Introduction
Social enterprises have often been proposed as an alternative channel for enhancing public health, especially among vulnerable people. Recently, a growing number of studies have suggested that social enterprises can provide various programs, products, and services to populations that are more likely to suffer from health inequalities (Roy & Hackett, Reference Roy and Hackett2017; Roy et al., Reference Roy, Donaldson, Baker and Kay2013; Thomson et al., Reference Thomson, Atkinson, Petticrew and Kearns2006). The use of social enterprises to enhance the public health of socially disadvantaged people is gaining widespread acceptance. Given that the sole efforts of governments can hardly solve the causes and problems of health inequalities, many attentions have been paid to the role of social enterprises (Roy et al., Reference Roy, Donaldson, Baker and Kay2013; Thomson et al., Reference Thomson, Atkinson, Petticrew and Kearns2006).
The results of previous studies on social enterprises’ contributions to public health can help describe the mechanisms through which social enterprises benefit socially disadvantaged sections (De Ruysscher et al., Reference De Ruysscher, Claes, Lee, Cui, Van Loon, De Maeyer and Schalock2017; Roy et al., Reference Roy, Donaldson, Baker and Kerr2014). Except for a few studies (Ferguson & Xie, Reference Ferguson and Xie2008; Jang et al., Reference Jang, Kim, Hong, Yoo and Park2018), most research has largely utilized qualitative approaches, including case studies with interviews, to examine the effects of social enterprise on the mental and physical health of socially disadvantaged groups (Bertotti et al., Reference Bertotti, Harden, Renton and Sheridan2012; Farmer et al., Reference Farmer, De Cotta, McKinnon, Barraket, Munoz, Douglas and Roy2016; Ferguson, Reference Ferguson2007; Ferguson & Islam, Reference Ferguson and Islam2008; Ferguson & Xie, Reference Ferguson and Xie2008; Munoz et al., Reference Munoz, Farmer, Winterton and Barraket2015). By linking relevant theories (e.g., social capital, capability, and a space of well-being) to empirical cases, several studies have systemically reviewed how social enterprises can enhance public health and well-being (Calò et al., Reference Calò, Teasdale, Donaldson, Roy and Baglioni2018; Roy et al., Reference Roy, Donaldson, Baker and Kay2013).
However, the extant studies on the relationship between social enterprises and vulnerable social groups’ health had some limitations. First, these studies drew largely from a small number of cases and interviews; this led to a simplification of what social enterprises concretely do (Macaulay et al., Reference Macaulay, Mazzei, Roy, Teasdale and Donaldson2018). Furthermore, previous studies disregarded how local contexts could affect the well-being and subjective health of low-income individuals. It is quite embarrassing that the orientation and the impact of social enterprises should be understood in their social and community contexts (Mazzei, Reference Mazzei2017; Mendell, Reference Mendell2010). Finally, prior studies were not concerned with the capacities of social enterprises, which directly and indirectly affect their effectiveness in supporting socially vulnerable people.
Therefore, this study attempts to answer the following questions through multilevel models, considering individual characteristics and local contexts simultaneously:
(1) Do social enterprises improve low-income residents’ subjective health in local communities? (2) Compared to other social enterprises, are high-capacity social enterprises more beneficial for the subjective health of low-income individuals?
Contribution of Social Enterprises to Well-Being of Low-Income People
Based on relevant studies, we suggest that social enterprises can enhance the health and well-being of vulnerable social groups by: (1) providing affordable healthcare products and services, (2) increasing health conditions and capabilities, and (3) acting as community “boundary spanners.” These three roles are entangled and variously combined.
First, social enterprises provide affordable healthcare goods and services. These needs are often not satisfied by markets and governments (Seelos & Mair, Reference Seelos and Mair2005). In particular, significant unmet healthcare needs have been observed among poor people living in remote areas (Allin et al., Reference Allin, Grignon and Le Grand2010). Thus, social enterprises deliver free services or low-cost healthcare services to those at the bottom of the societal pyramid (Prahalad, Reference Prahalad2005) and subsistence consumers (Viswanathan & Rosa, Reference Viswanathan and Rosa2007) through government-partnered collaborative efforts (Agarwal et al., Reference Agarwal, Chakrabarti, Brem and Bocken2018; Seelos & Mair, Reference Seelos and Mair2005; Weidner et al., Reference Weidner, Rosa and Viswanathan2010). In contrast to the traditional belief that subsistence consumers who face day-to-day life challenges cannot afford to buy healthcare services, the market consisting of such people is growing (Weidner et al., Reference Weidner, Rosa and Viswanathan2010). By identifying the health needs of subsistence or low-income consumers, social enterprises can introduce affordable healthcare products and services for this demographic. During the process, they can create a social impact and generate profits to sustain their businesses (Agarwal et al., Reference Agarwal, Chakrabarti, Brem and Bocken2018).
To serve low-income customers in the health market, social entrepreneurs should be innovative, as they may have to work with several resource constraints (Morais-da-Silva et al., Reference Morais-da-Silva, Segatto and Bezerra-de-Sousa2020; Shaw & Carter, Reference Shaw and Carter2007; Weidner et al., Reference Weidner, Rosa and Viswanathan2010). In this respect, social entrepreneurs can also deliver more affordable, accessible, and acceptable healthcare solutions to low-income individuals (Bhattacharyya et al., Reference Bhattacharyya, Khor, McGahan, Dunne, Daar and Singer2010). For instance, a study by Vickers et al. (Reference Vickers, Lyon, Sepulveda and McMullin2017) described how social enterprises adopted new or improved existing health services for their communities, especially for vulnerable groups. Social enterprises attempted to meet their communities’ healthcare needs with “value for money” strategies. Therefore, the contributions of social enterprises can take several forms such as improvements to current systems, solution creation, and the invention of new approaches for improving health conditions among low-income individuals (Seelos & Mair, Reference Seelos and Mair2005).
Second, through various programs and services for socially vulnerable groups, social enterprises can offer health interventions to improve mental and physical health (Chan, Reference Chan2016; Ferguson, Reference Ferguson2007). For instance, Ferguson and his colleagues found that social enterprise-based intervention (SEI) models, such as mentoring, job skills training, and clinical service referrals, positively affected the mental health status of homeless youth who participated in such programs (Ferguson, Reference Ferguson2007; Ferguson & Islam, Reference Ferguson and Islam2008; Ferguson & Xie, Reference Ferguson and Xie2008). In addition, recent case studies have also illustrated that participants who involved themselves in the physical activities provided by social enterprises experienced physical recovery or improved physical health (Ferguson & Islam, Reference Ferguson and Islam2008; Macaulay et al., Reference Macaulay, Mazzei, Roy, Teasdale and Donaldson2018; Munoz et al., Reference Munoz, Farmer, Winterton and Barraket2015). In this regard, social enterprises are thus suggested as potential spaces of well-being, where disadvantage people can experience therapeutic landscapes (Farmer et al., Reference Farmer, De Cotta, McKinnon, Barraket, Munoz, Douglas and Roy2016; Munoz et al., Reference Munoz, Farmer, Winterton and Barraket2015).
Several studies have employed the capability approach promoted by Sen (Reference Sen1992) and Nussbaum (Reference Nussbaum2000) to discuss how social enterprises can contribute to individual empowerment and realization of well-being (Chan et al., Reference Chan, Ryan and Quarter2017; Munoz et al., Reference Munoz, Farmer, Winterton and Barraket2015; Tanekenov et al., Reference Tanekenov, Fitzpatrick and Johnsen2018; Weaver, Reference Weaver2018). Based on improvements in their physical and mental health described above, participants were able to obtain relevant skills and qualifications that could increase their employment opportunities. As individuals gain greater access to income, they become more likely to feel self-esteem, empowerment, and social integration, which can positively affect their health and quality of life (Haugh, Reference Haugh, Mair, Robinson and Hockerts2006; Munoz et al., Reference Munoz, Farmer, Winterton and Barraket2015; Roy et al., Reference Roy, Donaldson, Baker and Kerr2014; Teasdale, Reference Teasdale2010).
Finally, social enterprises can help vulnerable people feel a sense of connectedness by acting as boundary spanners (Caló et al., Reference Caló, Roy, Donaldson, Teasdale and Baglioni2019; Farmer et al., Reference Farmer, De Cotta, McKinnon, Barraket, Munoz, Douglas and Roy2016). Boundary spanning refers to activities promoting significant transactions with out-group members that can facilitate intergroup contacts and effective intergroup relationships (Richter et al., Reference Richter, West, Van Dick and Dawson2006). Frequent contacts with other groups result in better communication and understanding of the values, cultures, and norms of two or more domains (Kilpatrick et al., Reference Kilpatrick, Auckland, Johns, Whelan and Doyle2007). In this vein, social enterprises span the domains of socially excluded people and local community to integrate marginalized people into the wider community (Farmer et al., Reference Farmer, De Cotta, McKinnon, Barraket, Munoz, Douglas and Roy2016).
Previous studies discerned that social enterprises act as boundary spanners by linking socially disconnected people to supportive environments in which social capital and trust can be created (Caló et al., Reference Caló, Roy, Donaldson, Teasdale and Baglioni2019). For instance, a recent study of Caló et al. (Reference Caló, Roy, Donaldson, Teasdale and Baglioni2019) reported that beneficiaries who had experienced chronic hospitalization and illness experienced “normality” and felt social reconnection, which can foster well-being, through the healthcare service provided by a social enterprise. In a similar approach, Barraket and Archer (Reference Barraket and Archer2010) described that community-based social enterprises promoted social inclusion through economic participation, social participation, civic participation, and access to various local and non-local services that could increase the well-being of community residents. Farmer et al. (Reference Farmer, De Cotta, McKinnon, Barraket, Munoz, Douglas and Roy2016) also suggested that several members and volunteers working for social enterprises play significant roles in connecting socially vulnerable people to community life.
Hence, it is expected that social enterprises can contribute to the health and well-being of socially vulnerable people in local communities through various channels. However, it is notable that these mechanisms are not mutually exclusive, which implies that the supply of affordable healthcare services, building capability to prevent social isolation in local communities, and boundary spanning during transactions and communication directed at increasing social trust are closely related.
Two Types of Social Enterprises in South Korea
It should be noted that the effectiveness of social enterprises in improving the health conditions of low-income residents can largely be influenced by their capacity to promote their missions (Caló et al., Reference Caló, Roy, Donaldson, Teasdale and Baglioni2019; Diochon & Anderson, Reference Diochon and Anderson2009). It means that not all social enterprises trying to increase the well-being of socially vulnerable people are effective. Access to available financial and human resources can be a critical factor affecting the performance of social enterprises (Caló et al.,, Reference Caló, Roy, Donaldson, Teasdale and Baglioni2019). To evaluate the resources and capacities of social enterprises, this study primarily explores two different types of social enterprises in South Korea in terms of a certification system managed by the Korea Social Enterprise Promotion Agency and government ministries, while there exist a variety of models of social enterprise in the country (Bidet et al., Reference Bidet, Eum and Ryu2018).
The first type of social enterprises is certified social enterprises, referring to entities that are registered as formal social enterprises with legal and relevant requirements based on the Social Enterprise Promotion Act enacted in 2006. The act clarifies that certified social enterprises should fulfil several administrative and financial conditions, such as sufficient profit making, employment of disadvantaged people, and a participatory decision-making process. Once they become certified social enterprises, they are eligible to receive financial and institutional support, such as subsidies for employees’ salaries, public procurements, R&D investments for innovation, tax exemptions, and subsidies for social insurance fees.
The second type is preliminary social enterprises, indicating informal social enterprises as they do not meet the specific legal requirements mentioned above. The differences between preliminary and certified social enterprises can be found in the process of business operations and financial support received from the government. Preliminary social enterprises are not sufficiently profitable to enable sustained operations, and lack participatory decision-making processes with interested groups, such as stakeholders and consumers. Hence, they are excluded from tax exemptions and subsidies for social insurance fees though other benefits and support provided to them are akin to those offered to certified enterprises. Therefore, it is obvious that preliminary social enterprises have lower capacities to generate sufficient profits and less available financial resources from the government compared to certified social enterprises.
Though the primary purpose of this study is not to explore the effects of financial support received from the government, it is noteworthy that certified social enterprises with abundant financial resources from their business activities and government are likely to achieve their social missions. For instance, recent studies illustrated that government funding and subsidy for certified social enterprises are positively associated with their social performance, such as employment of disadvantaged people and investment in community development (Choi et al., Reference Choi, Berry and Ghadimi2020; Kim & Moon, Reference Kim and Moon2017). These empirical findings can be understood by the argument that institutionally supportive frameworks and financial support enable social enterprises to promote social values because these favorable environments can protect them from pure market risks (Defourny & Nyssens, Reference Defourny and Nyssens2012).
To conclude, we posit that certified social enterprises with higher capacity are more likely to respond to the unmet needs of low-income people than preliminary social enterprises. Certified social enterprises have more financial resources at their disposal from their sufficient profitability and government support, and a more desirable decision-making process with their varied stakeholders. Despite the concern that grants and subsidies from governments may lead to weak autonomy, the available resources of social enterprises largely affect the extent of finding and addressing the needs of socially disadvantaged people. In addition, participatory decision-making processes can help make better decisions for socially vulnerable people in local communities.
Data and Methodology
Data
The data used in the analysis were collected from three independent sources. For the individual level, we used data from the 2017 Korean Community Health Survey (KCHS), which was conducted through collaborative processes among the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, various universities, and local community health centers. This survey has been conducted annually since 2008 with the aim of collecting standardized raw data that can be used while designing public health policies. As of 2017, the survey had covered 17 provinces and 254 cities and relevant entities across the nation with 228,381 samples.
Defining low-income residents is critical since how low-income residents are measured affects the estimation. To prevent arbitrary measurement of low-income people, the annual standard median income of the country, which has been adjusted and reported by the central government since 1973, was utilized (Ministry of Health & Welfare, 2016). Based on the annual report, we defined low-income individuals as those who earned less than 50% of the monthly median income, which is a popular and practical way to define low-income people (Spicker, Reference Spicker2012). As the median income for one person per month was about 1449 USD (1,652,931 KRW) in 2017, we set the cut-off value for low-income residents at approximately 724 USD (826,466 KRW). Among the whole sample, it was found that low-income individuals who earned less than the cut-off were 45,811 and accounted for 20.06% of the whole sample, corresponding to the lowest income quintile. Finally, we used 44,026 samples after excluding the missing data.
At the local level, the number of social enterprises and control variables, which are explained below, were obtained from the Korea Social Enterprise Promotion Agency and the Statistics Korea, respectively.
Data Measurement
In order to obtain robust results, we employed two dependent variables. Participants’ self-rated health (SRH) was measured considering their answer to the question: “Overall, how do you feel about your health?” On the one hand, this study employed a five-point Likert scale for a multilevel ordered logistic regression model, ranging from 1 to 5 (1 = “very poor,” 2 = “poor,” 3 = “fair,” 4 = “good,” and 5 = “very good”). On the other hand, SRH was measured using a dummy variable for a multilevel logistic regression, dichotomized into “good” (responses 3, 4, or 5) and “poor” (responses 1 or 2) to be consistent with previous studies (Meng & Chen, Reference Meng and Chen2014).
Our main independent variable was the number of social enterprises. It is notable that we included two types of social enterprises, certified and preliminary, due to their different characteristics as described in the previous section. For this reason, we calculated the number of certified and preliminary social enterprises divided by the number of for-profit firms per 100,000 inhabitants as of 2017.
This study also employed multiple control variables, which can have different effects on the SRH of low-income individuals. On the one hand, at the individual level, we included several demographic and socioeconomic variables, such as age, gender, income, education, marital status, employment, trust, and friendship based on previous studies (Baron-Epel & Kaplan, Reference Baron-Epel and Kaplan2001; Deeming, Reference Deeming2013; Fassio et al., Reference Fassio, Rollero and De Piccoli2013; Franzini & Fernandez-Esquer, Reference Franzini and Fernandez-Esquer2006; Meng & Chen, Reference Meng and Chen2014; Szwarcwald et al., Reference Szwarcwald, Souza-Júnior, Esteves, Damacena and Viacava2005; Van der Horst & Coffé, Reference Van der Horst and Coffé2012). On the other hand, at the local level, we considered several variables, including density, the number of doctors, and the welfare budgets of local governments following the extant studies illustrating the impact of local context on residents’ subjective health (Fassio et al., Reference Fassio, Rollero and De Piccoli2013; Forsyth et al., Reference Forsyth, Oakes, Schmitz and Hearst2007; Kim, Reference Kim2011; Veenhoven, Reference Veenhoven2000).
Specific measurements of variables used in the analyses are presented in Table 1.
Table 1 Description of variables

Variables |
Measurement |
|---|---|
Dependent variable |
|
Self-rated health |
1–5 Likert scale: 1 = Very poor; 2 = Poor; 3 = Fair; 4 = Good; and 5 = Very good |
Dummy variable: 1 = Good; and 0 = Poor |
|
Independent variable |
|
Social enterprise |
Number of social enterprises/(number of for-profit firms/100,000 inhabitants) |
Control variable |
|
Individual level |
|
Age |
2017–the year of birth |
Sex |
1 = male; and 0 = Female |
Income |
1 = less than approximately 500 US dollars; and 0 = more than approximately 500 US dollars |
Education |
1 = lower secondary school and below; 2 = upper secondary school; 3 = undergraduate; and 4 = graduate and above |
Marital status |
1 = married; and 0 = otherwise |
Employment |
1 = employed; and 0 = otherwise |
Trust |
1 = trust respondents’ neighborhoods; and 0 = otherwise |
Meeting with friends |
1 = less than once a month; 2 = once a month; 3 = two to three times a month; 4 = once a week; 5 = two to three times a week; and 6 = more than four times a week |
Local level |
|
Density |
Ln (number of people per kilometer) |
Doctor |
Number of doctors/(residents /1000 inhabitants) |
Welfare budget |
Percentage of local governments’ budget for welfare |
Analytical Method
Although SRH has been researched at the individual level, it is desirable to utilize a multilevel analysis to examine social enterprises as a contextual factor for low-income individuals’ subjective health. The use of a multilevel framework can allow for variations in SRH to be determined by individual factors and local factors simultaneously (Murayama et al., Reference Murayama, Fujiwara and Kwachi2012). Furthermore, multilevel analysis can provide much richer data by analyzing the extent of the relationship between local-level differences and SRH (Habibov & Afandi, Reference Habibov and Afandi2011).
Therefore, we analyzed the relationship between social enterprises and low-income residents’ SRH using multilevel logistic regression and multilevel ordered logistic regression with the following models. The level 1 model covered individual variables, whereas the level 2 model dealt with local attributes. Let
![]() refer to the probability that low-income residents, the ith individual in jth city and any equivalent entities, evaluate their SRH among the categories.
refer to the probability that low-income residents, the ith individual in jth city and any equivalent entities, evaluate their SRH among the categories.
SRH is initially a binary decision between
![]() = 1 denoting good SRH and
= 1 denoting good SRH and
![]() = 0 denoting poor SRH for the multilevel logistic model.
= 0 denoting poor SRH for the multilevel logistic model.
Let
![]() through
through
![]() refer to k predictor variables at the individual level (i.e., age, gender, income, education, marital status, employment, trust, and friendship). Let
refer to k predictor variables at the individual level (i.e., age, gender, income, education, marital status, employment, trust, and friendship). Let
![]() through
through
![]() refer to the m predictor variables at the local level (i.e., social enterprises, population density, number of doctors, and welfare budget).
refer to the m predictor variables at the local level (i.e., social enterprises, population density, number of doctors, and welfare budget).
Then, the dependent variable has five categories (very poor, poor, fair, good, and very good) as a set of cut-points on the link for each individual. A link transformation of
![]() corresponds to sequential positions on the sample (
corresponds to sequential positions on the sample (
![]() for the multilevel ordered logistic model:
for the multilevel ordered logistic model:
In the models, the effect of each independent variable was assumed to be a fixed parameter that had to be estimated. However, there was a random intercept: the large proportion of total variance in SRH results from city level differences. All independent variables were centered on their means, as centered data can increase the interpretability of intercept terms (Kreft et al., Reference Kreft, De Leeuw and Aiken1995).
The coefficients of all the models were converted into odds ratios (ORs) with 95% credible intervals (CIs). To explore the impact of the local level context and the model fit, we estimated intra-class correlation (ICC) for the multilevel logistic regression and multilevel ordered logistic regression. The analyses were conducted using the statistical software package STATA 15.0 with the melogit command for the multilevel logistic regression and the meologit command for multilevel ordered logistics regression.
Results
The Attributes of Respondents
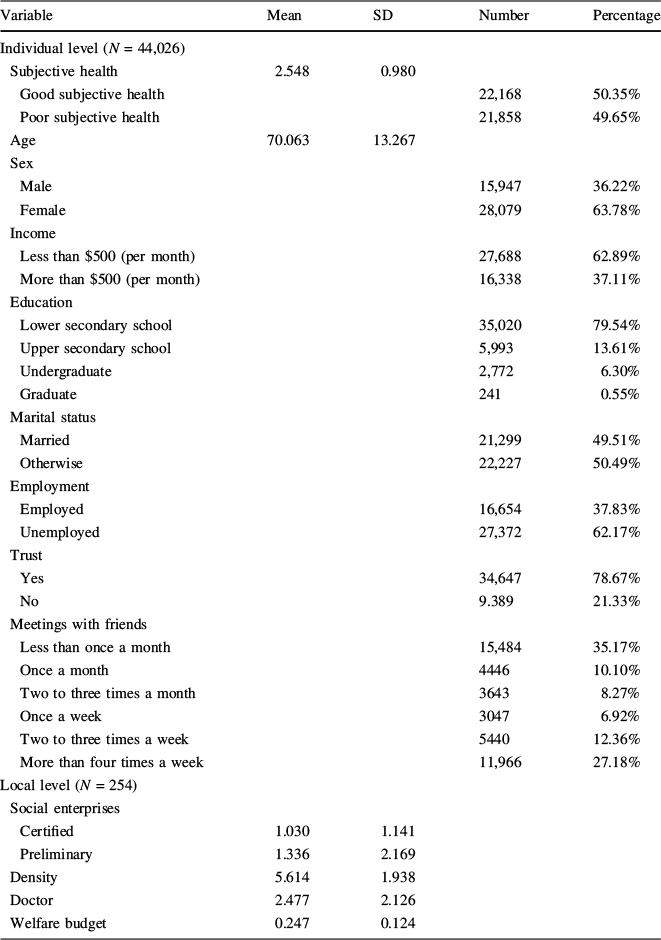
Table 2 presents the descriptive statistics of the selected variables. In the case of the individual level variables, there were distinctive features regarding the demographic and socio-economic variables. The average age was 70.1, which implied that elderly people made up a significant proportion of the low-income group, and respondents aged above 60 years formed about 84.4% of the sample. Regarding gender differences, females formed 63.8% of the sample. In addition, almost 62.9% of respondents earned less than 500 US dollars per month, which could be explained by the large proportion of elderly people in the sample. About 79.5% of respondents selected lower secondary school as their level of education. With regard to employment, 62.1% of the respondents did not have jobs for income. Thus, low-income respondents tended to be elderly, females, less educated, and unemployed.
Table 2 Descriptive statistics

Variable |
Mean |
SD |
Number |
Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Individual level (N = 44,026) |
||||
Subjective health |
2.548 |
0.980 |
||
Good subjective health |
22,168 |
50.35% |
||
Poor subjective health |
21,858 |
49.65% |
||
Age |
70.063 |
13.267 |
||
Sex |
||||
Male |
15,947 |
36.22% |
||
Female |
28,079 |
63.78% |
||
Income |
||||
Less than $500 (per month) |
27,688 |
62.89% |
||
More than $500 (per month) |
16,338 |
37.11% |
||
Education |
||||
Lower secondary school |
35,020 |
79.54% |
||
Upper secondary school |
5,993 |
13.61% |
||
Undergraduate |
2,772 |
6.30% |
||
Graduate |
241 |
0.55% |
||
Marital status |
||||
Married |
21,299 |
49.51% |
||
Otherwise |
22,227 |
50.49% |
||
Employment |
||||
Employed |
16,654 |
37.83% |
||
Unemployed |
27,372 |
62.17% |
||
Trust |
||||
Yes |
34,647 |
78.67% |
||
No |
9.389 |
21.33% |
||
Meetings with friends |
||||
Less than once a month |
15,484 |
35.17% |
||
Once a month |
4446 |
10.10% |
||
Two to three times a month |
3643 |
8.27% |
||
Once a week |
3047 |
6.92% |
||
Two to three times a week |
5440 |
12.36% |
||
More than four times a week |
11,966 |
27.18% |
||
Local level (N = 254) |
||||
Social enterprises |
||||
Certified |
1.030 |
1.141 |
||
Preliminary |
1.336 |
2.169 |
||
Density |
5.614 |
1.938 |
||
Doctor |
2.477 |
2.126 |
||
Welfare budget |
0.247 |
0.124 |
||
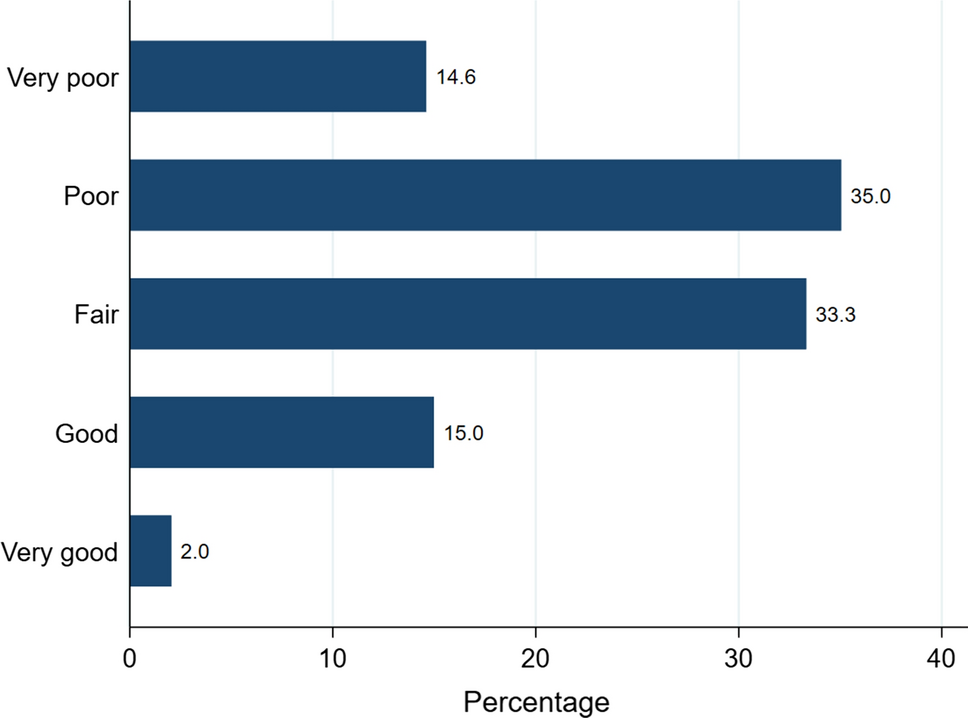
Figure 1 illustrates the distribution of SRH among the respondents. Respondents who answered with “poor” formed the largest portion (35.1%), followed by those who evaluated SRH to be “fair” (33.3%). The percentages of respondents who reported their SRH as being “very poor” and “good” had similar percentages, reaching about 15% each. The percentage of respondents who answered “very good” formed about 2% of the whole sample.

Fig. 1 Proportion of SRH among low-income respondents
The Results of Multilevel Logistic Regression
Table 3 shows the estimation results obtained from the multilevel logistic regression. We utilized a series of four models: Model 1 was a null model without any explanatory variables, which served as a benchmark for the size of the local-level difference in all the models. Model 2 included the individual-level demographic and socio-economic variables without any local level variables. Models 3 and 4 added social enterprises and local-level variables to the individual-level model. Models 3 and 4 included certified and preliminary social enterprises, respectively. These two models allowed us to investigate whether social enterprises could affect low-income individuals’ SRH and whether this relationship was affected by the type of social enterprise after controlling for all individual and local variables.
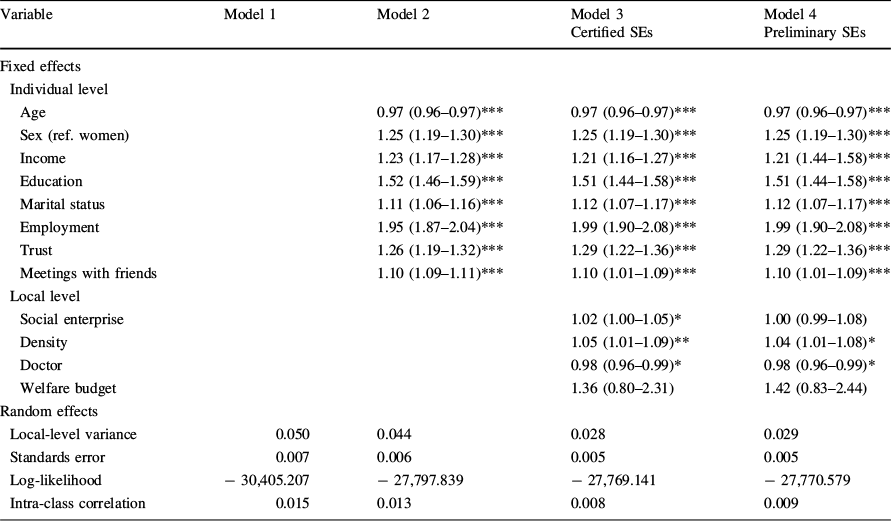
Table 3 Multilevel logistic regression estimates (odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals) and variance components of good health status (N = 44,026 individuals nested within N = 254 cities and equivalent entities)

Variable |
Model 1 |
Model 2 |
Model 3 |
Model 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Certified SEs |
Preliminary SEs |
|||
Fixed effects |
||||
Individual level |
||||
Age |
0.97 (0.96–0.97)*** |
0.97 (0.96–0.97)*** |
0.97 (0.96–0.97)*** |
|
Sex (ref. women) |
1.25 (1.19–1.30)*** |
1.25 (1.19–1.30)*** |
1.25 (1.19–1.30)*** |
|
Income |
1.23 (1.17–1.28)*** |
1.21 (1.16–1.27)*** |
1.21 (1.44–1.58)*** |
|
Education |
1.52 (1.46–1.59)*** |
1.51 (1.44–1.58)*** |
1.51 (1.44–1.58)*** |
|
Marital status |
1.11 (1.06–1.16)*** |
1.12 (1.07–1.17)*** |
1.12 (1.07–1.17)*** |
|
Employment |
1.95 (1.87–2.04)*** |
1.99 (1.90–2.08)*** |
1.99 (1.90–2.08)*** |
|
Trust |
1.26 (1.19–1.32)*** |
1.29 (1.22–1.36)*** |
1.29 (1.22–1.36)*** |
|
Meetings with friends |
1.10 (1.09–1.11)*** |
1.10 (1.01–1.09)*** |
1.10 (1.01–1.09)*** |
|
Local level |
||||
Social enterprise |
1.02 (1.00–1.05)* |
1.00 (0.99–1.08) |
||
Density |
1.05 (1.01–1.09)** |
1.04 (1.01–1.08)* |
||
Doctor |
0.98 (0.96–0.99)* |
0.98 (0.96–0.99)* |
||
Welfare budget |
1.36 (0.80–2.31) |
1.42 (0.83–2.44) |
||
Random effects |
||||
Local-level variance |
0.050 |
0.044 |
0.028 |
0.029 |
Standards error |
0.007 |
0.006 |
0.005 |
0.005 |
Log-likelihood |
− 30,405.207 |
− 27,797.839 |
− 27,769.141 |
− 27,770.579 |
Intra-class correlation |
0.015 |
0.013 |
0.008 |
0.009 |
*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. All independent variables are entered as centered variables
In Model 1, a 1.5% variance was observed in low-income individuals’ subjective health at the local level. After we added individual variables and local-level confounders, the ICC decreased, as shown in Models 2–4. In addition, the values of log-likelihood decreased as we added variables to Model 1. This indicates that Models 3–4 had a better fit compared to Model 2 in accordance with the principle of “the smaller the better” (Rathmann et al., Reference Rathmann, Ottova, Hurrelmann, de Looze, Levin, Molcho and Richter2015).
Looking at the estimates for certified social enterprises in Model 3, which consisted of individual- and local-level compounds, the analysis results indicated that certified social enterprises were positively related with SRH (OR = 1.02, p < 0.05). However, statistical significance was removed in the case of preliminary social enterprises in Model 4. Therefore, it could be inferred that only government-certified social enterprises can improve low-income individuals’ SRH, whereas preliminary social enterprises are not strongly associated with low-income individuals’ SRH.
The Results of Multilevel Ordered Logistic Regression
To obtain robust results with regard to the relationship between social enterprises and low-income respondents’ SRH, we analyzed multilevel ordered logistic regressions, as presented in Table 4. Similar to Table 3, Model 5 was an empty model, and Model 6 included individual-level variables. Models 7–8 added two types of social enterprises and local-level variables into Model 6. We summarized the ICC values, which were obtained from different models, to confirm whether the application of multilevel analysis was appropriate. As shown, the results of the ICC in Models 7–8 decreased compared to Model 6; this indicated that a multilevel analysis was preferable to a single level analysis.
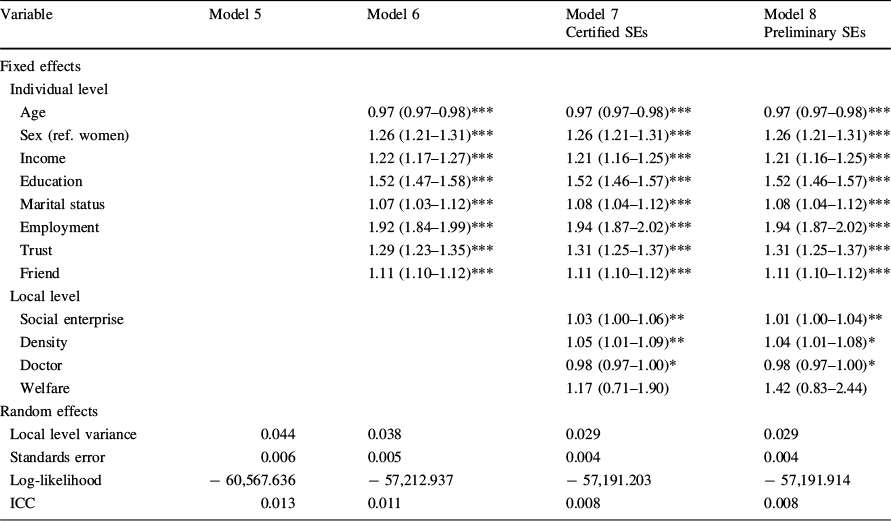
Table 4 Multilevel ordered logistic regression estimates (odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals) and variance components of good health status, N = 44,026 individuals nested within N = 254 cities and equivalent entities

Variable |
Model 5 |
Model 6 |
Model 7 |
Model 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Certified SEs |
Preliminary SEs |
|||
Fixed effects |
||||
Individual level |
||||
Age |
0.97 (0.97–0.98)*** |
0.97 (0.97–0.98)*** |
0.97 (0.97–0.98)*** |
|
Sex (ref. women) |
1.26 (1.21–1.31)*** |
1.26 (1.21–1.31)*** |
1.26 (1.21–1.31)*** |
|
Income |
1.22 (1.17–1.27)*** |
1.21 (1.16–1.25)*** |
1.21 (1.16–1.25)*** |
|
Education |
1.52 (1.47–1.58)*** |
1.52 (1.46–1.57)*** |
1.52 (1.46–1.57)*** |
|
Marital status |
1.07 (1.03–1.12)*** |
1.08 (1.04–1.12)*** |
1.08 (1.04–1.12)*** |
|
Employment |
1.92 (1.84–1.99)*** |
1.94 (1.87–2.02)*** |
1.94 (1.87–2.02)*** |
|
Trust |
1.29 (1.23–1.35)*** |
1.31 (1.25–1.37)*** |
1.31 (1.25–1.37)*** |
|
Friend |
1.11 (1.10–1.12)*** |
1.11 (1.10–1.12)*** |
1.11 (1.10–1.12)*** |
|
Local level |
||||
Social enterprise |
1.03 (1.00–1.06)** |
1.01 (1.00–1.04)** |
||
Density |
1.05 (1.01–1.09)** |
1.04 (1.01–1.08)* |
||
Doctor |
0.98 (0.97–1.00)* |
0.98 (0.97–1.00)* |
||
Welfare |
1.17 (0.71–1.90) |
1.42 (0.83–2.44) |
||
Random effects |
||||
Local level variance |
0.044 |
0.038 |
0.029 |
0.029 |
Standards error |
0.006 |
0.005 |
0.004 |
0.004 |
Log-likelihood |
− 60,567.636 |
− 57,212.937 |
− 57,191.203 |
− 57,191.914 |
ICC |
0.013 |
0.011 |
0.008 |
0.008 |
*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. All independent variables are entered as centered variables. Cut points are excluded from the output
In Models 7–8, the estimates for the social enterprises showed that both the certified and the preliminary social enterprises could improve SRH, regardless of government certification. Though the odds-ratio of preliminary social enterprises (OR = 1.01, p < 0.01) was lower than that of certified social enterprises (OR = 1.03, p < 0.01), the results implied that preliminary enterprises also enhanced low-income individuals’ SRH.
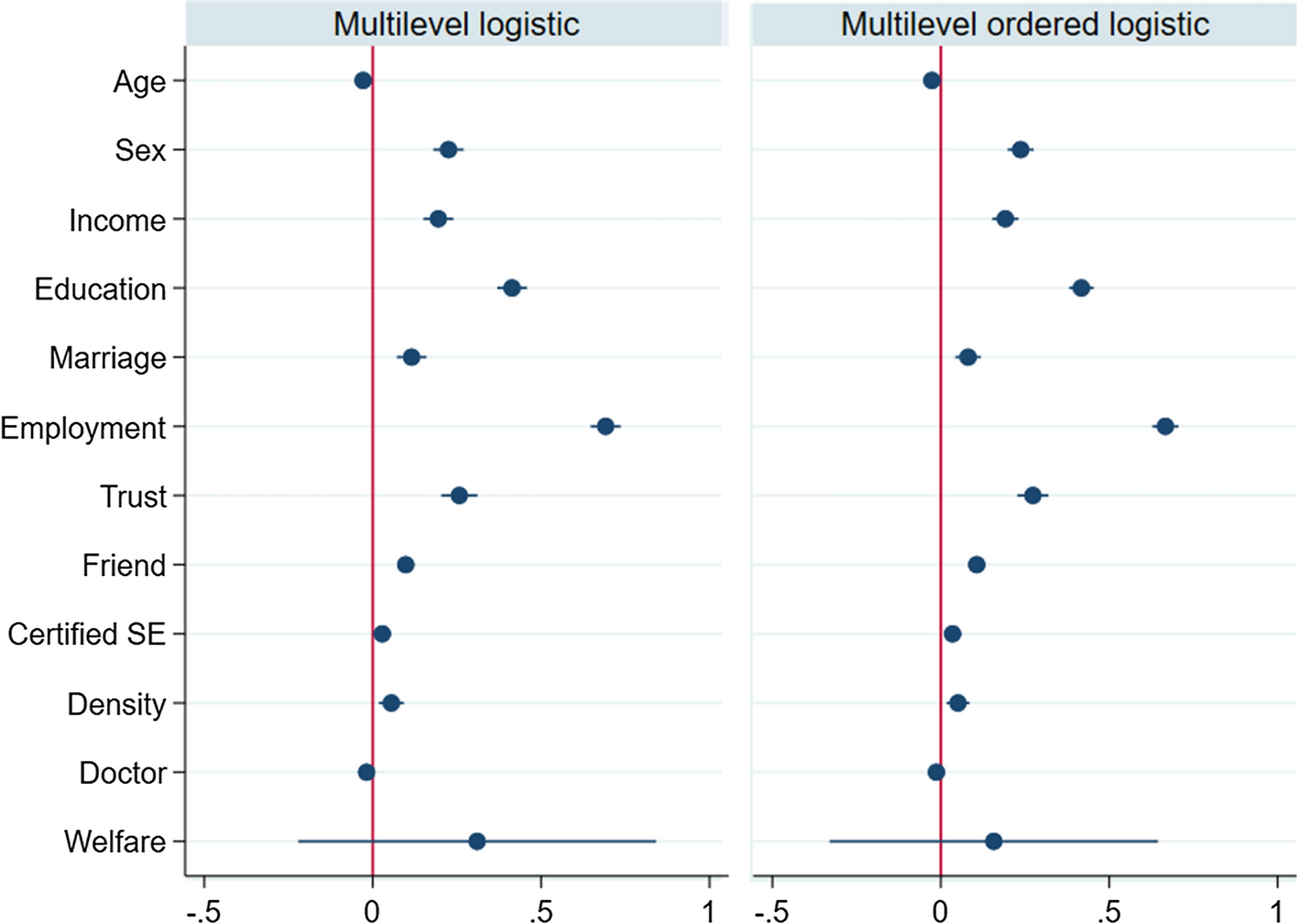
Excluding the statistical differences of social enterprises, the overall individual- and local-level variables showed extremely similar results in Models 2–5 and 6–8. Figure 2 shows the coefficients obtained from the multilevel logistic regression and multilevel ordered logistic regression. Among the individual levels, all individual variables were positively related with the SRH of low-income individuals, and age was the only exception to this trend. At the local level, population density was positively associated with subjective health, while the percentage of welfare budget was not statistically significant though it was positive. In contrast, the number of doctors was negatively associated with the SRH of low-income groups.

Fig. 2 Coefficients obtained from the multilevel logistic and the multilevel ordered logistic regressions. Note: Reference lines were added to show whether the coefficients were significantly different from zero
We more specifically discuss the results of control variables as follows. At the individual level, age was found to be negatively associated with SRH even though the relationship between age and SRH can be biased by the self-reporting of conditions (Baron-Epel & Kaplan, Reference Baron-Epel and Kaplan2001). Like the extant studies reporting a distinction between the sexes (Szwarcwald et al., Reference Szwarcwald, Souza-Júnior, Esteves, Damacena and Viacava2005), the results of this study indicated that men appeared to have better SRH than women. Though the sample used in our analysis was limited to the responses of low-income individuals, a relatively higher income was positively associated respondents’ SRH, which is consistent with previous studies (Fassio et al., Reference Fassio, Rollero and De Piccoli2013). The result showing that a lower education level can lead to poor SRH was also similar to previous studies (Deeming, Reference Deeming2013; Franzini & Fernandez-Esquer, Reference Franzini and Fernandez-Esquer2006). With regard to marital status, married people were more likely to have favorable SRH compared to others in the marital status sub-group, as married people tended to avoid isolation. This finding was similar to that of previous studies (Deeming, Reference Deeming2013; Fassio et al., Reference Fassio, Rollero and De Piccoli2013; Van der Horst & Coffé, Reference Van der Horst and Coffé2012). Turning to employment status, those who were employed were more likely to have better SRH compared to those who were unemployed, as they had the capability to improve their health conditions because of the income they earned from paid work (Deeming, Reference Deeming2013; Franzini & Fernandez-Esquer, Reference Franzini and Fernandez-Esquer2006). In addition, trust and friendship networks also indicated that these interpersonal relationships could help people experience a sense of receiving and providing social support and, thus, build better health (Habibov & Afandi, Reference Habibov and Afandi2011; Van der Horst & Coffé, Reference Van der Horst and Coffé2012).
At the local level, the positive relationship between population density and SRH can be explained by the following trend: densely populated areas tend to benefit low-income individuals because they can increase their accessibility to public transport and employment opportunities (Kim, Reference Kim2011). In addition, living in an area with higher density could accelerate physical activity and overall working, which, in turn, could positively affect SRH (Forsyth et al., Reference Forsyth, Oakes, Schmitz and Hearst2007). Meanwhile, the number of doctors was negatively associated with low-income individuals’ SRH, which is somewhat puzzling. Finally, like the previous study, the percentage of local government’s welfare budget did not improve the SRH of low-income residents (Veenhoven, Reference Veenhoven2000).
Discussion and Conclusion
It has been suggested that social enterprises can enhance health and well-being (Munoz et al., Reference Munoz, Farmer, Winterton and Barraket2015; Roy & Hackett, Reference Roy and Hackett2017; Roy et al., Reference Roy, Donaldson, Baker and Kay2013, Reference Roy, Donaldson, Baker and Kerr2014). However, previous studies dealing with the role of social enterprises in improving physical and mental health conditions have heavily relied on qualitative approaches. Whereas the various channels explaining how social enterprises contribute to the health of socially vulnerable people have been suggested, studies tackling this topic with empirical data are still sparse (Ferguson & Xie, Reference Ferguson and Xie2008; Jang et al., Reference Jang, Kim, Hong, Yoo and Park2018).
Given the paucity of quantitative research on social enterprises, the results obtained from our multilevel analyses reveal the positive effect of social enterprises, particularly the certified ones, on the SRH of low-income individuals. These findings corroborate the argument from illustrative cases demonstrating that social enterprises can enhance the SRH of socially vulnerable people. Furthermore, these results are in line with previous studies illustrating that certified social enterprises can accomplish various social values and performances in the country (Choi et al., Reference Choi, Berry and Ghadimi2020; Kim & Moon, Reference Kim and Moon2017).
The positive relationship between certified social enterprises and the SRH of low-income residents can be explained by two channels. First, it can be interpreted that certified social enterprises can deliver various affordable products and services to low-income individuals, which would directly and indirectly affect SHR (Prahalad, Reference Prahalad2005; Vickers et al., Reference Vickers, Lyon, Sepulveda and McMullin2017). The results indicate the important role of social enterprises in terms of health service delivery specially to low-income people, whereas the welfare budgets in the government sector showed an insignificant estimate. In turn, as reported by previous studies, certified social enterprises can recognize the needs of low-income residents who are dissatisfied by the market and their local government (Allin et al., Reference Allin, Grignon and Le Grand2010).
More importantly, during the transactions between social enterprises and low-income residents, certified social enterprises act as boundary spanners enhancing the SHR of low-income individuals (Caló et al., Reference Caló, Roy, Donaldson, Teasdale and Baglioni2019; Farmer et al., Reference Farmer, De Cotta, McKinnon, Barraket, Munoz, Douglas and Roy2016). This interpretation seems to be persuasive when one remembers the features of low-income respondents: the average age of respondents is more than 70 years, and more than one third of respondents usually meet their friends less than once a month. As such, a large portion of low-income residents are likely to suffer from irregular social interactions and isolation that can negatively affect their SRH and well-being. While the people face limited opportunities for social interaction, communication and interaction with social enterprises make the low-income residents feel socially connected.
Meanwhile, the relationships for preliminary social enterprises were not clear, as the statistical significance obtained from two different analyses were mixed. The insignificant estimate of preliminary social enterprises in the multilevel logistic regression could be because they do not possess sufficient capacity to recognize or meet the social needs of low-income residents in local communities. This lack of capacity of preliminary social enterprises can be due to their insufficient resources (i.e., financial and human resources) and limited involvement of relevant participants in strategic decisions for socially vulnerable people (Caló et al., Reference Caló, Roy, Donaldson, Teasdale and Baglioni2019; Diochon & Anderson, Reference Diochon and Anderson2009). The results illustrate that certified social enterprises with more financial resources and desirable decision-making processes are more effective than preliminary social enterprises in achieving the social mission of enhancing the health conditions of low-income individuals.
Based on these findings, this study draws the following policy implications. First, practitioners in the public sector are suggested to co-design welfare services with social enterprises to understand and reflect the needs of low-income people. As social enterprises communicate and interact with socially vulnerable residents, they can share their opinions derived from boundary spanning activities with practitioners when goods and services are designed. Given that the disparities in healthcare would further enlarge, the information and ideas of social enterprises about the potential needs of low-income people can be utilized in the development of welfare services. We also recommend providing relevant platforms for facilitating on- and off-line mentoring services between certified social enterprises and other social economy organizations, such as preliminary social enterprises, social cooperatives, and community enterprises. The voluntary interactions and communication among various social economy organizations will facilitate the exchange of essential know-how and knowledge that can enhance their abilities to sustain their social missions.
Despite the findings and implications of the current study, it has some limitations. First, it is necessary to consider the effect of income levels while comparing the effects of social enterprises on SRH. Although this study focused on low-income individuals, it is plausible that social enterprises may positively affect middle- and high-income individuals' subjective health. Second, although we included several local confounders, other variables, such as local crime rate (Hanslmaier, Reference Hanslmaier2013) and the level of income inequality (Kelley & Evans, Reference Kelley and Evans2017), could also affect SRH. However, as data are not available at the city-level and for other equivalent entities in the country, it is suggested that relevant local variables should be considered in future studies. Third, although we interpreted social enterprises to be positively associated with SRH among low-income individuals, it does not mean that the relationship between them is causal. A mixed approach combining both qualitative and quantitative methodologies could shed light on the causal relationship between social enterprise and SRH among low-income individuals. Finally, the study results may not be applicable to other countries with different institutions and contextual environments. Comparative studies examining the role of social enterprises in influencing residents’ health at the local level would be helpful to explore further the association between social enterprises and residents’ SRH. Future studies should bear in mind the limitations described above, and seek to further clarify the role of social enterprises in improving the health conditions of low-income people.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education of the Republic of Korea and the National Research Foundation of Korea under Grant (NRF-2018S1A3A2075117).
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Dr. HJ, and Dr. CW commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Declaration
Conflict of interest
The authors report no potential conflict of interest.