The inclusion of GM plants in animal feed and for human consumption has increased consistently over the past 15 years since they were first cultivated in 1996(Reference James1). During this time, the cultivation area of GM crops has increased eighty-seven-fold reaching 148 million hectares worldwide in 2010, making the procurement of exclusively non-GM crops more difficult and expensive. GM maize is the second most important biotech crop after GM soyabeans(Reference James1) and the first one to have a wider variety of genetic modifications than glyphosate-tolerant soyabean.
Since the introduction of GM crops, much debate, both within and outside the scientific community, has centred on issues related to safety for consumption. The most dominant agronomic traits introduced by genetic engineering include herbicide tolerance, insect resistance (Bt) and stacking of both of these traits(Reference James1). These genetically engineered traits offer the possibility of higher agronomic productivity in times of insect infestation without the use of insecticides and/or the use of less expensive broad-spectrum herbicides for weed control(Reference Bertoni and Marsan2). However, the increased usage of GM crops for direct human consumption and feeding to meat- and milk-producing animals has led to public concern(Reference Paparini and Romano-Spica3). These concerns, however, do not relate to the GM technology itself but to any unintended consequences that may arise from its use. Consumer concerns are mostly related to a perceived risk to health, development of toxicity, allergenicity of the transgenic proteins or the transfer of antibiotic resistance from the plant to bacteria residing in the human gastrointestinal tract(Reference Bertoni and Marsan2). Other concerns, such as gene transfer from GM crops to indigenous plants, reducing biodiversity and influence of the GM crops on non-target species(Reference Paparini and Romano-Spica3–Reference Hug6), are associated with environmental issues.
Bt MON810 maize is engineered to express the truncated Cry1Ab toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis, which confers resistance to the European maize borer. This toxin interacts with the target larvae's intestinal cells disrupting the intestinal lining leading to death(Reference Schnepf, Crickmore and Van Rie7–Reference Broderick, Robinson and McMahon9). However, the toxin is believed to be non-toxic to mammals, birds, reptiles and amphibians due to a lack of specific receptors in the intestinal tract(Reference Schnepf, Crickmore and Van Rie7). The Cry1Ab protein has no homology to any allergenic proteins and was successfully degraded in simulated gastric conditions(10). Trials conducted with Bt maize in pigs, cattle and poultry have shown no significant differences in performance or demonstrated any adverse health effects(Reference Reuter, Aulrich and Berk11–Reference Flachowsky, Aulrich and Bohme14). However, some studies found subtle histopathological changes in rats(Reference Kilic and Akay15) and altered immune responses in mice(Reference Finamore, Roselli and Britti16) and fish(Reference Sagstad, Sanden and Haugland17) that were fed Bt maize. Currently, GM organisms receive European Union authorisation for use following pre-market risk assessment, which focuses on the risk that untoward responses will arise from exposure to GM organisms. The main concern with GM organisms is that the unintended responses may not be evident until a genetically diverse population has been exposed to it for a long period of time. Post-market monitoring of GM organisms may reveal any long-term effects of GM exposure not identified during the short-term pre-market risk assessment(18).
In the present study, we evaluated in pigs the effects of 31 d of feeding Bt MON810 maize compared with an isogenic parent line maize. Particular attention was afforded to changes in growth performance, intestinal morphology and organ pathology and function in an attempt to identify any changes that may serve as an early warning sign for a biological effect. To our knowledge, this is the first study in pigs that has simultaneously evaluated the safety of Bt MON810 maize over such a wide range of physiological processes.
Materials and methods
Experimental design and diets
The pig trial complied with European Union Council Directive 91/630/EEC (outlines minimum standards for the protection of pigs) and European Union Council Directives 98/58/EC (concerns the protection of animals kept for farming purposes) and was approved by, and a licence obtained from, the Irish Department of Health and Children. Ethical approval was obtained from the Teagasc and Waterford Institute of Technology ethics committees. A total of thirty-two crossbred (Large White × Landrace) weanling pigs (entirely males) were weaned at approximately 28 d of age and were blocked by weight and litter, and randomly assigned to one of two dietary treatments: (1) non-GM isogenic parent line of maize (Pioneer PR34N43) and (2) GM maize (Pioneer PR34N44 event MON810). Planted seeds derived from MON810 and its parental control maize (PR34N44 and PR34N43 varieties, respectively) were grown simultaneously side by side in Valtierra, Navarra and Spain. A non-GM starter diet was fed ad libitum for the first 6 d post-weaning during a baseline acclimatisation period and either the non-GM or GM maize experimental diets were fed for the remaining 31 d. The diets were manufactured in the Moorepark feed mill and were formulated to meet or exceed the National Research Council(19) requirements for weanling pigs (Table 1). Stringent quality-control measures were used to avoid cross contamination of non-GM with GM diets. Carry-over in the feed manufacturing system was minimised by flushing the system with non-GM ingredients and the preparation of non-GM diets before diets containing the GM maize. In addition, non-GM soyabean meal was used in the manufacture of all diets. The cereals were ground by a hammer mill through a 3 mm screen before mixing. The diets were pelleted to 5 mm diameter after steam conditioning to 50–55°C. Proximate (FBA Laboratories, Waterford, Ireland) and amino acid analyses (Sciantec Analytical Services Limited, Cawood, UK) were performed on all diets. Representative samples of feed were taken from each treatment before feeding according to Hartnell et al. (Reference Hartnell, Cromwell, Dana and IIFB Committee20). Before analysis, the samples were ground through a 2 mm screen in a Christy Norris hammer mill. The DM was determined by oven drying for 4 h at 103°C. Ash was obtained by incineration in a muffle furnace (Gallenkamp, London, UK) at 550°C overnight. Crude protein was determined as N × 6·25 using a LECO FP – 2000 analyser (Leco Instruments Limited, Stockport, Cheshire, UK). Fat was determined by extraction with perchlorethylene in a Foss Let 15 300 (A/S N. Foss Electric, Hillerod, Denmark) according to the method described by Usher et al. (Reference Usher, Green and Smith21). Crude fibre was measured by a Fibertec semi-automatic system (Tecator, Hoganas, Sweden). Analysis of the carbohydrate fractions, amino acid profile (Sciantec Analytical Services Limited) and proximate composition (FBA Laboratories) of the GM and non-GM maize was also performed (Table 2). The carbohydrate fractions that were quantified included starch, sugar as sucrose, acid-detergent fibre, neutral-detergent fibre, water-soluble carbohydrate, enzyme-resistant starch and acid-detergent lignin. The quality of the manufactured pellets was also assessed, including pellet durability, diameter and hardness, as described previously by MacMahon & Payne(Reference McMahon and Payne22) (Table 1). The GM and non-GM maize was tested for the presence of the cry1Ab gene by MON810 event-specific PCR (IdentiGen, Dublin, Ireland). The GM and non-GM maize was analysed for aflatoxin (B1, B2, G1, G2), ochratoxin, zearalenone, vomitoxin, T2 toxin and fumonisin by ELISA (Oldcastle Laboratories Limited, Meath, Ireland). Both types of maize were also analysed for pesticide residues by testing against a panel of 355 different active substances (Pesticide Control Service, Department of Agriculture, Backweston, Kildare, Ireland).
Table 1 Composition of acclimatisation starter diet and experimental diets (as-is basis, %)
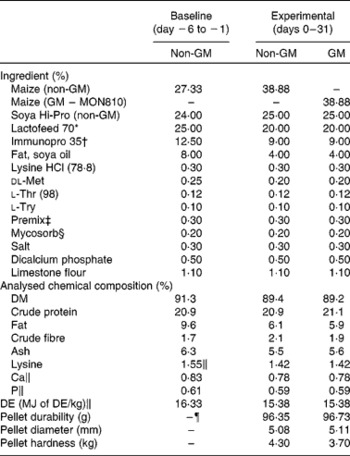
DE, digestible energy.
* Lactofeed 70 contains 70 % lactose, 11·5 % protein, 0·5 % oil, 7·5 % ash and 0·5 % fibre (Volac, Cambridge, UK).
† Immunopro 35 is a whey protein powder product containing 35 % protein (Volac).
‡ Premix provided per kg of complete diet: Cu, 155 mg; Fe, 90 mg; Mn, 47 mg; Zn, 120 mg, I, 0·6 mg; Se, 0·3 mg; vitamin A, 6000 IU; vitamin D3, 1000 IU; vitamin E, 100 IU; vitamin K, 4 mg; vitamin B12, 15 μg; riboflavin, 2 mg; nicotinic acid, 12 mg; pantothenic acid, 10 mg; choline chloride, 250 mg; vitamin B1, 2 mg; vitamin B6, 3 mg; endox, 60 mg.
§ Mycosorb is an organic mycotoxin absorbent (Allech, Inc., Dunboyne, County Meath, Ireland).
∥ Calculated values.
¶ Baseline non-GM maize diet was fed in the form of meal.
Table 2 Proximate, carbohydrate and amino acid analysis of Bt MON810 maize and isogenic parent line maize (as-is basis)
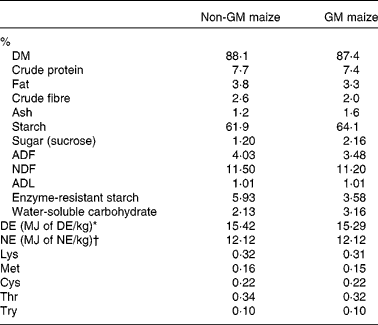
ADF, acid-detergent fibre; NDF, neutral-detergent fibre; ADL, acid-detergent lignin; DE, digestible energy; NE, net energy.
* Calculated from equation no. 24 in Noblet & Perez(Reference Noblet and Perez46) using analysed values on an as-is basis.
† Calculated from equation no. 11 in Noblet et al. (Reference Noblet, Fortune and Shi47) using analysed values on an as-is basis.
Animal housing and management
The pigs were housed individually in a total of four rooms with eight pigs per room (16 pigs/treatment). Each treatment group was represented in each room to avoid additional variations due to environment. The pigs were individually penned in fully slatted pens (1·07 m × 0·6 m) with plastic slats (Faroex, Manitoba, Canada). The pigs had unlimited access to water and feed through a single bowl drinker fitted in each pen and a door-mounted stainless-steel feed trough (410 mm long) with a centre divider, respectively. Heat was provided by a wall-mounted electric bar heater (Irish Dairy Services, Portlaoise, Ireland) and thermostatically controlled. The rooms were naturally ventilated with an air inlet in the door and exhaust by way of a roof-mounted chimney. Temperature was maintained at 28–30°C in the first week and reduced by 2°C per week to 22°C in the fourth week. The pigs were observed closely at least three times daily. Any pigs showing signs of ill health were treated as appropriate. All veterinary treatments were recorded including identity of pig, symptom, medication used and dosage. Individual body weight and feed disappearance were recorded on days − 6, 0, 7, 14, 21, 28 and 31 of the study.
Intestinal, organ and blood sampling
On day 31, ten pigs/treatment were killed by captive bolt stunning followed by exsanguination. The last meal was administered 3 h before killing. The heart, liver, spleen, kidneys and a sample of semi-tendinosus muscle were removed first, to prevent contamination with digesta, followed by the entire gastrointestinal tract. Samples were also taken from the duodenum (15 cm caudal from the pyloric junction), jejunum (midway between the pyloric junction and ileo-caecal junction) and ileum (15 cm cranial from the ileo-caecal junction) for histological analysis (as outlined below). Blood samples were taken from the anterior vena cava of ten pigs per treatment at slaughter (day 31) for plasma collection. Plasma was stored at − 20°C for subsequent blood biochemical analysis. The heart, liver, kidneys and spleen were removed, trimmed of any superficial fat or blood clots and weighed. Samples were then taken from the liver (distal end centre of central lobe), kidney (cortex and medulla), spleen (anterior end of spleen), heart (left ventricle wall) and semi-tendinosus muscle for histological examination.
Intestinal and organ histology
Small intestinal (duodenal, jejunal and ileal) and organ (heart, liver, kidney, spleen and muscle) samples were rinsed in PBS and placed in a No-Tox fixative (Scientific Device Lab, Des Plaines, IL, USA) on a shaker for a minimum of 48 h. The samples were then dehydrated through a graded alcohol series, cleared with a Sub-X clearing agent (Surgipath, Richmond, IL, USA) and embedded in paraffin. Tissue samples were sliced using a microtome (Leica RM2235, Wetzlar, Germany), mounted on a microscope slide and stained with haematoxylin and eosin (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) for light microscopic examination. Determination of the gross morphological parameters of the intestinal structure (villus height and crypt depth) was conducted according to Applegate et al. (Reference Applegate and Lilburn23) and Gao et al. (Reference Gao, Zhao and Gregersen24). For each pig, ten villi and crypts were measured on three to four fields of view, and the means were utilised for statistical analysis. The goblet cell number was determined by periodic acid-Schiff staining according to Thompson & Applegate(Reference Thompson and Applegate25). Positively stained periodic acid-Schiff cells were enumerated on ten villi/sample, and the means were utilised for statistical analysis. Organ samples were examined for any histological indicators of organ dysfunction by an experienced histopathologist and characterised based on the indicators of cell and organ dysfunction listed in Table 3.
Table 3 List of histological indicators used for the identification of cell and organ dysfunction in the liver, heart, spleen, kidneys and muscle of weanling pigs fed GM or non-GM maize for 31 d

Blood biochemistry
Liver and kidney function was assessed by measuring the concentrations of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, γ-glutamyltransferase, creatinine, urea and total protein in plasma taken at slaughter (day 31). Plasma samples were prepared using appropriate kits according to the manufacturer's instructions and analysed using an Alfa Wassermann ACE Clinical Chemistry system (Alfa Wassermann BV, Woerden, The Netherlands).
Statistical analysis
All data were analysed as a complete randomised block design using the GLM procedures of SAS (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA)(26). For all response criteria, the individual pig was the experimental unit. Treatment effect was tested against the residual error term with initial body weight as a blocking factor. Growth performance, gastrointestinal histology and blood biochemistry data were analysed as a one-factor ANOVA using the GLM procedure of SAS. Organ weights were also analysed as a one-factor ANOVA using the GLM procedure of SAS using the final body weight (day 31) as a covariate in the model. The level of significance for all tests was P < 0·05. Trends were reported up to P = 0·10.
Results
Analysis of GM and non-GM maize for the cry1Ab gene, mycotoxins, pesticide residues and carbohydrate fraction
GM maize was found to have a >5 % event-specific cry1Ab gene insert. However, the non-GM maize was also found to have event-specific cry1Ab gene insert but only of 0·20 %. Non-GM maize was also positive for the cp4epsp gene from Round-up Ready Soybean; however, this transgene could not be quantified due to the absence of a reference sample. The levels of all mycotoxins detected in the GM and non-GM maize were below the maximum allowable levels as outlined in the European Union legislation (Commission Regulation (EC) no. 1881/2006). GM and non-GM maize were also negative for all the pesticide residues tested. GM maize was found to have 2·2 % greater starch content, 1·03 % greater water-soluble carbohydrate content, 0·55 % greater acid detergent fibre, 1 % greater sucrose content and 2·35 % lesser enzyme-resistant starch than non-GM maize (Table 2). Neutral detergent fibre, acid detergent lignin and digestible energy content were similar in each of the two maize types. Non-GM and GM maize were also similar in chemical composition and amino acid concentration (Table 2).
Effect of feeding diets containing GM or non-GM maize on health, body weight and growth performance
At 2 weeks after the beginning of the study, two pigs (one from each treatment) were observed to have nasal discharge, difficulties in breathing and a lack of appetite. The pigs were administered with injectable Enrofloxacin (2·5 mg/kg body weight) for 3 d. By the end of the treatment period, both pigs no longer displayed symptoms of ill health. No other pigs displayed signs of ill health throughout the trial.
There were no differences in feed consumption, average daily gain and feed conversion efficiency between the treatment groups during the first 14 d. During days 14–30, the pigs fed the GM maize diet consumed more feed (Table 4; P = 0·02) and had poorer feed conversion efficiency than pigs fed the non-GM maize diet (P = 0·007). Overall, the pigs fed the GM maize diet had higher daily feed consumption (P = 0·03) and had numerically greater average daily gain and heavier body weight on day 30 compared with pigs fed the non-GM maize diet, but this was not statistically significant.
Table 4 Effects of feeding GM or non-GM maize for 30 d on weanling pig growth performance
(Mean values with their standard errors, n 16)
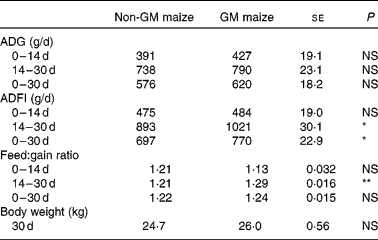
ADG, average daily gain; ADFI, average daily feed intake.
Mean values were significantly different between two treatments: *P < 0·05, **P < 0·01.
Effect of short-term feeding of GM and non-GM maize diets on organ weights
The weights of the heart, liver and spleen did not differ between treatments. However, the pigs fed GM maize diets tended to have heavier kidneys than control pigs (161·0 v. 145·2 g, respectively; P = 0·055; Table 5). There were no differences in organ weights between treatment groups when expressed as organosomatic indices (Table 5).
Table 5 Effects of feeding GM maize or non-GM maize for 31 d on organ weights and organosomatic indices of weanling pigs
(Mean values with their standard errors, n 10)
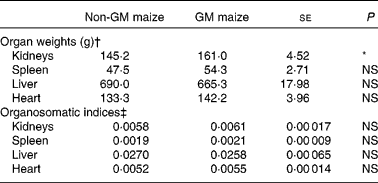
* Mean values were significantly different between two treatments (P < 0·10).
† Organ weights were calculated using final body weight on day 30 as a covariate.
‡ Organosomatic indices were calculated by expressing the organ weights as a fraction of the body weight on day 30.
Effect of feeding GM and non-GM maize diets on small intestinal and organ histology
Short-term feeding of GM maize to weanling pigs had no effect on duodenal, jejunal or ileal villus height, crypt depth or villus height:crypt depth ratio (Table 6). The number of goblet cells per villus in the duodenum, jejunum and ileum of the weaned pigs did not differ between treatment groups following a 31 d feeding period. However, there was a tendency (P = 0·10) for an increase in the number of goblet cells per μm of duodenal villus in control pigs compared with pigs fed GM maize (Table 6). There were no histopathological indicators of organ dysfunction identified in the samples examined (heart, liver, kidney, spleen and muscle).
Table 6 Effects of feeding GM maize or non-GM maize for 31 d on small intestinal histology of weanling pigs†
(Mean values with their standard errors, n 10)

* Mean values were significantly different between two treatments (P < 0·10).
† Ten villi and crypts were measured for each pig and the means were utilised for statistical analysis.
Effect of feeding GM and non-GM maize diets on liver and kidney function
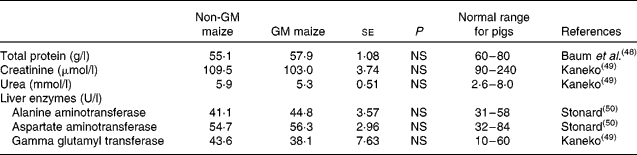
Short-term feeding of GM maize had no effect on plasma total protein or creatinine and urea concentrations, the latter being indicators of kidney function (Table 7). Similarly, there was no effect of treatment on plasma concentrations of the liver enzymes, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase and γ-glutamyl transferase. In addition, all parameters were within the normal range of values for pigs of this age (Table 7).
Table 7 Effects of feeding GM maize or non-GM maize for 31 d on serum concentrations of enzymes and other parameters to assess the liver and kidney function of weanling pigs
(Mean values with their standard errors, n 10)
Discussion
To date, research documenting the effect of feeding Bt MON810 maize to pigs has focused primarily on changes in growth response. To our knowledge, this is the first study in pigs that assesses the effects of feeding Bt MON810 maize on kidney and liver function, intestinal histology and growth performance. Changes in physiological processes in response to GM maize exposure have previously been investigated in other species such as rats, mice, poultry and fish. However, research in this area in pigs has been somewhat limited.
No consistent effects on feed intake and average daily gain have been reported in the numerous pig-feeding trials that have compared GM maize with conventional maize varieties(Reference Bressener, Hyun and Stanisiewski27–Reference Hyun, Bressner and Ellis29). However, Custodio et al. (Reference Custodio, Powers and Huff-Longergan12) reported an increase in average daily feed intake in grow-finish (17–120 kg) pigs fed transgenic Bt11 maize but not in pigs fed Bt11 maize from 60 to 120 kg. In a similar study with MON810 maize, pigs fed GM maize were reported to have increased average daily gain(Reference Piva, Morlacchini and Pietri30). This was, however, attributed to lower concentrations of the mycotoxin, fumonisin B in the GM maize. Similarly, higher weight in zebrafish fed MON810 maize compared with fish fed an isogenic parent-line maize was attributed to a lower level of mycotoxin in the Bt MON810 maize(Reference Sissener, Johannessen and Hevrøy31). In the present study, while there was a significant increase in feed intake following Bt MON810 maize consumption, growth rates and body weight of these pigs were only numerically higher than control pigs, suggesting a minimal effect of GM maize on growth parameters measured. Also, the levels of mycotoxin detected in both the GM and non-GM maize were below maximum allowable levels as outlined by European Union legislation (Commission Regulation (EC) no. 1881/2006) and as such cannot explain the difference in feed intake observed between treatments. Analysis of the carbohydrate fractions of GM and non-GM maize highlighted some differences between the two types of maize. Willis et al. (Reference Willis, Eldridge and Beiseigel32) found that not all types of fibre influence satiety equally, and that resistant starch had the greatest impact on satiety. GM maize fed to pigs in the present study had lower levels of resistant starch than non-GM maize. This may account for the higher feed intake observed in GM maize-fed pigs compared with pigs fed non-GM maize. However, an effect of feeding GM maize on pig growth may not become evident until the pig has been exposed for a longer period of time. With this in mind, we are currently conducting a longer-term pig-feeding study examining the effect of feeding GM maize to pigs from 12 d post-weaning to slaughter (110 d).
In the present 31 d study, we reported no effect of maize type on the absolute weights of the heart, liver and spleen but found a slight increase in the kidney weights of pigs fed the Bt MON810 maize, indicating possible renal toxicity. However, there was no evidence of any histopathological changes in the kidney or other organs examined. Furthermore, kidney and liver function were unaffected, as evidenced by blood biochemistry data. Similarly, no changes in organ weights were found in rats fed GM rice expressing the Cry1Ab protein for 90 d(Reference Schroder, Poulsen and Wilcks33) or in rats fed MON810 maize at inclusion rates of 11 or 33 %(Reference Hammond, Dudek and Lemen34). While some research has raised questions as to whether GM maize is responsible for signs of hepatorenal toxicity(Reference Seralini, Cellier and de Vendomois35), a three-generation study with rats using modified Bt maize reported no significant differences in relative organ weights and only minimal histopathological changes in the liver and kidneys, which were independent of diet(Reference Kilic and Akay15). The increase in kidney weight observed in GM maize-fed pigs in the present study may have arisen as a result of an adaptive phenomenon known as hyperfiltration, which can increase kidney weight in response to elevated serum urea(Reference Martin, Armstrong and Rodriguez36). Fermentable carbohydrates in the diet have been shown to enhance microbial fermentation in the caecum and the colon, thus increasing the demand for urea. This increased demand for urea has been shown to be satisfied through urea diffusion from the blood into the caecum and the colon, which in turn lowers the urea load to be filtered by the kidneys(Reference Younes, Demigné and Behr37, Reference Younes, Garleb and Behr38). The GM maize used in the present study was found to be lower in enzyme-resistant starch than the non-GM variety. Therefore, we hypothesise that there was less hindgut microbial fermentation in the GM maize-fed pigs and less urea therefore diffused from the blood into the hindgut. As a result, more serum urea was excreted by the kidneys, which resulted in hypertrophy. While there were no differences in serum urea concentrations between treatments in the present study, subsequent work by our group has reported an increase in serum urea concentration in GM maize-fed pigs after 30 d of exposure (SG Buzoianu, unpublished results).
The present study demonstrated a lack of effect of Bt MON810 maize on the small intestinal histology of weanling pigs. Similar findings were reported in studies with Atlantic salmon(Reference Sanden, Berntssen and Krogdahl39), where, although changes were observed in the intestines of Atlantic salmon parr, they could not be ascribed to dietary inclusion of GM plant material. There was, however, a slight decrease in the number of goblet cells per micrometre of duodenal villus of GM maize-fed pigs in the present study compared with control pigs. Ganessunker et al. (Reference Ganessunker, Gaskins and Zuckermann40) previously observed an increase in the number of goblet cells in the small intestine of pigs as a result of total parenteral nutrition, which was correlated with a change in gut microbiota, enhanced inflammation and decreased integrity of the mucosal barrier. The present results show that feeding GM maize does not compromise the small intestinal mucosal barrier, but the alterations in goblet cell number observed in the duodenum may be attributed to changes in gut microbial populations observed in these pigs. Preliminary data from an investigation of the gut microbiota of the GM maize-fed pigs would suggest differences in the relative abundance of certain intestinal microbial populations relative to the control group (SG Buzoianu, unpublished results). Changes in intestinal microbiota have been linked with alterations in the number of goblet cells in other studies(Reference Mair, Plitzner and Pfaffl41), and intestinal commensal microbiota have been reported to impact directly on intestinal epithelial functions including those of goblet cells(Reference Kim and Ho42) by producing mucin-degrading enzymes(Reference Macfarlane, Woodmansey and Macfarlane43) or by stimulation of mucin gene expression(Reference Dohrman, Miyata and Gallup44).
In conclusion, the results obtained from the short-term feeding of Bt MON810 maize to weanling pigs have demonstrated no adverse effects on growth performance or intestinal morphology. There were no changes in organ weights, with the exception of a tendency for an increase in kidney weight; however, this was not associated with histopathological or blood biochemical changes. Therefore, based on the parameters investigated in the present study, we can conclude that short-term feeding of Bt MON810 maize to pigs is safe. However, long-term studies are required to fully evaluate safety. Furthermore, since the pig is considered to be an excellent model for man due to similarities in gastrointestinal anatomy and physiology(Reference Moughan, Birtles and Cranwell45), similar responses to Bt MON810 maize consumption could be expected in humans. Therefore, the present findings offer at least some assurance to consumers as to the safety of short-term exposure to GM food and feed ingredients and give a greater insight into expected responses in pigs to short-term Bt MON810 maize exposure. However, to comprehensively evaluate the effects of feeding Bt MON810 maize to pigs, long-term feeding studies are necessary and are currently ongoing.
Acknowledgements
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Union's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement no. 211820 and the Teagasc Walsh Fellowship programme and independently of any commercial input, financial or otherwise. None of the authors had a financial or personal conflict of interest in regard to the present study. P. G. L., G. E. G., M. C. R. and R. P. R. secured the funding for the research. P. G. L and G. E. G designed the study. M. C. W., S. G. B., P. G. L. and G. E. G. conducted the study. M. C. W., S. G. B., G. E. G. and M. C. R. conducted the laboratory analysis. J. P. C. performed the histopathological examination of the organs. M. C. W., S. G. B., P. G. L., G. E. G. and M. C. R. wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.









