Epilepsy ranks fourth among neurological diseases, featuring spontaneous seizures and behavioural and cognitive impairments; it affects approximately 65 million people worldwide. Research indicates that axonal damage, neuroinflammation and oligodendrocyte loss may increase morbidity in epilepsy. Despite the availability of anti-epileptic drugs, 30 % of epileptics are resistant to treatment and > 52 % have serious adverse events(Reference Falco-Walter1). Therefore, new practical approaches to epilepsy management are urgently required.
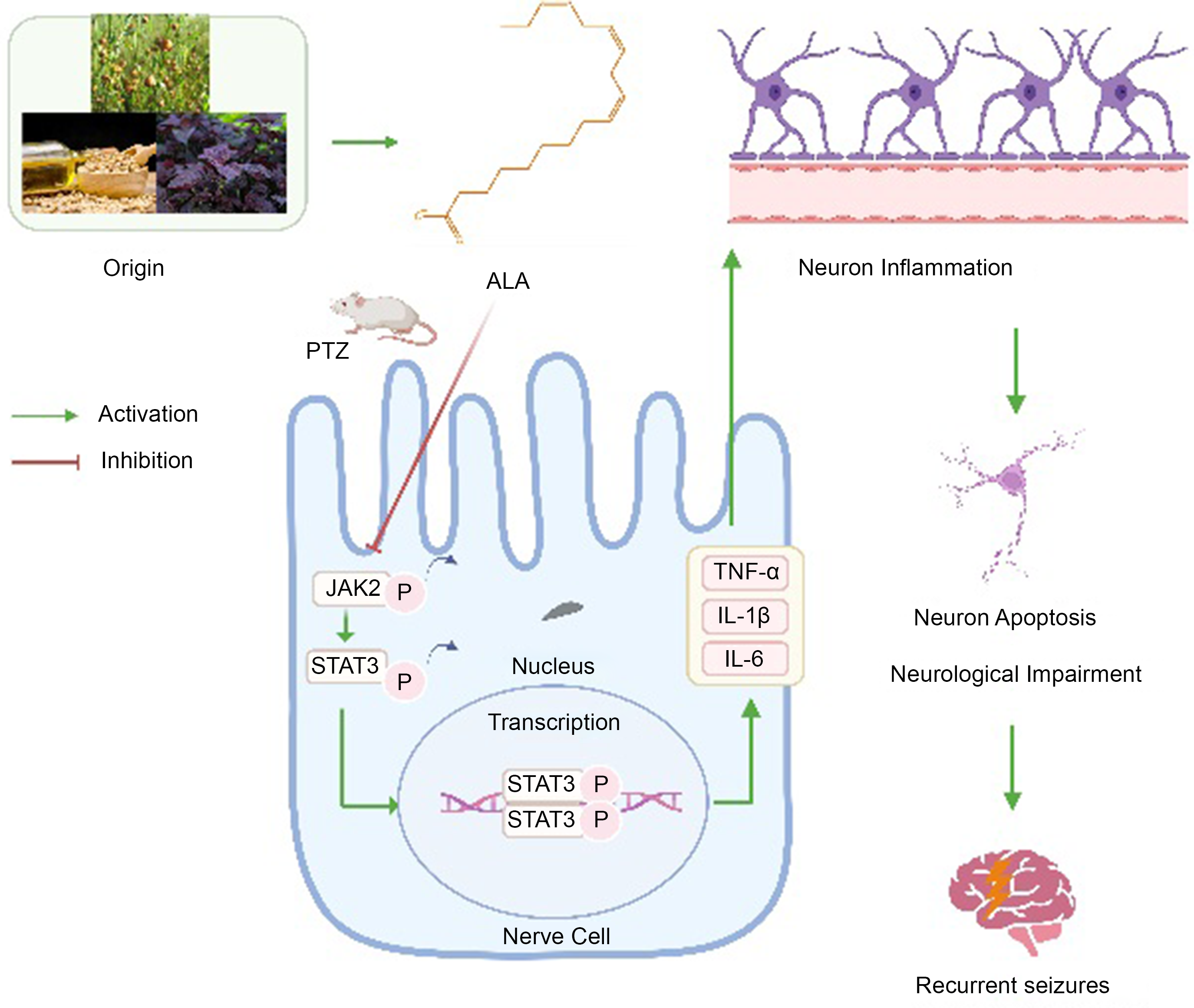
ALA (Fig. 1(a)), a PUFA abundant in walnut and rapeseed oil, is the only n-3 fatty acid produced by vegetables. Accumulating evidence suggests that ALA is essential in the proper operation of the central nervous system (CNS)(Reference Janmohamed, Brodie and Kwan2). ALA consumption alleviates various neuropathological conditions. Studies have found that ALA exhibits anticonvulsant effects, and possible mechanisms may include altering membrane composition of nerve cells, activating PPAR and reducing inflammation(Reference Yamashita, Takahashi and Takashima3,Reference Rezaie, Nasehi and Vaseghi4) . However, the results of clinical studies are inconsistent, and there is limited research on the effects and mechanisms of ALA in relation to epilepsy.

Fig. 1. Structure of α-linolenic acid and diagram flow. (a) The structure of α-linolenic. (b) The diagram flow of experiments. PTZ, pentylenetetrazol.
Status epilepticus (SE)-associated brain inflammation further aggravates SE, with induced neuronal dysfunction(Reference Foster, Rash and King5). During development and after brain damage, JAK2/STAT3 signalling regulates genes controlling cell survival and proliferation, the cell cycle and angiogenesis(Reference El-Gaphar, Abo-Youssef and Halal6). Recently, the potential role of the JAK/STAT pathway in CNS disorders has been investigated(Reference Xie, Li and Dai7,Reference Avila-Mendoza, Delgado-Rueda and Urban-Sosa8) . Researchers first demonstrated the effect of STAT3 polymorphism on epilepsy(Reference Li, Zhang and Liu9). Additional research identified a direct bond between IL-6 and CD5, resulting in STAT3 activation through glycoprotein130 and JAK2, its downstream kinase(Reference Guan, Wang and Liu10). JAK/STAT signalling, a key player in inflammation, can exert major effects on neuronal degeneration, memory formation and synaptic plasticity in the CNS(Reference Alhadidi and Shah11). JAK2/STAT3 pathway induction was detected after traumatic brain damage, pilocarpine and kainic acid-induced sE and ischaemia, indicating this pathway could be targeted to prevent and treat SE(Reference Ahmed, Carrel and Del Angel12). However, it is currently unknown whether ALA can affect sE through the JAK2/STAT3 pathway.
Pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) is a GABA receptor antagonist that induces epilepsy by inhibiting chloride ion channels in downstream signalling pathways. The PTZ model is capable of replicating myoclonic seizures observed in humans, offering a rapid disease model generation process and a low mortality rate. This model has been extensively utilised in anti-epileptic drug research(Reference Che Has13). KM mice, a natural strain without artificial selection or genetic modification, possess a stable genetic background and display neural structure and functionality similarities to humans. As a result, they serve as an ideal model for investigating the development and characteristics of human epilepsy(Reference Rebik, Riga and Smirnov14). In this study, we employed PTZ to induce epilepsy in mice and utilised this model to explore the ameliorative effect of ALA and its underlying mechanisms.
Materials and methods
Chemicals and reagents
ALA (> 98 % purity) and PTZ were provided by Sinopharm Chemical Reagent and Sigma, respectively. All ELISA kits were purchased from Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute. JAK2, STAT3, p-JAK2, p-STAT3 and β-actin antibodies were provided from Bioss Biotechnology Co. Ltd. Secondary antibody, horse radish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG, was obtained from Jackson.
Animals
Thirty male KM mice (18–22 g) from Wuhan University Laboratory Animal Centre were housed at 23·2°C under a 12-h photoperiod, with adequate food and water. All animal protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Wuhan University and carried in accordance with the requirements of the ARRIVE guidelines. All efforts were made to minimise the number of animals used and animal suffering in this study. All animals were intact and unmedicated prior to the experiment.
Experimental group
Thirty KM mice were randomly selected and assigned to three weight-matched groups (n 10, the sample size was calculated according to the resource equation method)(Reference Arifin and Zahiruddin15,Reference Festing16) , including the normal control, model and intervention groups (Fig. 1(b)), with the following treatments.
(1) The normal control group was injected with 0·9 % saline daily. (2) The model group received intraperitoneal administration of PTZ (37 mg/kg) in 0·9 % saline daily until level 4–5 epileptic seizures according to the Racine scale. (3) The intervention group was treated with PTZ as model mice and administered ALA at 4 ml/kg/d (37 mg/10 g/d), based on preliminary studies.
Body weight and survival of the mice
Body weights and survival rate of mice during the modelling process are important indicators reflecting the state of mice. Body weights were obtained every other day to assess animal fitness, and survival rates were determined at the end of the study.
Behavioural grading of seizures with the Racine scale
Epilepsy grade is an important indicator for evaluating the ameliorative effect of ALA. Following PTZ injections, mice were placed in empty cages for 30 min for behavioural assessment of seizure development by a blinded, independent volunteer as 0 (no abnormalities), 1 (mouth and facial movements), 2 (head nodding), 3 (forelimb clonus), 4 (rearing) and 5 (rearing followed by falling or death) points. The latency and score of each seizure were obtained.
Functional tests
Behavioural diseases, for example, depression and learning and memory impairments, occur in mice administered PTZ(Reference Zhou, Zhu and Guo17). Multiple assays were performed with Shenzhen RWD Instruments to assess behavioural changes. Light intensity was determined by the experimental setting.
Open field test
The open field test was performed for assessing psychomotor results and exploratory behaviour in a 45 cm × 45 cm × 40 cm black acrylic box arranged into twenty-five squares, as reported previously(Reference Tasdemir and Colak18).
Forced swimming test
The forced swimming test was performed to detect behaviour associated with depression(Reference Kraeuter, Guest and Sarnyai19), in a 140 mm × 200 mm Plexiglas cylinder containing 150 mm of water at 23–25°C, for 8 min. A blinded investigator scored the mouse’s last 6 min of immobility.
Tail suspension test
The tail suspension test also measures immobility, an indicator of depression, and was performed as described in a previous report(Reference Shao, Cui and Chen20). The entire immobility duration was computed using the software’s event count mode.
Morris water maze
This assay assesses spatial learning and reference memory and was carried out in accordance with the reported methodology(Reference Chernyuk, Bol’shakova and Vlasova21). The number of platform crossings and distance travelled in 60 s were analysed.
Haematoxylin–eosin and Nissl staining
At study end, the animals underwent euthanasia (n 6). Three mice per group were utilised for histological analyses, while the remaining three were used for western blot and ELISA. For haematoxylin–eosin and Nissl staining, the animals were perfused with 0·9 % NaCl and 4 % paraformaldehyde. Brain tissue specimens underwent overnight fixation with 4 % paraformaldehyde and paraffin embedding, deparaffinisation with xylene and rehydration with ethanol gradient. This was followed by haematoxylin–eosin staining or Nissl staining (0·1 % cresyl violet for 3 min), and dehydration. Histopathological hippocampal alterations were observed under an Olympus microscope.
TUNEL
Frozen sections were subjected to terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labelling (TUNEL) analysis upon fixation with 4 % paraformaldehyde. The avidin-labelled fluorescein or ABC kit (Vector) was utilised for this assay.
IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α levels
Euthanasia was performed after the behavioural trials, and hippocampal specimens were obtained (n 3). The specimens underwent homogenisation (10 % w/v) in cold potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7·4). Upon centrifugation (3000 rpm for 10 min) at 4°C, the resulting supernatants were obtained for ELISA assessment of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α with specific kits(Reference Hammitzsch, Chen and de Wit22,Reference Sexton, Hachem and Assi23) .
Molecular docking analysis
ALA’s 3D structure was drawn using Chem3D and imported into Discovery Studio (2019) for pre-processing of small molecules. At the same time, we downloaded the JAK2 (PDB ID: 5AEP) and STAT3 (PDB ID: 5AX3) proteins from the Uniport database and imported them into Discovery Studio (2019). Each imported protein was treated separately to remove unwanted water molecules and structures, followed by hydro-processing protein modification, and selection of docking sites. After the small molecule and protein were processed in ALA, the docking of the half flexible molecule between the protein and ALA was carried out. The association with the highest score for analysis was selected.
Immunoblot
Equal amounts of total protein (20 μ g) were resolved by 10 % SDS-PAGE, followed by transfer unto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. The samples underwent overnight incubation at 4°C with rabbit anti-JAK2 (1:500; Bioss Biotechnology), anti-p-JAK2 (1:500), anti-STAT3 (1:500; Boster Biotechnology) and anti-actin (1:10 000; TDY Biotechnology) primary antibodies, respectively. Then, the membranes were treated with goat anti-rabbit IgG linked to HRP at ambient for 120 min (1:10 000; Aspen). Electrochemiluminescence (ECL Plus) was utilised to identify and quantify signals(Reference Cao, Ma and Zhu24).
Immunofluorescence
After three PBS rinses, brain slices were incubated with PBS containing 10 % BSA and 0·3 % Triton X-100 for 1 h. The samples underwent successive incubations with rabbit polyclonal antibodies targeting p-JAK2 and p-STAT3 (1:500; Boster Biotechnology), respectively (overnight) and FITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibodies (1:1000; Beyotime) for 1 h. Mounting was performed with Prolong Gold antifade reagent (Invitrogen). An Olympus microscope and the Image-Pro software were utilised for analysis(Reference Zhang, Xin and Zhang25).
Statistical analysis
SPSS 19 was utilised for data analysis by unpaired Student’s t test, one-way ANOVA or two-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni test. Prism 6.0 (GraphPad Software) was utilised for further statistical analyses. The log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test was utilised for comparing mouse survival. Data are showed as means and standard deviations.
Results
α-Linolenic acid enhances mouse survival and body weight in mice
Deaths occurred during the course of the experiment, and this was a serious adverse reaction in both the model and intervention groups, and every effort was made to alleviate the animals’ suffering. Mouse survival is shown in online Supplementary Fig. 1(a). Survival was 60 % in PTZ-treated animals at 40 d, v. 100 % in control mice and 80 % in the ALA group. In addition, body weight changes of mice were recorded during the modelling (online Supplementary Fig. 1(b)). In control animals, mean body weight steadily increased from 19·92 g to 32·21 g, indicating a 61·8 % weight gain. However, the PTZ group had markedly reduced mean weight from 19·81 g to 15·71 g (20·7 % reduction; P < 0·05). In the PTZ + ALA group, the average body weight exhibited an upward trend from 20·12 g to 26·41 g (P < 0·01 v. control group). These findings indicated that pre-treatment with ALA by gavage reduced mortality and reversed PTZ-induced body weight loss.
α-Linolenic acid decreases the frequency of epileptic attacks
Mice displayed classic signs after PTZ injection, including early facial and mouth movements, rearing and significant convulsions, which were assessed using the Racine scale(Reference Kikuchi, Takase and Hayakawa26). On day 40, the average seizure level in the model group peaked at 4–5, indicating a propensity towards upgrading. Following therapy with ALA, seizures decreased significantly from days 20 to 40 (P < 0·05). This was not the case for the PTZ-induced group. In control mice, no seizures were seen (Fig. 2(a)). The PTZ group had starkly reduced latency of seizures compared with control mice (P < 0·001; Fig. 2(b)). Interestingly, ALA administration significantly increased the latency of seizures after PTZ treatment (P < 0·05).

Fig. 2. Anticonvulsive properties of ALA in PTZ-induced epilepsy model. In a PTZ-induced epilepsy paradigm, ALA’s effects on seizure score (a) and seizure latency (b) are shown. A significant group-by-day interaction was seen in two-way ANOVA for seizure score and latency to develop seizures. Data are mean ± standard deviation (n 6 in the PTZ group and n 10 in the other groups). n.s., no significance; ###P < 0·001 v. control group; *P < 0·05 and **P < 0·01 v. PTZ group. ALA, α-linolenic acid; PTZ, pentylenetetrazol; SE, status epilepticus.
Effect of α-linolenic acid on depression-like behaviour
The effects of ALA on depression-like behaviour in animals with seizures were investigated by the forced swimming and tail suspension tests. PTZ treatment resulted in a substantial elevation of immobility time (P < 0·05) in the tail suspension test, which was reversed by ALA (P < 0·01). (Fig. 3(a)). In the forced swimming test, the model group demonstrated considerably increased immobility time compared with controls (P < 0·01), and this effect was also reversed by ALA (P < 0·05). (Fig. 3(b)). Jointly, these findings suggested that ALA has significant antidepressant effects.

Fig. 3. Influence by α-linolenic acid on depression-like and exploration behaviour. (a) Tail suspension tests; (b) forced swimming tests; (c) total numbers of crossings in an open field; (d) percentage of open-field crossings in the centre; and (e) time spent in the open field’s centre. Data are mean ± standard deviation (n 6 in the PTZ group and n 10 in the other groups), with #P < 0·05 and ##P < 0·01 compared with control group, and *P < 0·05 and **P < 0·01 compared with PTZ group. One-way ANOVA was carried out with Bonferroni post-test (a)–(e). PTZ, pentylenetetrazol; ALA, α-linolenic acid; TST, tail suspension test; FST, forced swimming test.
α-Linolenic acid enhances animal exploration behaviour
In Kunming mice, a unique open-field activity box was employed to assess spontaneous motor activity and adaptability to a new environment. The model group had considerably fewer total crossings compared with controls (P < 0·05). A marked increase was found after ALA treatment (P < 0·05; Fig. 3(c)), indicating that ALA increased motor skills in epileptic mice. PTZ-treated animals exhibited increased uneasiness and moved about the box more than control mice, with a reduced number of centre crossings and time spent in the centre (P < 0·05 and P < 0·01, respectively). Pre-treatment with ALA starkly enhanced these parameters (P < 0·01; Fig. 3(d) and (e)). The above findings indicated that ALA enhanced exploratory behaviour in epileptic mice.
Effect of α-linolenic acid on spatial cognition and memory
The Morris water maze was used to investigate ALA’s effects on spatial learning and memory (Fig. 4(a)–(g)). All groups were comparable before treatments. Escape latency in the PTZ group increased from day 2 compared with control animals. This effect was particularly noticeable on the last training day (P < 0·05 and P < 0·001 on days 2–3 and 4, respectively). ALA administration reduced escape latency in PTZ-treated animals (P < 0·01 and P < 0·05 on days 2 and 3–4, respectively). In addition, PTZ decreased crossing times considerably v. control mice (P < 0·05). Meanwhile, ALA increased platform crossing significantly in PTZ-treated mice (P < 0·05; Fig. 4(b)). In comparison with control animals, the model group spent less time in the target quadrant (P < 0·01). Meanwhile, pre-treatment with ALA significantly reversed this effect (P < 0·01, Fig. 4(c)). In terms of the distance travelled inside the quadrant, the model group showed starkly lower values than controls (P < 0·05). ALA increased the travelled distance substantially in epileptic animals (P < 0·05; Fig. 4(d)). In the Morris water maze, representative photographs of mouse movements in the probe trial task were collected (Fig. 4(e)–(g)). These data indicated that impaired spatial learning and memory in mice induced by PTZ might be improved by ALA.

Fig. 4. Effect of α-linolenic acid (ALA) on spatial cognition and memory. The Morris Water Maze was used to determine ALA’s effects on pentylenetetrazol-induced spatial cognition and memory deficits. (a) For escape latency, two-way ANOVA is displayed as the mean of trials over 4 d. Crossover into the old site of the submerged platform (b). Time spent in the target quadrant (c) and distances travelled in the target quadrant (d) during the probing trial test. Swimming tracks obtained with a video tracking camera system are shown (e)–(g). Data were mean ± standard deviation (n 6 in the PTZ group and n 10 in the other groups). n.s., no significance; #P < 0·05, ##P < 0·01 and ###P < 0·001 v. Control group; *P < 0·05 and **P < 0·01 v. PTZ group. One-way ANOVA was utilised with Bonferroni post-test (b)–(d). PTZ, pentylenetetrazol.
Effects of α-linolenic acid on neuronal damage and neuron apoptosis
Next, the effects of ALA on neuronal damage and apoptosis were investigated. Histological investigation of hippocampal slices indicated normal cellular structure in control mice. In contrast, overt damage was found in the PTZ group, whose brain sections had overtly decreased cell volume, nuclear condensation, cell reduction and disarray, notably in the cornu ammonis (CA1) area. This nerve cell damage was reversed by ALA (Fig. 5(b)–(d)). Then, neuronal loss in brain specimens from mice with seizures was investigated by Nissl staining (Fig. 6(a)–(c) and (m)). The amounts of neurons in CA1 were obtained, demonstrating that PTZ-induced injury was linked with severe CA1 neuronal degeneration. Treatment with ALA could counteract this degeneration, as the PTZ + ALA group had more neurons in comparison with the model group (P < 0·001). TUNEL was used to examine the effect of ALA on apoptosis (Fig. 6(d)–(l) and (n)). While apoptosis was enhanced in the PTZ group v. control animals, ALA reduced the number of TUNEL-positive cells in the hippocampus of model mice (P < 0·001). These findings suggested that ALA could prevent neuronal necrosis and apoptosis in the hippocampus for a long time.

Fig. 5. Effects of ALA on neuronal damage (haematoxylin–eosin staining). Anatomical schematic representation of coronal brain sections (a). Histological analysis of hippocampal samples from control mice had normal cellular architecture (b). Meanwhile, PTZ-treated animals had the most severe damage among all groups, with brain sections exhibiting cell deflation, nuclear condensation, cell number decrease and disorganisation, particularly in CA1 (c). However, α-linolenic acid markedly reversed nerve cell injury (d). Arrowheads indicate damaged cells. Magnification of originals: 200×. Magnification of insets: 400×. Scale bars represent 200 μm. n 3. PTZ, pentylenetetrazol; CA1, cornu ammonis; ALA, α-linolenic acid.

Fig. 6. α-linolenic acid’s effects on neuronal loss and neuron apoptosis. Effects of α-linolenic acid on neuronal loss (Nissl staining) (a)–(c) and (m) and apoptosis (TUNEL) (d)–(l) and (n) in the hippocampal CA1 region. Magnification of originals: 200×. Magnification of insets: 400×. Scale bars represent 200 μm. White arrows, apoptotic cells. Data are means and standard deviations (n 3). ###P < 0·001 v. control group; ***P < 0·001 v. PTZ group. One-way ANOVA was performed with Bonferroni post-test for (m) and (n). TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labelling; CA1, cornu ammonis; PTZ, pentylenetetrazol; ALA, α-linolenic acid.
Effect of α-linolenic acid on hippocampal inflammatory response in pentylenetetrazol-treated mice
IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α amounts were evaluated to determine ALA’s effect on inflammatory response. The model group had starkly elevated IL-1β amounts compared with control animals (P < 0·001; Fig. 7(a)). However, the PTZ + ALA group had considerably lower levels of IL-1β (P < 0·05). Furthermore, in comparison with control mice, the model group had markedly increased IL-6 amounts (P < 0·05, Fig. 7(b)), and this effect was significantly alleviated by ALA (P < 0·01). Furthermore, PTZ induced a considerable rise in TNF-α level (P < 0·001; Fig. 7(c)), which was significantly reduced by ALA (P < 0·01). The findings implied that ALA regulated inflammation by considerably lowering IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α amounts.

Fig. 7. Effect of α-linolenic acid on inflammatory response. The effect of ALA on inflammatory response was examined. The hippocampal levels of IL-1β (a), IL-6 (b) and TNF-α (C) in PTZ-exposed mice are shown. Data are mean ± standard deviation (n 3). ###P < 0·001 and #P < 0·05 v. control group; *P < 0·05 and **P < 0·01 v. PTZ group. A Spark microplate reader was used to read absorbance at 450 nm (Tecan). One-way ANOVA was carried out with Bonferroni post-test (a)–(c). ALA, α-linolenic acid; PTZ, pentylenetetrazol.
Molecular docking of relation proteins of epilepsy
Using molecular docking, we performed an extensive search for the effects ALA has on the expression of potential downstream mediators. Table 1 shows the binding energy values of the ALA proteins and the relationship proteins obtained from the DS 3.0 binding energy programme. The interactions between ALA and JAK2 and STAT3 were shown to stable and powerful, with binding energies of –71·35 kcal/mol and –59·98 kcal/mol, respectively (Fig. 8).
Table 1. Binding energy values between ALA and different proteins

ALA, α-linolenic acid; JAK2, Janus kinase2; STAT3, Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription3.

Fig. 8. Molecular Docking of Relation Proteins of Epilepsy. The specific interactions between ALA and JAK2 or ATST3 after automated docking of ALA to the JAK2 or ATST3 binding site. Forecasting 3D structure of the JAK2 (Protein Data Bank; PDB ID: 5AEP) – ALA complex and 2D diagram A. Forecasting 3D structure of the STAT3 (PDB ID: 5AX3) – ALA complex and 2D diagram B. ALA, α-linolenic acid; JAK2, Janus kinase2.
As can be seen in figure, we have shown how amino acid residues in the JAK2 binding site interact with ALA in the following manner: ARG897 (slat bridge); PTR1008 and VAL1000 (conventional hydrogen bond); and LEU997 (alkyl). The amino acid residue interactions at the STAT3 binding site with ALA were as follows: LYS45 (attractive charge), TYR27 (conventional hydrogen bond and carbon hydrogen bond) and ILF22 (alkyl). Results showed that ALA binds to tyrosine, phosphoserine or valine of JAK2 and STAT3 proteins. Therefore, we speculated that ALA could affect the expression of JAK2 and STAT3, thereby exerting ameliorative effects in epilepsy.
α-Linolenic acid potently regulates JAK2/STAT3 signalling
In order to further elucidate the neuroprotective effects of ALA on epileptic seizures, we conducted an investigation involving the murine hippocampal tissue. We examined the protein expressions of p-JAK2, JAK2, p-STAT3 and STAT3. Representative bands of western blot were shown in Fig. 9(a), and relative protein expression levels were displayed in Fig. 9(b). PTZ-activated JAK2/STAT3 phosphorylation was blocked by ALA treatment. Immunofluorescence assays demonstrate that the expression of proteins in signalling pathways dramatically decreased with ALA treatment (online Supplementary Fig. S2(a)–(s)). There was a marked decline in the phosphorylation of JAK2 and STAT3 in the hippocampus, being P < 0·01 and P < 0·05, respectively, once ALA had been administered. These findings revealed that ALA inhibited PTZ-dependent JAK2 and STAT3 phosphorylation. Taken together, the ALA suppression of the onset of epileptic seizures may be via inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway.

Fig. 9. JAK2/STAT3 signalling is involved in PTZ-associated seizures. The protein amounts of JAK2, p-JAK2, STAT3 and p-STAT3 in the hippocampus were measured by western blot. Data are mean ± standard deviation (n 3). #P < 0·05 and ###P < 0·001 v. control group; *P < 0·05 v. PTZ group. One-way ANOVA was carried out with Bonferroni post-test (b). PTZ, pentylenetetrazol; ALA, α-linolenic acid; JAK2, Janus kinase2; STAT3, Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription3.
Discussion
Epilepsy is a persistent medical condition characterised by recurrent seizures and the degeneration of brain cells, resulting in cognitive impairments(Reference Pong, Xu and Klein27). The majority of patients necessitate ongoing therapy, resulting in substantial stress and suffering. Consequently, investigating efficacious drugs for the prevention and treatment of epilepsy carries substantial social and therapeutic consequences.
While ALA shows promise as a natural dietary ingredient with potential therapeutic effects, it is not a stand-alone medicine. Therefore, its usefulness in treating epilepsy still requires validation through research. Moreover, due to the limited number of studies and inconsistent results, more data are needed to confirm the therapeutic potential of ALA. Our research provides more evidence that ALA can successfully regulate the occurrence and intensity of seizures by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signalling pathway, which reduces neuroinflammation. This discovery has consequences for using ALA as a dietary intervention for patients with epilepsy. The results of this study illustrate the subsequent impacts of ALA: (a) significant reduction in the severity and duration of convulsions in mice. (b) Reversal of the loss or apoptosis of hippocampal neurons induced by PTZ toxicity, along with decreased levels of inflammatory markers such as IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β. Additionally, ALA treatment notably improved cognitive and functional impairments in epileptic mice. (c) The neuroprotective effect of ALA on epileptic mice is attributed to the activation of the JAK2/STAT3 signalling pathway.
In order to determine whether therapeutic interventions improve neurological function following epileptic convulsions, the rate and extent of neurological function recovery must be assessed. A range of functional assessment techniques were employed to evaluate the behavioural and functional recovery subsequent to the administration of ALA. These techniques included the open field test, tail suspension test, forced swimming test and Morris water maze(Reference Chen, Wang and Zhao28). Research has reported that ALA can significantly improve the antidepressant effect in PTZ-induced toxic mice, possibly due to the up-regulation of mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor during the forced swim task in the hippocampus(Reference Pan, Hu and Jacobowitz29,Reference Pan, Piermartiri and Chen30) . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor has been proven to have antidepressant and neuroprotective effects and is closely related to neuroinflammation(Reference McGonigal, Becker and Fath31). A decrease in motor activity might correspond to the emergence of symptoms resembling depression. As indicated by the reduced number of crossings, PTZ-induced epileptic mice exhibited substantially diminished motor activity in comparison with control mice, preferring to remain in the corners of the open field test box. The number of crossings increased substantially following ALA administration, indicating that the behavioural and cognitive disorder induced by pentetrazol in rats was ameliorated.
The impact of apoptosis or necrosis on seizure activity has been extensively demonstrated(Reference Cheng, Mai and Zeng32). Apoptosis and inflammatory response play crucial roles in the onset and progression of epilepsy, although their underlying mechanisms have yet to be fully elucidated. In this study, the administration of ALA significantly reduced the number of TUNEL-positive cells after seizures, indicating a reduction in neuronal damage. Additionally, the administration of ALA facilitated the formation of Nissl bodies, which serve as a marker for the preservation of neuronal structure. The main objective of this inquiry was to study the CA1 area of the hippocampus, which is continuously and severely impacted by seizures in experimental animals. Additionally, ALA treatment was associated with increased neurogenesis and the presence of mature neurons in the sub-granular zone of the dentate gyrus within a span of 30 d(Reference Blondeau, Nguemeni and Debruyne33–Reference Piermartiri, Pan and Chen35). Further experiments are warranted to evaluate the impact of ALA on the hippocampal dentate gyrus region.
Neuroinflammation plays a crucial regulatory role in the occurrence and progression of epilepsy. Inhibiting inflammation can reduce neuronal cell toxicity, improve neuronal apoptosis and neurofunctional impairment, enhance learning and memory abilities, and alleviate symptoms of epilepsy(Reference Dey, Kang and Qiu36). ALA is an n-3 PUFA that possesses significant antioxidant capacity and anti-inflammatory effects(Reference Kra, Daddam and Moallem37). Although ALA, as an unsaturated fatty acid, has significant physiological functions, its impact on epilepsy remains unclear. The physiological function of ALA is based on its conversion into EPA and DHA. ALA competes with linoleic acid for metabolic space, leading to a decrease in the level of arachidonic acid, as well as the quantity of class II PG and leukotrienes in tissue phospholipids(Reference Cambiaggi, Chakravarty and Noureddine38). By competing with cyclo-oxygenase and lipoxygenase, ALA and its derivatives (EPA and DHA) inhibit the synthesis of class I PG and leukotrienes, weaken the physiological activity of thromboxane and occupy thromboxane receptors, thereby inhibiting the production of inflammatory factors(Reference van Vliet, Aronica and Vezzani39). Research has reported its ability to significantly decrease the mRNA levels and protein content of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, improve spatial learning and memory abilities, and exert neuroprotective functions(Reference Wang and Wang40). In our current study, ALA exhibited significant reductions in the levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β. Hence, we hypothesise that ALA may mitigate epileptic seizures induced by pentetrazol intoxication through its anti-neuroinflammatory effects.
The continuous activation of the JAK2/STAT3 signalling pathway is closely associated with various inflammatory and immune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, sepsis and tumour-related diseases. During the inflammatory process, JAK2/STAT3 is the main signalling pathway regulated by cytokines, with a relatively simple signal transduction mechanism. JAK2 belongs to the tyrosine protein kinase family and is activated by certain cytokines and IL that act on transmembrane receptors during neural injury(Reference Li, Wang and Zhang41). Activated JAK2 can recognise the SH2 domain in STAT3 and induce its phosphorylation and activation. Research reports have shown that after phosphorylated STAT3 undergoes nuclear translocation, it can stimulate the expression of inflammatory genes and release inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6, thereby exacerbating the inflammatory response(Reference Ni, Liao and Zhang42). Inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 pathway activation can significantly alleviate the inflammatory response and reduce inflammation damage. Furthermore, JAK2/STAT3 signalling is largely involved in the development and protection of neurons and glia, as well as brain inflammation(Reference Zhang, Xu and Chen43). Activated STAT3, for example, has been detected in numerous CNS cells and linked to neuronal growth and regeneration. JAK2 and STAT3 have both been found to control hippocampal synaptic plasticity, which is associated with memory and learning(Reference Kong, Gong and Zhang44). JAK2/STAT3 signalling could be targeted for the treatment of epileptic seizures and other CNS illnesses, including depression, anxiety and Alzheimer’s disease(Reference Rabie, Fattah and Nassar45). Due to its strong link with the CNS immune system, investigators have responded to the JAK2/STAT3 pathway’s essential significance in treating epileptic seizures by encouraging its application for the treatment of mental illness. Therefore, it is speculated that down-regulating the JAK2/STAT3 pathway to inhibit inflammation may be the pharmacological mechanism by which ALA alleviates epileptic symptoms. In our study, we also utilised molecular docking and western blot studies to further confirm that ALA can down-regulate the JAK2/STAT3 signalling pathway. This down-regulation leads to a reduction in inflammatory factor levels and improvement in PTZ-induced neuron apoptosis and neurological impairment in mice. Moreover, ALA enhanced the cognitive function of mice with epilepsy and effectively alleviated seizure occurrences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this study discovered that ALA therapy reduces the severity of epileptic convulsions and reversed PTZ-induced necrosis or apoptosis of hippocampus neurons. Furthermore, pre-treatment with ALA down-regulated inflammatory markers, including IL-6, TNF-a and IL-1, and suppressed JAK2/STAT3 signalling. Several functional tests were conducted, with the findings demonstrating that ALA therapy enhanced neurological function considerably. These findings provide not only insights into the underlying mechanism of ALA, which appears to block hippocampal JAK2/STAT3 signalling, but also additional evidence for ALA’s therapeutic use in epileptic seizures. In addition, our study suggested that ALA might be a safe and effective candidate for neuroprotection in the therapy of epilepsy.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all undergraduates participated in this study. In addition, the authors would like to thank Professor Hong Ding for her help in the research design.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
X. Z. and F. L. were responsible for the whole experiment implementation and wrote the paper, Y. C. and J. G. checked all the statistical analyses, and D. H. did the final proofreading and approved the final manuscript. X. Z. and F. L.: conceptualisation, methodology, validation, writing draft and visualization. Y. C. and J. G.: formal analysis and data curation. D. H.: resources, writing - review & editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this study.
Supplementary material
For supplementary material/s referred to in this article, please visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114524000989