
as the quotient orbifold, if and only if
![]() $k$
divides
$k$
divides
![]() $N$
,
$N$
,
 $N=\text{lcm}(m,N/k)$
, and for
$N=\text{lcm}(m,N/k)$
, and for
 $t=(m,N/k)$
,
$t=(m,N/k)$
,
![]() $N/t$
is odd. Furthermore, in such case the algebraic genus of the surface is equal to
$N/t$
is odd. Furthermore, in such case the algebraic genus of the surface is equal to
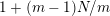 $1+(m-1)N/m$
and the number of topological conjugacy classes of such actions is
$1+(m-1)N/m$
and the number of topological conjugacy classes of such actions is
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)$
or
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)$
or
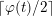 $\lceil \unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)/2\rceil$
if
$\lceil \unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)/2\rceil$
if
![]() $N$
is even or odd, respectively.
$N$
is even or odd, respectively.
2.7 Actions with a
 $2$
-punctured disc as the quotient orbifold
$2$
-punctured disc as the quotient orbifold
Theorem 2.8. There exists an action of a cyclic group of order
![]() $N$
on a bordered surface
$N$
on a bordered surface
![]() $S$
with
$S$
with
![]() $k$
boundary components, having a disc with two cone points of orders
$k$
boundary components, having a disc with two cone points of orders
![]() $m$
and
$m$
and
![]() $n$
as the quotient orbifold if and only if
$n$
as the quotient orbifold if and only if
![]() $S$
is orientable and
$S$
is orientable and
∙
 $N=\text{lcm}(m,n)$
;
$N=\text{lcm}(m,n)$
;∙
 $k$
divides
$k$
divides
 $t/(t,N/t)$
, where
$t/(t,N/t)$
, where
 $t=(m,n)$
;
$t=(m,n)$
;∙ if
 $N$
is even and
$N$
is even and
 $N/t$
is odd, then
$N/t$
is odd, then
 $k$
is even.
$k$
is even.
In such case the algebraic genus of
![]() $S$
is equal to
$S$
is equal to
 $1+N(1-1/m-1/n)$
and if
$1+N(1-1/m-1/n)$
and if
![]() $C$
denotes the biggest divisor of
$C$
denotes the biggest divisor of
![]() $t/k$
coprime to
$t/k$
coprime to
![]() $Nk/t$
, then the number of equivalence classes of such actions is
$Nk/t$
, then the number of equivalence classes of such actions is
∙
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t/kC)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)$
if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t/kC)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)$
if
 $n\neq m$
;
$n\neq m$
;∙
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(n/kC)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)/2+1$
if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(n/kC)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)/2+1$
if
 $n=m$
and
$n=m$
and
 $n/kC=2^{z}$
, where
$n/kC=2^{z}$
, where
 $z>1$
;
$z>1$
;∙
 $\lceil \unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(n/kC)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)/2\rceil$
otherwise.
$\lceil \unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(n/kC)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)/2\rceil$
otherwise.
2.8 Actions with a 1-punctured annulus as the quotient orbifold
First we deal with the actions on nonorientable surfaces.
Theorem 2.9. There exists an action of a cyclic group
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
on a nonorientable surface
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
on a nonorientable surface
![]() $S$
with
$S$
with
![]() $k$
boundary components, with an annulus having one cone point of order
$k$
boundary components, with an annulus having one cone point of order
![]() $m$
as the quotient orbifold, if and only if
$m$
as the quotient orbifold, if and only if
![]() $k$
divides
$k$
divides
![]() $N$
and
$N$
and
 $N=\text{lcm}(m,N/k)$
. Furthermore, in such case the algebraic genus of the surface is equal to
$N=\text{lcm}(m,N/k)$
. Furthermore, in such case the algebraic genus of the surface is equal to
 $1+N(m-1)/m$
and there are
$1+N(m-1)/m$
and there are
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)$
different topological types of such action, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)$
different topological types of such action, where
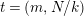 $t=(m,N/k)$
.
$t=(m,N/k)$
.
The case of orientable
![]() $S$
considered in the next theorem is much more involved. It has two parts. The first describes the necessary and sufficient conditions for existence of the actions, whereas the second has quantitative character and provides the numbers of equivalence classes of such actions. These numbers are expressed in terms of BSK-maps and therefore a reader less familiar with the study of periodic actions on compact surfaces from a combinatorial point of view should postpone the reading of (ii)–(iv) until Section 3, where these maps are introduced.
$S$
considered in the next theorem is much more involved. It has two parts. The first describes the necessary and sufficient conditions for existence of the actions, whereas the second has quantitative character and provides the numbers of equivalence classes of such actions. These numbers are expressed in terms of BSK-maps and therefore a reader less familiar with the study of periodic actions on compact surfaces from a combinatorial point of view should postpone the reading of (ii)–(iv) until Section 3, where these maps are introduced.
Theorem 2.10.
(i) There exists an action of a cyclic group
 $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
on an orientable surface
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
on an orientable surface
 $S$
with
$S$
with
 $k$
boundary components, with an annulus having one cone point of order
$k$
boundary components, with an annulus having one cone point of order
 $m$
as the quotient orbifold if and only if either
$m$
as the quotient orbifold if and only if either(1)
 $k$
divides
$k$
divides
 $N$
,
$N$
,
 $N=2\text{lcm}(m,N/k)$
and
$N=2\text{lcm}(m,N/k)$
and
 $N/2$
is odd; or
$N/2$
is odd; or(2)
 $m$
divides
$m$
divides
 $N$
and there exits an integer
$N$
and there exits an integer
 $n$
,
$n$
,
 $1\leqslant n<k$
, such that:
$1\leqslant n<k$
, such that:(a)
 $n$
and
$n$
and
 $k-n$
divide
$k-n$
divide
 $m$
;
$m$
;(b)
 $N/m$
,
$N/m$
,
 $n$
and
$n$
and
 $k-n$
are pairwise relatively prime;
$k-n$
are pairwise relatively prime;(c) if
 $N$
is even then one of
$N$
is even then one of
 $N/m$
,
$N/m$
,
 $n$
,
$n$
,
 $k-n$
is even.
$k-n$
is even.
In such case the algebraic genus of the surface is equal to
 $1+N(m-1)/m$
.
$1+N(m-1)/m$
.
(ii) Suppose that
 $N,m,k$
satisfy
$N,m,k$
satisfy
 $(1)$
and
$(1)$
and
 $t=(m,N/k)$
. Then there are
$t=(m,N/k)$
. Then there are
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)$
equivalence classes of BSK-maps
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)$
equivalence classes of BSK-maps
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
such that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
such that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}(c_{1})\neq \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}(c_{2})$
.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}(c_{1})\neq \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}(c_{2})$
.(iii) Suppose that
 $N,m,k$
satisfy
$N,m,k$
satisfy
 $(2)$
. Then the number of equivalence classes of BSK-maps
$(2)$
. Then the number of equivalence classes of BSK-maps
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
such that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
such that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(c_{1})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(c_{2})=0$
, and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(c_{1})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(c_{2})=0$
, and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(e_{1})$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(e_{1})$
and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(e_{2})$
have orders
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(e_{2})$
have orders
 $N/n$
and
$N/n$
and
 $N/(k-n)$
is
$N/(k-n)$
is∙
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(m/Cn(k-n))\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)$
if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(m/Cn(k-n))\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)$
if
 $k\neq 2$
;
$k\neq 2$
;∙
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(m/C)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)/2+1$
if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(m/C)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)/2+1$
if
 $k=2$
and
$k=2$
and
 $m/C=2^{z}$
, where
$m/C=2^{z}$
, where
 $z>1$
;
$z>1$
;∙
 $\lceil \unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(m/C)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)/2\rceil$
otherwise;
$\lceil \unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(m/C)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)/2\rceil$
otherwise;
where
 $C$
is the biggest divisor of
$C$
is the biggest divisor of
 $m/n(k-n)$
coprime to
$m/n(k-n)$
coprime to
 $Nn(k-n)/m$
.
$Nn(k-n)/m$
.(iv) Every BSK-map corresponding to a
 $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
-action on
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
-action on
 $S$
is equivalent either to some
$S$
is equivalent either to some
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}$
from the assertion
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}$
from the assertion
 $(\text{ii})$
, or to some
$(\text{ii})$
, or to some
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}$
from the assertion
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}$
from the assertion
 $\text{(iii)}$
.
$\text{(iii)}$
.
2.9 Actions with a 3-punctured disc as the quotient orbifold
The orders of the three cone points are either
![]() $2,2,m$
,
$2,2,m$
,
![]() $m\geqslant 2$
, or
$m\geqslant 2$
, or
![]() $2,3,m$
, where
$2,3,m$
, where
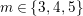 $m\in \{3,4,5\}$
. We consider these two cases separately.
$m\in \{3,4,5\}$
. We consider these two cases separately.
Theorem 2.11. There is an action of a cyclic group of order
![]() $N$
on a bordered surface
$N$
on a bordered surface
![]() $S$
with a disc having
$S$
with a disc having
![]() $3$
cone points of orders
$3$
cone points of orders
![]() $2,2,m$
as the quotient orbifold if and only if
$2,2,m$
as the quotient orbifold if and only if
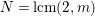 $N=\text{lcm}(2,m)$
. In such case
$N=\text{lcm}(2,m)$
. In such case
![]() $S$
is orientable, it has
$S$
is orientable, it has
![]() $N/m$
boundary components, its genus is equal to
$N/m$
boundary components, its genus is equal to
 $g=1+(m-2)N/2m$
and such an action is unique up to topological conjugation.
$g=1+(m-2)N/2m$
and such an action is unique up to topological conjugation.
Theorem 2.12. There is an action of a cyclic group of order
![]() $N$
on a bordered surface
$N$
on a bordered surface
![]() $S$
with a disc having
$S$
with a disc having
![]() $3$
cone points of orders
$3$
cone points of orders
![]() $2,3,m$
, where
$2,3,m$
, where
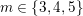 $m\in \{3,4,5\}$
, as the quotient orbifold if and only if
$m\in \{3,4,5\}$
, as the quotient orbifold if and only if
 $N=\text{lcm}(2,3,m)$
and
$N=\text{lcm}(2,3,m)$
and
![]() $S$
is an orientable surface of topological genus
$S$
is an orientable surface of topological genus
![]() $g$
with
$g$
with
![]() $k$
boundary components, where
$k$
boundary components, where
∙ if
 $m=3$
then
$m=3$
then
 $(g,k)=(3,1)$
or
$(g,k)=(3,1)$
or
 $(2,3)$
;
$(2,3)$
;∙ if
 $m=4$
then
$m=4$
then
 $(g,k)=(6,1)$
;
$(g,k)=(6,1)$
;∙ if
 $m=5$
then
$m=5$
then
 $(g,k)=(15,1)$
.
$(g,k)=(15,1)$
.
In each case the action is unique up to topological conjugation.
2.10 Actions with a 2-punctured disc with two corners as the quotient orbifold
The orders of the cone points are either
![]() $2,m$
,
$2,m$
,
![]() $m\geqslant 2$
, or
$m\geqslant 2$
, or
![]() $3,m$
, where
$3,m$
, where
 $m\in \{3,4,5\}$
. We consider these two cases separately.
$m\in \{3,4,5\}$
. We consider these two cases separately.
Theorem 2.13. There is an action of a cyclic group of order
![]() $N$
on a bordered surface
$N$
on a bordered surface
![]() $S$
with a disc having
$S$
with a disc having
![]() $2$
cone points of orders
$2$
cone points of orders
![]() $2,m$
and
$2,m$
and
![]() $2$
corners as the quotient orbifold if and only if
$2$
corners as the quotient orbifold if and only if
 $N=\text{lcm}(2,m)$
. In such case
$N=\text{lcm}(2,m)$
. In such case
![]() $S$
is nonorientable, it has
$S$
is nonorientable, it has
![]() $N/2$
boundary components, its genus is equal to
$N/2$
boundary components, its genus is equal to
 $g=2+(m-2)N/2m$
, and such an action is unique up to topological conjugation.
$g=2+(m-2)N/2m$
, and such an action is unique up to topological conjugation.
Theorem 2.14. There is an action of a cyclic group of order
![]() $N$
on a bordered surface
$N$
on a bordered surface
![]() $S$
with a disc having
$S$
with a disc having
![]() $2$
cone points of orders
$2$
cone points of orders
![]() $3,m$
, where
$3,m$
, where
 $m\in \{3,4,5\}$
, and
$m\in \{3,4,5\}$
, and
![]() $2$
corners as the quotient orbifold if and only if
$2$
corners as the quotient orbifold if and only if
 $N=\text{lcm}(2,3,m)$
,
$N=\text{lcm}(2,3,m)$
,
![]() $S$
has
$S$
has
![]() $N/2$
boundary components, and
$N/2$
boundary components, and
∙ if
 $m=3$
then
$m=3$
then
 $S$
is orientable of genus
$S$
is orientable of genus
 $2$
;
$2$
;∙ if
 $m=4$
then
$m=4$
then
 $S$
is nonorientable of genus
$S$
is nonorientable of genus
 $7$
;
$7$
;∙ if
 $m=5$
then
$m=5$
then
 $S$
is orientable of genus
$S$
is orientable of genus
 $8$
.
$8$
.
Furthermore, for
![]() $m=3$
there are two different topological types of such action, and for
$m=3$
there are two different topological types of such action, and for
 $m=4,5$
the action is unique up to topological conjugation.
$m=4,5$
the action is unique up to topological conjugation.
3 Preliminaries
In principle, we use a combinatorial approach, based on Riemann unformization theorem for compact Riemann surfaces, its generalization for nonorientable or bordered surfaces with dianalytic structures of Klein surfaces, good knowledge of discrete group of isometries of the hyperbolic plane and some elementary covering theory. For the reader’s convenience, we review the terminology of [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4] used in this paper.
3.1 Hurwitz–Nielsen geometrization and its generalizations
Let
![]() $G$
be a finite group of orientation-preserving self-homeomorphisms of a closed orientable surface
$G$
be a finite group of orientation-preserving self-homeomorphisms of a closed orientable surface
![]() $S_{g}$
of genus
$S_{g}$
of genus
![]() $g$
,
$g$
,
![]() $g\geqslant 2$
.
$g\geqslant 2$
.
By [Reference Hurwitz11] and [Reference Nielsen15], there exists a structure of a Riemann surface on
![]() $S_{g}$
, with respect to which the elements of
$S_{g}$
, with respect to which the elements of
![]() $G$
act as conformal automorphisms. This result was generalized to the case of actions containing orientation-reversing self-homeomorphisms and to closed nonorientable surfaces by Kerejarto [Reference Keréjártó12], and for bordered surfaces in a more recent monograph of Alling and Greenleaf [Reference Alling and Greenleaf1], who introduced the concept of a Klein surface. Thus, although the paper concerns topological classification of topological actions, we assume, whenever necessary, that a surface has such a structure of a bordered Klein surface, and the elements of
$G$
act as conformal automorphisms. This result was generalized to the case of actions containing orientation-reversing self-homeomorphisms and to closed nonorientable surfaces by Kerejarto [Reference Keréjártó12], and for bordered surfaces in a more recent monograph of Alling and Greenleaf [Reference Alling and Greenleaf1], who introduced the concept of a Klein surface. Thus, although the paper concerns topological classification of topological actions, we assume, whenever necessary, that a surface has such a structure of a bordered Klein surface, and the elements of
![]() $G$
act on it as dianalytic automorphisms. This assumption allows for effective conformally algebraic methods described in the following subsections.
$G$
act on it as dianalytic automorphisms. This assumption allows for effective conformally algebraic methods described in the following subsections.
3.2 Non-Euclidean crystallographic groups
By a non-Euclidean crystallographic group (NEC-group in short) we mean a discrete and cocompact subgroup of the group
![]() ${\mathcal{G}}$
of all isometries of the hyperbolic plane
${\mathcal{G}}$
of all isometries of the hyperbolic plane
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}$
. The algebraic structure of such a group
${\mathcal{H}}$
. The algebraic structure of such a group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
is encoded in its signature:
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
is encoded in its signature:
 $$\begin{eqnarray}s(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=(g;\pm ;[m_{1},\ldots ,m_{r}];\{(n_{11},\ldots ,n_{1s_{1}}),\ldots ,(n_{k1},\ldots ,n_{ks_{k}})\}),\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}s(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=(g;\pm ;[m_{1},\ldots ,m_{r}];\{(n_{11},\ldots ,n_{1s_{1}}),\ldots ,(n_{k1},\ldots ,n_{ks_{k}})\}),\end{eqnarray}$$
where the brackets
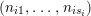 $(n_{i1},\ldots ,n_{is_{i}})$
are called the period cycles, the integers
$(n_{i1},\ldots ,n_{is_{i}})$
are called the period cycles, the integers
![]() $n_{ij}$
are the link periods,
$n_{ij}$
are the link periods,
![]() $m_{i}$
proper periods and finally
$m_{i}$
proper periods and finally
![]() $g$
the orbit genus of
$g$
the orbit genus of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. A group
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. A group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature (1) has the presentation with the following generators
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature (1) has the presentation with the following generators
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}x_{i} & \text{for}~1\leqslant i\leqslant r,\\ c_{ij},e_{i} & \text{for}~1\leqslant i\leqslant k,0\leqslant j\leqslant s_{i},\\ a_{i},b_{i} & \text{for}~1\leqslant i\leqslant g~\text{if the sign is}~+,\\ d_{i} & \text{for}~1\leqslant i\leqslant g~\text{if the sign is}~-,\end{array}\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}x_{i} & \text{for}~1\leqslant i\leqslant r,\\ c_{ij},e_{i} & \text{for}~1\leqslant i\leqslant k,0\leqslant j\leqslant s_{i},\\ a_{i},b_{i} & \text{for}~1\leqslant i\leqslant g~\text{if the sign is}~+,\\ d_{i} & \text{for}~1\leqslant i\leqslant g~\text{if the sign is}~-,\end{array}\end{eqnarray}$$
subject to the relations
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}x_{i}^{m_{i}}=1 & \text{for}~1\leqslant i\leqslant r,\\ c_{ij}^{2}=(c_{ij-1}c_{ij})^{n_{ij}}=1 & \text{for}~1\leqslant i\leqslant k,0\leqslant j\leqslant s_{i},\\ c_{is_{i}}=e_{i}c_{i0}e_{i}^{-1} & \text{for}~1\leqslant i\leqslant k,\\ x_{1}\cdots x_{r}e_{1}\cdots e_{k}[a_{1},b_{1}]\cdots [a_{g},b_{g}]=1 & \text{if the sign is}~+,\\ x_{1}\cdots x_{r}e_{1}\cdots e_{k}d_{1}^{2}\cdots d_{g}^{2}=1 & \text{if the sign is}~-,\end{array}\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}x_{i}^{m_{i}}=1 & \text{for}~1\leqslant i\leqslant r,\\ c_{ij}^{2}=(c_{ij-1}c_{ij})^{n_{ij}}=1 & \text{for}~1\leqslant i\leqslant k,0\leqslant j\leqslant s_{i},\\ c_{is_{i}}=e_{i}c_{i0}e_{i}^{-1} & \text{for}~1\leqslant i\leqslant k,\\ x_{1}\cdots x_{r}e_{1}\cdots e_{k}[a_{1},b_{1}]\cdots [a_{g},b_{g}]=1 & \text{if the sign is}~+,\\ x_{1}\cdots x_{r}e_{1}\cdots e_{k}d_{1}^{2}\cdots d_{g}^{2}=1 & \text{if the sign is}~-,\end{array}\end{eqnarray}$$
where
 $[x,y]=xyx^{-1}y^{-1}$
. Elements of any system of generators satisfying the above relations will be called canonical generators. The elements
$[x,y]=xyx^{-1}y^{-1}$
. Elements of any system of generators satisfying the above relations will be called canonical generators. The elements
![]() $x_{i}$
are elliptic transformations,
$x_{i}$
are elliptic transformations,
![]() $a_{i},b_{i}$
hyperbolic translations,
$a_{i},b_{i}$
hyperbolic translations,
![]() $d_{i}$
glide reflections and
$d_{i}$
glide reflections and
![]() $c_{ij}$
hyperbolic reflections. Reflections
$c_{ij}$
hyperbolic reflections. Reflections
![]() $c_{ij-1}$
and
$c_{ij-1}$
and
![]() $c_{ij}$
are called consecutive. It is essential for applications that every element of finite order in
$c_{ij}$
are called consecutive. It is essential for applications that every element of finite order in
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
is conjugate either to a canonical reflection, or to a power of some canonical elliptic element
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
is conjugate either to a canonical reflection, or to a power of some canonical elliptic element
![]() $x_{i}$
, or else to a power of the product of two consecutive canonical reflections.
$x_{i}$
, or else to a power of the product of two consecutive canonical reflections.
The orbit space
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
is a hyperbolic orbifold, with underlying surface of topological genus
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
is a hyperbolic orbifold, with underlying surface of topological genus
![]() $g$
with
$g$
with
![]() $k$
boundary components, and it is orientable if the sign is
$k$
boundary components, and it is orientable if the sign is
![]() $+$
and nonorientable otherwise. The image in
$+$
and nonorientable otherwise. The image in
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
of the fixed point of the canonical elliptic generator
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
of the fixed point of the canonical elliptic generator
![]() $x_{i}$
is called cone point of order
$x_{i}$
is called cone point of order
![]() $m_{i}$
, whereas the image of the fixed point of the product of two consecutive canonical reflections
$m_{i}$
, whereas the image of the fixed point of the product of two consecutive canonical reflections
![]() $c_{ij-1}c_{ij}$
is called corner point of order
$c_{ij-1}c_{ij}$
is called corner point of order
![]() $n_{ij}$
.
$n_{ij}$
.
Now, an abstract group with such presentation can be realized as an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
if and only if the value
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
if and only if the value
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g+k-2+\mathop{\sum }_{i=1}^{r}\left(1-\frac{1}{m_{i}}\right)+\frac{1}{2}\mathop{\sum }_{i=1}^{k}\mathop{\sum }_{j=1}^{s_{i}}\left(1-\frac{1}{n_{ij}}\right)\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g+k-2+\mathop{\sum }_{i=1}^{r}\left(1-\frac{1}{m_{i}}\right)+\frac{1}{2}\mathop{\sum }_{i=1}^{k}\mathop{\sum }_{j=1}^{s_{i}}\left(1-\frac{1}{n_{ij}}\right)\end{eqnarray}$$
is positive, where
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}=2$
if the sign is
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}=2$
if the sign is
![]() $+$
, or
$+$
, or
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}=1$
otherwise. This value turns out to be the normalized hyperbolic area
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}=1$
otherwise. This value turns out to be the normalized hyperbolic area
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
of an arbitrary fundamental region for such a group, and we have the following Hurwitz–Riemann formula
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
of an arbitrary fundamental region for such a group, and we have the following Hurwitz–Riemann formula
 $$\begin{eqnarray}[\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}^{\prime }]={\displaystyle \frac{\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}^{\prime })}{\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})}}\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}[\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}^{\prime }]={\displaystyle \frac{\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}^{\prime })}{\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})}}\end{eqnarray}$$
for a subgroup
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}^{\prime }$
of finite index in an NEC-group
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}^{\prime }$
of finite index in an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
.
Finally, NEC-groups without orientation-reversing elements are Fuchsian groups. They have signatures
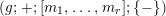 $(g;+;[m_{1},\ldots ,m_{r}];\{-\})$
usually abbreviated as
$(g;+;[m_{1},\ldots ,m_{r}];\{-\})$
usually abbreviated as
 $(g;m_{1},\ldots ,m_{r})$
. Given an NEC-group
$(g;m_{1},\ldots ,m_{r})$
. Given an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
containing orientation-reversing elements, its subgroup
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
containing orientation-reversing elements, its subgroup
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}^{+}$
consisting of the orientation-preserving elements is called the canonical Fuchsian subgroup of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}^{+}$
consisting of the orientation-preserving elements is called the canonical Fuchsian subgroup of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
, and by [Reference Singerman16], for
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
, and by [Reference Singerman16], for
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature (1),
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature (1),
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}^{+}$
has signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}^{+}$
has signature
 $$\begin{eqnarray}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g+k-1;m_{1},m_{1},\ldots ,m_{r},m_{r},n_{11},\ldots ,n_{ks_{k}}).\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g+k-1;m_{1},m_{1},\ldots ,m_{r},m_{r},n_{11},\ldots ,n_{ks_{k}}).\end{eqnarray}$$
A torsion free Fuchsian group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
is called a surface group and it has signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
is called a surface group and it has signature
![]() $(g;-)$
.
$(g;-)$
.
We also use other results concerning relationship between the signatures of an NEC-group and its finite index subgroup proved in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4, Chapter 2].
3.3 Bordered Riemann surfaces and their groups of automorphisms
By the Riemann uniformization theorem, every closed Riemann surface
![]() $S$
of genus
$S$
of genus
![]() $g\geqslant 2$
can be identified with the orbit space
$g\geqslant 2$
can be identified with the orbit space
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
of the hyperbolic plane with respect to an action of a Fuchsian group
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
of the hyperbolic plane with respect to an action of a Fuchsian group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
isomorphic to the fundamental group of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
isomorphic to the fundamental group of
![]() $S$
. A Klein surface is a compact bordered topological surface equipped with a dianalytic structure – historically it is also called bordered Riemann surface. For a given Klein surface
$S$
. A Klein surface is a compact bordered topological surface equipped with a dianalytic structure – historically it is also called bordered Riemann surface. For a given Klein surface
![]() $S$
, Alling and Greenleaf [Reference Alling and Greenleaf1] constructed certain canonical double cover
$S$
, Alling and Greenleaf [Reference Alling and Greenleaf1] constructed certain canonical double cover
![]() $S^{+}$
being a Riemann surface, such that
$S^{+}$
being a Riemann surface, such that
![]() $S$
is the quotient of
$S$
is the quotient of
![]() $S^{+}$
by an action of an antiholomorphic involution with fixed points. The algebraic genus
$S^{+}$
by an action of an antiholomorphic involution with fixed points. The algebraic genus
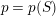 $p=p(S)$
of
$p=p(S)$
of
![]() $S$
is defined as the genus of
$S$
is defined as the genus of
![]() $S^{+}$
and it follows from the construction that
$S^{+}$
and it follows from the construction that
![]() $p$
coincides with the rank of the fundamental group of
$p$
coincides with the rank of the fundamental group of
![]() $S$
, and so for a surface of topological genus
$S$
, and so for a surface of topological genus
![]() $g$
having
$g$
having
![]() $k$
boundary components it is equal to
$k$
boundary components it is equal to
 $p=\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g+k-1$
, where
$p=\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g+k-1$
, where
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}=2$
if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}=2$
if
![]() $S$
is orientable and
$S$
is orientable and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}=1$
otherwise. It is well known (see [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4] for example) that any compact Klein surface
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}=1$
otherwise. It is well known (see [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4] for example) that any compact Klein surface
![]() $S$
of algebraic genus
$S$
of algebraic genus
![]() $p\geqslant 2$
can be represented as
$p\geqslant 2$
can be represented as
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
for some NEC-group
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
for some NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
. If
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
. If
![]() $S$
has topological genus
$S$
has topological genus
![]() $g$
and
$g$
and
![]() $k$
boundary components, then
$k$
boundary components, then
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
can be chosen to be a bordered surface group, that is, an NEC-group with the signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
can be chosen to be a bordered surface group, that is, an NEC-group with the signature
 $$\begin{eqnarray}(g;\pm ;[\;];\{(\;),\stackrel{k}{\ldots }\,,(\;)\}),\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}(g;\pm ;[\;];\{(\;),\stackrel{k}{\ldots }\,,(\;)\}),\end{eqnarray}$$
whose only elements of finite order are reflections. It has the presentation
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \left\langle a_{1},b_{1},\ldots ,a_{g},b_{g},e_{1},\ldots ,e_{k},c_{1},\ldots ,c_{k}\mid \right.\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \quad \left.c_{i}^{2},[e_{i},c_{i}],e_{1}\ldots e_{k}[a_{1},b_{1}]\ldots [a_{g},b_{g}]\right\rangle \nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \left\langle a_{1},b_{1},\ldots ,a_{g},b_{g},e_{1},\ldots ,e_{k},c_{1},\ldots ,c_{k}\mid \right.\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \quad \left.c_{i}^{2},[e_{i},c_{i}],e_{1}\ldots e_{k}[a_{1},b_{1}]\ldots [a_{g},b_{g}]\right\rangle \nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
if the sign is
![]() $+$
, or
$+$
, or
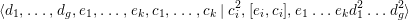 $$\begin{eqnarray}\langle d_{1},\ldots ,d_{g},e_{1},\ldots ,e_{k},c_{1},\ldots ,c_{k}\mid c_{i}^{2},[e_{i},c_{i}],e_{1}\ldots e_{k}d_{1}^{2}\ldots d_{g}^{2}\rangle\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\langle d_{1},\ldots ,d_{g},e_{1},\ldots ,e_{k},c_{1},\ldots ,c_{k}\mid c_{i}^{2},[e_{i},c_{i}],e_{1}\ldots e_{k}d_{1}^{2}\ldots d_{g}^{2}\rangle\end{eqnarray}$$
otherwise. Finally, a finite group
![]() $G$
is a group of automorphisms of
$G$
is a group of automorphisms of
 $S={\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
if and only if
$S={\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
if and only if
 $G\cong \unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
for some NEC-group
$G\cong \unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
for some NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. A convenient way of defining an action of a group
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. A convenient way of defining an action of a group
![]() $G$
on a bordered surface
$G$
on a bordered surface
![]() $S$
is by means of an epimorphism
$S$
is by means of an epimorphism
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow G$
whose kernel is a bordered surface group. In such a case
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow G$
whose kernel is a bordered surface group. In such a case
 $S={\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
, where
$S={\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
, where
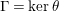 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
. We shall refer to such an epimorphism as to a bordered-surface-kernel epimorphism (BSK in short) or smooth epimorphism.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
. We shall refer to such an epimorphism as to a bordered-surface-kernel epimorphism (BSK in short) or smooth epimorphism.
Two actions of
![]() $G$
on
$G$
on
![]() $S$
are topologically conjugate (by a homeomorphism of
$S$
are topologically conjugate (by a homeomorphism of
![]() $S$
) if and only if the associated smooth epimorphisms are equivalent in the sense of the next definition (see [Reference Bujalance, Cirre, Conder and Szepietowski3, Proposition 2.2]). We say that two smooth epimorphisms
$S$
) if and only if the associated smooth epimorphisms are equivalent in the sense of the next definition (see [Reference Bujalance, Cirre, Conder and Szepietowski3, Proposition 2.2]). We say that two smooth epimorphisms
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{i}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow G$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{i}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow G$
,
![]() $i=1,2$
, are equivalent if and only if there exist automorphisms
$i=1,2$
, are equivalent if and only if there exist automorphisms
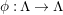 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}:G\rightarrow G$
such that the following diagram is commutative.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}:G\rightarrow G$
such that the following diagram is commutative.

3.4 Some elementary algebra
For integers
![]() $a,b$
we denote by
$a,b$
we denote by
![]() $(a,b)$
their greatest common divisor and we use additive notation for cyclic groups
$(a,b)$
their greatest common divisor and we use additive notation for cyclic groups
 $\mathbb{Z}_{N}=\mathbb{Z}/N\mathbb{Z}$
throughout the whole paper. Furthermore, by abuse of language, we write
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}=\mathbb{Z}/N\mathbb{Z}$
throughout the whole paper. Furthermore, by abuse of language, we write
![]() $a\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
for a nonnegative integer
$a\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
for a nonnegative integer
![]() $a<N$
. To avoid unnecessary parentheses, we denote expressions of the form
$a<N$
. To avoid unnecessary parentheses, we denote expressions of the form
![]() $a/(bc)$
simply as
$a/(bc)$
simply as
![]() $a/bc$
.
$a/bc$
.
We need the following version of the classical Chinese remainder theorem.
Lemma 3.1. Given integers
![]() $a,b$
, the system of congruences
$a,b$
, the system of congruences
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x\equiv a\;(m),\quad \\ x\equiv b\;(n),\quad \end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x\equiv a\;(m),\quad \\ x\equiv b\;(n),\quad \end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$
has a solution if and only if
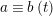 $a\equiv b\;(t)$
, where
$a\equiv b\;(t)$
, where
 $t=(m,n)$
and this solution is unique up to
$t=(m,n)$
and this solution is unique up to
 $\text{lcm}(m,n)$
.◻
$\text{lcm}(m,n)$
.◻
The following useful result can be proved using Dirichlet’s theorem on arithmetic progression (see [Reference Gromadzki, Szepietowski and Zhao7] for a more elementary, direct, argument).
Lemma 3.2. Given an integer
![]() $N$
and its divisor
$N$
and its divisor
![]() $n$
, the reduction map
$n$
, the reduction map
 $\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
is a group epimorphism.
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
is a group epimorphism.
Proof. Let
![]() $a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
, then
$a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
, then
 $(a,n)=1$
and so by Dirichlet theorem on arithmetic progression there exists infinitely many primes
$(a,n)=1$
and so by Dirichlet theorem on arithmetic progression there exists infinitely many primes
![]() $A$
of the form
$A$
of the form
![]() $a+bn$
and so
$a+bn$
and so
 $A\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
and its reduction modulo
$A\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
and its reduction modulo
![]() $n$
is equal to
$n$
is equal to
![]() $a$
.◻
$a$
.◻
We also need
Lemma 3.3. (Harvey, [Reference Harvey8])
The group
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is generated by three elements
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is generated by three elements
![]() $a$
,
$a$
,
![]() $b$
,
$b$
,
![]() $c$
of orders
$c$
of orders
![]() $m$
,
$m$
,
![]() $n$
,
$n$
,
![]() $l$
and such that
$l$
and such that
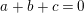 $a+b+c=0$
if and only if
$a+b+c=0$
if and only if
(i)
 $N=\text{lcm}(m,n)=\text{lcm}(m,l)=\text{lcm}(n,l)$
; and
$N=\text{lcm}(m,n)=\text{lcm}(m,l)=\text{lcm}(n,l)$
; and(ii) if
 $N$
is even, then exactly one of the numbers
$N$
is even, then exactly one of the numbers
 $N/m$
,
$N/m$
,
 $N/n$
,
$N/n$
,
 $N/l$
is even.
$N/l$
is even.
The condition (i) of Lemma 3.3 is equivalent to existence of pairwise relatively prime integers
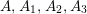 $A,A_{1},A_{2},A_{3}$
for which
$A,A_{1},A_{2},A_{3}$
for which
 $$\begin{eqnarray}m=AA_{2}A_{3},\qquad n=AA_{1}A_{3},\qquad l=AA_{1}A_{2},\qquad N=AA_{1}A_{2}A_{3}.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}m=AA_{2}A_{3},\qquad n=AA_{1}A_{3},\qquad l=AA_{1}A_{2},\qquad N=AA_{1}A_{2}A_{3}.\end{eqnarray}$$
The condition (ii) of Lemma 3.3 is that one of the numbers
![]() $A_{1}$
,
$A_{1}$
,
![]() $A_{2}$
,
$A_{2}$
,
![]() $A_{3}$
is even if
$A_{3}$
is even if
![]() $N$
is even. The quadruple
$N$
is even. The quadruple
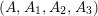 $(A,A_{1},A_{2},A_{3})$
is called Maclachlan decomposition of the triple
$(A,A_{1},A_{2},A_{3})$
is called Maclachlan decomposition of the triple
 $(m,n,l)$
after Hidalgo [Reference Hidalgo9].
$(m,n,l)$
after Hidalgo [Reference Hidalgo9].
4 Periodic self-homeomorphisms of compact bordered surfaces of big periods
From (3.1.0.1) and (3.1.0.2) in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4, p. 61] we immediately obtain the following result.
Lemma 4.1. There exists a structure of a bordered Klein surface
 $S=S_{g,\pm }^{k}$
of topological genus
$S=S_{g,\pm }^{k}$
of topological genus
![]() $h$
, with
$h$
, with
![]() $k$
boundary components and orientable or not according to the sign being plus or minus having a dianalytic automorphism
$k$
boundary components and orientable or not according to the sign being plus or minus having a dianalytic automorphism
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}$
of order
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}$
of order
![]() $N$
if and only if
$N$
if and only if
 $\mathbb{Z}_{N}\cong \unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
, where
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}\cong \unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
, where
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
have signatures respectively
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
have signatures respectively
 $$\begin{eqnarray}(g;\pm ;[\;];\{(\;),\stackrel{k}{\ldots }\,,(\;)\})\qquad \text{and}\qquad (g^{\prime };\pm ;[m_{1},\ldots ,m_{r}];\{C_{1},\ldots ,C_{k^{\prime }}\}),\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}(g;\pm ;[\;];\{(\;),\stackrel{k}{\ldots }\,,(\;)\})\qquad \text{and}\qquad (g^{\prime };\pm ;[m_{1},\ldots ,m_{r}];\{C_{1},\ldots ,C_{k^{\prime }}\}),\end{eqnarray}$$
where each cycle
![]() $C_{i}$
is either empty or consists of an even number of periods equal to
$C_{i}$
is either empty or consists of an even number of periods equal to
![]() $2$
. Furthermore, nonempty cycles do not appear for odd
$2$
. Furthermore, nonempty cycles do not appear for odd
![]() $N$
.
$N$
.
For the rest of this section we assume that
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
are as in Lemma 4.1 and we denote by
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
are as in Lemma 4.1 and we denote by
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
the canonical projection, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
the canonical projection, where
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
will be identified with
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
will be identified with
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
. Recall that
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
. Recall that
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is called BSK-epimorphism. In order to state the next lemma, we need one definition and some notation. We define a nonorientable word to be a word
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is called BSK-epimorphism. In order to state the next lemma, we need one definition and some notation. We define a nonorientable word to be a word
![]() $w$
in the canonical generators of
$w$
in the canonical generators of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
and their inverses, such that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
and their inverses, such that
![]() $w$
defines an orientation-reversing isometry of
$w$
defines an orientation-reversing isometry of
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}$
and the reflections
${\mathcal{H}}$
and the reflections
![]() $c_{ij}$
of
$c_{ij}$
of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
which belong to
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
which belong to
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
do not appear in
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
do not appear in
![]() $w$
. For
$w$
. For
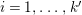 $i=1,\ldots ,k^{\prime }$
let
$i=1,\ldots ,k^{\prime }$
let
![]() $s_{i}$
be the length of the cycle
$s_{i}$
be the length of the cycle
![]() $C_{i}$
in the signature of
$C_{i}$
in the signature of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. Let
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. Let
![]() $l_{i}$
denote the order of
$l_{i}$
denote the order of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{i})$
in
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{i})$
in
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
and
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
and
 $$\begin{eqnarray}t_{i}=\left\{\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}0\quad & \text{if}~s_{i}=0~\text{and}~c_{i0}\notin \unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4},\\ N/l_{i}\quad & \text{if}~s_{i}=0~\text{and}~c_{i0}\in \unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4},\\ s_{i}N/4\quad & \text{if}~s_{i}>0.\end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}t_{i}=\left\{\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}0\quad & \text{if}~s_{i}=0~\text{and}~c_{i0}\notin \unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4},\\ N/l_{i}\quad & \text{if}~s_{i}=0~\text{and}~c_{i0}\in \unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4},\\ s_{i}N/4\quad & \text{if}~s_{i}>0.\end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$
The following lemma can be deduced from [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4].
Lemma 4.2. Let
![]() $S$
be the surface
$S$
be the surface
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
. Then:
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
. Then:
(a)
 $S$
is nonorientable if and only if
$S$
is nonorientable if and only if
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
contains a nonorientable word;
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
contains a nonorientable word;(b) the number of boundary components of
 $S$
is
$S$
is
 $k=t_{1}+\cdots +t_{k^{\prime }}$
.
$k=t_{1}+\cdots +t_{k^{\prime }}$
.
Proof. Indeed (a) follows from [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4, Theorems 2.1.2 and 2.1.3]. Now, with the above notation, each empty period cycle of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
whose corresponding canonical reflection belongs to
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
whose corresponding canonical reflection belongs to
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
, produces
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
, produces
![]() $N/l_{i}$
empty period cycles in
$N/l_{i}$
empty period cycles in
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
by [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4, Theorem 2.3.3] (see also Theorems 2.4.2 and 2.4.4 therein). Next, let
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
by [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4, Theorem 2.3.3] (see also Theorems 2.4.2 and 2.4.4 therein). Next, let
 $c_{0},c_{1},\ldots ,c_{2s}$
be a cycle of canonical reflections of
$c_{0},c_{1},\ldots ,c_{2s}$
be a cycle of canonical reflections of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
corresponding to a nonempty period cycle
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
corresponding to a nonempty period cycle
 $(2,\stackrel{2s}{\ldots }\,,2)$
. Then
$(2,\stackrel{2s}{\ldots }\,,2)$
. Then
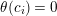 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{i})=0$
or
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{i})=0$
or
![]() $N/2$
. Observe however that two consecutive canonical reflections
$N/2$
. Observe however that two consecutive canonical reflections
![]() $c_{i-1},c_{i}$
have different images, since otherwise
$c_{i-1},c_{i}$
have different images, since otherwise
![]() $c_{i-1}c_{i}$
would be an orientation-preserving torsion element of
$c_{i-1}c_{i}$
would be an orientation-preserving torsion element of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
. So this cycle of reflections is mapped either on
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
. So this cycle of reflections is mapped either on
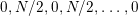 $0,N/2,0,N/2,\ldots ,0$
or on
$0,N/2,0,N/2,\ldots ,0$
or on
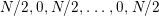 $N/2,0,N/2,\ldots ,0,N/2$
. In the former case each
$N/2,0,N/2,\ldots ,0,N/2$
. In the former case each
![]() $c_{i}$
for even
$c_{i}$
for even
![]() $i$
produces in
$i$
produces in
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
![]() $N/2$
empty period cycles, while in the latter case the same is true for every odd
$N/2$
empty period cycles, while in the latter case the same is true for every odd
![]() $i$
, and so each nonempty period cycle of length
$i$
, and so each nonempty period cycle of length
![]() $2s$
produces in
$2s$
produces in
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
![]() $s(N/2)$
empty period cycles in virtue of [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4, Theorem 2.3.2] (see also Theorem 2.4.4 therein).◻
$s(N/2)$
empty period cycles in virtue of [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4, Theorem 2.3.2] (see also Theorem 2.4.4 therein).◻
Observe that we can determine the topological type of the surface
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
by using Lemma 4.2 together with the Hurwitz–Riemann formula.
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
by using Lemma 4.2 together with the Hurwitz–Riemann formula.
Lemma 4.3. If
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
is a bordered surface group of algebraic genus
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
is a bordered surface group of algebraic genus
![]() $p$
and
$p$
and
 $N>p-1$
then
$N>p-1$
then
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has one of the following signatures:
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has one of the following signatures:
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}(1)~(0;+;[\;];\{(2,2,2,2,2,2)\}),\qquad & (2)~(0;+;[\;];\{(\;),(2,2)\}),\\ (3)~(1;-;[\;];\{(2,2)\}),\qquad & (4)~(0;+;[m];\{(2,2)\}),\\ (5)~(0;+;[m];\{(2,2,2,2)\}),\qquad & (6)~(1;-;[m];\{(\;)\}),\\ (7)~(0;+;[m,n];\{(\;)\}),\qquad & (8)~(0;+;[m];\{(\;),(\;)\}),\\ (9a)~(0;+;[2,3,m];\{(\;)\}),m=3,4,5,\qquad & (9b)~(0;+;[2,2,m];\{(\;)\}),\\ (10a)~(0;+;[3,m];\{(2,2)\}),m=3,4,5,\qquad & (10b)~(0;+;[2,m];\{(2,2)\}).\end{array}\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}(1)~(0;+;[\;];\{(2,2,2,2,2,2)\}),\qquad & (2)~(0;+;[\;];\{(\;),(2,2)\}),\\ (3)~(1;-;[\;];\{(2,2)\}),\qquad & (4)~(0;+;[m];\{(2,2)\}),\\ (5)~(0;+;[m];\{(2,2,2,2)\}),\qquad & (6)~(1;-;[m];\{(\;)\}),\\ (7)~(0;+;[m,n];\{(\;)\}),\qquad & (8)~(0;+;[m];\{(\;),(\;)\}),\\ (9a)~(0;+;[2,3,m];\{(\;)\}),m=3,4,5,\qquad & (9b)~(0;+;[2,2,m];\{(\;)\}),\\ (10a)~(0;+;[3,m];\{(2,2)\}),m=3,4,5,\qquad & (10b)~(0;+;[2,m];\{(2,2)\}).\end{array}\end{eqnarray}$$
Proof. By the Hurwitz–Riemann formula,
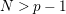 $N>p-1$
is equivalent to
$N>p-1$
is equivalent to
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})<1$
. For
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})<1$
. For
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
as in Lemma 4.1, we have
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
as in Lemma 4.1, we have
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g^{\prime }+k^{\prime }-2+\mathop{\sum }_{i=1}^{r}\left(1-\frac{1}{m_{i}}\right)+\frac{s}{4},\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g^{\prime }+k^{\prime }-2+\mathop{\sum }_{i=1}^{r}\left(1-\frac{1}{m_{i}}\right)+\frac{s}{4},\end{eqnarray}$$
where
![]() $s$
is the sum of lengths of nonempty period cycles. Observe that
$s$
is the sum of lengths of nonempty period cycles. Observe that
![]() $s$
is even and
$s$
is even and
![]() $k^{\prime }>0$
. We have
$k^{\prime }>0$
. We have
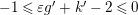 $-1\leqslant \unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g^{\prime }+k^{\prime }-2\leqslant 0$
.
$-1\leqslant \unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g^{\prime }+k^{\prime }-2\leqslant 0$
.
Suppose that
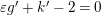 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g^{\prime }+k^{\prime }-2=0$
. Then, since
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g^{\prime }+k^{\prime }-2=0$
. Then, since
 $(1-1/m_{i})\geqslant 1/2$
,
$(1-1/m_{i})\geqslant 1/2$
,
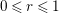 $0\leqslant r\leqslant 1$
. If
$0\leqslant r\leqslant 1$
. If
![]() $r=0$
, then
$r=0$
, then
![]() $s=2$
and
$s=2$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature (2) or (3). If
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature (2) or (3). If
![]() $r=1$
, then
$r=1$
, then
![]() $s=0$
and
$s=0$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature (6) or (8).
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature (6) or (8).
Suppose that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g^{\prime }+k^{\prime }-2=-1$
, hence
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g^{\prime }+k^{\prime }-2=-1$
, hence
 $(g^{\prime },k^{\prime })=(0,1)$
. Then
$(g^{\prime },k^{\prime })=(0,1)$
. Then
 $0\leqslant r\leqslant 3$
. If
$0\leqslant r\leqslant 3$
. If
![]() $r=0$
, then
$r=0$
, then
![]() $s=6$
and
$s=6$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has the signature (1). If
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has the signature (1). If
![]() $r=1$
, then
$r=1$
, then
![]() $s=2$
or
$s=2$
or
![]() $4$
and
$4$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature (4) or (5). If
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature (4) or (5). If
![]() $r=2$
, then
$r=2$
, then
![]() $s=0$
or
$s=0$
or
![]() $2$
. In the former case
$2$
. In the former case
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature (7). In the latter case
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature (7). In the latter case
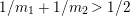 $1/m_{1}+1/m_{2}>1/2$
and
$1/m_{1}+1/m_{2}>1/2$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature (10a) or (10b). Finally, if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature (10a) or (10b). Finally, if
![]() $r=3$
then
$r=3$
then
![]() $s=0$
,
$s=0$
,
 $1/m_{1}+1/m_{2}+1/m_{3}>1$
and
$1/m_{1}+1/m_{2}+1/m_{3}>1$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature (9a) or (9b).◻
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature (9a) or (9b).◻
We close this section by a technical but simple lemma, which will be very useful in the next section.
Lemma 4.4. Suppose that
![]() $C_{i}$
is a nonempty cycle in the signature of
$C_{i}$
is a nonempty cycle in the signature of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. Then for some
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. Then for some
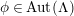 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}\circ \unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
maps the corresponding reflections
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}\circ \unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
maps the corresponding reflections
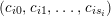 $(c_{i0},c_{i1},\ldots ,c_{is_{i}})$
on
$(c_{i0},c_{i1},\ldots ,c_{is_{i}})$
on
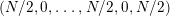 $(N/2,0,\ldots ,N/2,0,N/2)$
.
$(N/2,0,\ldots ,N/2,0,N/2)$
.
Proof. By Lemma 4.1, all the periods in
![]() $C_{i}$
are equal to 2 and by the proof of Lemma 4.2, consecutive canonical reflections
$C_{i}$
are equal to 2 and by the proof of Lemma 4.2, consecutive canonical reflections
 $c_{i0},c_{i1},\ldots ,c_{is_{i}}$
are mapped either on
$c_{i0},c_{i1},\ldots ,c_{is_{i}}$
are mapped either on
 $N/2,0,\ldots ,N/2,0,N/2$
, or on
$N/2,0,\ldots ,N/2,0,N/2$
, or on
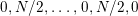 $0,N/2,\ldots ,0,N/2,0$
. In the former case we take
$0,N/2,\ldots ,0,N/2,0$
. In the former case we take
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
to be the identity, while in the latter case we define
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
to be the identity, while in the latter case we define
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
by
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
by
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}(c_{ij})=c_{ij-1}$
for
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}(c_{ij})=c_{ij-1}$
for
 $j=1,\ldots ,s_{i}$
,
$j=1,\ldots ,s_{i}$
,
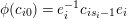 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}(c_{i0})=e_{i}^{-1}c_{is_{i}-1}e_{i}$
, and the identity on the remaining generators of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}(c_{i0})=e_{i}^{-1}c_{is_{i}-1}e_{i}$
, and the identity on the remaining generators of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
.◻
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
.◻
5 Automorphisms of NEC-groups versus mapping class groups
From diagram (6) in Section 3 we see that for a topological classification of group actions via smooth epimorphisms we need to know how to calculate automorphisms groups of NEC-groups
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. As we shall see, we need to know these automorphisms up to conjugation, which means that we actually need the groups
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. As we shall see, we need to know these automorphisms up to conjugation, which means that we actually need the groups
![]() $\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
of outer automorphisms of
$\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
of outer automorphisms of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
’s. From the previous section we see that in this paper we need them only for three signatures
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
’s. From the previous section we see that in this paper we need them only for three signatures
 $(1;-;[m];\{(\;)\})$
,
$(1;-;[m];\{(\;)\})$
,
 $(0;+;[m];\{(\;),(\;)\})$
,
$(0;+;[m];\{(\;),(\;)\})$
,
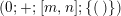 $(0;+;[m,n];\{(\;)\})$
, and the outer automorphism groups for these NEC-groups were found in [Reference Bujalance, Cirre, Conder and Szepietowski3, Section 4] by using a connection between
$(0;+;[m,n];\{(\;)\})$
, and the outer automorphism groups for these NEC-groups were found in [Reference Bujalance, Cirre, Conder and Szepietowski3, Section 4] by using a connection between
![]() $\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
and the mapping class group of the orbifold
$\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
and the mapping class group of the orbifold
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. For reader’s convenience we review these results and their proofs (illustrated with figures and easier to follow then the proofs in [Reference Bujalance, Cirre, Conder and Szepietowski3]). For an NEC-group
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. For reader’s convenience we review these results and their proofs (illustrated with figures and easier to follow then the proofs in [Reference Bujalance, Cirre, Conder and Szepietowski3]). For an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
, let
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
, let
 $\text{Mod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
be the group of isotopy classes of homeomorphisms over
$\text{Mod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
be the group of isotopy classes of homeomorphisms over
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
which map a cone point to a cone point of the same order, and analogously for the corner points, and
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
which map a cone point to a cone point of the same order, and analogously for the corner points, and
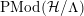 $\text{PMod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
be the group of isotopy classes of homeomorphisms over
$\text{PMod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
be the group of isotopy classes of homeomorphisms over
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
which fix the cone points and the corner points. For two elements
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
which fix the cone points and the corner points. For two elements
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}_{1}$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}_{1}$
,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}_{2}$
of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}_{2}$
of
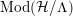 $\text{Mod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
,
$\text{Mod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}_{1}\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}_{2}$
means applying
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}_{1}\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}_{2}$
means applying
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}_{2}$
first and then applying
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}_{2}$
first and then applying
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}_{1}$
. Let
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}_{1}$
. Let
 $\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
be the subgroup of
$\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
be the subgroup of
![]() $\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
which acts trivially on the set of conjugacy classes of the stabilizers of the fixed points of elliptic elements of
$\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
which acts trivially on the set of conjugacy classes of the stabilizers of the fixed points of elliptic elements of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. Observe that these conjugacy classes are in one to one correspondence with the integers
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. Observe that these conjugacy classes are in one to one correspondence with the integers
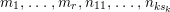 $m_{1},\ldots ,m_{r},n_{11},\ldots ,n_{ks_{k}}$
, and hence
$m_{1},\ldots ,m_{r},n_{11},\ldots ,n_{ks_{k}}$
, and hence
 $\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is a subgroup of finite index of
$\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is a subgroup of finite index of
![]() $\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
. The following lemma is proved in [Reference Bujalance, Cirre, Conder and Szepietowski3, Corollary 4.4].
$\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
. The following lemma is proved in [Reference Bujalance, Cirre, Conder and Szepietowski3, Corollary 4.4].
Lemma 5.1. If
 $\text{PMod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
has finite order
$\text{PMod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
has finite order
![]() $n$
, then
$n$
, then
 $\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
has order at most
$\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
has order at most
![]() $n$
.
$n$
.
In order to obtain presentations of these groups, we review mapping class groups of two elementary surfaces. Let
![]() $S_{0,3}$
be the sphere with three marked points
$S_{0,3}$
be the sphere with three marked points
![]() $p_{1}$
,
$p_{1}$
,
![]() $p_{2}$
and
$p_{2}$
and
![]() $p_{3}$
, and
$p_{3}$
, and
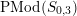 $\text{PMod}(S_{0,3})$
be the group of isotopy classes of orientation-preserving diffeomorphisms over the sphere preserving each of these three points. It is well known that
$\text{PMod}(S_{0,3})$
be the group of isotopy classes of orientation-preserving diffeomorphisms over the sphere preserving each of these three points. It is well known that
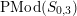 $\text{PMod}(S_{0,3})$
is trivial (see, for example, [Reference Farb and Margalit5, the proof of Proposition 2.3]). Let
$\text{PMod}(S_{0,3})$
is trivial (see, for example, [Reference Farb and Margalit5, the proof of Proposition 2.3]). Let
![]() $N_{1,2}$
be the real projective plane with two marked points
$N_{1,2}$
be the real projective plane with two marked points
![]() $p_{1}$
and
$p_{1}$
and
![]() $p_{2}$
, and
$p_{2}$
, and
 $\text{PMod}(N_{1,2})$
be the group of isotopy classes of diffeomorphisms over the real projective plane preserving each of these two points. Let
$\text{PMod}(N_{1,2})$
be the group of isotopy classes of diffeomorphisms over the real projective plane preserving each of these two points. Let
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}_{1}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}_{1}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}_{2}$
be the oriented circles shown in Figure 1, and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}_{2}$
be the oriented circles shown in Figure 1, and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{i}$
be the element of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{i}$
be the element of
 $\text{PMod}(N_{1,2})$
obtained by sliding
$\text{PMod}(N_{1,2})$
obtained by sliding
![]() $p_{i}$
once along
$p_{i}$
once along
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}_{i}$
(
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}_{i}$
(
![]() $i=1,2$
). Korkmaz [Reference Korkmaz13, Corollary 4.6] showed that
$i=1,2$
). Korkmaz [Reference Korkmaz13, Corollary 4.6] showed that
 $\text{PMod}(N_{1,2})$
is generated by
$\text{PMod}(N_{1,2})$
is generated by
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{2}$
, and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{2}$
, and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1}^{2}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{2}^{2}=(\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{2}\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1})^{2}=1$
. Let
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1}^{2}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{2}^{2}=(\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{2}\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1})^{2}=1$
. Let
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
be the reflection indicated in Figure 1. By investigating the action on the fundamental group, we can see
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
be the reflection indicated in Figure 1. By investigating the action on the fundamental group, we can see
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1}\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{2}$
. Therefore, we see that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1}\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{2}$
. Therefore, we see that
 $\text{PMod}(N_{1,2})$
is generated by
$\text{PMod}(N_{1,2})$
is generated by
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
, and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
, and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1}^{2}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}^{2}=(\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1})^{2}=1$
.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1}^{2}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}^{2}=(\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1})^{2}=1$
.
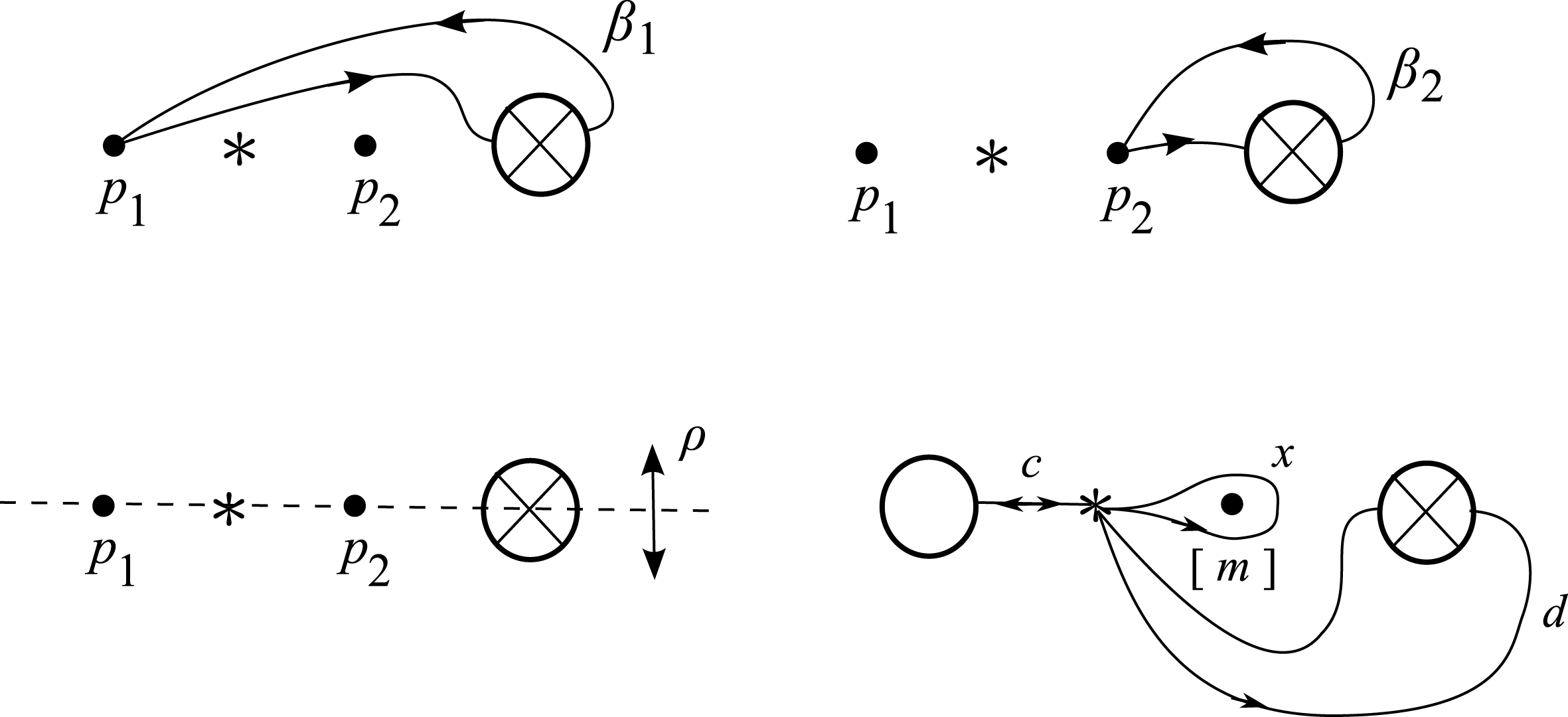
Figure 1.
![]() $\otimes$
indicates the place to attach a Möbius band. The loops
$\otimes$
indicates the place to attach a Möbius band. The loops
![]() $x$
,
$x$
,
![]() $c$
and
$c$
and
![]() $d$
represent the generators of
$d$
represent the generators of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
 $(1;-;[m];\{(\;)\})$
or the orbifold fundamental group of
$(1;-;[m];\{(\;)\})$
or the orbifold fundamental group of
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
whose base point is *.
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
whose base point is *.
Lemma 5.2. [Reference Bujalance, Cirre, Conder and Szepietowski3, Proposition 4.12]
Let
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
be an NEC-group with signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
be an NEC-group with signature
 $(1;-;[m];\{(\;)\})$
and canonical generators
$(1;-;[m];\{(\;)\})$
and canonical generators
![]() $x$
,
$x$
,
![]() $d$
,
$d$
,
![]() $c$
, satisfying the relations
$c$
, satisfying the relations
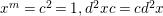 $x^{m}=c^{2}=1,d^{2}xc=cd^{2}x$
. Then
$x^{m}=c^{2}=1,d^{2}xc=cd^{2}x$
. Then
![]() $\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is isomorphic to the Klein four-group and is generated by classes of automorphisms
$\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is isomorphic to the Klein four-group and is generated by classes of automorphisms
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}$
,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}$
defined by
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}$
defined by
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x\mapsto x^{-1},\quad \\ d\mapsto x^{-1}d^{-1}x,\quad \\ c\mapsto c,\quad \end{array}\right.\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x\mapsto x,\quad \\ d\mapsto (dx)^{-1},\quad \\ c\mapsto (dx)^{-1}c(dx).\quad \end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x\mapsto x^{-1},\quad \\ d\mapsto x^{-1}d^{-1}x,\quad \\ c\mapsto c,\quad \end{array}\right.\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x\mapsto x,\quad \\ d\mapsto (dx)^{-1},\quad \\ c\mapsto (dx)^{-1}c(dx).\quad \end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$
Proof. Under the correspondence
![]() $p_{1}$
to the boundary, and
$p_{1}$
to the boundary, and
![]() $p_{2}$
to the cone point,
$p_{2}$
to the cone point,
 $\text{PMod}(N_{1,2})$
is isomorphic to
$\text{PMod}(N_{1,2})$
is isomorphic to
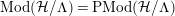 $\text{Mod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=\text{PMod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
. The action of
$\text{Mod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=\text{PMod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
. The action of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
on
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
on
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
is
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
is
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}$
and that of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}$
and that of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1}$
is
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D708}_{1}$
is
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}$
and these actions are of order 2 and not inner automorphisms of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}$
and these actions are of order 2 and not inner automorphisms of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. By Lemma 5.1, the order of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. By Lemma 5.1, the order of
 $\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is at most 4. Therefore, we see that
$\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is at most 4. Therefore, we see that
![]() $\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is the Klein four-group generated by
$\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is the Klein four-group generated by
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}$
.◻
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}$
.◻
Lemma 5.3. Let
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
be an NEC-group with signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
be an NEC-group with signature
 $(0;+;[m];\{(\;),(\;)\})$
with canonical generators
$(0;+;[m];\{(\;),(\;)\})$
with canonical generators
 $x,e,c_{1},c_{2}$
satisfying the following defining relations:
$x,e,c_{1},c_{2}$
satisfying the following defining relations:
 $x^{m}=c_{1}^{2}=c_{2}^{2}=1$
,
$x^{m}=c_{1}^{2}=c_{2}^{2}=1$
,
 $ec_{1}=c_{1}e$
,
$ec_{1}=c_{1}e$
,
 $xec_{2}=c_{2}xe$
. Then
$xec_{2}=c_{2}xe$
. Then
![]() $\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is isomorphic to the Klein four-group and is generated by classes of automorphisms
$\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is isomorphic to the Klein four-group and is generated by classes of automorphisms
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$
,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$
defined by
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$
defined by
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x\mapsto e^{-1}x^{-1}e,\quad \\ e\mapsto e^{-1},\quad \\ c_{1}\mapsto c_{1},\quad \\ c_{2}\mapsto c_{2},\quad \end{array}\right.\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x\mapsto e^{-1}xe,\quad \\ e\mapsto (xe)^{-1},\quad \\ c_{1}\mapsto c_{2},\quad \\ c_{2}\mapsto c_{1}.\quad \end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x\mapsto e^{-1}x^{-1}e,\quad \\ e\mapsto e^{-1},\quad \\ c_{1}\mapsto c_{1},\quad \\ c_{2}\mapsto c_{2},\quad \end{array}\right.\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x\mapsto e^{-1}xe,\quad \\ e\mapsto (xe)^{-1},\quad \\ c_{1}\mapsto c_{2},\quad \\ c_{2}\mapsto c_{1}.\quad \end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$
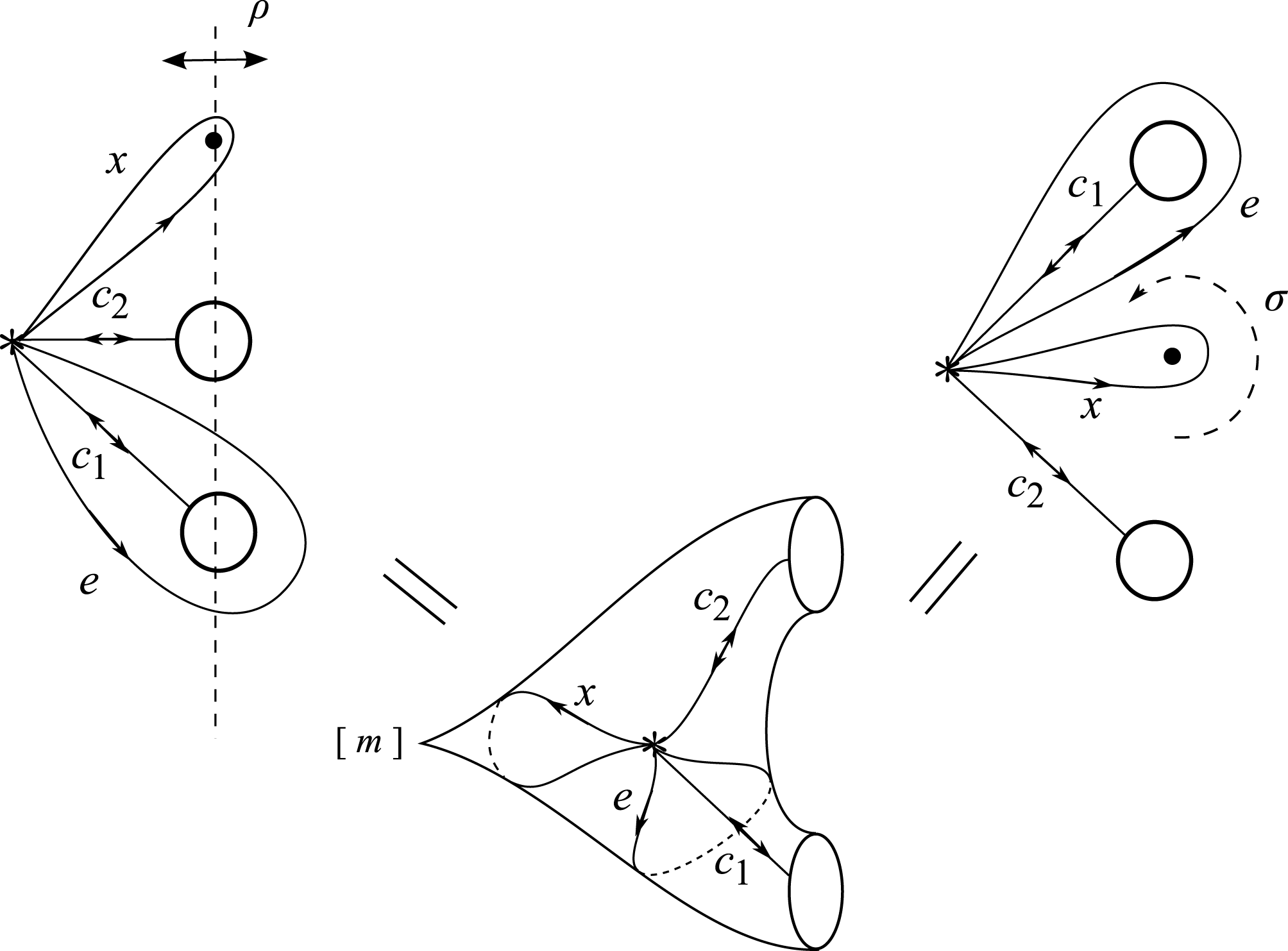
Figure 2. The loops
![]() $x$
,
$x$
,
![]() $c_{1}$
,
$c_{1}$
,
![]() $c_{2}$
and
$c_{2}$
and
![]() $e$
represent the generators of
$e$
represent the generators of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature (
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature (
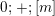 $0;+;[m]$
;
$0;+;[m]$
;
 $\{(\;),(\;)\}$
) or the orbifold fundamental group of
$\{(\;),(\;)\}$
) or the orbifold fundamental group of
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
whose base point is *.
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
whose base point is *.
Proof. Let
![]() $f$
be a homeomorphism over
$f$
be a homeomorphism over
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
fixing boundaries and a cone point, then we can regard
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
fixing boundaries and a cone point, then we can regard
![]() $f$
as an element of
$f$
as an element of
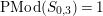 $\text{PMod}(S_{0,3})=1$
. Therefore, every element of
$\text{PMod}(S_{0,3})=1$
. Therefore, every element of
 $\text{PMod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=\text{Mod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is determined by its action on the boundary of
$\text{PMod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=\text{Mod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is determined by its action on the boundary of
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. Let
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. Let
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
be the reflection about the axis shown in Figure 2, and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
be the reflection about the axis shown in Figure 2, and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$
be the
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$
be the
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}$
-rotation about the cone point as shown in Figure 2.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}$
-rotation about the cone point as shown in Figure 2.
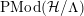 $\text{PMod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is generated by
$\text{PMod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is generated by
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$
, and its defining relations are
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$
, and its defining relations are
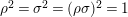 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}^{2}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}^{2}=(\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E})^{2}=1$
. The action of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}^{2}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}^{2}=(\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E})^{2}=1$
. The action of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
on
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
on
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
is
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
is
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$
and that of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$
and that of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$
is
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$
is
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$
and these actions are not inner automorphisms of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$
and these actions are not inner automorphisms of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. By Lemma 5.1, the order of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. By Lemma 5.1, the order of
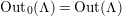 $\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is at most 4. Therefore, we see that
$\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is at most 4. Therefore, we see that
![]() $\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is the Klein four-group generated by
$\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is the Klein four-group generated by
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$
.◻
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$
.◻
Lemma 5.4. Let
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
be an NEC-group with a signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
be an NEC-group with a signature
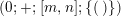 $(0;+;[m,n];\{(\;)\})$
and generators
$(0;+;[m,n];\{(\;)\})$
and generators
![]() $x_{1}$
,
$x_{1}$
,
![]() $x_{2}$
,
$x_{2}$
,
![]() $c$
, satisfying the following defining relations:
$c$
, satisfying the following defining relations:
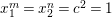 $x_{1}^{m}=x_{2}^{n}=c^{2}=1$
,
$x_{1}^{m}=x_{2}^{n}=c^{2}=1$
,
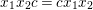 $x_{1}x_{2}c=cx_{1}x_{2}$
. Then if
$x_{1}x_{2}c=cx_{1}x_{2}$
. Then if
![]() $m\neq n$
then
$m\neq n$
then
![]() $\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
has order
$\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
has order
![]() $2$
and is generated by the class of automorphism
$2$
and is generated by the class of automorphism
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$
while if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$
while if
![]() $m=n$
and the Klein four-group generated by
$m=n$
and the Klein four-group generated by
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC},\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$
in the other case, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC},\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$
in the other case, where
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x_{1}\mapsto x_{1}^{-1},\quad \\ x_{2}\mapsto x_{1}x_{2}^{-1}x_{1}^{-1},\quad \\ c\mapsto c,\quad \end{array}\right.\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x_{1}\mapsto x_{2},\quad \\ x_{2}\mapsto x_{2}^{-1}x_{1}x_{2},\quad \\ c\mapsto c.\quad \end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x_{1}\mapsto x_{1}^{-1},\quad \\ x_{2}\mapsto x_{1}x_{2}^{-1}x_{1}^{-1},\quad \\ c\mapsto c,\quad \end{array}\right.\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x_{1}\mapsto x_{2},\quad \\ x_{2}\mapsto x_{2}^{-1}x_{1}x_{2},\quad \\ c\mapsto c.\quad \end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$

Figure 3. The loops
![]() $x_{1}$
,
$x_{1}$
,
![]() $x_{2}$
,
$x_{2}$
,
![]() $c$
are the generators of
$c$
are the generators of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
 $(0;+;[m,n];\{(\;)\})$
or the orbifold fundamental group of
$(0;+;[m,n];\{(\;)\})$
or the orbifold fundamental group of
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
whose base point is *.
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
whose base point is *.
Proof. Let
![]() $f$
be a homeomorphism over
$f$
be a homeomorphism over
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
fixing boundaries and a corner, then we can regard
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
fixing boundaries and a corner, then we can regard
![]() $f$
as an element of
$f$
as an element of
 $\text{PMod}(S_{0,3})=1$
. Therefore, every element of
$\text{PMod}(S_{0,3})=1$
. Therefore, every element of
 $\text{PMod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is determined by its action on the boundary of
$\text{PMod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is determined by its action on the boundary of
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. Let
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. Let
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
be the reflection about the axis shown in Figure 3. Then
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
be the reflection about the axis shown in Figure 3. Then
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
reverses the orientation of the boundary of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
reverses the orientation of the boundary of
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
.
${\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
.
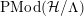 $\text{PMod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is generated by the involution
$\text{PMod}({\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is generated by the involution
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
. The action of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
. The action of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
on
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}$
on
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
is
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
is
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$
and is not inner automorphism of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$
and is not inner automorphism of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. By Lemma 5.1, the order of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
. By Lemma 5.1, the order of
 $\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is at most 2. Therefore,
$\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is at most 2. Therefore,
 $\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is generated by
$\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is generated by
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$
and
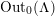 $\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is isomorphic to
$\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is isomorphic to
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{2}$
. If
$\mathbb{Z}_{2}$
. If
![]() $n\not =m$
,
$n\not =m$
,
 $\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
. If
$\text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
. If
![]() $n=m$
, there is a short exact sequence
$n=m$
, there is a short exact sequence
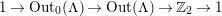 $1\rightarrow \text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})\rightarrow \text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{2}\rightarrow 1$
, where
$1\rightarrow \text{Out}_{0}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})\rightarrow \text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{2}\rightarrow 1$
, where
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{2}$
is the group of permutation of cones and is generated by
$\mathbb{Z}_{2}$
is the group of permutation of cones and is generated by
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$
in Figure 3. The action of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$
in Figure 3. The action of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$
on
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$
on
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
is
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
is
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$
. We conclude that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$
. We conclude that
![]() $\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is generated by
$\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
is generated by
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$
, and its defining relations are
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$
, and its defining relations are
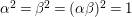 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}^{2}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}^{2}=(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD})^{2}=1$
.◻
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}^{2}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}^{2}=(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD})^{2}=1$
.◻
6 Proofs of the main results
In this section we prove the results stated in Section 2, that is we classify, up to topological conjugation, cyclic actions corresponding to the signatures given in Lemma 4.3.
6.1 Actions with a disc with 6 corner points as the quotient orbifold
This is the easiest case concerning an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signature
 $(0;+;[\;];\{(2,2,2,2,2,2)\})$
from Lemma 4.3. We denote the canonical reflections
$(0;+;[\;];\{(2,2,2,2,2,2)\})$
from Lemma 4.3. We denote the canonical reflections
![]() $c_{1i}$
simply by
$c_{1i}$
simply by
![]() $c_{i}$
for
$c_{i}$
for
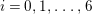 $i=0,1,\ldots ,6$
. We have
$i=0,1,\ldots ,6$
. We have
![]() $e_{1}=1$
and
$e_{1}=1$
and
![]() $c_{0}=c_{6}$
. It follows that
$c_{0}=c_{6}$
. It follows that
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has the presentation
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has the presentation
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\langle c_{0},\ldots ,c_{5}\mid c_{0}^{2}=\cdots =c_{5}^{2}=(c_{0}c_{1})^{2}=\cdots =(c_{4}c_{5})^{2}=1\rangle .\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\langle c_{0},\ldots ,c_{5}\mid c_{0}^{2}=\cdots =c_{5}^{2}=(c_{0}c_{1})^{2}=\cdots =(c_{4}c_{5})^{2}=1\rangle .\end{eqnarray}$$
Proof of Theorem 2.1.
By Lemma 4.4 there is only one, up to equivalence, BSK-epimorphism
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
, mapping
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
, mapping
 $(c_{0},c_{1},c_{2},c_{3},c_{4},c_{5})$
on
$(c_{0},c_{1},c_{2},c_{3},c_{4},c_{5})$
on
 $(N/2,0,N/2,0,N/2,0)$
. In particular, we see that
$(N/2,0,N/2,0,N/2,0)$
. In particular, we see that
![]() $N/2$
generates
$N/2$
generates
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
, hence
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
, hence
![]() $N=2$
. By Lemma 4.2 and the Hurwitz–Riemann formula,
$N=2$
. By Lemma 4.2 and the Hurwitz–Riemann formula,
![]() $S$
is a 3-holed sphere.◻
$S$
is a 3-holed sphere.◻
6.2 Actions with annulus with 2 corner points as the quotient orbifold
This case concerns an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signature
 $$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[\;];\{(\;),(2,2)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[\;];\{(\;),(2,2)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
from Lemma 4.3 which has the presentation
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \left\langle e_{1},e_{2},c_{10},c_{20},c_{21},c_{22}\,|\right.\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \quad \left.e_{1}e_{2}=c_{ij}^{2}=(c_{20}c_{21})^{2}=(c_{21}c_{22})^{2}=1,e_{1}c_{10}=c_{10}e_{1},e_{2}c_{20}=c_{22}e_{2}\right\rangle \!.\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \left\langle e_{1},e_{2},c_{10},c_{20},c_{21},c_{22}\,|\right.\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \quad \left.e_{1}e_{2}=c_{ij}^{2}=(c_{20}c_{21})^{2}=(c_{21}c_{22})^{2}=1,e_{1}c_{10}=c_{10}e_{1},e_{2}c_{20}=c_{22}e_{2}\right\rangle \!.\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
Proof of Theorem 2.2.
Let
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
be a BSK-epimorphism and let
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
be a BSK-epimorphism and let
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})=a$
. By Lemma 4.4 we may assume
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})=a$
. By Lemma 4.4 we may assume
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})=a,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{2})=-a,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{20})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{22})=N/2,\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{21})=0\qquad \text{and}\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{10})=0~\text{or}~N/2.\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})=a,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{2})=-a,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{20})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{22})=N/2,\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{21})=0\qquad \text{and}\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{10})=0~\text{or}~N/2.\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
Since
![]() $a$
and
$a$
and
![]() $N/2$
generate
$N/2$
generate
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
, we have
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
, we have
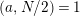 $(a,N/2)=1$
and it follows that the order of
$(a,N/2)=1$
and it follows that the order of
![]() $a$
is either
$a$
is either
![]() $N$
or
$N$
or
![]() $N/2$
, the latter being possible only for odd
$N/2$
, the latter being possible only for odd
![]() $N/2$
.
$N/2$
.
Suppose that the order of
![]() $a$
is
$a$
is
![]() $N$
. Then after composing
$N$
. Then after composing
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
with a suitable automorphism of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
with a suitable automorphism of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we can assume that
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we can assume that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})=1$
. By Lemma 4.2
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})=1$
. By Lemma 4.2
![]() $S$
is nonorientable, since
$S$
is nonorientable, since
![]() $e_{1}^{N/2}c_{20}$
is a nonorientable word in
$e_{1}^{N/2}c_{20}$
is a nonorientable word in
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
, and its number of boundary components is either
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
, and its number of boundary components is either
![]() $N/2$
if
$N/2$
if
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{10})\neq 0$
, or
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{10})\neq 0$
, or
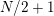 $N/2+1$
if
$N/2+1$
if
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{10})=0$
. From the Hurwitz–Riemann formula we easily compute that the genus of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{10})=0$
. From the Hurwitz–Riemann formula we easily compute that the genus of
![]() $S$
is respectively 2 or 1. Now suppose that the order of
$S$
is respectively 2 or 1. Now suppose that the order of
![]() $a$
is
$a$
is
![]() $N/2$
which is odd. As above, after composing
$N/2$
which is odd. As above, after composing
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
with a suitable automorphism of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
with a suitable automorphism of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we can assume that
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we can assume that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})=2$
and therefore again we obtain two nonequivalent BSK-maps, which give rise to two topologically nonconjugate actions. Observe however, that this time
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})=2$
and therefore again we obtain two nonequivalent BSK-maps, which give rise to two topologically nonconjugate actions. Observe however, that this time
![]() $S$
is orientable by Lemma 4.2, and it has either
$S$
is orientable by Lemma 4.2, and it has either
![]() $N/2$
or
$N/2$
or
 $N/2+2$
boundary components. By the Hurwitz–Riemann formula the genus of
$N/2+2$
boundary components. By the Hurwitz–Riemann formula the genus of
![]() $S$
is respectively 1 or 0.◻
$S$
is respectively 1 or 0.◻
6.3 Actions with Möbius band with 2 corner points as the quotient orbifold
This case concerns an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
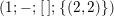 $(1;-;[\;];\{(2,2)\})$
from Lemma 4.3. We denote the canonical reflections
$(1;-;[\;];\{(2,2)\})$
from Lemma 4.3. We denote the canonical reflections
![]() $c_{1i}$
simply by
$c_{1i}$
simply by
![]() $c_{i}$
for
$c_{i}$
for
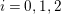 $i=0,1,2$
. After ruling out the redundant generator
$i=0,1,2$
. After ruling out the redundant generator
![]() $e_{1}$
, we can write a presentation for
$e_{1}$
, we can write a presentation for
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
as
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
as
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\langle d,c_{0},c_{1},c_{2}\mid c_{0}^{2}=c_{1}^{2}=c_{2}^{2}=(c_{0}c_{1})^{2}=(c_{1}c_{2})^{2}=1,c_{0}d^{2}=d^{2}c_{2}\rangle .\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\langle d,c_{0},c_{1},c_{2}\mid c_{0}^{2}=c_{1}^{2}=c_{2}^{2}=(c_{0}c_{1})^{2}=(c_{1}c_{2})^{2}=1,c_{0}d^{2}=d^{2}c_{2}\rangle .\end{eqnarray}$$
Proof of Theorem 2.3.
The proof is very similar to that of Theorem 2.2 above. By Lemma 4.4 every BSK-map
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is equivalent to one of the form
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is equivalent to one of the form
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{0})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=N/2,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{1})=0,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)=a,\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{0})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=N/2,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{1})=0,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)=a,\end{eqnarray}$$
for some
![]() $a\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
. By (b) of Lemma 4.2,
$a\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
. By (b) of Lemma 4.2,
![]() $S$
has
$S$
has
![]() $N/2$
boundary components, and from the Hurwitz–Riemann formula we compute that its genus is either 2 if it is nonorientable, or 1 otherwise. There are two cases, according to the order of
$N/2$
boundary components, and from the Hurwitz–Riemann formula we compute that its genus is either 2 if it is nonorientable, or 1 otherwise. There are two cases, according to the order of
![]() $a$
, which is either
$a$
, which is either
![]() $N$
or
$N$
or
![]() $N/2$
. If
$N/2$
. If
![]() $a$
has order
$a$
has order
![]() $N$
, then by composing
$N$
, then by composing
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
with a suitable automorphism of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
with a suitable automorphism of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we can assume that
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we can assume that
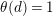 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)=1$
. Observe that here
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)=1$
. Observe that here
![]() $N/2$
can be arbitrary, but
$N/2$
can be arbitrary, but
![]() $S$
is nonorientable if and only if
$S$
is nonorientable if and only if
![]() $N/2$
is even, since only then
$N/2$
is even, since only then
![]() $d^{N/2}c_{0}$
is a nonorientable word in
$d^{N/2}c_{0}$
is a nonorientable word in
![]() $\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
. If the order of
$\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
. If the order of
![]() $a$
is
$a$
is
![]() $N/2$
then it must be odd, and by composing
$N/2$
then it must be odd, and by composing
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
with a suitable automorphism of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
with a suitable automorphism of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we can assume that
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we can assume that
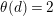 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)=2$
. In such case
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)=2$
. In such case
![]() $d^{N/2}$
is a nonorientable word in
$d^{N/2}$
is a nonorientable word in
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
and hence
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
and hence
![]() $S$
is nonorientable.◻
$S$
is nonorientable.◻
6.4 Actions with a 1-punctured disc with 2 corner points as the quotient orbifold
This is the case concerning an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signature
 $$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[m];\{(2,2)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[m];\{(2,2)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
from Lemma 4.3. We denote the canonical reflections
![]() $c_{1i}$
simply by
$c_{1i}$
simply by
![]() $c_{i}$
for
$c_{i}$
for
 $i=0,1,2$
. After ruling out the redundant generator
$i=0,1,2$
. After ruling out the redundant generator
![]() $e_{1}$
, we can rewrite the presentation for
$e_{1}$
, we can rewrite the presentation for
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
as
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
as
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\langle x,c_{0},c_{1},c_{2}\mid x^{m}=c_{0}^{2}=c_{1}^{2}=c_{2}^{2}=(c_{0}c_{1})^{2}=(c_{1}c_{2})^{2}=1,c_{0}x=xc_{2}\rangle .\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\langle x,c_{0},c_{1},c_{2}\mid x^{m}=c_{0}^{2}=c_{1}^{2}=c_{2}^{2}=(c_{0}c_{1})^{2}=(c_{1}c_{2})^{2}=1,c_{0}x=xc_{2}\rangle .\end{eqnarray}$$
Proof of Theorem 2.4.
Let
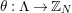 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
be a BSK-epimorphism. Then
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
be a BSK-epimorphism. Then
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is generated by
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is generated by
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
, which has order
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
, which has order
![]() $m$
, and
$m$
, and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{i})$
for some canonical reflection
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{i})$
for some canonical reflection
![]() $c_{i}$
which has order 2. Thus either
$c_{i}$
which has order 2. Thus either
![]() $N=m$
if
$N=m$
if
![]() $m$
is even, or
$m$
is even, or
 $N=2m$
if
$N=2m$
if
![]() $m$
is odd. By Lemma 4.4, we can assume that
$m$
is odd. By Lemma 4.4, we can assume that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{0})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=N/2$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{0})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=N/2$
,
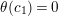 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{1})=0$
. If
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{1})=0$
. If
![]() $m=N$
then after composing
$m=N$
then after composing
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
with a suitable automorphism of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
with a suitable automorphism of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we can assume that
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we can assume that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)=1$
, and hence the action is unique. By (a) of Lemma 4.2,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)=1$
, and hence the action is unique. By (a) of Lemma 4.2,
![]() $S$
is nonorientable in this case, since
$S$
is nonorientable in this case, since
![]() $x^{N/2}c_{0}$
is a nonorientable word in
$x^{N/2}c_{0}$
is a nonorientable word in
![]() $\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
. Now assume that
$\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
. Now assume that
 $N=2m$
. Then after composing
$N=2m$
. Then after composing
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
with a suitable automorphism of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
with a suitable automorphism of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we can assume that
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we can assume that
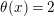 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)=2$
, and hence also in this case the action is unique up to topological conjugation. Observe that now
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)=2$
, and hence also in this case the action is unique up to topological conjugation. Observe that now
![]() $S$
is orientable, by (a) of Lemma 4.2. Finally, by (b) of Lemma 4.2,
$S$
is orientable, by (a) of Lemma 4.2. Finally, by (b) of Lemma 4.2,
![]() $S$
has
$S$
has
![]() $N/2$
boundary components in both cases, and its genus can be easily computed from the Hurwitz–Riemann formula.◻
$N/2$
boundary components in both cases, and its genus can be easily computed from the Hurwitz–Riemann formula.◻
6.5 Actions with a 1-punctured disc with 4 corner points as the quotient orbifold
This is the case concerning an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signature
 $$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[m];\{(2,2,2,2)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[m];\{(2,2,2,2)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
from Lemma 4.3. This case is very similar to that from the previous section. Now
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has the presentation
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has the presentation
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \!\!\!\left\langle x,c_{0},\ldots ,c_{4}\,|\right.\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \!\!\!\quad \left.x^{m}=c_{0}^{2}=\cdots =c_{4}^{2}=(c_{0}c_{1})^{2}=(c_{1}c_{2})^{2}=(c_{2}c_{3})^{2}=(c_{3}c_{4})^{2}=1,c_{0}x=xc_{4}\right\rangle \!.\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \!\!\!\left\langle x,c_{0},\ldots ,c_{4}\,|\right.\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \!\!\!\quad \left.x^{m}=c_{0}^{2}=\cdots =c_{4}^{2}=(c_{0}c_{1})^{2}=(c_{1}c_{2})^{2}=(c_{2}c_{3})^{2}=(c_{3}c_{4})^{2}=1,c_{0}x=xc_{4}\right\rangle \!.\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
The proof of Theorem 2.5 is almost identical as that of Theorem 2.4. We leave details to the reader.
6.6 Actions with 1-punctured Möbius band as the quotient orbifold
These actions correspond to an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
 $$\begin{eqnarray}(1;-;[m];\{(\;)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}(1;-;[m];\{(\;)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
from Lemma 4.3 which has the presentation
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\langle x,d,c,e\mid xed^{2}=x^{m}=c^{2}=1,ec=ce\rangle .\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\langle x,d,c,e\mid xed^{2}=x^{m}=c^{2}=1,ec=ce\rangle .\end{eqnarray}$$
We have
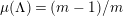 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=(m-1)/m$
.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=(m-1)/m$
.
Proof of Theorem 2.6.
Suppose that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is a BSK-epimorphism, such that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is a BSK-epimorphism, such that
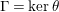 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is an orientable bordered surface group with
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is an orientable bordered surface group with
![]() $k$
empty period cycles. Since
$k$
empty period cycles. Since
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
contains a reflection, we have
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
contains a reflection, we have
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c)=0$
, and by (b) of Lemma 4.2,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c)=0$
, and by (b) of Lemma 4.2,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
has order
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
has order
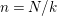 $n=N/k$
. In particular,
$n=N/k$
. In particular,
![]() $k$
divides
$k$
divides
![]() $N$
. Note that
$N$
. Note that
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
generate a subgroup of index at most 2 of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
generate a subgroup of index at most 2 of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
. Since
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
. Since
![]() $S$
is orientable, this has to be a proper subgroup of
$S$
is orientable, this has to be a proper subgroup of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
, for otherwise
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
, for otherwise
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
would contain a nonorientable word of the form
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
would contain a nonorientable word of the form
![]() $wd$
, where
$wd$
, where
![]() $w$
is a word in
$w$
is a word in
![]() $x$
and
$x$
and
![]() $e$
such that
$e$
such that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(w)=-\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)$
. It follows that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(w)=-\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)$
. It follows that
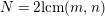 $N=2\text{lcm}(m,n)$
.
$N=2\text{lcm}(m,n)$
.
By multiplying
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
by an element of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
by an element of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
, we can assume that
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
, we can assume that
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)=N/m,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=aN/n,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)=b,\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)=N/m,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=aN/n,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)=b,\end{eqnarray}$$
for some
![]() $a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
and some
$a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
and some
![]() $b$
for which
$b$
for which
 $$\begin{eqnarray}N/m+aN/n+2b\equiv 0\;(N).\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}N/m+aN/n+2b\equiv 0\;(N).\end{eqnarray}$$
We denote such BSK-map by
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
, bearing in mind that the parameter
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
, bearing in mind that the parameter
![]() $a$
does not always determine it uniquely. Indeed, we have
$a$
does not always determine it uniquely. Indeed, we have
 $$\begin{eqnarray}b=-N/2m-aN/2n+\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}N/2=-n/t-am/t+\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}N/2\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}b=-N/2m-aN/2n+\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}N/2=-n/t-am/t+\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}N/2\end{eqnarray}$$
for some
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}\in \mathbb{Z}_{2}$
.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}\in \mathbb{Z}_{2}$
.
If
![]() $N/2$
is odd then for arbitrary
$N/2$
is odd then for arbitrary
![]() $a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
we have a unique odd
$a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
we have a unique odd
![]() $b$
, namely
$b$
, namely
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}=0$
if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}=0$
if
![]() $a$
is even, and
$a$
is even, and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}=1$
if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}=1$
if
![]() $a$
is odd. If
$a$
is odd. If
![]() $N/2$
is even but
$N/2$
is even but
![]() $t$
is odd, then
$t$
is odd, then
![]() $b$
is odd for arbitrary
$b$
is odd for arbitrary
![]() $a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
and
$a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}\in \mathbb{Z}_{2}$
. Finally, suppose that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}\in \mathbb{Z}_{2}$
. Finally, suppose that
![]() $t$
is even. Then
$t$
is even. Then
![]() $a$
must be odd since
$a$
must be odd since
 $(a,n)=1$
, and
$(a,n)=1$
, and
![]() $b$
is odd if and only if
$b$
is odd if and only if
![]() $n/t$
and
$n/t$
and
![]() $m/t$
have opposite parity. But since
$m/t$
have opposite parity. But since
![]() $n/t$
and
$n/t$
and
![]() $m/t$
are relatively prime,
$m/t$
are relatively prime,
![]() $b$
is odd if and only if
$b$
is odd if and only if
 $mn/t^{2}=N/2t$
is even and
$mn/t^{2}=N/2t$
is even and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}$
arbitrary.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}$
arbitrary.
Summarizing the above paragraph, we conclude that if
![]() $N/2$
is odd, then
$N/2$
is odd, then
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)$
is uniquely determined by
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)$
is uniquely determined by
![]() $a$
, whereas if
$a$
, whereas if
![]() $N/2$
is even, then
$N/2$
is even, then
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)$
is determined only modulo
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)$
is determined only modulo
![]() $N/2$
. However, the two different possibilities for
$N/2$
. However, the two different possibilities for
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)$
define equivalent BSK-epimorphisms. Indeed, set
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)$
define equivalent BSK-epimorphisms. Indeed, set
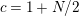 $c=1+N/2$
and note that
$c=1+N/2$
and note that
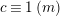 $c\equiv 1\;(m)$
,
$c\equiv 1\;(m)$
,
 $c\equiv 1\;(n)$
and
$c\equiv 1\;(n)$
and
![]() $c$
is odd, hence
$c$
is odd, hence
![]() $c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
. Furthermore, we have
$c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
. Furthermore, we have
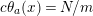 $c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x)=N/m$
,
$c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x)=N/m$
,
 $c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e)=aN/n$
and
$c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e)=aN/n$
and
 $c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)+N/2$
, because
$c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)+N/2$
, because
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)$
is odd.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)$
is odd.
Now, we determine the number of equivalence classes of BSK-epimorphisms. For
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
representing an element of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
representing an element of
![]() $\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
and a BSK-map
$\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
and a BSK-map
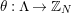 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
, let
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
, let
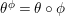 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}\circ \unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
. Since
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}\circ \unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
. Since
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is into an abelian target, for the generators of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is into an abelian target, for the generators of
![]() $\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
given in Lemma 5.2 we have
$\text{Out}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
given in Lemma 5.2 we have
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x\mapsto -\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x),\quad \\ e\mapsto -\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e),\quad \\ d\mapsto -\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d),\quad \end{array}\right.\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x\mapsto \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x),\quad \\ e\mapsto -\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e),\quad \\ d\mapsto -\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)-\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x).\quad \end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x\mapsto -\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x),\quad \\ e\mapsto -\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e),\quad \\ d\mapsto -\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d),\quad \end{array}\right.\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}}:\left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}}x\mapsto \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x),\quad \\ e\mapsto -\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e),\quad \\ d\mapsto -\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)-\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x).\quad \end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$
In particular, for every
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
we have
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
we have
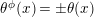 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}(x)=\pm \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}(x)=\pm \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}(e)=\pm \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}(e)=\pm \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
.
We claim that
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}$
are equivalent if and only if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}$
are equivalent if and only if
 $a\equiv \pm a^{\prime }\;(t)$
. For suppose that
$a\equiv \pm a^{\prime }\;(t)$
. For suppose that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}$
for some
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}$
for some
![]() $c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
and
$c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
. Then, by replacing
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
. Then, by replacing
![]() $c$
by
$c$
by
![]() $-c$
if necessary, we may assume that
$-c$
if necessary, we may assume that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(x)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x)$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(x)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x)$
and
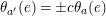 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(e)=\pm c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e)$
, which gives
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(e)=\pm c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e)$
, which gives
 $c\equiv 1\;(m)$
and
$c\equiv 1\;(m)$
and
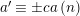 $a^{\prime }\equiv \pm ca\;(n)$
. It follows that
$a^{\prime }\equiv \pm ca\;(n)$
. It follows that
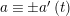 $a\equiv \pm a^{\prime }\;(t)$
. Conversely, suppose that
$a\equiv \pm a^{\prime }\;(t)$
. Conversely, suppose that
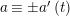 $a\equiv \pm a^{\prime }\;(t)$
. Then by Lemma 3.1 there exists
$a\equiv \pm a^{\prime }\;(t)$
. Then by Lemma 3.1 there exists
![]() $c$
, such that
$c$
, such that
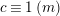 $c\equiv 1\;(m)$
and
$c\equiv 1\;(m)$
and
 $c\equiv \pm a^{\prime }a^{-1}\;(n)$
, where
$c\equiv \pm a^{\prime }a^{-1}\;(n)$
, where
![]() $a^{-1}$
denotes the inverse of
$a^{-1}$
denotes the inverse of
![]() $a$
modulo
$a$
modulo
![]() $n$
. Note that such
$n$
. Note that such
![]() $c$
is relatively prime to
$c$
is relatively prime to
![]() $m$
and
$m$
and
![]() $n$
, and hence to
$n$
, and hence to
![]() $N/2$
. If
$N/2$
. If
![]() $N/2$
is odd, then we can take
$N/2$
is odd, then we can take
![]() $c$
to be odd as well, so that
$c$
to be odd as well, so that
![]() $c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
. Now
$c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
. Now
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(x)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}(x)$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(x)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}(x)$
and
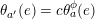 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(e)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}(e)$
, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(e)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}(e)$
, where
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}=\text{id}$
or
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}=\text{id}$
or
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}$
. If
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}$
. If
![]() $N/2$
is odd, then necessarily also
$N/2$
is odd, then necessarily also
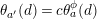 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(d)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}(d)$
, whereas if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(d)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}(d)$
, whereas if
![]() $N/2$
is even, then possibly
$N/2$
is even, then possibly
 $c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}(d)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(d)+N/2$
, in which case it suffices to replace
$c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}(d)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(d)+N/2$
, in which case it suffices to replace
![]() $c$
by
$c$
by
 $c+N/2$
.
$c+N/2$
.
Summarizing, on one hand each element of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{t}^{\ast }$
is the residue mod
$\mathbb{Z}_{t}^{\ast }$
is the residue mod
![]() $t$
of some
$t$
of some
![]() $a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
defining BSK-map
$a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
defining BSK-map
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
by Lemma 3.2. On the other hand
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
by Lemma 3.2. On the other hand
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}$
are equivalent if and only if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}$
are equivalent if and only if
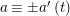 $a\equiv \pm a^{\prime }\;(t)$
. So the elements of the quotient group
$a\equiv \pm a^{\prime }\;(t)$
. So the elements of the quotient group
 $\mathbb{Z}_{t}^{\ast }/\{\pm 1\}$
parametrize the equivalence classes of BSK-maps (although it might happen that for a particular representative
$\mathbb{Z}_{t}^{\ast }/\{\pm 1\}$
parametrize the equivalence classes of BSK-maps (although it might happen that for a particular representative
![]() $x\in \mathbb{Z}_{t}^{\ast }$
,
$x\in \mathbb{Z}_{t}^{\ast }$
,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{x}$
is not a BSK-epimorphism, because
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{x}$
is not a BSK-epimorphism, because
![]() $x\notin \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
). Therefore, we have
$x\notin \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
). Therefore, we have
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)/2$
classes for
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)/2$
classes for
![]() $t>1$
and 1 class for
$t>1$
and 1 class for
![]() $t=1$
.◻
$t=1$
.◻
Proof of Theorem 2.7.
Suppose that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is a BSK-epimorphism, such that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is a BSK-epimorphism, such that
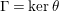 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is a nonorientable bordered surface group with
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is a nonorientable bordered surface group with
![]() $k$
empty period cycles. As in the proof of the previous theorem, we have
$k$
empty period cycles. As in the proof of the previous theorem, we have
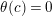 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c)=0$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c)=0$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
has order
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
has order
 $n=N/k$
. Since
$n=N/k$
. Since
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
contains a nonorientable word,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
contains a nonorientable word,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)$
is equal to
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)$
is equal to
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(w)$
for some word
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(w)$
for some word
![]() $w$
in
$w$
in
![]() $x$
and
$x$
and
![]() $e$
. It follows that
$e$
. It follows that
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is generated by
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is generated by
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
, hence
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
, hence
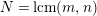 $N=\text{lcm}(m,n)$
. By multiplying
$N=\text{lcm}(m,n)$
. By multiplying
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
by an element of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
by an element of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
, we can assume that
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
, we can assume that
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
defined by (9) for some
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
defined by (9) for some
![]() $a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
and some
$a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
and some
![]() $b$
for which (10) is satisfied.
$b$
for which (10) is satisfied.
Now, if
![]() $N$
is odd then for arbitrary
$N$
is odd then for arbitrary
![]() $a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
we have a unique
$a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
we have a unique
![]() $b$
satisfying (10). By the same argument as in the previous proof,
$b$
satisfying (10). By the same argument as in the previous proof,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
is equivalent to
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
is equivalent to
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}$
if and only if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}$
if and only if
 $a\equiv \pm a^{\prime }\;(t)$
, and hence there are
$a\equiv \pm a^{\prime }\;(t)$
, and hence there are
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)/2$
equivalence classes of BSK-epimorphisms if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)/2$
equivalence classes of BSK-epimorphisms if
![]() $t>1$
, and one such class if
$t>1$
, and one such class if
![]() $t=1$
.
$t=1$
.
For the rest of the proof assume that
![]() $N$
is even. By (10),
$N$
is even. By (10),
 $N/m+aN/n=n/t+am/t$
is even, which is possible if and only if
$N/m+aN/n=n/t+am/t$
is even, which is possible if and only if
![]() $n/t$
and
$n/t$
and
![]() $m/t$
are both odd, hence
$m/t$
are both odd, hence
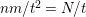 $nm/t^{2}=N/t$
is odd. Now
$nm/t^{2}=N/t$
is odd. Now
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)$
is determined by
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)$
is determined by
![]() $a$
only modulo
$a$
only modulo
![]() $N/2$
:
$N/2$
:
 $$\begin{eqnarray}b=-\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{N}{m}+a\frac{N}{n}\right)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}\frac{N}{2}\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}b=-\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{N}{m}+a\frac{N}{n}\right)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}\frac{N}{2}\end{eqnarray}$$
for some
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}\in \mathbb{Z}_{2}$
. We claim that given
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}\in \mathbb{Z}_{2}$
. We claim that given
 $a,a^{\prime }\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
,
$a,a^{\prime }\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}$
are equivalent if and only if either
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}$
are equivalent if and only if either
(1)
 $a\equiv a^{\prime }\;(t)$
and
$a\equiv a^{\prime }\;(t)$
and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(d)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)$
, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(d)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)$
, where
 $c$
is the unique element of
$c$
is the unique element of
 $\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
satisfying
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
satisfying
 $c\equiv 1\;(m)$
and
$c\equiv 1\;(m)$
and
 $ca\equiv a^{\prime }\;(n)$
; or
$ca\equiv a^{\prime }\;(n)$
; or(2)
 $a\equiv -a^{\prime }\;(t)$
and
$a\equiv -a^{\prime }\;(t)$
and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(d)=c(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x))$
, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(d)=c(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x))$
, where
 $c$
is the unique element of
$c$
is the unique element of
 $\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
satisfying
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
satisfying
 $c\equiv -1\;(m)$
and
$c\equiv -1\;(m)$
and
 $ca\equiv a^{\prime }\;(n)$
.
$ca\equiv a^{\prime }\;(n)$
.
To prove the claim suppose that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}$
for some
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}$
for some
![]() $c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
and
$c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
and
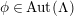 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
. By Lemma 5.2, we may suppose that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
. By Lemma 5.2, we may suppose that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \{1,\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE},\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF},\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}\}$
. If
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \{1,\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE},\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF},\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}\}$
. If
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}=1$
or
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}=1$
or
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}$
, then after replacing
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}$
, then after replacing
![]() $c$
by
$c$
by
![]() $-c$
in the latter case, we have
$-c$
in the latter case, we have
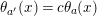 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(x)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x)$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(x)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x)$
,
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(e)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e)$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(e)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e)$
and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(d)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)$
. Thus
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(d)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)$
. Thus
![]() $c$
satisfies
$c$
satisfies
 $c\equiv 1\;(m)$
and
$c\equiv 1\;(m)$
and
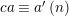 $ca\equiv a^{\prime }\;(n)$
. By Lemma 3.1, such (unique)
$ca\equiv a^{\prime }\;(n)$
. By Lemma 3.1, such (unique)
![]() $c$
exists if and only if
$c$
exists if and only if
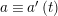 $a\equiv a^{\prime }\;(t)$
. Similarly, if
$a\equiv a^{\prime }\;(t)$
. Similarly, if
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}$
or
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}$
or
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}$
, then after replacing
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}=\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}$
, then after replacing
![]() $c$
by
$c$
by
![]() $-c$
in the former case, we have
$-c$
in the former case, we have
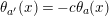 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(x)=-c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x)$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(x)=-c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x)$
,
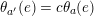 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(e)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e)$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(e)=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e)$
and
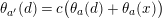 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(d)=c\big(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x)\big)$
. Such (unique)
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(d)=c\big(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(d)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x)\big)$
. Such (unique)
![]() $c$
again exists if and only if
$c$
again exists if and only if
 $a\equiv -a^{\prime }\;(t)$
. This completes the proof of the claim.
$a\equiv -a^{\prime }\;(t)$
. This completes the proof of the claim.
Suppose
![]() $t>2$
. It follows from the previous paragraph that there is a surjection
$t>2$
. It follows from the previous paragraph that there is a surjection
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}$
from the set of equivalence classes of BSK-maps onto
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}$
from the set of equivalence classes of BSK-maps onto
 $\mathbb{Z}_{t}^{\ast }/\{\pm 1\}$
, defined by
$\mathbb{Z}_{t}^{\ast }/\{\pm 1\}$
, defined by
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}([\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}])=[[a]_{t}]$
, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}([\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}])=[[a]_{t}]$
, where
![]() $a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
. We claim that
$a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
. We claim that
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}$
is a 2-over-one map. For let
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}$
is a 2-over-one map. For let
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
be a BSK-map defined by (9) and define
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
be a BSK-map defined by (9) and define
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\prime }$
by
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\prime }$
by
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\prime }(x)=N/m,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\prime }(e)=aN/n,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\prime }(d)=b+N/2.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\prime }(x)=N/m,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\prime }(e)=aN/n,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\prime }(d)=b+N/2.\end{eqnarray}$$
Evidently
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\prime })$
, but
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\prime })$
, but
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
is not equivalent to
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
is not equivalent to
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\prime }$
. For if they were equivalent, then (1) would be satisfied with
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\prime }$
. For if they were equivalent, then (1) would be satisfied with
![]() $c=1$
, hence
$c=1$
, hence
 $b=b+N/2$
. Now if
$b=b+N/2$
. Now if
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a})$
for some
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a})$
for some
![]() $a^{\prime }\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
, then
$a^{\prime }\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }$
, then
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}$
is equivalent either to
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}$
is equivalent either to
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
or to
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
or to
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\prime }$
, by (1) if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\prime }$
, by (1) if
 $a^{\prime }\equiv a\;(t)$
, or by (2) if
$a^{\prime }\equiv a\;(t)$
, or by (2) if
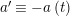 $a^{\prime }\equiv -a\;(t)$
.
$a^{\prime }\equiv -a\;(t)$
.
Finally, suppose
![]() $t=2$
. By (1) every BSK-map is equivalent to
$t=2$
. By (1) every BSK-map is equivalent to
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
such that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
such that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)=N/m$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)=N/m$
and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=N/n$
. Fix such
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=N/n$
. Fix such
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
and define
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
and define
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\prime }$
by
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\prime }$
by
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\prime }(x)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\prime }(x)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
,
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\prime }(e)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
, and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\prime }(e)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
, and
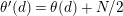 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\prime }(d)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)+N/2$
. We have to show that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\prime }(d)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)+N/2$
. We have to show that
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\prime }$
are equivalent. Let
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\prime }$
are equivalent. Let
![]() $c$
be the unique element of
$c$
be the unique element of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
such that
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
such that
 $c\equiv -1\;(m)$
and
$c\equiv -1\;(m)$
and
 $c\equiv 1\;(n)$
. By (2) it suffices to show that
$c\equiv 1\;(n)$
. By (2) it suffices to show that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\prime }(d)=c(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x))$
. We have
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\prime }(d)=c(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x))$
. We have
 $$\begin{eqnarray}2c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)=-c(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e))=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)-\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=2(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)).\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}2c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)=-c(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e))=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)-\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=2(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)).\end{eqnarray}$$
Either
 $c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
or
$c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
or
 $c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)+N/2$
. The former equality is not possible, because
$c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)+N/2$
. The former equality is not possible, because
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)=N/m$
is odd and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)=N/m$
is odd and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)(c-1)$
is even. Hence
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)(c-1)$
is even. Hence
 $$\begin{eqnarray}c(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x))=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)-\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)+N/2=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\prime }(d).\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}c(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x))=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)-\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d)+N/2=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{\prime }(d).\end{eqnarray}$$
It follows that all BSK-maps
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
are equivalent.◻
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
are equivalent.◻
6.7 Actions with a 2-punctured disc as the quotient orbifold
This case concerns an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
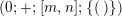 $(0;+;[m,n];\{(\;)\})$
from Lemma 4.3 which has the presentation
$(0;+;[m,n];\{(\;)\})$
from Lemma 4.3 which has the presentation
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\langle x_{1},x_{2},c,e\mid x_{1}^{m}=x_{2}^{n}=c^{2}=x_{1}x_{2}e=1,ec=ce\rangle .\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\langle x_{1},x_{2},c,e\mid x_{1}^{m}=x_{2}^{n}=c^{2}=x_{1}x_{2}e=1,ec=ce\rangle .\end{eqnarray}$$
We have
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=1-1/m-1/n$
.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=1-1/m-1/n$
.
Proof of Theorem 2.8.
Suppose that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is a BSK-map. Since
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is a BSK-map. Since
![]() $\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
contains a reflection,
$\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
contains a reflection,
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c)=0$
and it follows by (a) of Lemma 4.2 that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c)=0$
and it follows by (a) of Lemma 4.2 that
![]() $S$
is orientable. By (b) of Lemma 4.2 we have
$S$
is orientable. By (b) of Lemma 4.2 we have
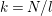 $k=N/l$
, where
$k=N/l$
, where
![]() $l$
is the order of
$l$
is the order of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
. Since
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
. Since
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is a surjection,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is a surjection,
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is generated by
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is generated by
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})$
,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{2})$
which have orders
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{2})$
which have orders
![]() $m$
and
$m$
and
![]() $n$
respectively and
$n$
respectively and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=-(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{2}))$
has order
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=-(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{2}))$
has order
![]() $l$
. It follows that the conditions (i) and (ii) of Lemma 3.3 are satisfied, in particular
$l$
. It follows that the conditions (i) and (ii) of Lemma 3.3 are satisfied, in particular
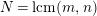 $N=\text{lcm}(m,n)$
. Let
$N=\text{lcm}(m,n)$
. Let
 $(A,A_{1},A_{2},A_{3})$
be the Maclachlan decomposition of
$(A,A_{1},A_{2},A_{3})$
be the Maclachlan decomposition of
 $(m,n,l)$
, as above. We have
$(m,n,l)$
, as above. We have
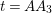 $t=AA_{3}$
,
$t=AA_{3}$
,
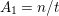 $A_{1}=n/t$
,
$A_{1}=n/t$
,
 $A_{2}=m/t$
and
$A_{2}=m/t$
and
![]() $A_{3}=k$
. We see that
$A_{3}=k$
. We see that
![]() $k$
divides
$k$
divides
![]() $t$
, and because
$t$
, and because
![]() $A_{3}$
is relatively prime to
$A_{3}$
is relatively prime to
![]() $A_{1}A_{2}$
,
$A_{1}A_{2}$
,
![]() $k$
is relatively prime to
$k$
is relatively prime to
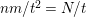 $nm/t^{2}=N/t$
. It follows that
$nm/t^{2}=N/t$
. It follows that
![]() $k$
divides
$k$
divides
 $t/(t,N/t)$
. Finally, if
$t/(t,N/t)$
. Finally, if
![]() $N$
is even, then by (ii) of Lemma 3.3, one of the numbers
$N$
is even, then by (ii) of Lemma 3.3, one of the numbers
![]() $k$
,
$k$
,
![]() $n/t$
,
$n/t$
,
![]() $m/t$
must be even. It follows that
$m/t$
must be even. It follows that
![]() $k$
must be even if
$k$
must be even if
 $N/t=nm/t^{2}$
is odd. Conversely, having
$N/t=nm/t^{2}$
is odd. Conversely, having
 $k,n,m,N$
satisfying the conditions of the theorem, one can easily define, using Lemma 3.3, an appropriate BSK-map defining a surface and an action in question.
$k,n,m,N$
satisfying the conditions of the theorem, one can easily define, using Lemma 3.3, an appropriate BSK-map defining a surface and an action in question.
Every BSK-map is equivalent to
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
defined by
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
defined by
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x_{1})=A_{1},\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x_{2})=aA_{2},\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e)=-(A_{1}+aA_{2}),\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(c)=0\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x_{1})=A_{1},\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x_{2})=aA_{2},\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e)=-(A_{1}+aA_{2}),\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(c)=0\end{eqnarray}$$
for some
![]() $a\in {\mathcal{L}}$
, where
$a\in {\mathcal{L}}$
, where
 $$\begin{eqnarray}{\mathcal{L}}=\{a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }\mid A_{1}+aA_{2}~\text{has order}~l\}.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}{\mathcal{L}}=\{a\in \mathbb{Z}_{n}^{\ast }\mid A_{1}+aA_{2}~\text{has order}~l\}.\end{eqnarray}$$
Suppose first that
![]() $m\neq n$
. Let
$m\neq n$
. Let
 $S=\{c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }\mid c\equiv 1\;(m)\}$
. For
$S=\{c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }\mid c\equiv 1\;(m)\}$
. For
![]() $a,b\in {\mathcal{L}}$
, we claim that
$a,b\in {\mathcal{L}}$
, we claim that
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{b}$
are equivalent if and only if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{b}$
are equivalent if and only if
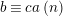 $b\equiv ca\;(n)$
for some
$b\equiv ca\;(n)$
for some
![]() $c\in S$
. Indeed, suppose that
$c\in S$
. Indeed, suppose that
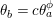 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{b}=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}$
for some
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{b}=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}}$
for some
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
and
![]() $c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
. By Lemma 5.4, either
$c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
. By Lemma 5.4, either
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}(x_{i}))=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x_{i})$
for
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}(x_{i}))=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x_{i})$
for
![]() $i=1,2$
, or
$i=1,2$
, or
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}(x_{i}))=-\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x_{i})$
for
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}(x_{i}))=-\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x_{i})$
for
![]() $i=1,2$
. By changing
$i=1,2$
. By changing
![]() $c$
to
$c$
to
![]() $-c$
in the latter case, we have
$-c$
in the latter case, we have
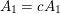 $A_{1}=cA_{1}$
and
$A_{1}=cA_{1}$
and
 $bA_{2}=caA_{2}$
, and the claim follows. Thus, the equivalence classes of BSK-maps are parametrized by the orbits of the action of
$bA_{2}=caA_{2}$
, and the claim follows. Thus, the equivalence classes of BSK-maps are parametrized by the orbits of the action of
![]() $S$
on
$S$
on
![]() ${\mathcal{L}}$
. Since this action is free, the number of orbits is
${\mathcal{L}}$
. Since this action is free, the number of orbits is
![]() $|{\mathcal{L}}|/|S|$
. Let
$|{\mathcal{L}}|/|S|$
. Let
 $B=A/C=t/kC$
and write
$B=A/C=t/kC$
and write
 $B=B_{1}B_{2}B_{3}$
, where for
$B=B_{1}B_{2}B_{3}$
, where for
 $i=1,2,3$
each prime dividing
$i=1,2,3$
each prime dividing
![]() $B_{i}$
divides
$B_{i}$
divides
![]() $A_{i}$
. By [Reference Bagiński, Carvacho, Gromadzki and Hidalgo2, Theorem 3.4] we have
$A_{i}$
. By [Reference Bagiński, Carvacho, Gromadzki and Hidalgo2, Theorem 3.4] we have
 $$\begin{eqnarray}|{\mathcal{L}}|=\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{1}B)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{1}B_{1})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B_{2})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B_{3})\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C).\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}|{\mathcal{L}}|=\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{1}B)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{1}B_{1})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B_{2})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B_{3})\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C).\end{eqnarray}$$
We also have
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle |S|=\frac{\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(N)}{\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(m)}=\frac{\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{1}B_{1})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{2}B_{2})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{3}B_{3})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(C)}{\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B_{1})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{2}B_{2})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{3}B_{3})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(C)}=\frac{\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{1}B_{1})}{\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B_{1})}\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle |{\mathcal{L}}|/|S|=\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B_{1})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B_{2})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B_{3})\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C).\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle |S|=\frac{\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(N)}{\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(m)}=\frac{\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{1}B_{1})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{2}B_{2})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{3}B_{3})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(C)}{\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B_{1})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{2}B_{2})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{3}B_{3})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(C)}=\frac{\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(A_{1}B_{1})}{\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B_{1})}\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle |{\mathcal{L}}|/|S|=\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B_{1})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B_{2})\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B_{3})\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)=\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C).\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
This completes the proof in the case
![]() $m\neq n$
.
$m\neq n$
.
Now suppose that
![]() $m=n$
. This common value is equal to
$m=n$
. This common value is equal to
![]() $N$
and we have
$N$
and we have
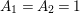 $A_{1}=A_{2}=1$
and
$A_{1}=A_{2}=1$
and
 $$\begin{eqnarray}{\mathcal{L}}=\{a\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }\mid 1+a~\text{has order}~l\}.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}{\mathcal{L}}=\{a\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }\mid 1+a~\text{has order}~l\}.\end{eqnarray}$$
Now
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}(x_{1}))=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x_{2})$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}(x_{1}))=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x_{2})$
and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}(x_{2}))=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x_{1})$
for
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}(x_{2}))=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x_{1})$
for
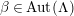 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
from Lemma 5.4. Consequently,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
from Lemma 5.4. Consequently,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{b}$
are equivalent if and only if either
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{b}$
are equivalent if and only if either
![]() $a=b$
or
$a=b$
or
![]() $ab=1$
. It follows that the number of equivalence classes of BSK-maps is
$ab=1$
. It follows that the number of equivalence classes of BSK-maps is
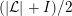 $(|{\mathcal{L}}|+I)/2$
, where
$(|{\mathcal{L}}|+I)/2$
, where
![]() $I$
is the number of
$I$
is the number of
![]() $a\in {\mathcal{L}}$
for which
$a\in {\mathcal{L}}$
for which
![]() $a^{2}=1$
. As in the case
$a^{2}=1$
. As in the case
![]() $m\neq n$
, we have
$m\neq n$
, we have
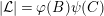 $|{\mathcal{L}}|=\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)$
, where
$|{\mathcal{L}}|=\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)$
, where
![]() $C$
is the biggest divisor of
$C$
is the biggest divisor of
![]() $l$
coprime with
$l$
coprime with
![]() $k$
, and
$k$
, and
 $B=l/C$
.
$B=l/C$
.
In order to compute
![]() $I$
, suppose that
$I$
, suppose that
![]() $a^{2}=1$
for some
$a^{2}=1$
for some
![]() $a\in {\mathcal{L}}$
. We have
$a\in {\mathcal{L}}$
. We have
 $N=kBC$
, and since
$N=kBC$
, and since
![]() $kB$
and
$kB$
and
![]() $C$
are coprime,
$C$
are coprime,
 $\mathbb{Z}_{N}\cong \mathbb{Z}_{kB}\oplus \mathbb{Z}_{C}$
. Under this isomorphism, we write
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}\cong \mathbb{Z}_{kB}\oplus \mathbb{Z}_{C}$
. Under this isomorphism, we write
 $a=(a_{1},a_{2})$
, where
$a=(a_{1},a_{2})$
, where
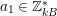 $a_{1}\in \mathbb{Z}_{kB}^{\ast }$
and
$a_{1}\in \mathbb{Z}_{kB}^{\ast }$
and
 $a_{2}\in \mathbb{Z}_{C}^{\ast }$
. We have
$a_{2}\in \mathbb{Z}_{C}^{\ast }$
. We have
 $a_{1}^{2}\equiv 1\;(kB)$
and
$a_{1}^{2}\equiv 1\;(kB)$
and
 $a_{2}^{2}\equiv 1\;(C)$
. Since
$a_{2}^{2}\equiv 1\;(C)$
. Since
![]() $1+a$
has order
$1+a$
has order
![]() $l$
, we have
$l$
, we have
 $1+a_{1}=ks$
for some
$1+a_{1}=ks$
for some
![]() $s\in \mathbb{Z}_{B}^{\ast }$
and
$s\in \mathbb{Z}_{B}^{\ast }$
and
 $1+a_{2}\in \mathbb{Z}_{C}^{\ast }$
.
$1+a_{2}\in \mathbb{Z}_{C}^{\ast }$
.
In suitable rings we have
 $$\begin{eqnarray}0=1-a_{i}^{2}=(1+a_{i})(1-a_{i}).\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}0=1-a_{i}^{2}=(1+a_{i})(1-a_{i}).\end{eqnarray}$$
Since
 $(1+a_{2})$
is invertible in
$(1+a_{2})$
is invertible in
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{C}$
,
$\mathbb{Z}_{C}$
,
![]() $a_{2}=1$
. In
$a_{2}=1$
. In
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{kB}$
we have
$\mathbb{Z}_{kB}$
we have
 $$\begin{eqnarray}0=(1+a_{1})(1-a_{1})=ks(2-ks).\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}0=(1+a_{1})(1-a_{1})=ks(2-ks).\end{eqnarray}$$
Since
![]() $s$
is invertible, it follows that
$s$
is invertible, it follows that
![]() $B$
divides
$B$
divides
![]() $2-ks$
, hence
$2-ks$
, hence
 $(B,k)\leqslant 2$
. Observe that every prime divisor of
$(B,k)\leqslant 2$
. Observe that every prime divisor of
![]() $B$
divides
$B$
divides
![]() $k$
, hence also
$k$
, hence also
![]() $(B,k)$
. It follows that
$(B,k)$
. It follows that
![]() $B$
is a power of 2. If
$B$
is a power of 2. If
![]() $B\leqslant 2$
then
$B\leqslant 2$
then
![]() $s=1$
and
$s=1$
and
 $a=(a_{1},a_{2})=(k-1,1)$
. If
$a=(a_{1},a_{2})=(k-1,1)$
. If
![]() $B=2^{z}$
for
$B=2^{z}$
for
![]() $z>1$
, then
$z>1$
, then
![]() $k/2$
is coprime to
$k/2$
is coprime to
![]() $B/2$
. Let
$B/2$
. Let
 $k^{\prime }\in \mathbb{Z}_{B/2}^{\ast }$
denote the inverse of
$k^{\prime }\in \mathbb{Z}_{B/2}^{\ast }$
denote the inverse of
![]() $k/2$
. Then, since
$k/2$
. Then, since
![]() $B/2$
divides
$B/2$
divides
 $1-sk/2$
, we have
$1-sk/2$
, we have
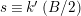 $s\equiv k^{\prime }\;(B/2)$
, and hence
$s\equiv k^{\prime }\;(B/2)$
, and hence
![]() $s=k^{\prime }$
or
$s=k^{\prime }$
or
 $s=k^{\prime }+B/2$
. Summarizing, we have
$s=k^{\prime }+B/2$
. Summarizing, we have
 $$\begin{eqnarray}I=\left\{\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}2\quad & \text{for}~B=2^{z},z>1,\\ 1\quad & \text{for}~B\leqslant 2,\\ 0\quad & \text{otherwise.}\end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}I=\left\{\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}2\quad & \text{for}~B=2^{z},z>1,\\ 1\quad & \text{for}~B\leqslant 2,\\ 0\quad & \text{otherwise.}\end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$
To finish the proof, observe that since
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)$
is odd, and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)$
is odd, and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B)$
is even if and only if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B)$
is even if and only if
![]() $B>2$
, we have
$B>2$
, we have
 $I\equiv \unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)~(\text{mod}~2)$
. It follows that
$I\equiv \unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(B)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)~(\text{mod}~2)$
. It follows that
 $(|{\mathcal{L}}|+I)/2=\lceil |{\mathcal{L}}|/2\rceil$
if
$(|{\mathcal{L}}|+I)/2=\lceil |{\mathcal{L}}|/2\rceil$
if
![]() $I\neq 2$
.◻
$I\neq 2$
.◻
6.8 Actions with a 1-punctured annulus as the quotient orbifold
This case concerns an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signature
 $$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[m];\{(\;),(\;)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[m];\{(\;),(\;)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
from Lemma 4.3 which has the presentation
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\langle x,e_{1},e_{2},c_{1},c_{2}\mid xe_{1}e_{2}=x^{m}=c_{1}^{2}=c_{2}^{2}=1,e_{1}c_{1}=c_{1}e_{1},e_{2}c_{2}=c_{2}e_{2}\rangle .\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\langle x,e_{1},e_{2},c_{1},c_{2}\mid xe_{1}e_{2}=x^{m}=c_{1}^{2}=c_{2}^{2}=1,e_{1}c_{1}=c_{1}e_{1},e_{2}c_{2}=c_{2}e_{2}\rangle .\end{eqnarray}$$
We have
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=(m-1)/m$
.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D707}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})=(m-1)/m$
.
Proof of Theorem 2.9.
Suppose that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is a BSK-map, such that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is a BSK-map, such that
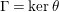 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is a nonorientable bordered surface group. Then, since
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is a nonorientable bordered surface group. Then, since
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
is bordered, some of the canonical reflections, say
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
is bordered, some of the canonical reflections, say
![]() $c_{1}$
belongs to
$c_{1}$
belongs to
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
. Furthermore, by (b) of Lemma 4.2, the order of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
. Furthermore, by (b) of Lemma 4.2, the order of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})$
is
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})$
is
![]() $N/k$
. But since
$N/k$
. But since
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
is nonorientable, it contains a nonorientable word, by (a) of Lemma 4.2, which is possible if and only if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
is nonorientable, it contains a nonorientable word, by (a) of Lemma 4.2, which is possible if and only if
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=N/2$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=N/2$
and
![]() $N/2$
is in the subgroup of
$N/2$
is in the subgroup of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
generated by
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
generated by
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})$
, and thus we obtain the condition
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})$
, and thus we obtain the condition
 $N=\text{lcm}(m,N/k)$
. Conversely, if the last condition is satisfied, then for
$N=\text{lcm}(m,N/k)$
. Conversely, if the last condition is satisfied, then for
 $a\in \mathbb{Z}_{N/k}^{\ast }$
we can define a BSK-map
$a\in \mathbb{Z}_{N/k}^{\ast }$
we can define a BSK-map
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x)=N/m,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e_{1})=ak,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e_{2})=-(N/m+ak),\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(c_{1})=0,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(c_{2})=N/2,\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(x)=N/m,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e_{1})=ak,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e_{2})=-(N/m+ak),\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(c_{1})=0,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(c_{2})=N/2,\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
and every BSK-map is equivalent to some
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
. Let
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
. Let
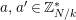 $a,a^{\prime }\in \mathbb{Z}_{N/k}^{\ast }$
and suppose that
$a,a^{\prime }\in \mathbb{Z}_{N/k}^{\ast }$
and suppose that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
for some
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
for some
![]() $c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
and some
$c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
and some
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
. By Lemma 5.3,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
. By Lemma 5.3,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
maps
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
maps
![]() $(x,e_{1})$
on
$(x,e_{1})$
on
 $\pm (N/m,ak)$
and so by replacing
$\pm (N/m,ak)$
and so by replacing
![]() $c$
by
$c$
by
![]() $-c$
if necessary in the latter case, we obtain that
$-c$
if necessary in the latter case, we obtain that
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(x)=cN/m,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(e_{1})=cak,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e_{2})=-c(N/m+ak),\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(c_{1})=0,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(c_{2})=N/2,\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(x)=cN/m,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}(e_{1})=cak,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(e_{2})=-c(N/m+ak),\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(c_{1})=0,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}(c_{2})=N/2,\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
which give
 $c\equiv 1\;(m)$
and
$c\equiv 1\;(m)$
and
 $a^{\prime }\equiv ca\;(N/k)$
. As in the proof of Theorem 2.6, we conclude that
$a^{\prime }\equiv ca\;(N/k)$
. As in the proof of Theorem 2.6, we conclude that
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}$
are equivalent if and only if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}$
are equivalent if and only if
 $a^{\prime }\equiv a\;(t)$
, and hence, the number of equivalence classes of such BSK-maps is
$a^{\prime }\equiv a\;(t)$
, and hence, the number of equivalence classes of such BSK-maps is
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)$
.◻
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)$
.◻
As we already mentioned in Section 2, the case of orientable
![]() $S$
is much more involved.
$S$
is much more involved.
Proof of Theorem 2.10.
Suppose that an action exists and let
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
be the corresponding BSK-map. Since
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
be the corresponding BSK-map. Since
![]() $S$
is bordered,
$S$
is bordered,
![]() $\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
contains at least one canonical reflection, and we can assume
$\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
contains at least one canonical reflection, and we can assume
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{1})=0$
. We consider two cases: (1)
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{1})=0$
. We consider two cases: (1)
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})\neq 0$
and (2)
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})\neq 0$
and (2)
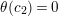 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=0$
.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=0$
.
Case 1.
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})\neq 0$
. By (b) of Lemma 4.2,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})\neq 0$
. By (b) of Lemma 4.2,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})$
has order
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})$
has order
![]() $N/k$
, in particular
$N/k$
, in particular
![]() $k|N$
. Since
$k|N$
. Since
![]() $S$
is orientable,
$S$
is orientable,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})$
generate the subgroup of index 2 of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})$
generate the subgroup of index 2 of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
, by (a) of Lemma 4.2. Hence
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
, by (a) of Lemma 4.2. Hence
 $N=2\text{lcm}(m,N/k)$
, and
$N=2\text{lcm}(m,N/k)$
, and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=N/2$
is odd. Conversely, if (1) is satisfied, then for each
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=N/2$
is odd. Conversely, if (1) is satisfied, then for each
 $a\in \mathbb{Z}_{N/k}^{\ast }$
we can define a BSK-map
$a\in \mathbb{Z}_{N/k}^{\ast }$
we can define a BSK-map
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{1}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
by
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{1}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
by
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{1}(x)=N/m,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{1}(e_{1})=ak,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{1}(e_{2})=-(N/m+ak),\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{1}(c_{1})=0,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{1}(c_{2})=N/2.\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{1}(x)=N/m,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{1}(e_{1})=ak,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{1}(e_{2})=-(N/m+ak),\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{1}(c_{1})=0,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{1}(c_{2})=N/2.\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
Case 2.
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=0$
. Let
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=0$
. Let
![]() $l_{i}$
denote the order of
$l_{i}$
denote the order of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{i})$
and set
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{i})$
and set
 $n_{i}=N/l_{i}$
for
$n_{i}=N/l_{i}$
for
![]() $i=1,2$
. Then, by (b) of Lemma 4.2 we have
$i=1,2$
. Then, by (b) of Lemma 4.2 we have
 $n_{1}+n_{2}=k$
. Now
$n_{1}+n_{2}=k$
. Now
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x)$
,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{1})$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{2})$
generate
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e_{2})$
generate
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
and hence the triple
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
and hence the triple
 $(l_{1},l_{2},m)$
satisfies the conditions of Lemma 3.3. Consider the Maclachlan decomposition of
$(l_{1},l_{2},m)$
satisfies the conditions of Lemma 3.3. Consider the Maclachlan decomposition of
 $(l_{1},l_{2},m)$
$(l_{1},l_{2},m)$
 $$\begin{eqnarray}l_{1}=AA_{2}A_{3},\qquad l_{2}=AA_{1}A_{3},\qquad m=AA_{1}A_{2}.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}l_{1}=AA_{2}A_{3},\qquad l_{2}=AA_{1}A_{3},\qquad m=AA_{1}A_{2}.\end{eqnarray}$$
We have
 $A_{1}=n_{1}=n$
,
$A_{1}=n_{1}=n$
,
 $A_{2}=n_{2}$
,
$A_{2}=n_{2}$
,
 $A_{3}=N/m$
and the conditions (a), (b), (c) follow from the properties of the Maclachlan decomposition. Conversely, if (2) is satisfied, then by Lemma 3.3,
$A_{3}=N/m$
and the conditions (a), (b), (c) follow from the properties of the Maclachlan decomposition. Conversely, if (2) is satisfied, then by Lemma 3.3,
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is generated by three elements
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is generated by three elements
![]() $a$
,
$a$
,
![]() $b$
and
$b$
and
![]() $c$
of orders
$c$
of orders
![]() $m$
,
$m$
,
![]() $l_{1}$
and
$l_{1}$
and
![]() $l_{2}$
, respectively such that
$l_{2}$
, respectively such that
 $a+b+c=0$
. We define
$a+b+c=0$
. We define
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
by
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
by
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(x)=a,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(e_{1})=b,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(e_{2})=c,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(c_{1})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(c_{2})=0.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(x)=a,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(e_{1})=b,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(e_{2})=c,\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(c_{1})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}(c_{2})=0.\end{eqnarray}$$
This completes the proof of assertion (i).
Now we shall find the number of conjugacy classes of actions. The proof of assertion (ii) is analogous to that of Theorem 2.9 and we omit it.
To prove (iii), consider the Maclachlan decomposition
 $(A,A_{1},A_{2},A_{3})$
of the triple
$(A,A_{1},A_{2},A_{3})$
of the triple
 $(N/n,N/(k-n),m)$
. We have
$(N/n,N/(k-n),m)$
. We have
![]() $A_{1}=n$
,
$A_{1}=n$
,
 $A_{2}=k-n$
,
$A_{2}=k-n$
,
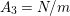 $A_{3}=N/m$
and
$A_{3}=N/m$
and
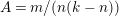 $A=m/(n(k-n))$
. Every BSK-map is equivalent to
$A=m/(n(k-n))$
. Every BSK-map is equivalent to
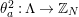 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{2}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
defined by
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{2}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
defined by
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{2}(e_{1})=A_{1},\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{2}(e_{2})=aA_{2},\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{2}(x)=-(A_{1}+aA_{2}),\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{2}(c_{1})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{2}(c_{2})=0\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{2}(e_{1})=A_{1},\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{2}(e_{2})=aA_{2},\qquad \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{2}(x)=-(A_{1}+aA_{2}),\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{2}(c_{1})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{2}(c_{2})=0\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
for some
![]() $a\in {\mathcal{L}}$
, where
$a\in {\mathcal{L}}$
, where
 $$\begin{eqnarray}{\mathcal{L}}=\{a\in \mathbb{Z}_{N/(k-n)}^{\ast }\mid A_{1}+aA_{2}~\text{has order}~m\}.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}{\mathcal{L}}=\{a\in \mathbb{Z}_{N/(k-n)}^{\ast }\mid A_{1}+aA_{2}~\text{has order}~m\}.\end{eqnarray}$$
It follows form Lemma 5.3, that for
 $a,a^{\prime }\in {\mathcal{L}}$
,
$a,a^{\prime }\in {\mathcal{L}}$
,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{2}$
is equivalent to
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a}^{2}$
is equivalent to
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}^{2}$
if and only if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{a^{\prime }}^{2}$
if and only if
![]() $a^{\prime }=ca$
for some
$a^{\prime }=ca$
for some
 $c\equiv 1\;(N/n)$
, or
$c\equiv 1\;(N/n)$
, or
![]() $aa^{\prime }=1$
, the latter being possible only for
$aa^{\prime }=1$
, the latter being possible only for
 $n=n-k=1$
. Now, the formulas for the number of equivalence classes of BSK-maps can be obtained by repeating the calculations from the proof of Theorem 2.8. The assertion (iv) is evident.◻
$n=n-k=1$
. Now, the formulas for the number of equivalence classes of BSK-maps can be obtained by repeating the calculations from the proof of Theorem 2.8. The assertion (iv) is evident.◻
Theorem 2.10 has some delicate subtlety which we illustrate with two remarks and two examples.
Remark 6.1. For some triples
 $(N,m,k)$
both conditions (1) and (2) are satisfied, as for instance in Example 6.3 below. In such a case,
$(N,m,k)$
both conditions (1) and (2) are satisfied, as for instance in Example 6.3 below. In such a case,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}$
are not equivalent. For suppose that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}$
are not equivalent. For suppose that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
for some
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
for some
![]() $c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
and some
$c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
and some
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
. By Lemma 5.3,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
. By Lemma 5.3,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
preserves
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
preserves
![]() $\{c_{1},c_{2}\}$
, hence
$\{c_{1},c_{2}\}$
, hence
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}(c_{i})=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}(c_{i})=0$
for
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}(c_{i})=c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{2}\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}(c_{i})=0$
for
![]() $i=1,2$
. This is a contradiction, because
$i=1,2$
. This is a contradiction, because
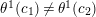 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}(c_{1})\neq \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}(c_{2})$
.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}(c_{1})\neq \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}^{1}(c_{2})$
.
Remark 6.2. Suppose that
 $N,m,k$
satisfy the condition (2), and let
$N,m,k$
satisfy the condition (2), and let
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{1}^{2}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{1}^{2}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{2}^{2}$
be BSK-maps, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{2}^{2}$
be BSK-maps, where
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{1}^{2}(e_{1})$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{1}^{2}(e_{1})$
,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{1}^{2}(e_{2})$
have orders
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{1}^{2}(e_{2})$
have orders
![]() $N/n_{1}$
,
$N/n_{1}$
,
![]() $N/n_{2}$
, where
$N/n_{2}$
, where
 $n_{1}+n_{2}=k$
and
$n_{1}+n_{2}=k$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{2}^{2}(e_{1})$
, and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{2}^{2}(e_{1})$
, and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{2}^{2}(e_{2})$
have orders
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{2}^{2}(e_{2})$
have orders
![]() $N/n_{1}^{\prime }$
,
$N/n_{1}^{\prime }$
,
![]() $N/n_{2}^{\prime }$
, where
$N/n_{2}^{\prime }$
, where
 $n_{1}^{\prime }+n_{2}^{\prime }=k$
. If
$n_{1}^{\prime }+n_{2}^{\prime }=k$
. If
 $\{n_{1},n_{2}\}\neq \{n_{1}^{\prime },n_{2}^{\prime }\}$
then
$\{n_{1},n_{2}\}\neq \{n_{1}^{\prime },n_{2}^{\prime }\}$
then
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{1}^{2}$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{1}^{2}$
and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{2}^{2}$
are not equivalent. This follows from Lemma 5.3, because for every
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{2}^{2}$
are not equivalent. This follows from Lemma 5.3, because for every
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{1}^{2}\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
maps
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{1}^{2}\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}$
maps
![]() $(e_{1},e_{2})$
on
$(e_{1},e_{2})$
on
 $\pm (\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{1}^{2}(e_{1}),\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{1}^{2}(e_{2}))$
.
$\pm (\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{1}^{2}(e_{1}),\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{1}^{2}(e_{2}))$
.
Example 6.3. Suppose
![]() $k=2$
,
$k=2$
,
![]() $2m\mid N$
and
$2m\mid N$
and
![]() $N/2$
is odd. Then both conditions (1) and (2) are satisfied (
$N/2$
is odd. Then both conditions (1) and (2) are satisfied (
![]() $n=1$
in (2)). The number of BSK-maps of type (1) is
$n=1$
in (2)). The number of BSK-maps of type (1) is
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(m)$
by the assertion (ii), and the number of BSK-maps of type (2) is
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(m)$
by the assertion (ii), and the number of BSK-maps of type (2) is
 $\lceil \unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(m/C)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)/2\rceil$
, where
$\lceil \unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(m/C)\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(C)/2\rceil$
, where
![]() $C$
is the biggest divisor of
$C$
is the biggest divisor of
![]() $m$
coprime to
$m$
coprime to
![]() $N/m$
, by the assertion (iii). By adding up these two numbers we obtain the total number of topological types of
$N/m$
, by the assertion (iii). By adding up these two numbers we obtain the total number of topological types of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
-action on
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
-action on
![]() $S$
, with the prescribed quotient orbifold. By the Hurwitz–Riemann formula, the genus of
$S$
, with the prescribed quotient orbifold. By the Hurwitz–Riemann formula, the genus of
![]() $S$
is
$S$
is
 $N(m-1)/2m$
.
$N(m-1)/2m$
.
Example 6.4. Consider
 $m=N=12$
and
$m=N=12$
and
![]() $k=7$
. Then (1) is not satisfied, but (2) is by two different pairs
$k=7$
. Then (1) is not satisfied, but (2) is by two different pairs
 $\{n,k-n\}$
, namely
$\{n,k-n\}$
, namely
![]() $\{1,6\}$
and
$\{1,6\}$
and
![]() $\{3,4\}$
. By the assertion (iii) of Proposition 2.10, for each of these pairs, the corresponding BSK-map is unique up to equivalence. Thus we have two different topological types of
$\{3,4\}$
. By the assertion (iii) of Proposition 2.10, for each of these pairs, the corresponding BSK-map is unique up to equivalence. Thus we have two different topological types of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{12}$
-action on
$\mathbb{Z}_{12}$
-action on
![]() $S$
, with the prescribed quotient orbifold. By the Hurwitz–Riemann formula, the genus of
$S$
, with the prescribed quotient orbifold. By the Hurwitz–Riemann formula, the genus of
![]() $S$
is 3.
$S$
is 3.
6.9 Actions with a 3-punctured disc as the quotient orbifold
This subsection concerns NEC-groups
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signatures
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signatures
 $$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[2,3,m];\{(\;)\})\quad \text{for}~m=3,4,5\qquad \text{and}\qquad (0;+;[2,2,m];\{(\;)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[2,3,m];\{(\;)\})\quad \text{for}~m=3,4,5\qquad \text{and}\qquad (0;+;[2,2,m];\{(\;)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
from Lemma 4.3 which have the presentation
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\langle x_{1},x_{2},x_{3},e,c\mid x_{1}^{2}=x_{2}^{n}=x_{3}^{m}=x_{1}x_{2}x_{3}e=c^{2}=1,ce=ec\rangle ,\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\langle x_{1},x_{2},x_{3},e,c\mid x_{1}^{2}=x_{2}^{n}=x_{3}^{m}=x_{1}x_{2}x_{3}e=c^{2}=1,ce=ec\rangle ,\end{eqnarray}$$
where
![]() $n=2$
or
$n=2$
or
![]() $n=3$
.
$n=3$
.
Proof of Theorem 2.11.
Suppose that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is a BSK-map, such that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is a BSK-map, such that
![]() $\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is a bordered surface group. Then
$\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is a bordered surface group. Then
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c)=0$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c)=0$
,
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{2})=N/2$
, and by multiplying
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{2})=N/2$
, and by multiplying
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
by an element of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
by an element of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
, we may assume
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
, we may assume
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{3})=N/m$
, and hence
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{3})=N/m$
, and hence
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=-N/m$
. Evidently, such BSK-map is unique up to equivalence. Since
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=-N/m$
. Evidently, such BSK-map is unique up to equivalence. Since
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is an epimorphism, we have
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is an epimorphism, we have
 $N=\text{lcm}(2,m)$
. By Lemma 4.2,
$N=\text{lcm}(2,m)$
. By Lemma 4.2,
![]() $S$
is orientable and has
$S$
is orientable and has
![]() $N/m$
boundary components. The genus of
$N/m$
boundary components. The genus of
![]() $S$
is uniquely determined by the Hurwitz–Riemann formula.◻
$S$
is uniquely determined by the Hurwitz–Riemann formula.◻
Proof of Theorem 2.12.
Here the cyclic group
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is generated by three elements of orders
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is generated by three elements of orders
![]() $2,3$
and
$2,3$
and
![]() $m$
and hence
$m$
and hence
 $N=\text{lcm}(2,3,m)$
. For any BSK-map
$N=\text{lcm}(2,3,m)$
. For any BSK-map
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we have
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we have
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c)=0$
, and it follows from Lemma 4.2, that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c)=0$
, and it follows from Lemma 4.2, that
![]() $S$
is orientable and its number of boundary components is
$S$
is orientable and its number of boundary components is
![]() $N/l$
, where
$N/l$
, where
![]() $l$
is the order of
$l$
is the order of
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=-(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{2})+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{3}))$
. We have
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=-(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{2})+\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{3}))$
. We have
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})=N/2$
, and by multiplying
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})=N/2$
, and by multiplying
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
by a suitable element of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
by a suitable element of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
we may assume
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
we may assume
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{2})=N/3$
.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{2})=N/3$
.
For
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signature
 $(0;+;[2,3,3];\{(\;)\})$
, any BSK-epimorphism
$(0;+;[2,3,3];\{(\;)\})$
, any BSK-epimorphism
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{6}$
is equivalent to one mapping
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{6}$
is equivalent to one mapping
 $(x_{1},x_{2},x_{3})$
either on
$(x_{1},x_{2},x_{3})$
either on
![]() $(3,2,2)$
or
$(3,2,2)$
or
![]() $(3,2,4)$
. In the former case we have
$(3,2,4)$
. In the former case we have
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=5$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=5$
and
![]() $S$
has
$S$
has
![]() $1$
boundary component and genus 3. In the later case we have
$1$
boundary component and genus 3. In the later case we have
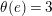 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=3$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=3$
and
![]() $S$
has 3 boundary component and genus 2.
$S$
has 3 boundary component and genus 2.
If
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature
 $(0;+;[2,3,4];\{(\;)\})$
or
$(0;+;[2,3,4];\{(\;)\})$
or
 $(0;+;[2,3,5];\{(\;)\})$
, then by Chinese reminder theorem, there is
$(0;+;[2,3,5];\{(\;)\})$
, then by Chinese reminder theorem, there is
![]() $c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
such that
$c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
such that
![]() $c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
maps
$c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
maps
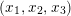 $(x_{1},x_{2},x_{3})$
on
$(x_{1},x_{2},x_{3})$
on
 $(N/2,N/3,N/m)$
. In both cases we have
$(N/2,N/3,N/m)$
. In both cases we have
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=-1$
, hence
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=-1$
, hence
![]() $S$
has one boundary component. The genus of
$S$
has one boundary component. The genus of
![]() $S$
is easily computed from the Hurwitz–Riemann formula.◻
$S$
is easily computed from the Hurwitz–Riemann formula.◻
6.10 Actions with a 2-punctured disc with two corners as the quotient orbifold
This case concerns NEC-groups
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signatures
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signatures
 $$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[3,m];\{(2,2)\})\quad \text{for}~m=3,4,5\qquad \text{and}\qquad (0;+;[2,m];\{(2,2)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[3,m];\{(2,2)\})\quad \text{for}~m=3,4,5\qquad \text{and}\qquad (0;+;[2,m];\{(2,2)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
from Lemma 4.3 which have the presentation
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \left\langle x_{1},x_{2},e,c_{0},c_{1},c_{2}\,|\right.\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \quad \left.x_{1}^{n}=x_{2}^{m}=c_{0}^{2}=c_{1}^{2}=c_{2}^{2}=(c_{0}c_{1})^{2}=(c_{1}c_{2})^{2}=x_{1}x_{2}e=1,c_{2}e=ec_{0}\right\rangle \!,\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle \left\langle x_{1},x_{2},e,c_{0},c_{1},c_{2}\,|\right.\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle \quad \left.x_{1}^{n}=x_{2}^{m}=c_{0}^{2}=c_{1}^{2}=c_{2}^{2}=(c_{0}c_{1})^{2}=(c_{1}c_{2})^{2}=x_{1}x_{2}e=1,c_{2}e=ec_{0}\right\rangle \!,\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
where
![]() $n=2$
or
$n=2$
or
![]() $n=3$
.
$n=3$
.
Proof of Theorem 2.13.
Suppose that
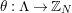 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is a BSK-map, such that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is a BSK-map, such that
![]() $\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is a bordered surface group. By Lemma 4.4, we may assume that
$\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is a bordered surface group. By Lemma 4.4, we may assume that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{0})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=N/2$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{0})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=N/2$
and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{1})=0$
. We have
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{1})=0$
. We have
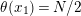 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})=N/2$
, and by multiplying
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})=N/2$
, and by multiplying
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
by an element of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
by an element of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
, we may assume
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
, we may assume
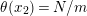 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{2})=N/m$
, and hence
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{2})=N/m$
, and hence
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=N/2-N/m$
. Evidently, such BSK-map is unique up to equivalence. Since
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=N/2-N/m$
. Evidently, such BSK-map is unique up to equivalence. Since
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is an epimorphism, we have
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is an epimorphism, we have
 $N=\text{lcm}(2,m)$
. By Lemma 4.2,
$N=\text{lcm}(2,m)$
. By Lemma 4.2,
![]() $S$
has
$S$
has
![]() $N/2$
boundary components and is nonorientable, as
$N/2$
boundary components and is nonorientable, as
![]() $x_{1}c_{0}$
is a nonorientable word in
$x_{1}c_{0}$
is a nonorientable word in
![]() $\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
. The genus of
$\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
. The genus of
![]() $S$
is uniquely determined by the Hurwitz–Riemann formula.◻
$S$
is uniquely determined by the Hurwitz–Riemann formula.◻
Proof of Theorem 2.14.
Suppose that
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is a BSK-map, such that
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is a BSK-map, such that
![]() $\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is a bordered surface group. As in the previous proof, we can assume
$\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is a bordered surface group. As in the previous proof, we can assume
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{0})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=N/2$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{0})=\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{2})=N/2$
,
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{1})=0$
and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{1})=0$
and
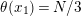 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})=N/3$
. Since
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})=N/3$
. Since
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is an epimorphism,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is an epimorphism,
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is generated by three elements of orders 2, 3 and
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
is generated by three elements of orders 2, 3 and
![]() $m$
and hence
$m$
and hence
 $N=\text{lcm}(2,3,m)$
. By (b) of Lemma 4.2,
$N=\text{lcm}(2,3,m)$
. By (b) of Lemma 4.2,
![]() $S$
has
$S$
has
![]() $N/2$
boundary components.
$N/2$
boundary components.
For
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the signature
 $(0;+;[3,3];\{(\;)\})$
, any BSK-epimorphism
$(0;+;[3,3];\{(\;)\})$
, any BSK-epimorphism
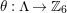 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{6}$
is equivalent to one mapping
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{6}$
is equivalent to one mapping
![]() $(x_{1},x_{2})$
either on
$(x_{1},x_{2})$
either on
![]() $(2,2)$
or
$(2,2)$
or
![]() $(2,4)$
. By [Reference Bujalance, Cirre, Conder and Szepietowski3, Lemma 4.6 and Proposition 4.14], for every
$(2,4)$
. By [Reference Bujalance, Cirre, Conder and Szepietowski3, Lemma 4.6 and Proposition 4.14], for every
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}\in \text{Aut}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC})$
,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}(e)$
is conjugate to
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}(e)$
is conjugate to
![]() $e$
or
$e$
or
![]() $e^{-1}$
, and hence the order of
$e^{-1}$
, and hence the order of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
is an equivalence invariant. It follows that the two maps described above are not equivalent. Indeed, for the first one
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)$
is an equivalence invariant. It follows that the two maps described above are not equivalent. Indeed, for the first one
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=2$
has order 3, whereas for the second one
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=2$
has order 3, whereas for the second one
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=0$
has order 1. In both cases
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(e)=0$
has order 1. In both cases
![]() $S$
is orientable, because
$S$
is orientable, because
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})$
,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{1})$
,
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{2})$
are even, whereas
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(x_{2})$
are even, whereas
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{0})=3$
is odd, and hence there is no nonorientable word in
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(c_{0})=3$
is odd, and hence there is no nonorientable word in
![]() $\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
.
$\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
.
If
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has signature
 $(0;+;[3,4];\{(\;)\})$
or
$(0;+;[3,4];\{(\;)\})$
or
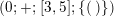 $(0;+;[3,5];\{(\;)\})$
, then by Chinese reminder theorem, there is
$(0;+;[3,5];\{(\;)\})$
, then by Chinese reminder theorem, there is
![]() $c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
such that
$c\in \mathbb{Z}_{N}^{\ast }$
such that
![]() $c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
maps
$c\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
maps
![]() $(x_{1},x_{2})$
on
$(x_{1},x_{2})$
on
 $(N/3,N/m)$
. It follows that
$(N/3,N/m)$
. It follows that
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is unique up to equivalence. For
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is unique up to equivalence. For
![]() $m=4$
we have a nonorientable word
$m=4$
we have a nonorientable word
![]() $x_{2}^{2}c_{0}$
in
$x_{2}^{2}c_{0}$
in
![]() $\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
, hence
$\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
, hence
![]() $S$
is nonorientable. For
$S$
is nonorientable. For
![]() $m=5$
there is no such word, hence
$m=5$
there is no such word, hence
![]() $S$
is orientable. The genus of
$S$
is orientable. The genus of
![]() $S$
is easily computed from the Hurwitz–Riemann formula.◻
$S$
is easily computed from the Hurwitz–Riemann formula.◻
7 On uniqueness of actions realizing the solutions of the minimum genus and maximum order problems
Throughout the rest of the paper the letter
![]() $p$
, used before to denote algebraic genus, will be used also to denote a prime integer, which will not lead to any ambiguity; for the genus we assume
$p$
, used before to denote algebraic genus, will be used also to denote a prime integer, which will not lead to any ambiguity; for the genus we assume
![]() $p\geqslant 2$
.
$p\geqslant 2$
.
7.1 The minimum genus and maximum order problems for finite groups acting on bordered surfaces
We start with the following easy proposition which justifies later definitions.
Proposition 7.1. Let
![]() $G$
be a finite group. Then there exists a bordered topological surface
$G$
be a finite group. Then there exists a bordered topological surface
![]() $S$
, which can be assumed to be orientable or not, such that
$S$
, which can be assumed to be orientable or not, such that
![]() $G$
acts on
$G$
acts on
![]() $S$
by homeomorphisms. Furthermore, if
$S$
by homeomorphisms. Furthermore, if
![]() $S$
is assumed to be orientable, then the action of
$S$
is assumed to be orientable, then the action of
![]() $G$
can be chosen to contain orientation-reversing elements if and only if
$G$
can be chosen to contain orientation-reversing elements if and only if
![]() $G$
has a subgroup
$G$
has a subgroup
![]() $G^{\prime }$
of index
$G^{\prime }$
of index
![]() $2$
.
$2$
.
Proof. Let
 $g_{1},\ldots ,g_{r}$
be a set of generators of
$g_{1},\ldots ,g_{r}$
be a set of generators of
![]() $G$
and
$G$
and
 $g_{r+1}=(g_{1}\ldots g_{r})^{-1}$
. Clearly we can assume that
$g_{r+1}=(g_{1}\ldots g_{r})^{-1}$
. Clearly we can assume that
![]() $r\geqslant 2$
. Let
$r\geqslant 2$
. Let
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
be an NEC-group with the signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
be an NEC-group with the signature
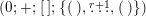 $(0;+;[\;];\{(\;),\stackrel{r+1}{\ldots },(\;)\})$
and let us define an epimorphism
$(0;+;[\;];\{(\;),\stackrel{r+1}{\ldots },(\;)\})$
and let us define an epimorphism
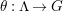 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow G$
mapping
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow G$
mapping
![]() $e_{i}$
to
$e_{i}$
to
![]() $g_{i}$
for
$g_{i}$
for
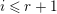 $i\leqslant r+1$
and all
$i\leqslant r+1$
and all
![]() $c_{i}$
to
$c_{i}$
to
![]() $1$
, the identity element of
$1$
, the identity element of
![]() $G$
. Then, for
$G$
. Then, for
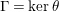 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
, we have
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
, we have
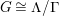 $G\cong \unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
acting as a group of conformal automorphisms on
$G\cong \unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
acting as a group of conformal automorphisms on
 $S={\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
, which has the conformal structure of orientable bordered Klein surface inherited from the hyperbolic plane
$S={\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
, which has the conformal structure of orientable bordered Klein surface inherited from the hyperbolic plane
![]() ${\mathcal{H}}$
. Now assume that
${\mathcal{H}}$
. Now assume that
![]() $G$
contains a subgroup
$G$
contains a subgroup
![]() $G^{\prime }$
of index 2. Assume that
$G^{\prime }$
of index 2. Assume that
![]() $G^{\prime }$
is generated as above, let
$G^{\prime }$
is generated as above, let
 $x\in G\setminus G^{\prime }$
, consider an NEC-group
$x\in G\setminus G^{\prime }$
, consider an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
 $(1;-;[\;];\{(\;),\stackrel{r+2}{\ldots },(\;)\})$
and define an epimorphism
$(1;-;[\;];\{(\;),\stackrel{r+2}{\ldots },(\;)\})$
and define an epimorphism
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow G$
mapping all reflections
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow G$
mapping all reflections
![]() $c_{i}$
to 1,
$c_{i}$
to 1,
![]() $e_{i}$
to
$e_{i}$
to
![]() $g_{i}$
for
$g_{i}$
for
 $1\leqslant i\leqslant r+1$
,
$1\leqslant i\leqslant r+1$
,
![]() $e_{r+2}$
to
$e_{r+2}$
to
![]() $x^{-2}$
, and
$x^{-2}$
, and
![]() $d_{1}$
to
$d_{1}$
to
![]() $x$
. Then for
$x$
. Then for
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
, we have
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
, we have
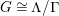 $G\cong \unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
acting as a group of conformal or anticonformal automorphisms on
$G\cong \unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
acting as a group of conformal or anticonformal automorphisms on
 $S={\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
, where
$S={\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
, where
![]() $x$
reverses orientation. If we need the action on a nonorientable surface, then it is sufficient to take an NEC-group
$x$
reverses orientation. If we need the action on a nonorientable surface, then it is sufficient to take an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
 $(1;-;[\;];\{(\;),\stackrel{r+1}{\ldots },(\;)\})$
and define
$(1;-;[\;];\{(\;),\stackrel{r+1}{\ldots },(\;)\})$
and define
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
on
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
on
![]() $e_{i},c_{i}$
as above and
$e_{i},c_{i}$
as above and
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d_{1})=1$
, in virtue of (a) of Lemma 4.2.◻
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d_{1})=1$
, in virtue of (a) of Lemma 4.2.◻
So, let
![]() ${\mathcal{K}}_{+}(N)$
(resp.
${\mathcal{K}}_{+}(N)$
(resp.
![]() ${\mathcal{K}}_{-}(N)$
) be the family of orientable (resp. nonorientable) bordered topological surfaces, admitting a self-homeomorphism of order
${\mathcal{K}}_{-}(N)$
) be the family of orientable (resp. nonorientable) bordered topological surfaces, admitting a self-homeomorphism of order
![]() $N$
. Denote by
$N$
. Denote by
 $p=p(S)$
the algebraic genus of a bordered surface
$p=p(S)$
the algebraic genus of a bordered surface
![]() $S$
and recall that it is the rank of the fundamental group of
$S$
and recall that it is the rank of the fundamental group of
![]() $S$
equal to
$S$
equal to
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g+k-1$
, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}g+k-1$
, where
![]() $g$
is the topological genus of
$g$
is the topological genus of
![]() $S$
,
$S$
,
![]() $k$
is the number of its boundary components and
$k$
is the number of its boundary components and
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}=2$
or 1 if
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D700}=2$
or 1 if
![]() $S$
is orientable or not. By
$S$
is orientable or not. By
![]() $S_{p}^{\pm }$
will be denoted a bordered surface of algebraic genus
$S_{p}^{\pm }$
will be denoted a bordered surface of algebraic genus
![]() $p$
, orientable if the sign is
$p$
, orientable if the sign is
![]() $+$
and nonorientable otherwise, and similar meaning will have
$+$
and nonorientable otherwise, and similar meaning will have
![]() $S_{g,k}^{\pm }$
.
$S_{g,k}^{\pm }$
.
Denote by
![]() $\text{H}_{\text{p}}(S)$
the set of all periodic self-homeomorphisms of
$\text{H}_{\text{p}}(S)$
the set of all periodic self-homeomorphisms of
![]() $S$
and consider two of its subsets
$S$
and consider two of its subsets
![]() $\text{H}_{\text{p}}^{+}(S)$
and
$\text{H}_{\text{p}}^{+}(S)$
and
![]() $\text{H}_{\text{p}}^{-}(S)$
, consisting of respectively orientation-preserving and orientation-reversing self-homeomorphisms when
$\text{H}_{\text{p}}^{-}(S)$
, consisting of respectively orientation-preserving and orientation-reversing self-homeomorphisms when
![]() $S$
is orientable. Finally let
$S$
is orientable. Finally let
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle {\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{+}(N)=\{S\in {\mathcal{K}}_{+}(N)\mid \exists \,\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}\in \text{H}_{\text{p}}^{+}(S)~\text{such that}~\#(\unicode[STIX]{x1D711})=N\},\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle {\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{-}(N)=\{S\in {\mathcal{K}}_{+}(N)\mid \exists \,\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}~\text{of}~\text{H}_{\text{p}}^{-}(S)~\text{such that}~\#(\unicode[STIX]{x1D711})=N\},\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle {\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{+}(N)=\{S\in {\mathcal{K}}_{+}(N)\mid \exists \,\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}\in \text{H}_{\text{p}}^{+}(S)~\text{such that}~\#(\unicode[STIX]{x1D711})=N\},\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle {\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{-}(N)=\{S\in {\mathcal{K}}_{+}(N)\mid \exists \,\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}~\text{of}~\text{H}_{\text{p}}^{-}(S)~\text{such that}~\#(\unicode[STIX]{x1D711})=N\},\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
where the operator
![]() $\#$
stands for the order. With these notations we define:
$\#$
stands for the order. With these notations we define:
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle p_{+}(N)=\min \{p(S)\mid S\in {\mathcal{K}}_{+}(N)\},\qquad p_{-}(N)=\min \{p(S)\mid S\in {\mathcal{K}}_{-}(N)\} & & \displaystyle \nonumber\\ \displaystyle p_{+}^{+}(N)=\min \{p(S)\mid S\in {\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{+}(N)\},\qquad p_{+}^{-}(N)=\min \{p(S)\mid S\in {\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{-}(N)\} & & \displaystyle \nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle p_{+}(N)=\min \{p(S)\mid S\in {\mathcal{K}}_{+}(N)\},\qquad p_{-}(N)=\min \{p(S)\mid S\in {\mathcal{K}}_{-}(N)\} & & \displaystyle \nonumber\\ \displaystyle p_{+}^{+}(N)=\min \{p(S)\mid S\in {\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{+}(N)\},\qquad p_{+}^{-}(N)=\min \{p(S)\mid S\in {\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{-}(N)\} & & \displaystyle \nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
and
 $$\begin{eqnarray}p(N)=\min \{p_{+}(N),p_{-}(N)\}.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}p(N)=\min \{p_{+}(N),p_{-}(N)\}.\end{eqnarray}$$
The calculation of the above five values is known as the minimal genus problem. A bordered surface
![]() $S$
is called
$S$
is called
![]() $N$
-minimal if
$N$
-minimal if
![]() $p(S)$
attains
$p(S)$
attains
![]() $p(N)$
,
$p(N)$
,
![]() $p_{\pm }(N)$
or
$p_{\pm }(N)$
or
![]() $p_{+}^{\pm }(N)$
.
$p_{+}^{\pm }(N)$
.
Another problem of a similar type is the maximum order problem which consists in finding, for a given
![]() $p$
, the maximal order of a finite action on a bordered topological surface of algebraic genus
$p$
, the maximal order of a finite action on a bordered topological surface of algebraic genus
![]() $p$
. For
$p$
. For
 $G=\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we refine this problem by considering
$G=\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
we refine this problem by considering
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle N_{+}^{+}(p)=\max \{N\mid S_{p}^{+}\in {\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{+}(N)\},\qquad N_{+}^{-}(p)=\max \{N\mid S_{p}^{-}\in {\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{-}(N)\}\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle N_{+}(p)=\max \{N_{+}^{+}(p),N_{+}^{-}(p)\},\qquad N_{-}(p)=\max \{N\mid S_{p}^{-}\in {\mathcal{K}}_{-}(N)\}\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle N_{+}^{+}(p)=\max \{N\mid S_{p}^{+}\in {\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{+}(N)\},\qquad N_{+}^{-}(p)=\max \{N\mid S_{p}^{-}\in {\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{-}(N)\}\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle N_{+}(p)=\max \{N_{+}^{+}(p),N_{+}^{-}(p)\},\qquad N_{-}(p)=\max \{N\mid S_{p}^{-}\in {\mathcal{K}}_{-}(N)\}\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
and
 $$\begin{eqnarray}N(p)=\max \{N_{+}(p),N_{-}(p)\}.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}N(p)=\max \{N_{+}(p),N_{-}(p)\}.\end{eqnarray}$$
These problems, of minimal genus and maximal order, were solved in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4], and here we consider the question of uniqueness of topological type of self-homeomorphisms of maximal order and self-homeomorphisms acting on surfaces of minimal genus.
7.2 On topological type of cyclic actions of a given nonprime order on bordered orientable surfaces of minimal genus
Theorem 7.2. [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4, Theorem 3.2.5]
Let
![]() $N$
be a nonprime odd integer and let
$N$
be a nonprime odd integer and let
![]() $p$
be the smallest prime dividing
$p$
be the smallest prime dividing
![]() $N$
. Then
$N$
. Then
 $$\begin{eqnarray}p_{+}^{+}(N)=p_{+}(N)=\left\{\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}(p-1){\displaystyle \frac{N}{p}}\quad & \text{if}~p^{2}\mid N,\\ (p-1){\displaystyle \frac{N-p}{p}}\quad & \text{if}~p^{2}\not |\;N,\end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}p_{+}^{+}(N)=p_{+}(N)=\left\{\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}(p-1){\displaystyle \frac{N}{p}}\quad & \text{if}~p^{2}\mid N,\\ (p-1){\displaystyle \frac{N-p}{p}}\quad & \text{if}~p^{2}\not |\;N,\end{array}\right.\end{eqnarray}$$
and the corresponding
![]() $N$
-minimal surface has
$N$
-minimal surface has
![]() $1$
boundary component.
$1$
boundary component.
Corollary 7.3. The action realizing
![]() $p_{+}^{+}(N)$
and
$p_{+}^{+}(N)$
and
![]() $p_{+}(N)$
given in Theorem 7.2 is unique up to topological conjugation if
$p_{+}(N)$
given in Theorem 7.2 is unique up to topological conjugation if
![]() $p^{2}$
does not divide
$p^{2}$
does not divide
![]() $N$
and there are
$N$
and there are
![]() $p-1$
classes of such action in the other case.
$p-1$
classes of such action in the other case.
Proof. In the proof of Theorem 7.2 given in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4] it is shown that the minimum genus is realized just for an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
having signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
having signature
 $$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[p,q];\{(\;)\}),\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[p,q];\{(\;)\}),\end{eqnarray}$$
where
![]() $q=N$
if
$q=N$
if
![]() $p^{2}\mid N$
, and otherwise
$p^{2}\mid N$
, and otherwise
 $q=N/p$
. We have
$q=N/p$
. We have
![]() $k=1$
, and
$k=1$
, and
 $t=(p,q)$
is equal to
$t=(p,q)$
is equal to
![]() $p$
and 1 respectively. By Theorem 2.8, there are
$p$
and 1 respectively. By Theorem 2.8, there are
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)$
topological types of action corresponding to this signature.◻
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D711}(t)$
topological types of action corresponding to this signature.◻
Theorem 7.4. [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4, Theorem 3.2.6]
Let
![]() $N\neq 2$
be an even integer not divisible by
$N\neq 2$
be an even integer not divisible by
![]() $4$
. Then
$4$
. Then
 $p_{+}^{+}(N)=p_{+}^{-}(N)=N/2-1$
. Moreover any
$p_{+}^{+}(N)=p_{+}^{-}(N)=N/2-1$
. Moreover any
![]() $N$
-minimal surface from
$N$
-minimal surface from
![]() ${\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{+}(N)$
has one boundary component, whilst any such surface from
${\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{+}(N)$
has one boundary component, whilst any such surface from
![]() ${\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{-}(N)$
has
${\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{-}(N)$
has
![]() $N/2$
boundary components.
$N/2$
boundary components.
Corollary 7.5. The actions realizing
![]() $p_{+}^{+}(N)$
and
$p_{+}^{+}(N)$
and
![]() $p_{+}^{-}(N)$
given in Theorem 7.4 are unique up to topological conjugation.
$p_{+}^{-}(N)$
given in Theorem 7.4 are unique up to topological conjugation.
Proof. In the proof of Theorem 7.4 given in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4] it is shown that
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
determining the minimal genera must have signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
determining the minimal genera must have signature
 $(0;+;[2,N/2];\{(\;)\})$
in the case of
$(0;+;[2,N/2];\{(\;)\})$
in the case of
![]() $p_{+}^{+}(N)$
and
$p_{+}^{+}(N)$
and
 $(0;+;[N/2];\{(2,2)\})$
in the case of
$(0;+;[N/2];\{(2,2)\})$
in the case of
![]() $p_{+}^{-}(N)$
. In the first case there is a unique class of such action by Theorem 2.8. In the second case the action is unique by Theorem 2.4.◻
$p_{+}^{-}(N)$
. In the first case there is a unique class of such action by Theorem 2.8. In the second case the action is unique by Theorem 2.4.◻
Theorem 7.6. [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4, Theorem 3.2.7]
Let
![]() $4$
divide
$4$
divide
![]() $N$
. Then
$N$
. Then
 $p_{+}^{+}(N)=N/2,p_{+}^{-}(N)=N/2+1$
. Moreover any
$p_{+}^{+}(N)=N/2,p_{+}^{-}(N)=N/2+1$
. Moreover any
![]() $N$
-minimal surface from
$N$
-minimal surface from
![]() ${\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{+}(N)$
has one boundary component, whilst any such surface from
${\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{+}(N)$
has one boundary component, whilst any such surface from
![]() ${\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{-}(N)$
has
${\mathcal{K}}_{+}^{-}(N)$
has
![]() $2$
boundary components if
$2$
boundary components if
![]() $8$
divides
$8$
divides
![]() $N$
, and otherwise
$N$
, and otherwise
![]() $4$
boundary components.
$4$
boundary components.
Corollary 7.7. The actions realizing
![]() $p_{+}^{+}(N)$
and
$p_{+}^{+}(N)$
and
![]() $p_{+}^{-}(N)$
given in Theorem 7.6 are unique up to topological conjugation.
$p_{+}^{-}(N)$
given in Theorem 7.6 are unique up to topological conjugation.
Proof. Also here it was shown in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4] that the action realizing
![]() $p_{+}^{+}(N)$
is given just by an NEC-group
$p_{+}^{+}(N)$
is given just by an NEC-group
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signature
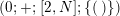 $(0;+;[2,N];\{(\;)\})$
and so the action is unique by Theorem 2.8. In turn the signature
$(0;+;[2,N];\{(\;)\})$
and so the action is unique by Theorem 2.8. In turn the signature
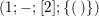 $(1;-;[2];\{(\;)\})$
is the unique one realizing
$(1;-;[2];\{(\;)\})$
is the unique one realizing
![]() $p_{+}^{-}(N)$
and so this action is unique by Theorem 2.6.◻
$p_{+}^{-}(N)$
and so this action is unique by Theorem 2.6.◻
7.3 On topological type of cyclic actions of a given nonprime order on bordered nonorientable surfaces of minimal genus
Theorem 7.8. [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4, Theorem 3.2.8]
Let
![]() $N$
be a nonprime odd integer and let
$N$
be a nonprime odd integer and let
![]() $p$
be the smallest prime dividing
$p$
be the smallest prime dividing
![]() $N$
. Then
$N$
. Then
 $p_{-}(N)=(p-1)N/p+1$
and the corresponding
$p_{-}(N)=(p-1)N/p+1$
and the corresponding
![]() $N$
-minimal surface has
$N$
-minimal surface has
![]() $1$
boundary component if
$1$
boundary component if
![]() $p^{2}$
divides
$p^{2}$
divides
![]() $N$
, and
$N$
, and
![]() $1$
or
$1$
or
![]() $p$
boundary components if
$p$
boundary components if
![]() $p^{2}$
does not divide
$p^{2}$
does not divide
![]() $N$
and both of these cases can actually occur.
$N$
and both of these cases can actually occur.
Corollary 7.9. The actions realizing
![]() $p_{-}(N)$
given in Theorem 7.8 are unique up to topological conjugation if
$p_{-}(N)$
given in Theorem 7.8 are unique up to topological conjugation if
![]() $k=p$
and there are
$k=p$
and there are
 $(p-1)/2$
types of action for
$(p-1)/2$
types of action for
![]() $k=1$
.
$k=1$
.
Proof. In the proof of Theorem 7.10 given in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4] it is shown that
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
realizing the minimum genus must have signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
realizing the minimum genus must have signature
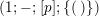 $(1;-;[p];\{(\;)\})$
. So the corollary follows from Theorem 2.7.◻
$(1;-;[p];\{(\;)\})$
. So the corollary follows from Theorem 2.7.◻
Theorem 7.10. [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4, Theorem 3.2.9]
Let
![]() $N$
be even and
$N$
be even and
![]() $N\neq 2$
. Then
$N\neq 2$
. Then
 $p_{-}(N)=N/2$
and any
$p_{-}(N)=N/2$
and any
![]() $N$
-minimal surface from
$N$
-minimal surface from
![]() ${\mathcal{K}}_{-}(N)$
is a projective plane with
${\mathcal{K}}_{-}(N)$
is a projective plane with
![]() $N/2$
boundary components.
$N/2$
boundary components.
Corollary 7.11. The actions realizing
![]() $p_{-}(N)$
given in Theorem 7.10 is unique up to topological conjugation.
$p_{-}(N)$
given in Theorem 7.10 is unique up to topological conjugation.
Proof. Also here it was shown in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4], that
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
must be an NEC-group with the signature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
must be an NEC-group with the signature
 $(0;+;[N];\{(2,2)\})$
and so our corollary follows from Theorem 2.4.◻
$(0;+;[N];\{(2,2)\})$
and so our corollary follows from Theorem 2.4.◻
7.4 On topological type of actions of a prime order
 $N$
on surfaces of minimal genus
$N$
on surfaces of minimal genus
Observe that all results from the previous section concerning minimal genus were formulated and proved for
![]() $N$
being nonprime. For prime
$N$
being nonprime. For prime
![]() $N$
, more general results concerning the minimum genus
$N$
, more general results concerning the minimum genus
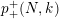 $p_{+}^{+}(N,k)$
,
$p_{+}^{+}(N,k)$
,
 $p_{+}^{-}(N,k)$
and
$p_{+}^{-}(N,k)$
and
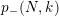 $p_{-}(N,k)$
of surfaces with specified number
$p_{-}(N,k)$
of surfaces with specified number
![]() $k$
of boundary components are given in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4]. These functions are periodic with respect to
$k$
of boundary components are given in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4]. These functions are periodic with respect to
![]() $k$
, and so their knowledge obviously gives an effective way to solve the minimum genus problem by simply taking the minimum of
$k$
, and so their knowledge obviously gives an effective way to solve the minimum genus problem by simply taking the minimum of
 $p_{\ast }^{\ast }(N,k)$
for varying
$p_{\ast }^{\ast }(N,k)$
for varying
![]() $k$
, and in this way the problem was solved in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4]. One can however calculate the minimum genus for a given prime
$k$
, and in this way the problem was solved in [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4]. One can however calculate the minimum genus for a given prime
![]() $N$
directly or using results of the previous; which is more relevant for our purpose which is also topological classification of actions realizing
$N$
directly or using results of the previous; which is more relevant for our purpose which is also topological classification of actions realizing
![]() $p_{\ast }^{\ast }$
.
$p_{\ast }^{\ast }$
.
Proposition 7.12. We have
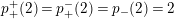 $p_{+}^{+}(2)=p_{+}^{-}(2)=p_{-}(2)=2$
. The topological type of a
$p_{+}^{+}(2)=p_{+}^{-}(2)=p_{-}(2)=2$
. The topological type of a
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{2}$
-action on a bordered surface of algebraic genus
$\mathbb{Z}_{2}$
-action on a bordered surface of algebraic genus
![]() $2$
is determined by the surface and the quotient orbifold. Up to topological conjugacy there are:
$2$
is determined by the surface and the quotient orbifold. Up to topological conjugacy there are:
∙
 $2$
actions realizing
$2$
actions realizing
 $p_{+}^{+}(2)$
:
$p_{+}^{+}(2)$
:
 $1$
on
$1$
on
 $1$
-holed torus and
$1$
-holed torus and
 $1$
on
$1$
on
 $3$
-holed sphere;
$3$
-holed sphere;∙
 $4$
actions realizing
$4$
actions realizing
 $p_{+}^{-}(2)$
:
$p_{+}^{-}(2)$
:
 $2$
on
$2$
on
 $1$
-holed torus and
$1$
-holed torus and
 $2$
on
$2$
on
 $3$
-holed sphere;
$3$
-holed sphere;∙
 $8$
actions realizing
$8$
actions realizing
 $p_{-}(2)$
:
$p_{-}(2)$
:
 $3$
on
$3$
on
 $2$
-holed projective plane and
$2$
-holed projective plane and
 $5$
on
$5$
on
 $1$
-holed Klein bottle.
$1$
-holed Klein bottle.
Proof. We shall see that
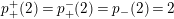 $p_{+}^{+}(2)=p_{+}^{-}(2)=p_{-}(2)=2$
– the smallest admissible genus. Since in such case
$p_{+}^{+}(2)=p_{+}^{-}(2)=p_{-}(2)=2$
– the smallest admissible genus. Since in such case
 $N=2>1=p-1$
all the possible involved signatures appear in Lemma 4.3. We are interested with the ones with the normalized area
$N=2>1=p-1$
all the possible involved signatures appear in Lemma 4.3. We are interested with the ones with the normalized area
![]() $1/2$
and we list all of them here for the reader’s convenience:
$1/2$
and we list all of them here for the reader’s convenience:
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}(1)~(0;+;[\;];\{(2,2,2,2,2,2)\}),\qquad & (2)~(0;+;[\;];\{(\;),(2,2)\}),\\ (3)~(1;-;[\;];\{(2,2)\}),\qquad & (5)~(0;+;[2];\{(2,2,2,2)\}),\\ (6)~(1;-;[2];\{(\;)\})\qquad & (8)~(0;+;[2];\{(\;),(\;)\}),\\ (9b)~(0;+;[2,2,2];\{(\;)\})\qquad & (10b)~(0;+;[2,2];\{(2,2)\}).\end{array}\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}(1)~(0;+;[\;];\{(2,2,2,2,2,2)\}),\qquad & (2)~(0;+;[\;];\{(\;),(2,2)\}),\\ (3)~(1;-;[\;];\{(2,2)\}),\qquad & (5)~(0;+;[2];\{(2,2,2,2)\}),\\ (6)~(1;-;[2];\{(\;)\})\qquad & (8)~(0;+;[2];\{(\;),(\;)\}),\\ (9b)~(0;+;[2,2,2];\{(\;)\})\qquad & (10b)~(0;+;[2,2];\{(2,2)\}).\end{array}\end{eqnarray}$$
Now the signature (1) give rise to a reflection of the 3-holed sphere with the disk with 6 corner points as the orbit space which is unique up to topological conjugacy by Theorem 2.1. By Theorem 2.2 the signature (2) provides four actions of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{2}$
: on 1-holed Klein bottle, 2-holed projective plane and orientation-reversing reflections of 1-holed torus and 3-holed sphere. By Theorem 2.3 the signature (3) provides two actions of
$\mathbb{Z}_{2}$
: on 1-holed Klein bottle, 2-holed projective plane and orientation-reversing reflections of 1-holed torus and 3-holed sphere. By Theorem 2.3 the signature (3) provides two actions of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{2}$
: on 1-holed Klein bottle and an orientation-reversing action on 1-holed torus. By Theorem 2.5 the signature (5) gives rise to one action on 2-holed projective plane. By Theorem 2.6 the signature (6) does not provide any action on bordered orientable surface, whereas by Theorem 2.7 it gives rise to one action on 1-holed Klein bottle. By Theorem 2.9, the signature (8) gives rise to two actions on 1-holed Klein bottle and 2-holed projective plane, whereas by Theorem 2.10 it gives rise to an orientation-preserving action on 3-holed sphere. By Theorem 2.11, the signature (9b) gives rise to the orientation-preserving action on 1-holed torus. Finally the signature (10b) gives rise to the unique action on 1-holed Klein bottle by Theorem 2.13. Observe also that any two actions corresponding to different signatures are not topologically conjugate. ◻
$\mathbb{Z}_{2}$
: on 1-holed Klein bottle and an orientation-reversing action on 1-holed torus. By Theorem 2.5 the signature (5) gives rise to one action on 2-holed projective plane. By Theorem 2.6 the signature (6) does not provide any action on bordered orientable surface, whereas by Theorem 2.7 it gives rise to one action on 1-holed Klein bottle. By Theorem 2.9, the signature (8) gives rise to two actions on 1-holed Klein bottle and 2-holed projective plane, whereas by Theorem 2.10 it gives rise to an orientation-preserving action on 3-holed sphere. By Theorem 2.11, the signature (9b) gives rise to the orientation-preserving action on 1-holed torus. Finally the signature (10b) gives rise to the unique action on 1-holed Klein bottle by Theorem 2.13. Observe also that any two actions corresponding to different signatures are not topologically conjugate. ◻
Observe now that for odd
![]() $N$
, there are no surfaces admitting orientation-reversing self-homeomorphisms of order
$N$
, there are no surfaces admitting orientation-reversing self-homeomorphisms of order
![]() $N$
, and so we have to look only for
$N$
, and so we have to look only for
![]() $p_{-}(N)$
and
$p_{-}(N)$
and
![]() $p_{+}^{+}(N)$
, and classify topologically all actions realizing them.
$p_{+}^{+}(N)$
, and classify topologically all actions realizing them.
Proposition 7.13. Let
![]() $N$
be an odd prime. Then
$N$
be an odd prime. Then
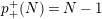 $p_{+}^{+}(N)=N-1$
, and
$p_{+}^{+}(N)=N-1$
, and
 $p_{-}(N)=N$
. Furthermore, in both cases the corresponding surface has
$p_{-}(N)=N$
. Furthermore, in both cases the corresponding surface has
![]() $k=N$
or
$k=N$
or
![]() $k=1$
boundary components. Up to topological conjugation, there are:
$k=1$
boundary components. Up to topological conjugation, there are:
∙
 $2$
actions of order
$2$
actions of order
 $N$
on the
$N$
on the
 $N$
-holed nonorientable surface of algebraic genus
$N$
-holed nonorientable surface of algebraic genus
 $p_{-}(N)$
. The orbit spaces of these actions are
$p_{-}(N)$
. The orbit spaces of these actions are
 $1$
-punctured Möbius band and
$1$
-punctured Möbius band and
 $1$
-punctured annulus;
$1$
-punctured annulus;∙
 $3(N-1)/2$
actions of order
$3(N-1)/2$
actions of order
 $N$
on the
$N$
on the
 $1$
-holed nonorientable surface of algebraic genus
$1$
-holed nonorientable surface of algebraic genus
 $p_{-}(N)$
;
$p_{-}(N)$
;
 $N-1$
with a
$N-1$
with a
 $1$
-punctured annulus and
$1$
-punctured annulus and
 $(N-1)/2$
with a
$(N-1)/2$
with a
 $1$
-punctured Möbius band as orbit spaces of the actions;
$1$
-punctured Möbius band as orbit spaces of the actions;∙ unique action of order
 $N$
on the
$N$
on the
 $N$
-holed orientable surface of algebraic genus
$N$
-holed orientable surface of algebraic genus
 $p_{+}^{+}(N)$
;
$p_{+}^{+}(N)$
;∙
 $(N-1)/2$
actions of order
$(N-1)/2$
actions of order
 $N$
on the
$N$
on the
 $1$
-holed orientable surface of algebraic genus
$1$
-holed orientable surface of algebraic genus
 $p_{+}^{+}(N)$
.
$p_{+}^{+}(N)$
.
Proof. Let
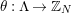 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
be a BSK-epimorphism defining an action of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}_{N}$
be a BSK-epimorphism defining an action of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
on a bordered surface. Then
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
on a bordered surface. Then
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has an empty period cycle in order to produce holes in the corresponding surface
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
has an empty period cycle in order to produce holes in the corresponding surface
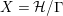 $X={\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
for
$X={\mathcal{H}}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$
for
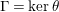 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
. Now all periods in
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}=\ker \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
. Now all periods in
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
, if exists, are equal to
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
, if exists, are equal to
![]() $N$
and so
$N$
and so
 $(0;+;[N,N];\{(\;)\})$
is the signature of
$(0;+;[N,N];\{(\;)\})$
is the signature of
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the minimal possible area here.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with the minimal possible area here.
On the other hand Theorem 2.8 asserts that such an epimorphism indeed exist, and the corresponding surface is orientable and has
![]() $N$
or
$N$
or
![]() $1$
boundary components. Furthermore, up to topological equivalence, there is unique such action or
$1$
boundary components. Furthermore, up to topological equivalence, there is unique such action or
 $\lceil \unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(N)/2\rceil =(N-1)/2$
actions respectively. This completes the part of the proof concerning
$\lceil \unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(N)/2\rceil =(N-1)/2$
actions respectively. This completes the part of the proof concerning
![]() $p_{+}^{+}(N)$
and also shows that for the study of
$p_{+}^{+}(N)$
and also shows that for the study of
![]() $p_{-}(N)$
and its attainments, we need to consider NEC-groups with bigger area.
$p_{-}(N)$
and its attainments, we need to consider NEC-groups with bigger area.
The second smallest area in this case have NEC-groups
![]() $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signatures
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$
with signatures
 $$\begin{eqnarray}(1;-;[N];\{(\;)\})\qquad \text{and}\qquad (0;+;[N];\{(\;),(\;)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}(1;-;[N];\{(\;)\})\qquad \text{and}\qquad (0;+;[N];\{(\;),(\;)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
which indeed, due to the Hurwitz–Riemann formula, concern actions of
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
on surfaces of algebraic genus
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
on surfaces of algebraic genus
![]() $p=N$
. In the first case, such action indeed exists by Theorem 2.7. Furthermore, the corresponding surface has
$p=N$
. In the first case, such action indeed exists by Theorem 2.7. Furthermore, the corresponding surface has
![]() $N$
or 1 boundary components and therefore, up to topological conjugacy, the corresponding action is respectively unique or there are
$N$
or 1 boundary components and therefore, up to topological conjugacy, the corresponding action is respectively unique or there are
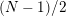 $(N-1)/2$
topological classes of such actions. The second signature may realize
$(N-1)/2$
topological classes of such actions. The second signature may realize
![]() $\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
-actions both on orientable (Theorem 2.10) and nonorientable (Theorem 2.9) surfaces and in the latter case either
$\mathbb{Z}_{N}$
-actions both on orientable (Theorem 2.10) and nonorientable (Theorem 2.9) surfaces and in the latter case either
![]() $k=N$
and the action is unique, or
$k=N$
and the action is unique, or
![]() $k=1$
and there are
$k=1$
and there are
![]() $N-1$
actions up to topological conjugation mentioned in Theorem 2.9.◻
$N-1$
actions up to topological conjugation mentioned in Theorem 2.9.◻
7.5 On topological type of cyclic actions of maximal order on bordered surfaces of given algebraic genus
Theorem 7.14. [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4, Theorem 3.2.18]
Let
![]() $p\geqslant 2$
be an integer. Then
$p\geqslant 2$
be an integer. Then
∙
 $N_{-}(p)=2p$
;
$N_{-}(p)=2p$
;∙
 $N_{+}^{+}(p)=\left\{\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}2(p+1)\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is even},\\ 2p\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is odd};\end{array}\right.$
$N_{+}^{+}(p)=\left\{\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}2(p+1)\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is even},\\ 2p\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is odd};\end{array}\right.$
∙
 $N_{+}^{-}(p)=\left\{\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}2(p+1)\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is even},\\ 2(p-1)\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is odd}.\end{array}\right.$
$N_{+}^{-}(p)=\left\{\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}2(p+1)\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is even},\\ 2(p-1)\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is odd}.\end{array}\right.$
In particular
 $$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle N_{+}(p)=\left\{\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}2(p+1)\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is even},\\ 2p\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is odd},\end{array}\right.\qquad \text{and}\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle N(p)=\left\{\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}2(p+1)\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is even},\\ 2p\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is odd}.\end{array}\right.\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\displaystyle & & \displaystyle N_{+}(p)=\left\{\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}2(p+1)\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is even},\\ 2p\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is odd},\end{array}\right.\qquad \text{and}\nonumber\\ \displaystyle & & \displaystyle N(p)=\left\{\begin{array}{@{}ll@{}}2(p+1)\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is even},\\ 2p\quad & \text{if}~p~\text{is odd}.\end{array}\right.\nonumber\end{eqnarray}$$
Corollary 7.15. All actions realizing the solutions of the maximum order problem described in Theorem 7.14 are unique up to topological conjugacy.
Proof. By the proof of [Reference Bujalance, Etayo, Gamboa and Gromadzki4, Theorem 3.2.18],
![]() $N_{-}(p)$
for arbitrary
$N_{-}(p)$
for arbitrary
![]() $p$
and
$p$
and
![]() $N_{+}^{-}(p)$
for even
$N_{+}^{-}(p)$
for even
![]() $p$
are realized by NEC-groups with signatures
$p$
are realized by NEC-groups with signatures
 $$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[2p];\{(2,2)\})\qquad \text{and}\qquad (0;+;[p+1];\{(2,2)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[2p];\{(2,2)\})\qquad \text{and}\qquad (0;+;[p+1];\{(2,2)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
respectively, and so these actions are unique by Theorem 2.4. Next,
![]() $N_{+}^{+}(p)$
is realized by signatures
$N_{+}^{+}(p)$
is realized by signatures
 $$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[2,p+1];\{(\;)\})\qquad \text{and}\qquad (0;+;[2,2p];\{(\;)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}(0;+;[2,p+1];\{(\;)\})\qquad \text{and}\qquad (0;+;[2,2p];\{(\;)\})\end{eqnarray}$$
for
![]() $p$
even and odd respectively, the corresponding surface has one boundary component, and so these actions are unique by Theorem 2.8. Finally,
$p$
even and odd respectively, the corresponding surface has one boundary component, and so these actions are unique by Theorem 2.8. Finally,
![]() $N_{+}^{-}(p)$
for odd
$N_{+}^{-}(p)$
for odd
![]() $p$
is realized by signature
$p$
is realized by signature
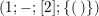 $(1;-;[2];\{(\;)\})$
, and the corresponding surface has 2 boundary components if 4 divides
$(1;-;[2];\{(\;)\})$
, and the corresponding surface has 2 boundary components if 4 divides
![]() $p-1$
and 4 boundary components otherwise, so this action is unique again by Theorem 2.6.◻
$p-1$
and 4 boundary components otherwise, so this action is unique again by Theorem 2.6.◻
Acknowledgments
This paper was initiated, and partially written, when G. Gromadzki visited Max-Planck Mathematical Institute in Bonn and Tokyo University of Science. The authors thank the referees for suggestions concerning the exposition and for comments and questions mentioned in the introduction.