No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 September 2021
For an ascending HNN-extension 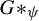 $G*_{\psi }$
of a finitely generated abelian group G, we study how a synchronization between the geometry of the group and weak periodicity of a configuration in
$G*_{\psi }$
of a finitely generated abelian group G, we study how a synchronization between the geometry of the group and weak periodicity of a configuration in 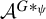 $\mathcal {A}^{G*_{\psi }}$
forces global constraints on it, as well as in subshifts containing it. A particular case are Baumslag–Solitar groups
$\mathcal {A}^{G*_{\psi }}$
forces global constraints on it, as well as in subshifts containing it. A particular case are Baumslag–Solitar groups  $\mathrm {BS}(1,N)$
,
$\mathrm {BS}(1,N)$
, 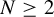 $N\ge 2$
, for which our results imply that a
$N\ge 2$
, for which our results imply that a 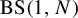 $\mathrm {BS}(1,N)$
-subshift of finite type which contains a configuration with period
$\mathrm {BS}(1,N)$
-subshift of finite type which contains a configuration with period 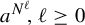 $a^{N^\ell }\!, \ell \ge 0$
, must contain a strongly periodic configuration with monochromatic
$a^{N^\ell }\!, \ell \ge 0$
, must contain a strongly periodic configuration with monochromatic 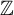 $\mathbb {Z}$
-sections. Then we study proper n-colorings,
$\mathbb {Z}$
-sections. Then we study proper n-colorings, 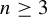 $n\ge 3$
, of the (right) Cayley graph of
$n\ge 3$
, of the (right) Cayley graph of 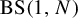 $\mathrm {BS}(1,N)$
, estimating the entropy of the associated subshift together with its mixing properties. We prove that
$\mathrm {BS}(1,N)$
, estimating the entropy of the associated subshift together with its mixing properties. We prove that 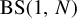 $\mathrm {BS}(1,N)$
admits a frozen n-coloring if and only if
$\mathrm {BS}(1,N)$
admits a frozen n-coloring if and only if 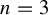 $n=3$
. We finally suggest generalizations of the latter results to n-colorings of ascending HNN-extensions of finitely generated abelian groups.
$n=3$
. We finally suggest generalizations of the latter results to n-colorings of ascending HNN-extensions of finitely generated abelian groups.