Our patient is a 61-year-old female who underwent repeat bilateral ventrointermediate nucleus implantation of a deep brain stimulation (DBS) system for essential tremor. Previously, she had been implanted with a DBS system, but this was explanted secondary to infection. This second surgery was successful and resulted in a marked reduction of her tremors. She presented 3 months postoperatively with complaints of pain and tenderness in the left side of her neck. Plain radiographs revealed twisting of the extension leads in the neck (Figure 1A,B). She was taken for successful revision of these extension leads; however, she presented again 3 weeks later with purulent drainage from her subclavicular pouch and tenderness along the extension lead tract. She was taken back to surgery, where the entire system was found to be contaminated and was therefore explanted. We have decided to not reimplant the system at this time.
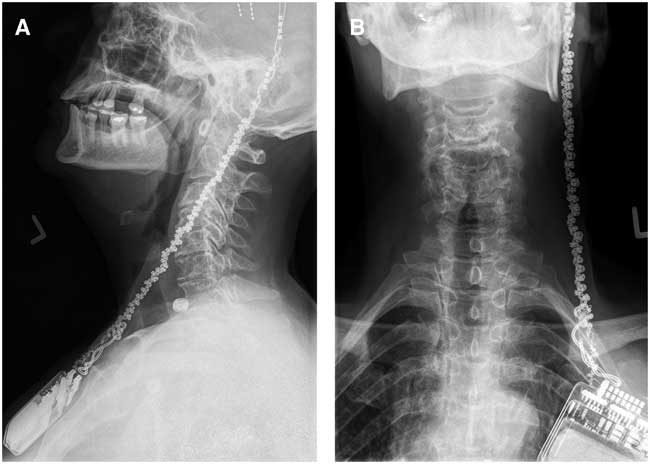
Figure 1 Lateral (A) and AP (B) x-rays showing extensive twisting of DBS extension leads.
Twiddler’s syndrome in the neuromodulation population is a rare but important cause of hardware failure, occurring in approximately 1% of cases.Reference Burdick, Okun and Haq 1 , Reference Al-Mahfoudh, Chan, Chong and Farah 2 This phenomenon was originally reported in 1968 in the setting of implantable cardiac devices.Reference Bayliss, Beanlands and Baird 3 Since then, it has become a recognized complication of implantable devices, including both DBS and spinal cord stimulation (SCS) systems.Reference Burdick, Okun and Haq 1 , Reference Al-Mahfoudh, Chan, Chong and Farah 2 , Reference Morishita, Foote and Burdick 4 As its name suggests, it is thought to be due to direct patient manipulation of the pulse generator, although this has been questioned by some.Reference Silva, Chamadoira, Costa, Linhares, Rosas and Vaz 5 Known risk factors include psychiatric illness, obesity, and age.Reference Silva, Chamadoira, Costa, Linhares, Rosas and Vaz 5 , Reference Astradsson, Schweder, Joint, Green and Aziz 6 Patients typically present with early or late reemergence of symptoms, which can be accompanied by wound complications, localized pain, and tenderness of the lead tract, as well as elevated impedance recordings on routine follow-up.Reference Burdick, Okun and Haq 1 , Reference Al-Mahfoudh, Chan, Chong and Farah 2 , Reference Silva, Chamadoira, Costa, Linhares, Rosas and Vaz 5 – Reference Moens, Petit and Goudman 7 Diagnosis is usually made with plain radiographs. Imaging of the brain should be considered, as severe cases can result in intracranial electrode retraction.Reference Silva, Chamadoira, Costa, Linhares, Rosas and Vaz 5 , Reference Gelabert-Gonzalez, Relova-Quinteiro and Castro-Garcia 8 , Reference Sobstyl, Ząbek, Górecki and Brzuszkiewicz-Kuźmicka 9 Treatment options include revision surgery or explantation of the neuromodulation system, though this is usually only reserved for cases of secondary infection, as was the case in our patient. Revision surgery can involve simple resuturing of the pulse generator within its subcutaneous pouch; however, some cases may require more extensive revision and replacement of hardware if damage has been incurred to the leads or the intracranial electrode has been withdrawn.
Disclosures
The authors hereby state that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.



