Schizophrenia is a severe mental disorder that is typically associated with several unfavourable outcomes. In addition to causing cognitive impairment and compromising socio-occupational function, people with schizophrenia have a two to four times higher mortality rate and at least a 10-year shorter life expectancy than the general populationReference Plana-Ripoll, Pedersen, Agerbo, Holtz, Erlangsen and Canudas-Romo1,Reference Correll, Solmi, Croatto, Schneider, Rohani-Montez and Fairley2 Furthermore, a more significant mortality gap is noted in younger people, not only owing to suicide but also because of natural causes.Reference Bitter, Czobor, Borsi, Feher, Nagy and Bacskai3 Accordingly, developing treatment modalities is imperative for reducing premature and excessive mortality in individuals with schizophrenia.
Dysregulated lipid metabolism has been proposed as the putative pathophysiological mechanism underlying schizophrenia. Growing evidence suggests that dysregulation of lipid homeostasis precedes the onset of psychosis,Reference Dickens, Sen, Kempton, Barrantes-Vidal, Iyegbe and Nordentoft4 impairs cognitive function,Reference Hagi, Nosaka, Dickinson, Lindenmayer, Lee and Friedman5 interferes with response to antipsychotic medications,Reference Kim, Barr, Fredrikson, Honer and Procyshyn6 increases the risk of suicideReference Sankaranarayanan, Pratt, Anoop, Smith, Espinoza and Ramachandran7 and constitutes a trait marker of schizophrenia.Reference Tkachev, Stekolshchikova, Vanyushkina, Zhang, Morozova and Zozulya8 Moreover, hyperlipidemia is prevalent in individuals with schizophreniaReference Pillinger, Beck, Stubbs and Howes9 and is associated with an elevated risk of mortality.Reference Kugathasan, Horsdal, Aagaard, Jensen, Laursen and Nielsen10 Lipid-modifying agents mitigate not only the risk of cardiovascular disordersReference Kugathasan, Horsdal, Aagaard, Jensen, Laursen and Nielsen10 but also the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.Reference Nomura, Kishi, Ikuta and Iwata11,Reference Shen, Li, Yan, Zhou, Feng and Zhao12 These agents likely exert their effects through various biological pathways encompassing the reduction of lipid levels in cerebral vessels, protection of the neuronal cell membrane and function, and exertion of antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects through metabolic master enzymes (e.g. peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor).Reference Nierenberg, Ghaznavi, Sande Mathias, Ellard, Janos and Sylvia13,Reference Sodero and Barrantes14 However, no evidence-based studies have investigated the potential associations of lipid-modifying agents with risks of natural and suicide mortality in individuals with schizophrenia. The lack of studies may be attributable to the lack of sufficient mortality cases in people with schizophrenia receiving lipid-modifying agents.
To address the aforementioned literature gap, we conducted this prospective nationwide cohort study in Taiwan to investigate the associations between the use of lipid-modifying agents and mortality risk among people with schizophrenia. We estimated hazard ratios for mortality associated with lipid-modifying agents by using multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression with a time-dependent model. This approach is advantageous for the analysis of effect variables that change over time, particularly useful in clinical studies where medication prescriptions often change because of disease progression and intolerable side effects. We hypothesised that lipid-modifying agents reduce mortality risk in people with schizophrenia, and that different lipid-modifying agents exhibit different associations with mortality risk because of their unique pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles. Furthermore, we performed sensitivity analyses to assess the robustness of the primary results by examining the long-term effects of lipid-modifying agents on mortality risk, the benefits of lipid-modifying agents in the at-risk subpopulations and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular mortality, and the potential confounding effects of adherence to antipsychotic medications.
Method
Data source
Relevant data were collected from Taiwan's National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD), which contains the data of approximately 23 000 000 residents of Taiwan. Launched in 1995, the National Health Insurance (NHI) programme provides comprehensive and accessible medical care to approximately 99% of Taiwan's population. The NHIRD contains the registration files and medical claims data of NHI beneficiaries. This database is maintained by the Health and Welfare Data Science Center. Data from the NHIRD have been used extensively for research purposes and have served as the basis for numerous epidemiological studies published in peer-reviewed journals. The present study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Taipei City Hospital (TCHIRB-10905022-E). The requirement for informed consent was waived because of the de-identified and retrospective nature of the data. The present study adhered to the REporting of studies Conducted using Observational Routinely-collected health Data (RECORD) Statement.Reference Benchimol, Smeeth, Guttmann, Harron, Moher and Petersen15
Identification of schizophrenia cohort
From the NHIRD, we selected the data of people who had received a principal diagnosis of schizophrenia (International Classification of Diseases, ninth revision, clinical modification [ICD-9-CM] code 295.xx; International Classification of Diseases, tenth revision [ICD-10] codes F20.x, F25.x) over the period between 1 January 2001 and 31 December 2019 (N = 212 601; Supplementary e-Fig. 1 available at https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.2024.85). To consolidate the certainty of schizophrenia diagnosis, we excluded people who had received at least one diagnosis of bipolar disorder (ICD-9-CM codes 296.0–296.16, 296.4–296.81, 296.89, 296.9; ICD-10 codes F30.x, F31.x) over the same period (n = 99 011). The date of first being diagnosed as having schizophrenia was defined as the baseline. We subsequently omitted individuals without information on gender or birth date (n = 3290). Finally, we included 110 300 people with schizophrenia in our study cohort.
Identification of mortality
The data of each individual in the study cohort were electronically linked with the Department of Health Death Certification System – the national mortality database in Taiwan – for the period from 1 January 2001 to 31 December 2019, by using patients’ national identification number as an identifier. In Taiwan, national cause-of-death statistics were classified on the basis of ICD-9-CM codes for all deaths until 31 December 2014, and have been classified on the basis of ICD-10 codes for all deaths after 1 January 2015. The ICD-9 codes for deaths from suicide are E950 to E959, and the ICD-10 codes for deaths from suicide are X60 to X84 and Y87.0.
Measurement of exposure to lipid-modifying agents
We retrieved data regarding the use of lipid-modifying agents from prescription files from the out-patient and in-patient units derived from the NHIRD. Lipid-modifying agents were categorised into statins, fibrates, bile acid sequestrants, and nicotinic acid and its derivatives, as per the recommendations of the Taiwan Lipid Guidelines for High Risk Patients.Reference Li, Ueng, Jeng, Charng, Lin and Chien16 To assess the time-dependent effects of lipid-modifying agents on mortality risk, we applied 30-day time windows from the baseline. Specifically, we traced the use of lipid-modifying agents for each individual until the occurrence of mortality or the end of the study period (31 December 2019). We first recorded any exposure to a specific lipid-modifying agent of interest (yes/no) in each 30-day time window. An exposed time window was defined as any 30-day window during which a lipid-modifying agent of interest had been prescribed on any day. We subsequently evaluated the dose-dependent effect of specific lipid-modifying agents on mortality risk. Specifically, we calculated the defined daily dose (DDD) for each lipid-modifying agent on the basis of the Anatomic Therapeutic Chemical classification system (Supplementary e-Table 1). For each individual, the cumulative dose was calculated as the total number of DDDs of a specific lipid-modifying agent within a 30-day time window; moreover, the cumulative treatment duration was calculated as the total number of days for which a specific lipid-modifying agent was prescribed during a 30-day time window.
Covariates
The study covariates were gender, age, employment status, comorbidities and exposure to concomitant drugs other than lipid-modifying agents. Regarding comorbidities, we included physical and psychiatric comorbidities diagnosed within 180 days before the index date (Supplementary e-Tables 2 and 3 provide detailed information on diagnostic codes). Exposure was recorded for each 30-day time window by using the same exposure assessment method as that used for lipid-modifying agents.
Statistical analysis
We calculated the survival (contributed) time for each individual in the study cohort from the baseline until mortality or the end of the study period. We used the Gehan generalised Wilcoxon test to evaluate differences between incidence rates by gender. The standardised mortality ratio (SMR) was estimated as the ratio of deaths in the schizophrenia cohort to the expected number of deaths in the general Taiwanese population between 1 January 2001 and 31 December 2019.
We applied a multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression model using the baseline study variables (i.e. demographic characteristics and physical and psychiatric comorbidities) and time-varying variables (i.e. exposure to lipid-modifying agents and other concomitant drugs) measured after the baseline. Univariable Cox proportional hazards analyses were performed to estimate crude HRs for each demographic variable and physical or psychiatric comorbidities at baseline. Each covariate with P < 0.01 was further included in a multivariable regression model through backward selection. Subsequently, multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression with a time-dependent model was conducted to estimate adjusted HRs (aHRs) for mortality associated with each lipid-modifying agent (time window: 30 days) in a 5-year period. Our measurement of the effect of exposure to lipid-modifying agents on mortality risk was confined to the first 5 years after the baseline because many factors could influence the risk of mortality over a prolonged period. The cumulative dose (per 10 DDDs) and duration (per 10 days) of exposure to each lipid-modifying agent were regarded as continuous variables in our statistical models. All statistical analyses were conducted using SAS for Windows (version 9.4; SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina, USA; see https://www.sas.com). A P value of < 0.01 was considered significant.
Sensitivity analyses
In the first sensitivity analysis, we investigated the associations of the use of lipid-modifying agents with the risks of all-cause, natural and suicide mortality in the schizophrenia cohort during the 10-year study period (long-term analysis). Additionally, we assessed the associations between cumulative exposure (i.e. dose [per 10 DDDs] and duration [per 10 days]) to lipid-modifying agents and the risk of each mortality outcome across the 10-year study. In the second sensitivity analysis, we examined the associations in the at-risk subpopulations of individuals with schizophrenia (i.e. individuals with comorbid cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease or depressive disorder, respectively). Furthermore, to ascertain whether lipid-modifying agents benefit people with schizophrenia who did not have any cardiovascular or cerebrovascular comorbidity, we analysed the associations in a sub-population without any cardiovascular or cerebrovascular comorbidity. In the third sensitivity analysis, we evaluated the associations of the use of lipid-modifying agents and the risks of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular mortality. The final sensitivity analysis was performed to determine whether adherence to antipsychotic drugs exerts a confounding effect on risk estimation. Medication possession ratio, a proxy measure of medication adherence, was calculated by dividing the total days of antipsychotic drug dispensed to an individual by the treatment period (day) during a 30-day time window. Our multivariate models were adjusted for this parameter. Medication possession ratios of ≥80% and <80% indicated good adherence and poor adherence, respectively.
Results
Characteristics of the study cohort
This study enrolled 110 300 people with schizophrenia, of whom 22 528 died between 1 January 2001 and 31 December 2019. Among the various causes of mortality, natural causes accounted for 19 754 (87.7%) deaths, and suicide accounted for 1606 (7.1%) deaths. The SMRs for all-cause, natural and suicide mortality were 5.85 (95% CI: 5.77–5.93), 5.82 (95% CI: 5.74–5.90) and 9.89 (95% CI: 9.41–10.38), respectively (Supplementary e-Table 4). We plotted survival curves for the cumulative incidence rates of all-cause, natural and suicide mortality; the curves revealed that mortality rates were greater among men than among women in the study cohort during the 5-year follow-up period (Supplementary e-Fig. 2).
Factors associated with mortality
Table 1 presents the associations of clinical characteristics with all-cause, natural and suicide mortality, as determined from our univariable Cox proportional hazards regression. The risk of suicide was highest among individuals aged <45 years and decreased with age (linear trend, P < 0.001). By contrast, the risks of all-cause and natural mortality were the highest in people aged >65 years, and these risks increased with age (P < 0.001 for both). Unemployment was associated with elevated risks of all-cause and natural mortality but a reduced risk of suicide mortality. Regarding comorbidities, the presence of physical comorbidities across all organ systems and psychiatric comorbidities (e.g. neurocognitive disorder and alcohol use disorder) was positively associated with all-cause and natural mortality. Furthermore, the prevalence of all categories of psychiatric comorbidities, except neurocognitive disorder and intellectual disabilities, was positively associated with suicide mortality.
Table 1 Associations of all-cause, natural and suicide mortality with clinical characteristics of a national cohort of patients with schizophrenia during 2001–2019 (N = 110 300), as determined from Cox proportional hazards regression
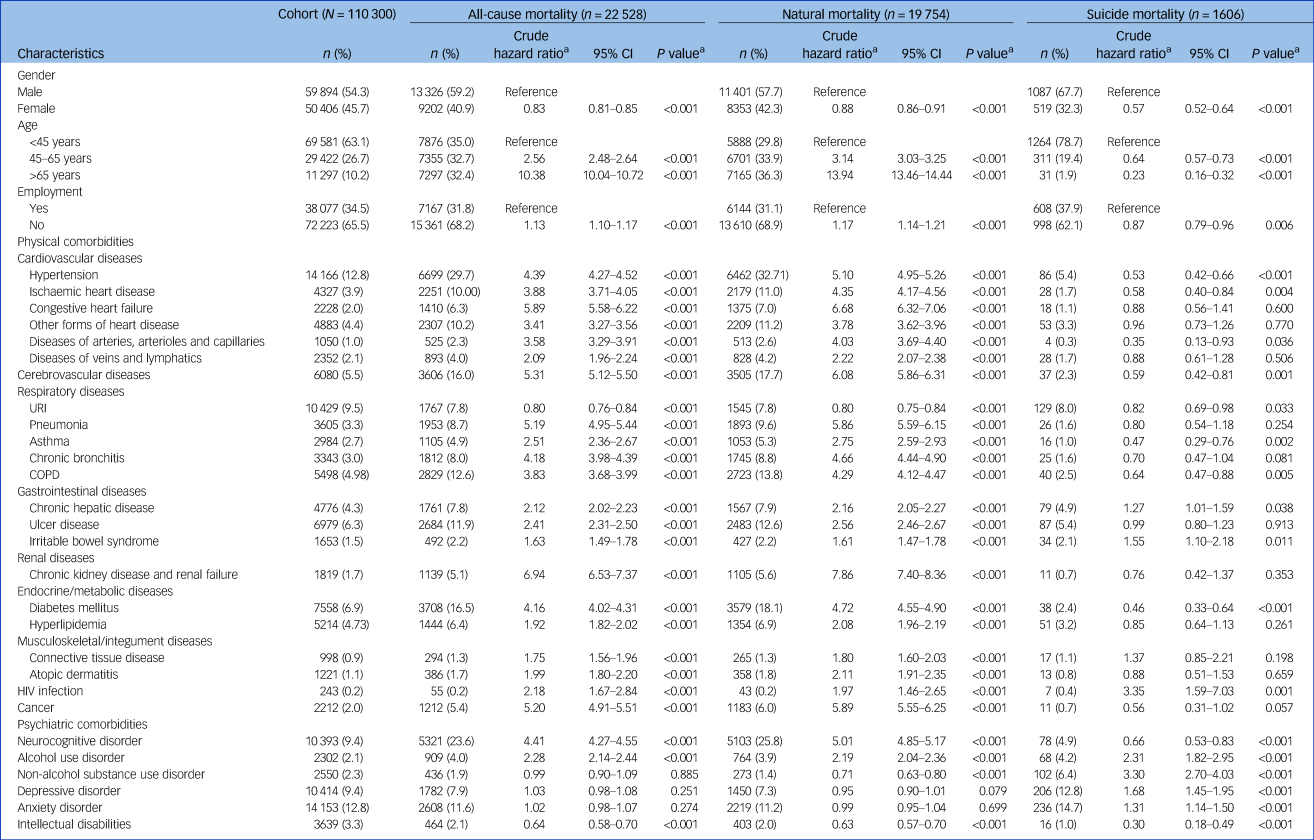
a. Estimated using univariable Cox proportional hazards regression.
COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; URI, upper respiratory tract infection.
As indicated in Table 2, lipid-modifying agents, nasal preparations, anti-Parkinson drugs and second-generation antipsychotics were the medications significantly associated with decreased risks of all-cause, natural and suicide mortality during the 5-year follow-up period respectively (Supplementary e-Tables 5, 6 and 7 provide detailed information on proportions of concomitant drug use).
Table 2 Associations of risks of all-cause, natural and suicide mortality with medication use during 5-year follow-up period in schizophrenia cohort (N = 110 300; total contributed person-years = 446 430)

a. Contributed person-years for a specified drug used in a 5-year period.
b. Contributed person-years for a specified drug used in a 5-year period/contributed person-years.
c. Estimated using univariable Cox proportional hazards regression with a time-dependent model.
Lipid-modifying agents and risk of mortality
Table 3 presents the associations of the use of lipid-modifying agents with the risks of all-cause, natural and suicide mortality during the 5-year follow-up period in the study cohort (Supplementary e-Table 8 provides detailed information on unadjusted associations). The use of lipid-modifying agents was associated with significantly reduced risks of all-cause (aHR: 0.37, P < 0.001) and natural mortality (aHR: 0.37, P < 0.001). The multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression model showed that the use of lipid-modifying agents was associated with a decreased risk of suicide marginally in statistics (aHR: 0.42, P = 0.028). Regarding the various categories of lipid-modifying agents, we observed that statins and fibrates were associated with lower risks of all-cause (aHRs: 0.37 and 0.39, respectively; P < 0.001 for both) and natural mortality (aHRs: 0.37 and 0.42, respectively; P < 0.001 for both) (Fig. 1).
Table 3 Associations of adjusted risks of all-cause, natural and suicide mortality with use of lipid-modifying agents during 5-year follow-up period in schizophrenia cohort (N = 110 300)
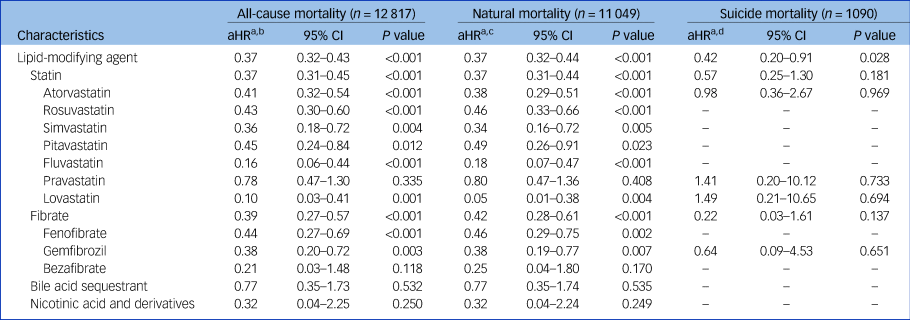
a. Estimated using multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression with time-dependent model.
b. All-cause mortality: adjusted for selected significant variables in multivariable regression (P < 0.01) in Table 1 and all time-varying variables in Table 2.
c. Natural mortality: adjusted for selected significant variables in multivariable regression (P < 0.01) in Table 1 and all time-varying variables in Table 2.
d. Suicide mortality: adjusted for selected significant variables in multivariable regression (P < 0.01) in Table 1 and all time-varying variables in Table 2.
aHR, adjusted hazard ratio.
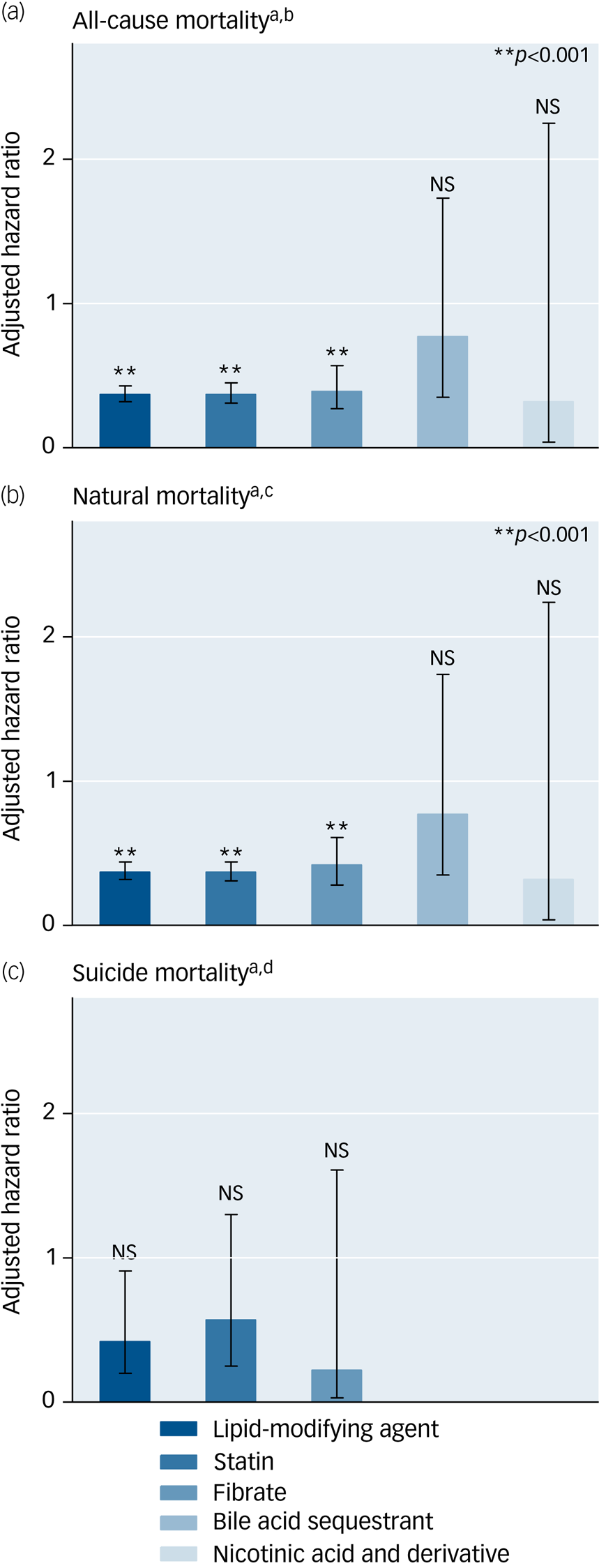
Fig. 1 Protective effects of lipid-modifying agents against all-cause, suicide and natural mortality in a national cohort of schizophrenia within a 5-year follow-up period after index admission (N = 110 300). Error bars show 95% CIs associated with adjusted hazard ratios.
a Estimated using multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression with a time-dependent model. b All-cause mortality: adjusted for significant selected variables in multivariable regression (P < 0.01) in Table 1 and all time-varying variables in Table 2. c Natural mortality: adjusted for significant selected variables in multivariable regression (P < 0.01) in Table 1 and all time-varying variables in Table 2. d Suicide mortality: adjusted for significant selected variables in multivariable regression (P < 0.01) in Table 1 and all time-varying variables in Table 2. NS, not significant.
We analysed the dose-dependent effects of lipid-modifying agents on mortality risk in our cohort during the 5-year period (Supplementary e-Table 9). The results revealed that long-term exposure to statins and fibrates was associated with reduced risks of all-cause mortality (aHRs: 0.71 and 0.76, respectively; P < 0.001 for both) and natural mortality (aHRs: 0.70 and 0.77, respectively; P < 0.001 for both). Furthermore, higher cumulative doses of statins and fibrates were associated with lower risks of all-cause mortality (aHRs: 0.67 and 0.70, respectively; P < 0.001 for both) and natural mortality (aHRs: 0.66 and 0.71, respectively; P < 0.001 for both).
Sensitivity analyses
The first sensitivity analysis revealed that the use of lipid-modifying agents was significantly associated with reduced risks of all-cause (aHR: 0.33; P < 0.001), natural (aHR: 0.34; P < 0.001) and suicide (aHR: 0.38; P = 0.003) mortality in schizophrenia cohort during the 10 years (Supplementary e-Table 10). Additionally, statins and fibrates were associated with significantly reduced risks of all-cause and natural mortality, respectively. The associations of the use of statins and fibrates with the risk of suicide mortality were marginally significant (aHR: 0.49 [P = 0.051] and 0.27 [P = 0.064], respectively). Furthermore, the dose-dependent analyses during the 10 years showed that long-term exposure to statins and fibrates was significantly associated with decreased risks of all-cause mortality (aHR: 0.72 [P < 0.001] and 0.80 [P < 0.001], respectively; Supplementary e-Table 11) and natural mortality (aHR: 0.71 [P < 0.001] and 0.81 [P < 0.001], respectively).
The second sensitivity analysis revealed that the use of lipid-modifying agents was significantly associated with reduced risks of all-cause and natural mortality in people with schizophrenia and comorbid cardiovascular disease (n = 15 307) (aHR: 0.33 [P < 0.001] and 0.31 [P < 0.001], respectively; Supplementary e-Table 12), those with schizophrenia and comorbid cerebrovascular disease (n = 6080) (aHR: 0.45 [P < 0.001] and 0.46 [P < 0.001], respectively; Supplementary e-Table 13), and those with schizophrenia and comorbid depressive disorder (n = 10 414) (aHR: 0.40 [P < 0.001] and 0.38 [P < 0.001], respectively; Supplementary e-Table 14). Among people with comorbid depressive disorder, only 8 of 160 individuals who died by suicide had received lipid-modifying agents. No significant association was observed between the use of lipid-modifying agents and the risk of suicide. As for people with schizophrenia without any cardiovascular or cerebrovascular comorbidity (n = 88 913), the use of lipid-modifying agents was also associated with significantly lower risks of all-cause and natural mortality (aHR: 0.38 [P < 0.001] and 0.41 [P < 0.001], respectively; Supplementary e-Table 15). In addition, the use of lipid-modifying agents was associated with decreased risks of suicide marginally in statistics (aHR: 0.22, P = 0.031).
The third sensitivity analysis revealed that the use of lipid-modifying agents, particularly statins, was significantly associated with reduced risks of cardiovascular (lipid-modifying agents: aHR: 0.59; P < 0.001; statins: aHR: 0.63; P = 0.009) and cerebrovascular (lipid-modifying agents: aHR: 0.20; P < 0.001; statins: aHR: 0.23; P < 0.001) mortality in the schizophrenia cohort during the study period (Supplementary e-Table 16). However, no significant association was noted between the use of fibrates and the risk of cardiovascular or cerebrovascular mortality.
The final sensitivity analysis, with adjustment for antipsychotic drug possession ratio (Supplementary e-Table 17), revealed that the use of lipid-modifying agents was significantly associated with reduced risks of all-cause (aHR: 0.37; P < 0.001) and natural (aHR: 0.38; P < 0.001) mortality in our cohort during the 5-year period. Statins and fibrates were associated with reduced risks of all-cause and natural mortality, respectively.
Discussion
This large prospective nationwide cohort study revealed that people with schizophrenia had a greater mortality risk than the general population. The SMRs for all-cause, natural and suicide mortality were 5.85, 5.82 and 9.89, respectively, among the people with schizophrenia; these SMRs are close to those reported in previous studies on mortality risk in individuals with schizophrenia or other disorders in various countries.Reference Correll, Solmi, Croatto, Schneider, Rohani-Montez and Fairley2,Reference Walker, McGee and Druss17 Moreover, our time-dependent Cox regression model demonstrated that exposure to lipid-modifying agents was significantly associated with reduced risks of all-cause and natural mortality in individuals with schizophrenia; according to our review of the literature, our study is the first to demonstrate this association. These findings underline the potential role of lipid-modifying agents in reducing mortality risk among individuals with schizophrenia.
This study revealed that statins and fibrates were the primary lipid-modifying agents associated with reduced risks of all-cause and natural mortality in people with schizophrenia. The mechanisms underlying the protective effects of these two types of lipid-modifying agents may involve pleiotropic actions. The risk of hyperlipidemia was two times higher in individuals who died from natural causes than in the entire study cohort. Therefore, one of the potential pathways mediating the protective effects of statins and fibrates against natural mortality is through the lipid-lowering effects. Nevertheless, it is worth noting that statins and fibrates also exhibit anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.Reference Nierenberg, Ghaznavi, Sande Mathias, Ellard, Janos and Sylvia13,Reference Sodero and Barrantes14 Substantial evidence indicates that proinflammatory pathways and oxidative stress are implicated in the link between schizophrenia and medical comorbidity.Reference Pillinger, D'Ambrosio, McCutcheon and Howes18,Reference Pillinger, Osimo, de Marvao, Shah, Francis and Huang19 Future studies should investigate biological markers that reflect inflammation and oxidative stress, in order to provide a clearer understanding of the mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects of statins and fibrates on mortality outcomes in schizophrenia.
The use of lipid-modifying agents was significantly associated with reduced risks of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular mortality in our entire cohort. Furthermore, we found significant associations between the use of lipid-modifying agents, particularly statins and fibrates, and reduced risks of all-cause and natural mortality in people with schizophrenia and comorbid cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease. Collectively, these findings suggest that lipid-modifying agents reduce mortality risk in individuals with schizophrenia, particularly at-risk subpopulations with comorbid cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease.
Our dose-dependent primary analyses revealed that the long-term use and high cumulative dose of lipid-modifying agents, particularly statins and fibrates, were associated with reduced risks of all-cause and natural mortality in the study cohort during the 5-year period. These findings suggest that statins and fibrates dose-dependently protect these people against all-cause and natural mortality. Similar results were reported in a cardiology study indicating considerably reduced mortality risks by the high-intensity use of statins.Reference Rodriguez, Maron, Knowles, Virani, Lin and Heidenreich20 The aforementioned findings are also corroborated by the results of our long-term sensitivity analysis, which revealed significant associations between the use of lipid-modifying agents and reduced risks of all-cause and natural mortality during the 10-year period. Evidence suggests that the risk of mortality is considerably high in people with schizophrenia receiving suboptimal cardioprotective care (e.g. statins).Reference Pillinger, Beck, Stubbs and Howes9,Reference Blackburn, Osborn, Walters, Nazareth and Petersen21,Reference Chang, Chan, Wong, Hai, Or and Chen22 Our study expands the literature by demonstrating the role of intensive cardioprotective care in reducing the risk of mortality in people with schizophrenia.
Adjunctive therapy with statins ameliorates the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.Reference Nomura, Kishi, Ikuta and Iwata11,Reference Shen, Li, Yan, Zhou, Feng and Zhao12 Lipid-modifying agents, such as statins, may have an antidepressant potential as an augmentation strategy with antidepressants.Reference De Giorgi, Waters, Pesci, Rosso, Cowen and Harmer23 Therefore, statins may attenuate suicide risk in schizophrenia through their therapeutic effects on schizophrenia symptoms. Our primary univariate analyses revealed that the use of lipid-modifying agents, particularly statins, reduced the risk of suicide mortality in the study cohort during the 5-year period. However, this association was marginally significant in our primary multivariate analyses and sensitivity analysis for people with schizophrenia and comorbid depressive disorder. One explanation for the lack of significant associations in the multivariable analyses may be the relatively small sample of the suicide group. Another reason may be the insufficient duration of medication exposure. Notably, our long-term sensitivity analysis of the 10-year follow-up period revealed a significant association between the use of lipid-modifying agents and a reduced risk of suicide mortality in the univariate analysis. By conducting long-term, large-scale studies, researchers should investigate the effects of lipid-modifying agents on the risk of suicide mortality to clarify the benefits of these agents against schizophrenia.
Because of varying pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles, different lipid-modifying agents exhibit different associations with mortality risk. For instance, we found that atorvastatin and rosuvastatin were mainly and significantly associated with reduced risks of all-cause and natural mortality in individuals with schizophrenia and comorbid cardiovascular disease (Supplementary e-Table 11). The roles of atorvastatin and rosuvastatin in mitigating mortality risk may result from their efficiency in reducing the levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.Reference Rodriguez, Maron, Knowles, Virani, Lin and Heidenreich20 A clinical trial indicated that simvastatin, a lipophilic statin that can cross the blood–brain barrier, outperforms other statins in mitigating depressive symptoms.Reference Abbasi, Mohammadinejad, Shahmansouri, Salehiomran, Beglar and Zeinoddini24 However, because of a small sample size, the trial could not clarify whether the use of simvastatin is associated with a reduced risk of suicide mortality. Our findings may guide future evidence-based research aimed at helping clinicians select the optimal statin for reducing mortality in individuals with schizophrenia.
Antipsychotic drugs are associated with increased adherence to cardiometabolic medications.Reference Solmi, Tiihonen, Lahteenvuo, Tanskanen, Correll and Taipale25 Antipsychotic drugs have been demonstrated to reduce the risks of all-cause and natural mortality in people with schizophrenia.Reference Correll, Solmi, Croatto, Schneider, Rohani-Montez and Fairley2 These findings prompted us to investigate adherence to antipsychotic drugs as a factor modifying the associations between lipid-modifying agents and mortality risk in people with schizophrenia. Our sensitivity analyses indicated that associations between the use of lipid-modifying agents and reduced risks of all-cause and natural mortality remained significant after adjustment for adherence to antipsychotic drugs. Therefore, adherence to antipsychotic drugs does not compromise the beneficial role of lipid-modifying agents in reducing the risk of mortality in individuals with schizophrenia.
This study has several strengths. First, we included a large and nationally representative sample. Second, because the NHIRD contains detailed information on the prescriptions of all NHI beneficiaries, we could comprehensively assess the use of various lipid-modifying agents during the study period. Finally, the multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis performed using a time-dependent model enabled us to estimate the time-varying effects of lipid-modifying agents on mortality risk. This is clinically relevant because prescriptions of lipid-modifying agents may vary or be discontinued during the course of schizophrenia.
Our study has several limitations. First, our analyses were based on the prescription – not the consumption – of medications because information regarding actual medication adherence could not be obtained from the claims database; nonetheless, we analysed the medication possession ratio as a proxy measure of medication adherence. Evidence suggests that people with schizophrenia exhibit non-adherence to cardiometabolic medications.Reference Solmi, Tiihonen, Lahteenvuo, Tanskanen, Correll and Taipale25 Thus, non-adherence might have led to the underestimation of mortality risk because of nondifferential exposure misclassification. Second, unhealthy lifestyle habits, such as cigarette smoking, alcohol consumption, sedentary behaviour and socioeconomic disadvantages, contribute to increased mortality in people with severe mental illness. However, we could not obtain information regarding these variables. Third, the NHIRD does not contain the laboratory data of patients. The availability of such data might have helped us elucidate mechanisms underlying the associations between the use of lipid-modifying agents and the risk of mortality in people with schizophrenia. Fourth, some individuals who died by suicide might have been misclassified as having died from a different cause (e.g. accidental death). Therefore, the risk of suicide mortality in our cohort might have been underestimated. Fifth, we cannot rule out the potential positive association between the use of lipid-modifying agents and the receipt of primary care – a factor whose effects on mortality may be stronger than those of lipid-modifying agents. Finally, the Taiwanese healthcare sector lacks specific guidelines for the prescription of lipid-modifying agents to individuals with schizophrenia. Thus, our findings may not be generalisable across people with schizophrenia in other populations.
Conclusion
This nationwide, population-based cohort study indicates that exposure to lipid-modifying agents, particularly statins and fibrates, is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in individuals with schizophrenia. These people often receive insufficient cardiovascular care. Our findings may help bridge the large mortality gap between people with schizophrenia and the general population by guiding the effective administration of lipid-modifying agents.
Supplementary material
Supplementary material is available online at https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.2024.85
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analysed in this study.
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Wallace Academic Editing for the language and grammar review.
Author contributions
P.-H.C., C.-H.P. and C.-J.K. conceived and designed this study. C.-J.K. acquired the data. S.-S.S. performed statistical analyses. P.-H.C. and C.-J.K. drafted the manuscript. P.-H.C. and P.-Y.C. made critical revisions to the manuscript on the basis of crucial intellectual content. S.-Y.T. and C.-C.C. provided administrative and technical support and supervised this study.
Funding
This study was supported by the the National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan (grant numbers: MOST 108-2314-B-532-005 and 110-2314-B-532-003-MY3). In addition, it was supported by Taipei City Hospital, Taiwan (grant numbers: 11001-62-006, 11101-62-003 and 11201-62-002). The funding agencies had no involvement in the study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, report preparation or manuscript submission-related decision.
Declaration of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.








eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.