Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Cheng, Maggie X.
Ling, Yi
and
Sadler, Brian M.
2014.
Wireless ad hoc networks connectivity assessment and relay node deployment.
p.
399.
García Trillos, Nicolás
and
Slepčev, Dejan
2016.
Continuum Limit of Total Variation on Point Clouds.
Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis,
Vol. 220,
Issue. 1,
p.
193.
Cheng, Maggie X.
Ling, Yi
and
Sadler, Brian M.
2017.
Network connectivity assessment and improvement through relay node deployment.
Theoretical Computer Science,
Vol. 660,
Issue. ,
p.
86.
Chalupa, David
Hawick, Ken A.
and
Walker, James A.
2018.
Hybrid Bridge-Based Memetic Algorithms for Finding Bottlenecks in Complex Networks.
Big Data Research,
Vol. 14,
Issue. ,
p.
68.
Davis, Erik
and
Sethuraman, Sunder
2018.
Consistency of modularity clustering on random geometric graphs.
The Annals of Applied Probability,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 4,
García Trillos, Nicolás
and
Slepčev, Dejan
2018.
A variational approach to the consistency of spectral clustering.
Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis,
Vol. 45,
Issue. 2,
p.
239.
Grohs, Philipp
and
Rathmair, Martin
2019.
Stable Gabor Phase Retrieval and Spectral Clustering.
Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics,
Vol. 72,
Issue. 5,
p.
981.
Sakaridis, Christos
Kolotouros, Nikos
Drakopoulos, Kimon
and
Maragos, Petros
2019.
Processing, Analyzing and Learning of Images, Shapes, and Forms: Part 2.
Vol. 20,
Issue. ,
p.
149.
Garcia Trillos, Nicolas
2019.
Variational Limits of $k$-NN Graph-Based Functionals on Data Clouds.
SIAM Journal on Mathematics of Data Science,
Vol. 1,
Issue. 1,
p.
93.
Anis, Aamir
El Gamal, Aly
Avestimehr, A. Salman
and
Ortega, Antonio
2019.
A Sampling Theory Perspective of Graph-Based Semi-Supervised Learning.
IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,
Vol. 65,
Issue. 4,
p.
2322.
Müller, Tobias
and
Penrose, Mathew D.
2020.
Optimal Cheeger cuts and bisections of random geometric graphs.
The Annals of Applied Probability,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 3,
Mulas, Raffaella
2021.
A Cheeger Cut for Uniform Hypergraphs.
Graphs and Combinatorics,
Vol. 37,
Issue. 6,
p.
2265.
Chen, Xiaohui
and
Yang, Yun
2021.
Diffusion K-means clustering on manifolds: Provable exact recovery via semidefinite relaxations.
Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis,
Vol. 52,
Issue. ,
p.
303.
García Trillos, Nicolás
Murray, Ryan
and
Thorpe, Matthew
2022.
From Graph Cuts to Isoperimetric Inequalities: Convergence Rates of Cheeger Cuts on Data Clouds.
Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis,
Vol. 244,
Issue. 3,
p.
541.

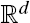 with a smooth boundary. We relate the Cheeger constant of
with a smooth boundary. We relate the Cheeger constant of 