Article contents
Polarimetric scattering from a layer of spatially oriented metamaterial small spheroids
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 April 2005
Abstract
Complex scattering amplitude functions of a small metamaterial spheroid are derived. The Mueller matrix solution for polarimetric bistatic scattering from a layer of random metamaterial small spheroids is then constructed. Bistatic scattering of metamaterial and dielectric spheroids are numerically calculated. Linearly co-polarized backscattering coefficients $\sigma _{hh} $ 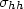 , $\sigma _{vv} $
, $\sigma _{vv} $ 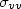 and $\sigma _{hh} -\sigma _{vv} $
and $\sigma _{hh} -\sigma _{vv} $  are presented to show the dependence upon frequency. The co-polarized and cross-polarized backscattering coefficients and polarizability degree of a layer of non-uniformly oriented metamaterial spheroids under illumination of an elliptic polarized plane wave are numerically simulated. Effects of metamaterial parameters on scattering pattern and scattering mechanism are interpreted. Numerical results indicate that the bistatic scattering of metamaterial particles is enhanced largely and demonstrates asymmetric directivity. Meanwhile, polarized difference of $\sigma _{hh} -\sigma _{vv} $
are presented to show the dependence upon frequency. The co-polarized and cross-polarized backscattering coefficients and polarizability degree of a layer of non-uniformly oriented metamaterial spheroids under illumination of an elliptic polarized plane wave are numerically simulated. Effects of metamaterial parameters on scattering pattern and scattering mechanism are interpreted. Numerical results indicate that the bistatic scattering of metamaterial particles is enhanced largely and demonstrates asymmetric directivity. Meanwhile, polarized difference of $\sigma _{hh} -\sigma _{vv} $  strongly varies with frequency due to constitutive dispersion of $\varepsilon (\omega )$
strongly varies with frequency due to constitutive dispersion of $\varepsilon (\omega )$ 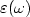 and $\mu (\omega )$
and $\mu (\omega )$ 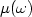 .
.
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © EDP Sciences, 2005
References
- 2
- Cited by

