Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Peng, Zhuowei
Pan, Qinglin
Cai, Shan
Li, Jinfeng
and
Liang, Wenjie
2019.
Effect of different aging processes on the corrosion behavior of new Al–Cu–Li–Zr–Sc alloys.
Materials and Corrosion,
Vol. 70,
Issue. 12,
p.
2266.
Zhang, Jin-Yu
Gao, Yi-Han
Yang, Chong
Zhang, Peng
Kuang, Jie
Liu, Gang
and
Sun, Jun
2020.
Microalloying Al alloys with Sc: a review.
Rare Metals,
Vol. 39,
Issue. 6,
p.
636.
Snopiński, P.
Król, M.
Wróbel, T.
Matus, K.
Woźniak, A.
Tański, T.
and
Palček, P.
2020.
Effects of modifying the hypoeutectic AlMg5Si2Mn alloy via addition of Al10Sr and/or Al5TiB.
Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering,
Vol. 21,
Issue. 1,
Wang, Qian
Liu, Changzhi
Yao, Ruijuan
Zhu, Hong
Liu, Xiaomin
Wang, Mingliang
Chen, Zhe
and
Wang, Haowei
2020.
First-principles study on the stability and work function of low-index surfaces of TiB2.
Computational Materials Science,
Vol. 172,
Issue. ,
p.
109356.
Sun, Jing
Wang, Fei
Liu, Yuwen
Guo, Lijie
and
Wang, Haowei
2021.
The effect of V on the morphology of TiB2 particles in as-cast aluminum composites.
International Journal of Materials Research,
Vol. 112,
Issue. 11,
p.
890.
Xu, Pian
Lu, Gang
Zhang, Lei
Zhou, Shitong
Yan, Yuping
Yan, Qingsong
and
Jiang, Lihong
2021.
Effect of holding time on the growth morphology of in-situ TiB2 particles.
Materials Today Communications,
Vol. 29,
Issue. ,
p.
102953.
Wang, Qian
Li, Yuanyuan
Chen, Siyi
Liu, Xiaomin
Chen, Zhe
Wang, Mingliang
Zhu, Hong
and
Wang, Haowei
2021.
Interface Alloying Design to Improve the Dispersion of TiB2 Nanoparticles in Al Composites: A First-Principles Study.
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C,
Vol. 125,
Issue. 10,
p.
5937.
Mao, Hongkui
Li, Cong
Dong, Yuan
Wang, Yu
Xu, Hong
Yu, Qi
Shang, Yuncong
Li, Xiaofeng
and
Zhao, Zhanyong
2022.
The effect of Mn on particles morphology and property of 5 wt% TiB2/Al-4.5Cu-0.4Mn alloys.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds,
Vol. 904,
Issue. ,
p.
163907.
Singh, Chandan
Prywer, Jolanta
and
Yadav, Devinder
2023.
On the Three-Dimensional Morphology of In Situ Grown TiB2 Particles in Molten Aluminum.
Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 20,
p.
9396.
Kong, Xiang
Wang, Yu
Fan, Haotian
Wu, Junteng
Xu, Hong
and
Mao, Hongkui
2023.
Effect of high cooling rate on the solidification microstructure of Al–Cu/TiB2 alloy fabricated by freeze-ablation casting.
Journal of Materials Research and Technology,
Vol. 25,
Issue. ,
p.
593.
Li, Cong
Xu, Hong
Mao, Hongkui
Lian, Peng
Wei, Qi
Song, Feng
and
Wang, Yu
2023.
The effect of V on the morphology transformation of TiB2 particles in Al-4.5Cu-0.18 V matrix.
Journal of Materials Research,
Vol. 38,
Issue. 5,
p.
1377.
Ma, Siming
Shang, Zhongxia
Shang, Anyu
Zhang, Peter
Tang, Chenglu
Huang, Yuze
Leung, Chu Lun Alex
Lee, Peter D.
Zhang, Xinghang
and
Wang, Xiaoming
2023.
Additive manufacturing enabled synergetic strengthening of bimodal reinforcing particles for aluminum matrix composites.
Additive Manufacturing,
Vol. 70,
Issue. ,
p.
103543.
Wang, Xiaoming
2024.
Additive Manufacturing Using Al-Cu-Mg-Sc-TiB2 Composite Powders to Overcome the Strength–Ductility Trade-Off.
JOM,
Vol. 76,
Issue. 1,
p.
71.
Zhuang, Weibin
Jia, Jing
Liu, Jingfu
Qin, Longjian
Li, Jinghui
and
Meng, Chao
2024.
Microstructure evolution and properties improvement of in-situ TiB2/6061 composites via trace Mn addition.
Journal of Molecular Structure,
Vol. 1301,
Issue. ,
p.
137423.
Zhu, Hongyi
Wang, Qian
Yang, Chen
Wang, Yihao
Xia, Cunjuan
Zhao, Dechao
Zhang, Huawei
Wang, Mingliang
Chen, Zhe
and
Wang, Haowei
2024.
Improving TiB2 dispersion in Al-Si composites by interfacial projection: High-throughput first-principles calculations and experimental verification.
Materials & Design,
Vol. 244,
Issue. ,
p.
113184.
Huang, Ting
Zhao, Lijun
Sun, Xiujuan
Xu, Junhua
Wang, Zhidong
Yu, Lihua
Lu, Zhengping
Ding, Yi
long, Lin
and
Zhang, Hao
2025.
Synergistic strengthening effect of Sc and TiB2 particles on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 7055 aluminum composites.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds,
Vol. 1024,
Issue. ,
p.
179980.
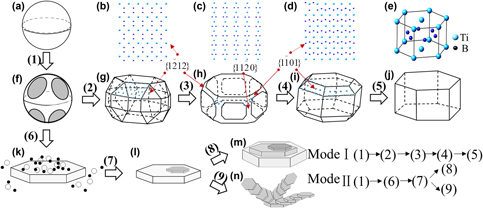
 ${\bf \left\{ {1{\bf \overline{2}}12} \right\}}$,
${\bf \left\{ {1{\bf \overline{2}}12} \right\}}$,  ${\bf \left\{ {11\overline{2}0} \right\}}$, and
${\bf \left\{ {11\overline{2}0} \right\}}$, and  ${\bf \left\{ {10\overline{1}1} \right\}}$ which would inhibit the growth of these faces effectively and retain a lower-energy state of the polyhedral or quasispherical TiB2 particles in Al–Sc systems.
${\bf \left\{ {10\overline{1}1} \right\}}$ which would inhibit the growth of these faces effectively and retain a lower-energy state of the polyhedral or quasispherical TiB2 particles in Al–Sc systems.
