Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Moyle, Todd M.
Walker, Lynn M.
and
Anna, Shelley L.
2012.
Predicting conditions for microscale surfactant mediated tipstreaming.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 24,
Issue. 8,
Rubio-Rubio, M.
Sevilla, A.
and
Gordillo, J. M.
2013.
On the thinnest steady threads obtained by gravitational stretching of capillary jets.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 729,
Issue. ,
p.
471.
Gordillo, J. M.
Sevilla, A.
and
Campo-Cortés, F.
2014.
Global stability of stretched jets: conditions for the generation of monodisperse micro-emulsions using coflows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 738,
Issue. ,
p.
335.
Ray, Bahni
and
Prosperetti, Andrea
2014.
On skirted drops in an immiscible liquid.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 108,
Issue. ,
p.
213.
Rodríguez-Rodríguez, Javier
Sevilla, Alejandro
Martínez-Bazán, Carlos
and
Gordillo, José Manuel
2015.
Generation of Microbubbles with Applications to Industry and Medicine.
Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 47,
Issue. 1,
p.
405.
Castro-Hernández, Elena
García-Sánchez, Pablo
Tan, Say Hwa
Gañán-Calvo, Alfonso M.
Baret, Jean-Christophe
and
Ramos, Antonio
2015.
Breakup length of AC electrified jets in a microfluidic flow-focusing junction.
Microfluidics and Nanofluidics,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 4,
p.
787.
Fu, Taotao
and
Ma, Youguang
2015.
Bubble formation and breakup dynamics in microfluidic devices: A review.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 135,
Issue. ,
p.
343.
Anna, Shelley Lynn
2016.
Droplets and Bubbles in Microfluidic Devices.
Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 1,
p.
285.
Castro Hernandez, Elena
Guerrero, Josefa
Fernandez-Nieves, Alberto
and
Gordillo, Jose M.
2016.
Fluids, Colloids and Soft Materials: An Introduction to Soft Matter Physics.
p.
1.
Castro-Hernández, Elena
Kok, Maarten P.
Versluis, Michel
and
Fernandez Rivas, David
2016.
Study of the geometry in a 3D flow-focusing device.
Microfluidics and Nanofluidics,
Vol. 20,
Issue. 2,
Castro-Hernández, Elena
García-Sánchez, Pablo
Alzaga-Gimeno, Javier
Tan, Say Hwa
Baret, Jean-Christophe
and
Ramos, Antonio
2016.
AC electrified jets in a flow-focusing device: Jet length scaling.
Biomicrofluidics,
Vol. 10,
Issue. 4,
Evangelio, A.
Campo-Cortés, F.
and
Gordillo, J. M.
2016.
Simple and double microemulsions via the capillary breakup of highly stretched liquid jets.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 804,
Issue. ,
p.
550.
Rivero-Rodríguez, J.
and
Pérez-Saborid, M.
2017.
An efficient finite volume method for one-dimensional problems with application to the dynamics of capillary jets.
Computers & Fluids,
Vol. 154,
Issue. ,
p.
132.
Zhu, Pingan
and
Wang, Liqiu
2017.
Passive and active droplet generation with microfluidics: a review.
Lab on a Chip,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 1,
p.
34.
Lan, Wenjie
Jing, Shan
Guo, Xuqiang
and
Li, Shaowei
2017.
Study on “interface – shrinkage – driven” breakup of droplets in co-flowing microfluidic devices.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 158,
Issue. ,
p.
58.
Brosseau, Quentin
and
Vlahovska, Petia M.
2017.
Streaming from the Equator of a Drop in an External Electric Field.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 119,
Issue. 3,
Lan, Wenjie
Wang, Zhihui
Du, Yinjie
Guo, Xuqiang
and
Li, Shaowei
2018.
Interface‐shrinkage‐driven breakup of droplets in microdevices with different dispersed fluid channel shape.
AIChE Journal,
Vol. 64,
Issue. 1,
p.
367.
Zhao, Jingzhou
and
Li, Xiaochun
2018.
A Long Wavelength Model for Manufacturing of Continuous Metal Microwires by Thermal Fiber Drawing From a Preform.
Journal of Micro and Nano-Manufacturing,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 1,
Dong, Jun
Meissner, Max
Faers, Malcolm A.
Eggers, Jens
Seddon, Annela M.
and
Royall, C. Patrick
2018.
Opposed flow focusing: evidence of a second order jetting transition.
Soft Matter,
Vol. 14,
Issue. 41,
p.
8344.
Castro-Hernández, Elena
García-Sánchez, Pablo
León-Rodríguez, Marta
Fernandez Rivas, David
and
Ramos, Antonio
2019.
Controllable production of Janus ligaments by AC fields in a flow-focusing junction.
Microfluidics and Nanofluidics,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 1,
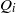 of a fluid with a viscosity
of a fluid with a viscosity 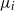 discharges into an immiscible liquid of viscosity
discharges into an immiscible liquid of viscosity 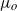 that flows in parallel with the axis of the injector. When the outer capillary number verifies the condition
that flows in parallel with the axis of the injector. When the outer capillary number verifies the condition 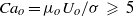 , where
, where 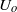 and
and 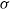 indicate, respectively, the outer velocity and the interfacial tension coefficient, and if the inner-to-outer velocity ratio is such that
indicate, respectively, the outer velocity and the interfacial tension coefficient, and if the inner-to-outer velocity ratio is such that 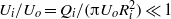 , with
, with 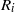 the inner radius of the injector, a jet is formed with the same type of cone–jet geometry as predicted by the numerical results of Suryo & Basaran (Phys. Fluids, vol. 18, 2006, p. 082102). For extremely low values of the velocity ratio
the inner radius of the injector, a jet is formed with the same type of cone–jet geometry as predicted by the numerical results of Suryo & Basaran (Phys. Fluids, vol. 18, 2006, p. 082102). For extremely low values of the velocity ratio 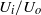 , we find that the diameter of the jet emanating from the tip of the cone is so small that drops with sizes below
, we find that the diameter of the jet emanating from the tip of the cone is so small that drops with sizes below 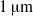 can be formed. We also show that, through this simple method, concentrated emulsions composed of micrometre-sized drops with a narrow size distribution can be generated. Moreover, thanks to the information extracted from numerical simulations of boundary-integral type and using the slender-body approximation due to Taylor (Proceedings of the 11th International Congress of Applied Mechanics, Munich, 1964, pp. 790–796), we deduce a third-order, ordinary differential equation that predicts, for arbitrary values of the three dimensionless numbers that control this physical situation, namely,
can be formed. We also show that, through this simple method, concentrated emulsions composed of micrometre-sized drops with a narrow size distribution can be generated. Moreover, thanks to the information extracted from numerical simulations of boundary-integral type and using the slender-body approximation due to Taylor (Proceedings of the 11th International Congress of Applied Mechanics, Munich, 1964, pp. 790–796), we deduce a third-order, ordinary differential equation that predicts, for arbitrary values of the three dimensionless numbers that control this physical situation, namely, 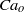 ,
, 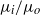 and
and 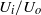 , the shape of the jet and the sizes of the drops generated. Most interestingly, the influence of the geometry of the injector system on the jet shape and drop size enters explicitly into the third-order differential equation through two functions that can be easily calculated numerically. Therefore, our theory can be used as an efficient tool for the design of new emulsification devices.
, the shape of the jet and the sizes of the drops generated. Most interestingly, the influence of the geometry of the injector system on the jet shape and drop size enters explicitly into the third-order differential equation through two functions that can be easily calculated numerically. Therefore, our theory can be used as an efficient tool for the design of new emulsification devices.
