Article contents
Lagrangian transport by deep-water surface gravity wavepackets: effects of directional spreading and stratification
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 28 November 2019
Abstract
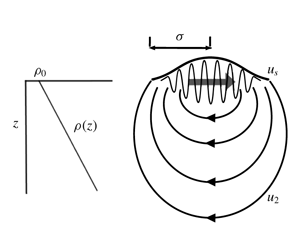
The Lagrangian mass transport by non-dissipating surface gravity wavepackets consists of the Stokes drift and the wave-induced return flow. We examine how directional spreading and density stratification affect this mass transport for an isolated non-dissipating wavepacket in deep water using a perturbation expansion. For an unstratified ocean, we show that the net displacement by the return flow is finite, negative, the same at all vertical levels and inversely proportional to the depth for spanwise-infinite packets representing unidirectional (two-dimensional) seas, but zero for spanwise-localised packets representing directionally spread seas (three-dimensional). We resolve this difference by demonstrating that a transition between two-dimensional-like (finite) and three-dimensional-like (zero) displacement occurs on a time scale inversely proportional to the degree of directional spreading. For a stratified ocean, we show that in two dimensions the net displacement profile by the return flow oscillates slowly with depth, with a wavelength dependent on the ratio of buoyancy frequency to the surface wave group velocity, and infinite displacements are predicted when the surface wavepacket resonantly excites internal waves. In three dimensions, the net displacement remains zero in the presence of stratification, but finite-time displacements may be appreciably altered.
Information
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2019 Cambridge University Press
References
- 5
- Cited by

