AKATHISIA AS A CLINICAL CHALLENGE
Neuroleptic-induced akathisia (NIA) is characterised by a subjective sense of inner restlessness and objective fidgety movements. It is a major extrapyramidal side-effect of conventional antipsychotic agents. Despite its high incidence (20-45%), the underlying mechanisms have not yet been adequately explained. Diagnosis may be difficult owing to the existence of various forms of NIA, namely acute, chronic, withdrawal and tardive, along with diurnal variations in its expression and its common association with other extrapyramidal syndromes (EPS). The complex interplay of the subjective and observable components of NIA may account for the reported difficulties in differentiating NIA from psychotic excitement, agitated depression and anxiety.
The early detection and adequate treatment of NIA are important because of its negative clinical consequences and serious adverse effects. Akathisia is thought to be a risk factor for the development of tardive dyskinesia; it may be predictive of more severe psychopathology; and it seems to herald a poor response to treatment. Moreover, it may be a contributing factor in the suicidal and violent behaviour of patients with schizophrenia. Finally, the mental distress that often accompanies akathisia makes it one of the most common reasons for non-adherence with antipsychotic drug treatment.
CURRENT TREATMENT OF AKATHISIA
The traditional recommended treatment approach to NIA consists of a reduction in the neuroleptic dosage, discontinuation of the culprit neuroleptic agent or switching to a low-potency antipsychotic agent.
Anticholinergics
Extrapyramidal syndromes, including akathisia, are attributed to the dopamine/acetylcholine imbalance produced by the neuroleptic blockage of the D2 receptors in the nigrostriatal system. This assumption is based on the inverse relationship between the affinity of conventional neuroleptic agents for muscarinic receptors and their propensity for causing EPS. However, although anticholinergic agents have proven efficacious in the treatment of neuroleptic-induced Parkinsonism and acute dystonia, they produced equivocal results in NIA (Reference Fleischhacker, Roth and KaneFleischhacker et al, 1990). Furthermore, the use of anticholinergic agents is limited by their side-effects (e.g. cognitive impairment, blurred vision, constipation, urinary retention). The tendency of patients with akathisia associated with Parkinsonian symptoms to respond to anticholinergic agents has led to the suggestion of a specific Parkinsonian-related subtype of akathisia (Reference Barnes and McPhillipsBarnes & McPhillips, 1999).
Adrenergic agents: beta-blockers and clonidine
Later studies have demonstrated the anti-NIA efficacy of lipophilic beta-adrenergic blockers. Propranolol remains one of the most efficacious and well-tolerated therapeutic agents for NIA, and its beneficial effect has been extended to other centrally acting non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists (Reference Adler, Angrist and RetterAdler et al, 1989). Clonidine, a selective α-2 adrenergic presynaptic agonist, can also improve NIA; however, its use is frequently complicated by side-effects of sedation and hypotension. The mechanism of the anti-NIA effect of agents that reduce central noradrenergic transmission is still unclear, because akathisia is predominantly induced by compounds with a marked dopamine D2 receptor antagonism.
Benzodiazepines and amantadine
The benzodiazepines (e.g. clonazepam, lorazepam, diazepam) constitute a third group of agents with some therapeutic efficacy in NIA, presumably owing to their non-specific sedating and tranquillising properties. Amantadine, a dopamine reuptake inhibitor, was also suggested as an optimal treatment for NIA (Reference Fleischhacker, Roth and KaneFleischhacker et al, 1990).
AKATHISIA AND THE SEROTONERGIC SYSTEM
The high rate of non-response to the conventional anti-akathisic agents led clinicians to search in new directions. It was suggested that 5-HT2 receptor antagonism, by counteracting dopamine D2 blockade may prevent the onset or mitigate the severity of neuroleptic-induced EPS (Reference MeltzerMeltzer et al, 1999). Dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area and substantia nigra — brain regions apparently involved in the patho-physiology of EPS and NIA — receive inhibitory 5-HT input from midbrain raphe nuclei. Some researchers have hypothesised that a reduction in brain 5-HT function (5-HT2a antagonists, 5-HT1a agonists, raphe lesions) may increase the basal activity of dopaminergic neurons and thereby alleviate EPS induced by D2 receptor antagonists (for a review, see Reference Kapur and RemingtonKapur & Remington, 1996). An indication of a link between EPS (Reference LaneLane, 1998) and the serotonergic system was provided by studies showing that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which apparently increase 5-HT neurotransmission, have a propensity to induce EPS and an ‘akathisia-like syndrome’ (Reference LaneLane, 1998). Moreover, the novel atypical antipsychotic agents, which display low propensity to induce EPS and NIA, share at least one pharmacological property that distinguishes them from typical neuroleptics — a preponderance of 5-HT2a receptor blockade over D2 receptor antagonism. (The affinity of atypical antipsychotics to the various 5-HT receptor subtypes is shown in Table 1.) This property supports the use of agents with marked 5-HT2a antagonistic effect in the treatment of NIA.
Table 1 In vitro binding affinities (Ki values in nM)1 of currently available atypical antipsychotics for 5-HT receptor subtypes
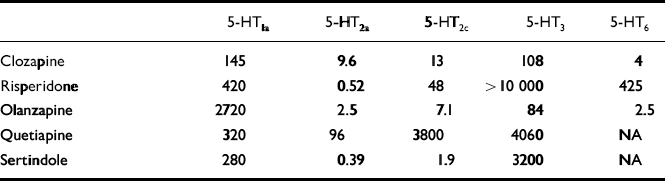
| 5-HT1a | 5-HT2a | 5-HT2c | 5-HT3 | 5-HT6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clozapine | 145 | 9.6 | 13 | 108 | 4 |
| Risperidone | 420 | 0.52 | 48 | > 10 000 | 425 |
| Olanzapine | 2720 | 2.5 | 7.1 | 84 | 2.5 |
| Quetiapine | 320 | 96 | 3800 | 4060 | NA |
| Sertindole | 280 | 0.39 | 1.9 | 3200 | NA |
RELEVANCE OF 5-HT RECEPTOR SUBTYPES TO PHARMACOTHERAPY OF NIA
5-HT2 antagonists
The results of clinical trials with serotonergic agents in the treatment of acute NIA are summarised in Table 2. Although there are no selective 5-HT2a antagonists available for clinical use, three compounds with pronounced 5-HT2a antagonistic activity, ritanserin, cyproheptadine and mianserin, have been suggested as anti-akathisia remedies.
Table 2 Reports on the efficacy of serotonergic agents in patients with neuroleptic-induced akathisia (NIA)
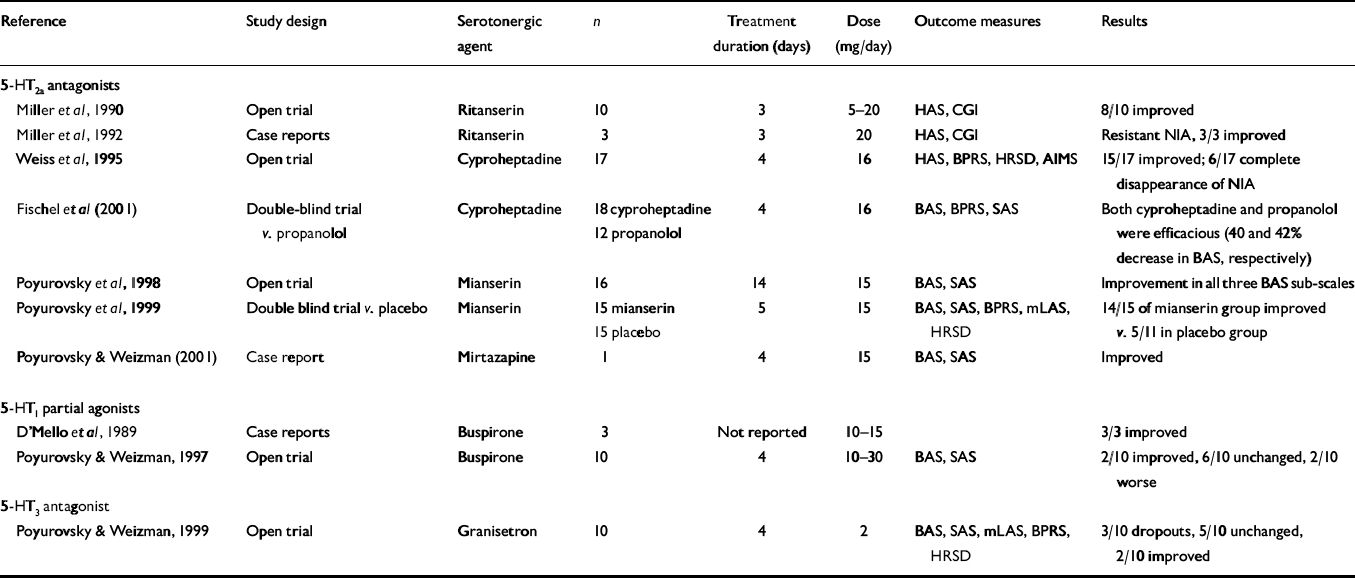
| Reference | Study design | Serotonergic agent | n | Treatment duration (days) | Dose (mg/day) | Outcome measures | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT2a antagonists | |||||||
| Reference Miller, Fleischhacker and EhrmanMiller et al, 1990 | Open trial | Ritanserin | 10 | 3 | 5-20 | HAS, CGI | 8/10 improved |
| Reference Miller, Hummer and PychaMiller et al, 1992 | Case reports | Ritanserin | 3 | 3 | 20 | HAS, CGI | Resistant NIA, 3/3 improved |
| Reference Weiss, Aizenberg and HermeshWeiss et al, 1995 | Open trial | Cyproheptadine | 17 | 4 | 16 | HAS, BPRS, HRSD, AIMS | 15/17 improved; 6/17 complete disappearance of NIA |
| Fischel et al (Reference Fischel, Hermesh and Alzenberg2001) | Double-blind trial v. propanolol | Cyproheptadine | 18 cyproheptadine 12 propanolol | 4 | 16 | BAS, BPRS, SAS | Both cyproheptadine and propanolol were efficacious (40 and 42% decrease in BAS, respectively) |
| Reference Poyurovsky, Fuchs and WeizmanPoyurovsky et al, 1998 | Open trial | Mianserin | 16 | 14 | 15 | BAS, SAS | Improvement in all three BAS sub-scales |
| Reference Poyurovsky, Shardorodsky and FuchsPoyurovsky et al, 1999 | Double blind trial v. placebo | Mianserin | 15 mianserin 15 placebo | 5 | 15 | BAS, SAS, BPRS, mLAS, HRSD | 14/15 of mianserin group improved v. 5/11 in placebo group |
| Poyurovsky & Weizman (Reference Poyurovsky and Weizman2001) | Case report | Mirtazapine | 1 | 4 | 15 | BAS, SAS | Improved |
| 5-HT1 partial agonists | |||||||
| Reference D'Mello, McNeil and HarrisD'Mello et al, 1989 | Case reports | Buspirone | 3 | Not reported | 10-15 | 3/3 improved | |
| Reference Poyurovsky and WeizmanPoyurovsky & Weizman, 1997 | Open trial | Buspirone | 10 | 4 | 10-30 | BAS, SAS | 2/10 improved, 6/10 unchanged, 2/10 worse |
| 5-HT3 antagonist | |||||||
| Reference Poyurovsky and WeizmanPoyurovsky & Weizman, 1999 | Open trial | Granisetron | 10 | 4 | 2 | BAS, SAS, mLAS, BPRS, HRSD | 3/10 dropouts, 5/10 unchanged, 2/10 improved |
Ritanserin
Miller et al (Reference Miller, Fleischhacker and Ehrman1990) were among the first researchers to directly evaluate the putative anti-akathisia properties of ritanserin, an agent with a pronounced 5-HT2a and 5-HT2c antagonistic activity. In an open-label study, they treated 10 patients with NIA with ritanserin (5-20 mg/day) and noted a reduction of more than 50% in the Hillside Akathisia Scale score in six of them and a reduction close to 50% in two others. Only two of the 10 patients did not respond. The effect of ritanserin was rapid and clinically significant, and no significant side-effects were noted. The same group of investigators (Reference Miller, Hummer and PychaMiller et al, 1992) subsequently reported a beneficial effect of ritanserin (10 mg twice daily) in three patients with NIA who had a proven resistance to anticholinergics, benzodiazepines and beta-blockers. A large-scale placebo-controlled study is still necessary to substantiate these important preliminary findings.
Data on the efficacy of ritanserin in other movement disorders, such as neuroleptic-induced parkinsonism, are less consistent.
Cyproheptadine
Cyproheptadine is a potent 5-HT2a and 5-HT2c antagonist with additional antihistaminergic and anticholinergic activity. Its anti-akathitic properties were explored by Weiss et al (Reference Weiss, Aizenberg and Hermesh1995) in an open clinical trial of 17 patients with acute NIA. The drug was administered in a fixed oral dose of 16 mg/day, in four divided doses for 4 days, and the severity of akathisia was assessed with the Barnes Akathisia Scale (BAS). The therapeutic effect of cyproheptadine was pronounced and could be discerned already by Day 2 of treatment. By Day 4, all 17 participants had improved to some degree, and 15 showed a more than 50% reduction in the BAS score. In six patients, the NIA disappeared completely. The drug was well tolerated, and side-effects of mild sedation, dry mouth and blurred vision occurred only in those patients receiving concurrent anticholinergic medication. Although the contribution of cyproheptadine's sedative action to its anti-akathitic effect cannot be disregarded, it seems unlikely that the robust improvement in the akathisia was due solely to a non-specific sedative effect. These encouraging preliminary results have recently been replicated in a double-blind comparison study of cyproheptadine (n=18, 16 mg/day) and propranolol (n=12, 80 mg/day) in patients with acute NIA (Reference Fischel, Hermesh and AlzenbergFischel et al, 2001). Both drugs demonstrated significant anti-NIA activity (46% v. 42% decrease in the BAS score, respectively) within 4 days of treatment. In contrast to findings in NIA, the benefit of cyproheptadine in the treatment of neuroleptic-induced parkinsonism is far from conclusive.
Mianserin
Mianserin is a tetracyclic antidepressant with marked 5-HT2a and 5-HT2c antagonism as well as antihistaminergic and α-2 antagonistic activity, without anticholinergic properties. So far, mianserin has been the most intensively investigated 5-HT2a/2c antagonist in the treatment of acute NIA.
Poyurovsky et al (Reference Poyurovsky, Fuchs and Weizman1998), in a preliminary open trial, treated 16 patients with acute NIA with low-dose mianserin (15 mg/day). A beneficial effect was detected in 14 patients on the third day of treatment, consisting primarily of the disappearance of the subjective sense of inner restlessness, followed by a substantial decrease in the characteristic akathitic movements. The drug was well tolerated, and the only side-effect, mild sedation in five patients, was transient. These promising preliminary results were confirmed in a double-blind placebo-controlled study by the same team (Reference Poyurovsky, Shardorodsky and FuchsPoyurovsky et al, 1999), wherein patients who met the DSM-IV (American Psychiatric Association, 1994) criteria for acute NIA were randomly allocated to receive either low-dose mianserin (15 mg/day; n=15) or placebo (n=15) once a day (at 08.00 h) for 5 days. Treatment response was defined as a reduction of at least one point on the BAS global sub-scale. Results indicated that 14 of the 15 patients treated with mianserin (93.3%) responded, compared with only five of the 11 patients (45.6%) given placebo who completed the trial. When a more rigorous response criterion was applied, namely, reduction of at least two points on the BAS, the positive response rate was 40% in the mianserin group and only 9.1% in the placebo group. Complete disappearance of the NIA occurred in four patients in the mianserin group (26.6%) but in none of the placebo group. Moreover, the beneficial effect of mianserin was accompanied by a corresponding reduction in neuroleptic-induced dysphoria and psychotic symptoms, indicating an association between these clinical phenomena and akathisia. By contrast, mianserin had no effect on concurrent symptoms of neuroleptic-induced parkinsonism in these NIA patients. Furthermore, the response rate for mianserin (40%) and the mean rate of reduction in akathisia scores (52.2%) reported by our group (Reference Poyurovsky, Shardorodsky and FuchsPoyurovsky et al, 1999) were similar to those for the currently used anti-NIA compounds, propranolol and benzatropine (Reference Adler, Angrist and RetterAdler et al, 1989). Our studies (Poyurovsky et al, Reference Poyurovsky, Fuchs and Weizman1998, Reference Poyurovsky, Shardorodsky and Fuchs1999) confirmed the tolerability and safety of low-dose mianserin; mild, transient sedation and clinically irrelevant orthostatic hypotension were the only side-effects. In a recent case report, mirtazapine, a tetracyclic antidepressant structurally and pharmacologically similar to mianserin, an agent with 5-HT2a/2c and 5-HT3 antagonistic properties, was also found to possess anti-akathisia activity (Reference Poyurovsky and WeizmanPoyurovsky & Weizman, 2001).
5-HT1a PARTIAL AGONISTS
Buspirone
Despite the encouraging results reported for 5-HT2a antagonists, these agents fail to yield a response in a substantial proportion of NIA patients. Furthermore, some studies of atypical novel antipsychotics have found that despite their high 5-HT2a receptor occupancy rate (>90%), they can still induce EPS and akathisia. This suggests that the protective action of 5-HT2a blockers against akathisia due to D2 blockade may not be universal, and other pathophysiological mechanisms may be involved (Reference Kapur and RemingtonKapur & Remington, 1996). Extensive evidence indicates that 5-HT1a receptor antagonists have effects similar to 5-HT2a receptor antagonists in a variety of systems (Reference MeltzerMeltzer, 1999).
Buspirone, an azaperone, acting as a partial agonist of 5-HT1a somatodendritic and terminal autoreceptors, appears to inhibit the firing of 5-HT neurons located in the median and dorsal raphe nuclei. The inhibitory effect of buspirone on 5-HT neurotransmission might disinhibit dopamine release and counteract the dopamine blockade induced by neuroleptics (Reference D'Mello, McNeil and HarrisD'Mello et al, 1989). However, in a more recent open-label short-term clinical trial, buspirone (15-30 mg/day for 4 days) exerted a moderate therapeutic effect in only two out of 10 NIA patients (Reference Poyurovsky and WeizmanPoyurovsky & Weizman, 1997). Furthermore, seven of the eight buspirone non-responders who were subsequently switched to mianserin (15 mg/day) showed an improvement; in five of them, the NIA completely disappeared. The open nature of this study, the small sample size and the short duration of treatment precluded definitive conclusions. Furthermore, new evidence of cross-talk of the 5-HT1a receptor with the 5-HT1a with the 5-HT2a receptors (Reference MeltzerMeltzer, 1999), makes buspirone's lack of anti-akathitic effect even more surprising. Along the same lines, beta-blockers, which are well-documented anti-akathisia agents, exhibit antagonistic activity at the 5-HT1a receptor. Thus, it is possible that it is their predominantly antagonistic activity rather than their agonistic activity at the presynaptic 5-HT1a receptor that contributes to their anti-akathitic effect. Further research is needed in this area.
5-HT3 ANTAGONISTS
Granisetron
Since mianserin, mirtazapine and some novel atypical antipsychotics also possess 5-HT3 antagonistic properties (Reference RichelsonRichelson, 1996), it is possible that 5-HT3 blockade may play a role in the anti-akathitic effect. However, this was disproved in a study of 10 patients with acute NIA treated with the 5-HT3 receptor antagonist granisetron (2 mg/day for 4 days) (Reference Poyurovsky and WeizmanPoyurovsky & Weizman, 1999). Three of the patients discontinued the drug because of lack of response, and the remainder showed no significant change in BAS score during the trial. The symptoms of NIA remained unchanged or worsened in five patients (71.4%) and showed insignificant improvement in two. It seems that 5-HT3 antagonists are of limited value in the treatment of acute NIA.
SUMMARY AND CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS
Overall, the results of the systematic evaluation of serotonin-active agents with predominant affinity for different subtypes of 5-HT receptors indicate that within the 5-HT system, the 5-HT2a receptors rather than the other subtypes (e.g. 5-HT1a and 5-HT3) are involved in the pharmacotherapy of acute NIA. In at least some patients with acute NIA, 5-HT2a post-synaptic antagonism (ritanserin, cyproheptadine, mianserin) rather than a presynaptic 5-HT1a modulatory effect (buspirone) or post-synaptic 5-HT3 antagonism (granisetron) might be required to produce a rapid and efficient anti-NIA effect.
Currently, the treatment of acute NIA involves two major strategies: the modification of the antipsychotic drug regimen and/or the addition of anti-akathisia agents. Today, the traditional approach of a reduction in neuroleptic dosage and a switch to a low-potency conventional neuroleptic (e.g. thioridazine) is followed, as necessary, by a switch to a novel atypical antipsychotic (e.g. risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine, ziprasidone), and finally, initiation of clozapine (see Fig. 1). When the decision is made to initiate an anti-akathisia compound, the beta-adrenergic blocking agent propranolol (40-120 mg/day) or a 5-HT2a antagonist (mianserin, 15-30 mg/day, cyproheptadine 8-16 mg/day, or ritanserin 5-20 mg/day) are the first choices. In cases of NIA associated with neuroleptic-induced parkinsonism, priority may be given to anticholinergic agents (biperiden 4-12 mg/day, benzatropine 1.5-8 mg/day or trihexyphenidyl 2-10 mg/day), although their efficacy is still controversial. A benzodiazepine (lorazepam 2 mg/day, clonazepam 0.5 mg/day, or diazepam 5-15 mg/day) may need to be added to propranolol or an anticholinergic compound to provide additional anxiolytic or sedative effects, especially in patients with subjective distress. It seems that the addition of a benzodiazepine to the available 5-HT2a antagonists should be avoided owing to the sedative effects of both compounds. If all these agents are ineffective, amantadine or clonidine can be tried. The suggested guidelines are summarised in Fig. 1.

Fig. 1 Therapeutic options for acute neuroleptic-induced akathisia.
FUTURE DIRECTIONS
The rapid increase in the number of identified 5-HT receptor subtypes has prompted a new hypothesis regarding their involvement in the development of NIA and the anti-NIA activity of putative anti-akathisia compounds. Recent studies have demonstrated a high affinity of some of the novel atypical antipsychotics, primarily clozapine, to the molecularly cloned 5-HT6 receptor. Because of the abundance of 5-HT6 receptors in the striatum and limbic system, it may be the ability of at least some of the atypical antipsychotics to interact with the 5-HT6 receptor that contributes to the lack of EPS (Reference MeltzerMeltzer, 1999). The future use of selective 5-HT6 receptor agents may clarify the role of 5-HT6 in the pathophysiology and pharmacotherapy of neuroleptic-induced EPS and akathisia.
Non-serotonergic receptor mechanisms also apparently play a critical role in the development of EPS and NIA and may be relevant in the search for new, potentially active anti-EPS compounds. A sub-threshold level (<75%) of D2 receptor occupancy at clinically relevant doses (e.g. clozapine, low-doses of risperidone) may be the reason for freedom from EPS (Reference Kapur and RemingtonKapur & Remington, 1996). Furthermore, along an intriguing new line of thought, some researchers suggest that antipsychotic agents with ‘loose’ binding of the dopamine D2 receptor (e.g. clozapine and quetiapine) may exhibit a lesser propensity to provoke EPS and akathisia (Reference Seeman and TallericoSeeman & Tallerico, 1998). A promising direction is the development of new EPS-sparing antipsychotic agents possessing this specific pharmacodynamic property.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Professor Thomas R. E. Barnes for his useful comments and Gloria Ginzach, Marian Propp and Rena Kurs for their editorial and secretarial assistance. We also thank the Sarah and Moshe Mayer Foundation for their support.






eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.