No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
On the almost everywhere convergence of the ergodic averages†
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 September 2008
Abstract
Let (X, 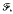 ν) be a finite measure space and let T: X → X be a measurable transformation. In this paper we prove that the averages
ν) be a finite measure space and let T: X → X be a measurable transformation. In this paper we prove that the averages 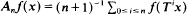 converge a.e. for every f in Lp(dν), 1 < p < ∞, if and only if there exists a measure γ equivalent to ν such that the averages apply uniformly Lp(dν) into weak-Lp(dγ). As a corollary, we get that uniform boundedness of the averages in Lp(dν) implies a.e. convergence of the averages (a result recently obtained by Assani). In order to do this, we first study measures v equivalent to a finite invariant measure μ, and we prove that supn≥0An(dν/dμ)−1/(p−1) a.e. is a necessary and sufficient condition for the averages to converge a.e. for every f in Lp(dν).
converge a.e. for every f in Lp(dν), 1 < p < ∞, if and only if there exists a measure γ equivalent to ν such that the averages apply uniformly Lp(dν) into weak-Lp(dγ). As a corollary, we get that uniform boundedness of the averages in Lp(dν) implies a.e. convergence of the averages (a result recently obtained by Assani). In order to do this, we first study measures v equivalent to a finite invariant measure μ, and we prove that supn≥0An(dν/dμ)−1/(p−1) a.e. is a necessary and sufficient condition for the averages to converge a.e. for every f in Lp(dν).
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 1990

