No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Effect of shaping on turbulent dynamics in reversed-field pinch simulations
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 November 2021
Abstract
We study the influence of the shape of the plasma container on the dynamics of the reversed-field pinch (RFP). The geometries we consider are periodic cylinders with elliptical and circular-shaped cross-sections. Numerical simulations of fully nonlinear viscoresistive magnetohydrodynamics are carried out to illustrate how the plasma dynamics is affected by shaping. It is shown that independent of the plasma shape, the quantity $\beta$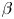 , comparing the hydrodynamic pressure to the magnetic pressure, decreases for increasing values of the Lundquist number, but the pressure gradient fluctuations remain roughly constant, when compared to the Lorentz force. Different elliptical shapes of the cross-section of the domain lead to the excitation of different toroidal (or axial) magnetic and dynamic modes. Furthermore, it is found that in a geometry with circular cross-section, a significant local poloidal angular momentum is observed, absent in the geometries with elliptical cross-section. Because the confinement is dominantly determined by plasma movement, and the dynamics of the velocity and magnetic field are modified by the modification of the geometry, shaping can thus affect the performance of RFP devices.
, comparing the hydrodynamic pressure to the magnetic pressure, decreases for increasing values of the Lundquist number, but the pressure gradient fluctuations remain roughly constant, when compared to the Lorentz force. Different elliptical shapes of the cross-section of the domain lead to the excitation of different toroidal (or axial) magnetic and dynamic modes. Furthermore, it is found that in a geometry with circular cross-section, a significant local poloidal angular momentum is observed, absent in the geometries with elliptical cross-section. Because the confinement is dominantly determined by plasma movement, and the dynamics of the velocity and magnetic field are modified by the modification of the geometry, shaping can thus affect the performance of RFP devices.
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press
Footnotes
Present address: Rio Tinto Aluminium, Voreppe, France.


