Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 November 2018
We investigate analytically and numerically the semi-collisional regime of the plasmoid instability, defined by the inequality 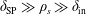 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}_{\text{SP}}\gg \unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}_{s}\gg \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}_{\text{in}}$, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}_{\text{SP}}\gg \unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}_{s}\gg \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}_{\text{in}}$, where 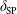 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}_{\text{SP}}$ is the width of a Sweet–Parker current sheet,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}_{\text{SP}}$ is the width of a Sweet–Parker current sheet, 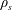 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}_{s}$ is the ion sound Larmor radius and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}_{s}$ is the ion sound Larmor radius and 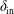 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}_{\text{in}}$ is the width of the boundary layer that arises in the plasmoid instability analysis. Theoretically, this regime is predicted to exist if the Lundquist number
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}_{\text{in}}$ is the width of the boundary layer that arises in the plasmoid instability analysis. Theoretically, this regime is predicted to exist if the Lundquist number 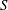 $S$ and the length of the current sheet
$S$ and the length of the current sheet 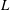 $L$ are such that
$L$ are such that 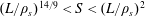 $(L/\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}_{s})^{14/9}<S<(L/\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}_{s})^{2}$ (for a sinusoidal-like magnetic configuration; for a Harris-type sheet the lower bound is replaced with
$(L/\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}_{s})^{14/9}<S<(L/\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}_{s})^{2}$ (for a sinusoidal-like magnetic configuration; for a Harris-type sheet the lower bound is replaced with 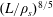 $(L/\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}_{s})^{8/5}$). These bounds are validated numerically by means of simulations using a reduced gyrokinetic model (Zocco & Schekochihin, Phys. Plasmas, vol. 18 (10), 2011, 102309) conducted with the code Viriato. Importantly, this regime is conjectured to allow for plasmoid formation at relatively low, experimentally accessible, values of the Lundquist number. Our simulations obtain plasmoid instability at values of
$(L/\unicode[STIX]{x1D70C}_{s})^{8/5}$). These bounds are validated numerically by means of simulations using a reduced gyrokinetic model (Zocco & Schekochihin, Phys. Plasmas, vol. 18 (10), 2011, 102309) conducted with the code Viriato. Importantly, this regime is conjectured to allow for plasmoid formation at relatively low, experimentally accessible, values of the Lundquist number. Our simulations obtain plasmoid instability at values of 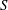 $S$ as low as
$S$ as low as 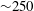 ${\sim}250$. The simulations do not prescribe a Sweet–Parker sheet; rather, one is formed self-consistently during the nonlinear evolution of the initial tearing mode configuration. This proves that this regime of the plasmoid instability is realizable, at least at the relatively low values of the Lundquist number that are accessible to current dedicated experiments.
${\sim}250$. The simulations do not prescribe a Sweet–Parker sheet; rather, one is formed self-consistently during the nonlinear evolution of the initial tearing mode configuration. This proves that this regime of the plasmoid instability is realizable, at least at the relatively low values of the Lundquist number that are accessible to current dedicated experiments.