Book contents
- Transient Ischemic Attack and Stroke
- Transient Ischemic Attack and Stroke
- Copyright page
- Contents
- Preface to the Second Edition
- Section 1 Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Pathophysiology, and Causes of Transient Ischemic Attacks and Stroke
- Section 2 Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Investigation
- Section 3 Prognosis of Transient Ischemic Attack and Stroke
- Chapter 14 Methods of Determining Prognosis
- Chapter 15 Short-Term Prognosis after Transient Ischemic Attack and Minor Stroke
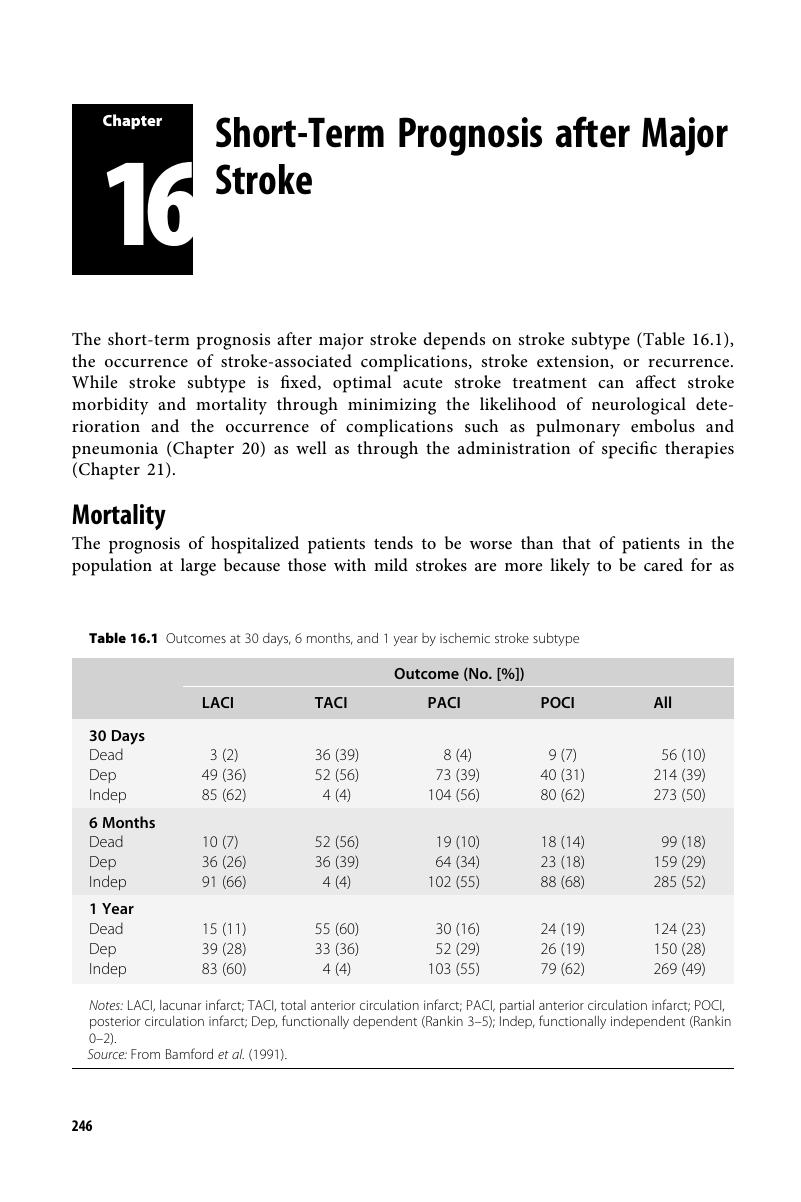
- Chapter 16 Short-Term Prognosis after Major Stroke
- Chapter 17 Long-Term Prognosis after Transient Ischemic Attack and Stroke
- Section 4 Treatment of Transient Ischemic Attack and Stroke
- Section 5 Secondary Prevention
- Section 6 Miscellaneous Disorders
- Index
- References
Chapter 16 - Short-Term Prognosis after Major Stroke
from Section 3 - Prognosis of Transient Ischemic Attack and Stroke
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 August 2018
- Transient Ischemic Attack and Stroke
- Transient Ischemic Attack and Stroke
- Copyright page
- Contents
- Preface to the Second Edition
- Section 1 Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Pathophysiology, and Causes of Transient Ischemic Attacks and Stroke
- Section 2 Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Investigation
- Section 3 Prognosis of Transient Ischemic Attack and Stroke
- Chapter 14 Methods of Determining Prognosis
- Chapter 15 Short-Term Prognosis after Transient Ischemic Attack and Minor Stroke
- Chapter 16 Short-Term Prognosis after Major Stroke
- Chapter 17 Long-Term Prognosis after Transient Ischemic Attack and Stroke
- Section 4 Treatment of Transient Ischemic Attack and Stroke
- Section 5 Secondary Prevention
- Section 6 Miscellaneous Disorders
- Index
- References
Summary
Information
- Type
- Chapter
- Information
- Transient Ischemic Attack and StrokeDiagnosis, Investigation and Treatment, pp. 246 - 252Publisher: Cambridge University PressPrint publication year: 2018
