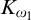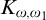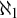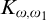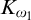1 Introduction
Games on graphs are a very natural concept and so it is no wonder that this field has emerged jointly with graph theory as a whole. For finite boards one often considers strong games, i.e., where two players interchangeably colour edges of a finite graph G with the aim to be the first player to have some previously agreed upon graph contained as a subgraph in the graph induced by their respective coloured edges. Another important kind of games is the so-called “Maker–Breaker games.” A typical setup for such games on (potentially infinite) graphs is the following: at each turn, Maker claims an edge of
![]() $ G $
(not previously claimed by either player) after which Breaker claims an unclaimed edge. There is either a fixed number of turns or they play until the whole edge set is distributed. The set of winning sets of Maker is public knowledge and usually has some combinatorial description. Classical games of this type are for example the Shannon switching game, in which Maker’s goal is to connect two vertices by a path (see [Reference Lehman11]), and the game where Maker’s goal is to build a spanning tree (see [Reference Chvátal and Erdős4]) or more generally a base of a matroid (see [Reference Bednarska and Pikhurko2]).
$ G $
(not previously claimed by either player) after which Breaker claims an unclaimed edge. There is either a fixed number of turns or they play until the whole edge set is distributed. The set of winning sets of Maker is public knowledge and usually has some combinatorial description. Classical games of this type are for example the Shannon switching game, in which Maker’s goal is to connect two vertices by a path (see [Reference Lehman11]), and the game where Maker’s goal is to build a spanning tree (see [Reference Chvátal and Erdős4]) or more generally a base of a matroid (see [Reference Bednarska and Pikhurko2]).
For recent results about Maker–Breaker games on infinite graphs we refer to [Reference Bowler, Emde and Gut3, Reference Nicholas Day and Falgas-Ravry12]. Some games (like the base-exchange game in [Reference Aharoni and Pouzet1]) can be phrased more naturally in the language of infinite matroids. It is worth mentioning that Maker–Breaker games have been investigated in an even more abstract settings as well (see [Reference Csirmaz and Nagy5]).
Let G and G, be graphs. Then we denote by
![]() $\mathfrak{MB}(G, H) $
the Maker–Breaker game where G (more precisely the set of edges) is the board, there are turns (indexed by ordinals) each of which begins with Maker claiming a previously unclaimed edge, after which Breaker does likewise. The game terminates when all the edges are claimed and Maker wins if and only if at the end of the game the subgraph
$\mathfrak{MB}(G, H) $
the Maker–Breaker game where G (more precisely the set of edges) is the board, there are turns (indexed by ordinals) each of which begins with Maker claiming a previously unclaimed edge, after which Breaker does likewise. The game terminates when all the edges are claimed and Maker wins if and only if at the end of the game the subgraph
![]() $ G_M $
of
$ G_M $
of
![]() $ G $
induced by the edges claimed by Maker contains a subgraph isomorphic to
$ G $
induced by the edges claimed by Maker contains a subgraph isomorphic to
![]() $ H $
. Let us recall that a graph
$ H $
. Let us recall that a graph
![]() $ G $
is an ordered pair
$ G $
is an ordered pair
![]() $ (V,E) $
with
$ (V,E) $
with
![]() $ E\subseteq [V]^{2} $
where
$ E\subseteq [V]^{2} $
where
![]() $ V $
is called the vertex set and
$ V $
is called the vertex set and
![]() $ E $
is the edge set of
$ E $
is the edge set of
![]() $ G $
. The complete graph on
$ G $
. The complete graph on
![]() $ \kappa $
is
$ \kappa $
is
![]() $ K_\kappa :=(\kappa , [\kappa ]^{2}) $
. The complete bipartite graph with vertex classes of size
$ K_\kappa :=(\kappa , [\kappa ]^{2}) $
. The complete bipartite graph with vertex classes of size
![]() $ \lambda $
and
$ \lambda $
and
![]() $ \kappa $
is denoted by
$ \kappa $
is denoted by
![]() $ K_{\lambda ,\kappa } $
, its vertex set is
$ K_{\lambda ,\kappa } $
, its vertex set is
![]() $ (\lambda \times \{ 0 \})\cup (\kappa \times \{ 1 \}) $
, and its edge set is
$ (\lambda \times \{ 0 \})\cup (\kappa \times \{ 1 \}) $
, and its edge set is
![]() $ \{ (\alpha ,0), (\beta , 1):\ \alpha <\lambda , \beta <\kappa \} $
. Note that the vertex sets of these graphs are already well-ordered, and so we generally do not need to invoke the axiom of choice. It was shown that in the game
$ \{ (\alpha ,0), (\beta , 1):\ \alpha <\lambda , \beta <\kappa \} $
. Note that the vertex sets of these graphs are already well-ordered, and so we generally do not need to invoke the axiom of choice. It was shown that in the game
![]() $ \mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega }, K_{\omega }) $
Maker has a winning strategy (see [Reference Bowler, Emde and Gut3]). In this note we analyse similar games on uncountable graphs.
$ \mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega }, K_{\omega }) $
Maker has a winning strategy (see [Reference Bowler, Emde and Gut3]). In this note we analyse similar games on uncountable graphs.
Note that each outcome of the game defines a 2-colouring of
![]() $E(G)$
. This suggests a possible connection to Ramsey type problems, although in the current context the colourings in question are not arbitrary but are produced by players with particular goals in mind. There are colourings of the edges of a
$E(G)$
. This suggests a possible connection to Ramsey type problems, although in the current context the colourings in question are not arbitrary but are produced by players with particular goals in mind. There are colourings of the edges of a
![]() $K_{\omega _1}$
with two colours without any monochromatic
$K_{\omega _1}$
with two colours without any monochromatic
![]() $K_{\omega _1}$
in ZFC (see [Reference Sierpiński13]), but if instead of the axiom of choice one assumes DC+AD, then there is always a monochromatic
$K_{\omega _1}$
in ZFC (see [Reference Sierpiński13]), but if instead of the axiom of choice one assumes DC+AD, then there is always a monochromatic
![]() $K_{\omega _1}$
because
$K_{\omega _1}$
because
![]() $\omega _1$
becomes measurable (see [Reference Kanamori9, Theorem 28.2]) and hence weakly compactFootnote
1
.
$\omega _1$
becomes measurable (see [Reference Kanamori9, Theorem 28.2]) and hence weakly compactFootnote
1
.
The existence of a monochromatic
![]() $K_{\omega ,\omega _1}$
when colouring the edges of a
$K_{\omega ,\omega _1}$
when colouring the edges of a
![]() $K_{\omega ,\omega _1}$
with two colours is even more dependent on the set-theoretic framework. While there is a colouring without a monochromatic copy in ZFC+CH, there is no such colouring in ZFC+
$K_{\omega ,\omega _1}$
with two colours is even more dependent on the set-theoretic framework. While there is a colouring without a monochromatic copy in ZFC+CH, there is no such colouring in ZFC+
![]() $\omega _1<\mathfrak {p} $
. Since we could not find these particular statements formulated anywhere in the literature on infinite Ramsey theory, for the sake of completeness we include them here as Corollaries 2.2 and 3.3.
$\omega _1<\mathfrak {p} $
. Since we could not find these particular statements formulated anywhere in the literature on infinite Ramsey theory, for the sake of completeness we include them here as Corollaries 2.2 and 3.3.
These Ramsey-type results compare well to the corresponding results about the existence of a winning strategy for either player. Our main results are as follows:
Theorem 1.1. It is independent of ZFC if Breaker has a winning strategy in the game
![]() $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega , \omega _1}, K_{\omega ,\omega _1}) $
. He has one under ZFC+GCH,Footnote
2
while Maker has one under ZFC
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega , \omega _1}, K_{\omega ,\omega _1}) $
. He has one under ZFC+GCH,Footnote
2
while Maker has one under ZFC
![]() $+\omega _1<\mathfrak {p}$
.
$+\omega _1<\mathfrak {p}$
.
Theorem 1.2. It is independent of ZFC if every
![]() $ 2 $
-colouring of the edges of
$ 2 $
-colouring of the edges of
![]() $ K_{\omega , \omega _1} $
admits a monochromatic copy of
$ K_{\omega , \omega _1} $
admits a monochromatic copy of
![]() $ K_{\omega , \omega _1} $
. It is true in ZFC
$ K_{\omega , \omega _1} $
. It is true in ZFC
![]() $+\omega _1<\mathfrak {p} $
but fails under ZFC+CH.
$+\omega _1<\mathfrak {p} $
but fails under ZFC+CH.
Theorem 1.3. Assuming the consistency of AD, it is independent of ZF+DC if Breaker has winning strategies in the games
![]() $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _n}, K_{\omega _n}) $
for
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _n}, K_{\omega _n}) $
for
![]() $ n\in \{ 1,2 \} $
. He has such winning strategies under ZFC+GCH, while Maker has winning strategies in these games under ZF+DC+AD.
$ n\in \{ 1,2 \} $
. He has such winning strategies under ZFC+GCH, while Maker has winning strategies in these games under ZF+DC+AD.
Let
![]() $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\kappa }, K_{\mathsf {club}}) $
be the game in which Maker’s goal is to build a “
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\kappa }, K_{\mathsf {club}}) $
be the game in which Maker’s goal is to build a “
![]() $K_{\mathsf {club}}$
,” i.e., a complete graph whose vertex set is a closed unbounded subset of
$K_{\mathsf {club}}$
,” i.e., a complete graph whose vertex set is a closed unbounded subset of
![]() $ \kappa $
.
$ \kappa $
.
Theorem 1.4. Assuming the consistency of AD, it is independent of ZF+DC if Breaker has a winning strategy in the game
![]() $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _1}, K_{\mathsf {club}}) $
.
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _1}, K_{\mathsf {club}}) $
.
Our results raise the following natural questions:
Question 1.5. Is it consistent with ZFC that neither Maker nor Breaker has a winning strategy in the game
![]() $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega , \omega _1}, K_{\omega ,\omega _1}) $
?
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega , \omega _1}, K_{\omega ,\omega _1}) $
?
Question 1.6. Does Breaker have a winning strategy in
![]() $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _1}, K_{\omega _1})$
under ZFC?
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _1}, K_{\omega _1})$
under ZFC?
Question 1.7. Does Maker have a winning strategy in
![]() $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _1}, K_{\mathsf {club}}) $
under ZF+DC+AD?
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _1}, K_{\mathsf {club}}) $
under ZF+DC+AD?
2 The winning strategies of Breaker under GCH
Proposition 2.1 (ZFC+GCH).
For every infinite cardinal
![]() $ \kappa $
, Breaker has a winning strategy in the game
$ \kappa $
, Breaker has a winning strategy in the game
![]() $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\kappa ^{+}}, K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}}) $
.
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\kappa ^{+}}, K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}}) $
.
Proof Let us assume that
![]() $ K_{\kappa ^{+}} $
is represented as the complete graph on the vertex set
$ K_{\kappa ^{+}} $
is represented as the complete graph on the vertex set
![]() $\kappa ^+$
. Working under GCH, we fix an enumeration
$\kappa ^+$
. Working under GCH, we fix an enumeration
![]() $ \{ A_\alpha : \alpha <\kappa ^{+} \} $
of
$ \{ A_\alpha : \alpha <\kappa ^{+} \} $
of
![]() $ [\kappa ^{+}]^{\kappa } $
and for each
$ [\kappa ^{+}]^{\kappa } $
and for each
![]() $\alpha <\kappa ^{+}$
, we pick a surjective function
$\alpha <\kappa ^{+}$
, we pick a surjective function
![]() $ f_\alpha : \kappa \rightarrow \{ A_\beta : \beta \leq \alpha \}$
). Whenever Maker plays an edge
$ f_\alpha : \kappa \rightarrow \{ A_\beta : \beta \leq \alpha \}$
). Whenever Maker plays an edge
![]() $ \{ \beta , \alpha \} $
with
$ \{ \beta , \alpha \} $
with
![]() $ \beta < \alpha $
and there is a
$ \beta < \alpha $
and there is a
![]() $ \gamma <\kappa $
such that this is the
$ \gamma <\kappa $
such that this is the
![]() $(\gamma +1) $
st downwards edge from
$(\gamma +1) $
st downwards edge from
![]() $ \alpha $
she claims, Breaker chooses the smallest
$ \alpha $
she claims, Breaker chooses the smallest
![]() $\delta \in f_\alpha (\gamma ) $
for which
$\delta \in f_\alpha (\gamma ) $
for which
![]() $ \{ \delta , \alpha \} $
is available, and plays
$ \{ \delta , \alpha \} $
is available, and plays
![]() $ \{ \delta , \alpha \} $
if such a
$ \{ \delta , \alpha \} $
if such a
![]() $ \delta $
exists—otherwise he plays arbitrarily.
$ \delta $
exists—otherwise he plays arbitrarily.
Suppose for a contradiction that Maker manages to build a
![]() $ K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}} $
(despite Breaker playing as above) and let
$ K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}} $
(despite Breaker playing as above) and let
![]() $ A $
be its smaller and
$ A $
be its smaller and
![]() $ B $
its bigger vertex class. Then there is an
$ B $
its bigger vertex class. Then there is an
![]() $ \alpha <\kappa ^{+} $
with
$ \alpha <\kappa ^{+} $
with
![]() $A_{\alpha }=A$
. Fix a
$A_{\alpha }=A$
. Fix a
![]() $ \beta \in B $
with
$ \beta \in B $
with
![]() $ \beta> \max \{\alpha , \sup A\} $
and let
$ \beta> \max \{\alpha , \sup A\} $
and let
![]() $ \gamma < \kappa $
with
$ \gamma < \kappa $
with
![]() $ f_\beta (\gamma )=A $
. At the turn when Maker claims a downwards edge from
$ f_\beta (\gamma )=A $
. At the turn when Maker claims a downwards edge from
![]() $ \beta $
for the
$ \beta $
for the
![]() $ (\gamma +1) $
st time, there are still
$ (\gamma +1) $
st time, there are still
![]() $ \kappa $
many
$ \kappa $
many
![]() $ \delta \in A $
for which
$ \delta \in A $
for which
![]() $ \{ \delta , \beta \} $
is available, and thus Breaker’s next play is
$ \{ \delta , \beta \} $
is available, and thus Breaker’s next play is
![]() $ \{ \delta , \beta \} $
for the smallest such
$ \{ \delta , \beta \} $
for the smallest such
![]() $ \delta $
. This contradicts
$ \delta $
. This contradicts
![]() $ \{ \delta , \beta \}\in E(G_M) $
.
$ \{ \delta , \beta \}\in E(G_M) $
.
The corresponding negative Ramsey-result can be proved in a similar manner:
Corollary 2.2 (ZFC+GCH).
For every infinite cardinal
![]() $ \kappa $
, there exists a
$ \kappa $
, there exists a
![]() $ 2 $
-colouring of the edge set of
$ 2 $
-colouring of the edge set of
![]() $ K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}} $
without a monochromatic copy of
$ K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}} $
without a monochromatic copy of
![]() $ K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}} $
.
$ K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}} $
.
Proof Let
![]() $ \{ v_\alpha : \alpha <\kappa ^{+} \} $
be an enumeration of the larger vertex class and let
$ \{ v_\alpha : \alpha <\kappa ^{+} \} $
be an enumeration of the larger vertex class and let
![]() $ \{ A_\alpha : \alpha <\kappa ^{+} \} $
be an enumeration of
$ \{ A_\alpha : \alpha <\kappa ^{+} \} $
be an enumeration of
![]() $ [\kappa ^{+}]^{\kappa } $
. For each
$ [\kappa ^{+}]^{\kappa } $
. For each
![]() $ \alpha <\kappa ^{+} $
, we colour the edges incident with
$ \alpha <\kappa ^{+} $
, we colour the edges incident with
![]() $ v_\alpha $
in such a way that for every
$ v_\alpha $
in such a way that for every
![]() $ \beta \leq \alpha $
both colours appear among the edges between
$ \beta \leq \alpha $
both colours appear among the edges between
![]() $ v_\alpha $
and
$ v_\alpha $
and
![]() $ A_\beta $
. This clearly ensures that no set
$ A_\beta $
. This clearly ensures that no set
![]() $ A $
can be the smaller vertex class of a monochromatic copy of
$ A $
can be the smaller vertex class of a monochromatic copy of
![]() $ K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}} $
and therefore no such a monochromatic copy exists.
$ K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}} $
and therefore no such a monochromatic copy exists.
Observation 2.3. If Breaker has a winning strategy in
![]() $ \mathfrak {MB}(G,H) $
, then he also has one in every game
$ \mathfrak {MB}(G,H) $
, then he also has one in every game
![]() $ \mathfrak {MB}(G',H') $
where
$ \mathfrak {MB}(G',H') $
where
![]() $ G' $
is a subgraph of
$ G' $
is a subgraph of
![]() $ G $
and
$ G $
and
![]() $ H' $
is a supergraph of
$ H' $
is a supergraph of
![]() $ H $
.
$ H $
.
Since
![]() $ K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}} $
is a subgraph of
$ K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}} $
is a subgraph of
![]() $ K_{\kappa ^{+}} $
, Observation 2.3 guarantees that Proposition 2.1 has the following consequences:
$ K_{\kappa ^{+}} $
, Observation 2.3 guarantees that Proposition 2.1 has the following consequences:
Corollary 2.4 (ZFC+GCH).
For every infinite cardinal
![]() $ \kappa $
, Breaker has a winning strategy in the following games:
$ \kappa $
, Breaker has a winning strategy in the following games:
-
(1)
 $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}}, K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}}) $
,
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}}, K_{\kappa , \kappa ^{+}}) $
, -
(2)
 $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\kappa ^{+}}, K_{\kappa ^{+}}) $
,
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\kappa ^{+}}, K_{\kappa ^{+}}) $
, -
(3)
 $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\kappa ^{+}}, K_{\mathsf {club}}). $
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\kappa ^{+}}, K_{\mathsf {club}}). $
3 Winning strategies for Maker
During the course of play in
![]() $\mathfrak {MB}(G,H)$
we will refer to a vertex as fresh if no edge incident with that vertex has been claimed yet by either player.
$\mathfrak {MB}(G,H)$
we will refer to a vertex as fresh if no edge incident with that vertex has been claimed yet by either player.
3.1 A winning strategy for Maker in
 $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega , \omega _1}, K_{\omega , \omega _1})$
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega , \omega _1}, K_{\omega , \omega _1})$
A set
![]() $\mathcal {F}$
of sets has the strong finite intersection property if the intersection of any finitely many elements of
$\mathcal {F}$
of sets has the strong finite intersection property if the intersection of any finitely many elements of
![]() $\mathcal {F}$
is infinite. Given two sets X and Y, write
$\mathcal {F}$
is infinite. Given two sets X and Y, write
![]() $X \subseteq ^*Y$
if
$X \subseteq ^*Y$
if
![]() $X \setminus Y$
is finite. A pseudo-intersection for a set
$X \setminus Y$
is finite. A pseudo-intersection for a set
![]() $\mathcal {F}$
of sets is a set P with
$\mathcal {F}$
of sets is a set P with
![]() $P \subseteq ^* F$
for all
$P \subseteq ^* F$
for all
![]() $F \in \mathcal {F}$
. The cardinal
$F \in \mathcal {F}$
. The cardinal
![]() $\mathfrak {p}$
is the minimum cardinality of a set
$\mathfrak {p}$
is the minimum cardinality of a set
![]() $\mathcal {F}$
of subsets of
$\mathcal {F}$
of subsets of
![]() $\omega $
that has the strong finite intersection property but does not admit an infinite pseudo-intersection. Clearly
$\omega $
that has the strong finite intersection property but does not admit an infinite pseudo-intersection. Clearly
![]() $\aleph _0<\mathfrak {p} \leq 2^{\aleph _0}$
and it is known that
$\aleph _0<\mathfrak {p} \leq 2^{\aleph _0}$
and it is known that
![]() $ \omega _1<\mathfrak {p} $
is consistent relative to ZFC (see [Reference Kunen10, Lemma III.3.22 on p. 176]).
$ \omega _1<\mathfrak {p} $
is consistent relative to ZFC (see [Reference Kunen10, Lemma III.3.22 on p. 176]).
Proposition 3.1. Maker has a winning strategy in
![]() $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega , \omega _1}, K_{\omega , \omega _1}) $
if
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega , \omega _1}, K_{\omega , \omega _1}) $
if
![]() $ \omega _1<\mathfrak {p} $
.
$ \omega _1<\mathfrak {p} $
.
Proof Let
![]() $ U$
and
$ U$
and
![]() $ V $
be the two sides of the bipartite graph
$ V $
be the two sides of the bipartite graph
![]() $ K_{\omega , \omega _1} $
, where
$ K_{\omega , \omega _1} $
, where
![]() $ \left |U\right |=\omega $
and
$ \left |U\right |=\omega $
and
![]() $ \left |V\right |=\omega _1 $
. We denote the subgraph of
$ \left |V\right |=\omega _1 $
. We denote the subgraph of
![]() $ G $
induced by the edges Maker claimed before turn
$ G $
induced by the edges Maker claimed before turn
![]() $ \alpha $
by
$ \alpha $
by
![]() $ G^{\alpha }_M $
and we write
$ G^{\alpha }_M $
and we write
![]() $ N_{G^{\alpha }_{M}}(v) $
for the set of the neighbours of v in this graph.
$ N_{G^{\alpha }_{M}}(v) $
for the set of the neighbours of v in this graph.
During the game Maker will choose a sequence
![]() $\langle v_{\alpha } \colon \alpha < \kappa \rangle \langle v_{\alpha } \colon \alpha < \omega _1 \rangle $
of distinct vertices from V and a sequence
$\langle v_{\alpha } \colon \alpha < \kappa \rangle \langle v_{\alpha } \colon \alpha < \omega _1 \rangle $
of distinct vertices from V and a sequence
![]() $\langle N_{\alpha } \colon \alpha < \kappa \rangle $
of subsets of U in such a way as to ensure that for any
$\langle N_{\alpha } \colon \alpha < \kappa \rangle $
of subsets of U in such a way as to ensure that for any
![]() $\alpha < \kappa $
and a sequence
$\alpha < \kappa $
and a sequence
![]() $\langle N_{\alpha } \colon \alpha < \omega _1\rangle $
of subsets of U in such a way as to ensure that for any
$\langle N_{\alpha } \colon \alpha < \omega _1\rangle $
of subsets of U in such a way as to ensure that for any
![]() $\alpha < \omega _1$
$\alpha < \omega _1$
-
(1)
 $N_{\alpha } \subseteq N_{G_M}^{\omega \cdot (\alpha + 1)}(v_{\alpha })$
,
$N_{\alpha } \subseteq N_{G_M}^{\omega \cdot (\alpha + 1)}(v_{\alpha })$
, -
(2) the set
 $\{N_{\beta } \colon \beta \leq \alpha \}$
has the strong finite intersection property.
$\{N_{\beta } \colon \beta \leq \alpha \}$
has the strong finite intersection property.
Assume that turn
![]() $ \alpha \cdot \omega $
has just begun for some
$ \alpha \cdot \omega $
has just begun for some
![]() $\alpha <\omega _1$
and that Maker has constructed suitable
$\alpha <\omega _1$
and that Maker has constructed suitable
![]() $v_{\beta }$
and
$v_{\beta }$
and
![]() $N_{\beta }$
for all
$N_{\beta }$
for all
![]() $\beta < \alpha $
. She picks
$\beta < \alpha $
. She picks
![]() $ v_{\alpha }$
to be any fresh vertex in V. Using (2) for all
$ v_{\alpha }$
to be any fresh vertex in V. Using (2) for all
![]() $\beta < \alpha $
, we know that the set
$\beta < \alpha $
, we know that the set
![]() $\{N_{\beta } \colon \beta < \alpha \}$
has the strong finite intersection property. Let
$\{N_{\beta } \colon \beta < \alpha \}$
has the strong finite intersection property. Let
![]() $P_\alpha $
be an infinite pseudo-intersection of this family. In each of the next
$P_\alpha $
be an infinite pseudo-intersection of this family. In each of the next
![]() $ \omega $
turns, Maker claims an edge
$ \omega $
turns, Maker claims an edge
![]() $ \{ u, v_\alpha \} $
with
$ \{ u, v_\alpha \} $
with
![]() $ u\in P_\alpha $
. Let
$ u\in P_\alpha $
. Let
![]() $N_{\alpha }$
be the set of all the endpoints
$N_{\alpha }$
be the set of all the endpoints
![]() $u \in U$
of these edges. It is easy to check that this construction satisfies (1) and (2) for
$u \in U$
of these edges. It is easy to check that this construction satisfies (1) and (2) for
![]() $\alpha $
.
$\alpha $
.
At the end of the game
![]() $ \{N_{\alpha } \colon \alpha <\omega _1 \} $
has the strong finite intersection property and hence (by the assumption
$ \{N_{\alpha } \colon \alpha <\omega _1 \} $
has the strong finite intersection property and hence (by the assumption
![]() $ \omega _1<\mathfrak {p} $
) admits an infinite pseudo-intersection
$ \omega _1<\mathfrak {p} $
) admits an infinite pseudo-intersection
![]() $ P $
. By the definition of
$ P $
. By the definition of
![]() $ P $
, for each
$ P $
, for each
![]() $ \alpha <\omega _1 $
, the set
$ \alpha <\omega _1 $
, the set
![]() $ P\setminus N_\alpha $
is finite. Then there exists an uncountable
$ P\setminus N_\alpha $
is finite. Then there exists an uncountable
![]() $ O\subseteq \omega _1 $
and a finite
$ O\subseteq \omega _1 $
and a finite
![]() $ F\subseteq P $
such that
$ F\subseteq P $
such that
![]() $ P\setminus N_\alpha =F $
for every
$ P\setminus N_\alpha =F $
for every
![]() $ \alpha \in O $
. Finally,
$ \alpha \in O $
. Finally,
![]() $ (P\setminus F)\cup \{ v_\alpha : \alpha \in O \} $
induces a copy of
$ (P\setminus F)\cup \{ v_\alpha : \alpha \in O \} $
induces a copy of
![]() $ K_{\omega , \omega _1} $
, all of whose edges have been claimed by Maker.
$ K_{\omega , \omega _1} $
, all of whose edges have been claimed by Maker.
Remark 3.2. The same proof shows that Maker has a winning strategy in
![]() $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega , \kappa }, K_{\omega , \kappa }) $
for every
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega , \kappa }, K_{\omega , \kappa }) $
for every
![]() $\kappa <\mathfrak {p}$
with
$\kappa <\mathfrak {p}$
with
![]() $ \mathsf {cf}(\kappa )>\aleph _0 $
.
$ \mathsf {cf}(\kappa )>\aleph _0 $
.
The proof of Proposition 3.1 leads to the following positive Ramsey result:
Corollary 3.3. If
![]() $ \omega _1<\mathfrak {p} $
, then any
$ \omega _1<\mathfrak {p} $
, then any
![]() $ 2 $
-colouring of the edges of
$ 2 $
-colouring of the edges of
![]() $ K_{\omega , \omega _1} $
admits a monochromatic copy of
$ K_{\omega , \omega _1} $
admits a monochromatic copy of
![]() $ K_{\omega , \omega _1} $
.
$ K_{\omega , \omega _1} $
.
Proof Call the colours red and blue, and call the countable and uncountable sides of the original graph U and V respectively. We pick a free ultrafilter
![]() $ \mathcal {U} $
on
$ \mathcal {U} $
on
![]() $ U $
. Then for each
$ U $
. Then for each
![]() $ v\in V $
either the set
$ v\in V $
either the set
![]() $ N_r(v) $
of the red neighbours of
$ N_r(v) $
of the red neighbours of
![]() $ v $
is in
$ v $
is in
![]() $ \mathcal {U} $
or the set
$ \mathcal {U} $
or the set
![]() $N_b(v)$
of the blue neighbours. We may assume that there is an uncountable
$N_b(v)$
of the blue neighbours. We may assume that there is an uncountable
![]() $ V'\subseteq V $
such that
$ V'\subseteq V $
such that
![]() $ N_r(v)\in \mathcal {U} $
for each
$ N_r(v)\in \mathcal {U} $
for each
![]() $ v\in V' $
. Since
$ v\in V' $
. Since
![]() $ \mathcal {U} $
is a free ultrafilter, the family
$ \mathcal {U} $
is a free ultrafilter, the family
![]() $ \{ N_r(v): v\in V' \} $
has the strong finite intersection property and therefore (by
$ \{ N_r(v): v\in V' \} $
has the strong finite intersection property and therefore (by
![]() $ \omega _1<\mathfrak {p} $
) admits an infinite pseudo-intersection
$ \omega _1<\mathfrak {p} $
) admits an infinite pseudo-intersection
![]() $ P $
. This means that for every
$ P $
. This means that for every
![]() $ v\in V' $
the set
$ v\in V' $
the set
![]() $ P\setminus N_r(v) $
is finite. Then there exists an uncountable
$ P\setminus N_r(v) $
is finite. Then there exists an uncountable
![]() $ V"\subseteq V' $
and finite
$ V"\subseteq V' $
and finite
![]() $ F\subseteq P $
such that
$ F\subseteq P $
such that
![]() $ P\setminus N_r(v)=F $
for each
$ P\setminus N_r(v)=F $
for each
![]() $ v\in V" $
and hence
$ v\in V" $
and hence
![]() $ (P\setminus F)\cup V" $
induces a red copy of
$ (P\setminus F)\cup V" $
induces a red copy of
![]() $ K_{\omega , \omega _1} $
.
$ K_{\omega , \omega _1} $
.
Question 3.4. Is it consistent with ZFC
![]() $+\aleph _\omega <2^{\aleph _0}$
that Maker has a winning strategy in the game
$+\aleph _\omega <2^{\aleph _0}$
that Maker has a winning strategy in the game
![]() $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega , \omega _\omega }, K_{\omega , \omega _\omega }) $
?
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega , \omega _\omega }, K_{\omega , \omega _\omega }) $
?
Theorem 1.1 is implied by the case
![]() $ \kappa =\omega $
of Corollary 2.4/(1) together with Proposition 3.1. Similarly, Theorem 1.2 follows from Corollaries 2.2 and 3.3.
$ \kappa =\omega $
of Corollary 2.4/(1) together with Proposition 3.1. Similarly, Theorem 1.2 follows from Corollaries 2.2 and 3.3.
3.2 A winning strategy for Maker in
 $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _1}, K_{\omega _1})$
and
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _1}, K_{\omega _1})$
and
 $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _2}, K_{\omega _2})$
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _2}, K_{\omega _2})$
Proposition 3.5 (ZF).
If either
![]() $ \kappa $
is measurable or
$ \kappa $
is measurable or
![]() $ \kappa =\omega $
, then Maker has a winning strategy in the game
$ \kappa =\omega $
, then Maker has a winning strategy in the game
![]() $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\kappa }, K_{\kappa }) $
.
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\kappa }, K_{\kappa }) $
.
Proof A sub-binary Hausdorff tree is a set theoretic tree
![]() $ T $
in which each vertex has at most two children and no two vertices at any limit level have the same set of predecessors.
$ T $
in which each vertex has at most two children and no two vertices at any limit level have the same set of predecessors.
During the game Maker builds a sequence
![]() $ \left \langle T_\alpha : \alpha \leq \kappa \right \rangle $
of sub-binary Hausdorff trees with root
$ \left \langle T_\alpha : \alpha \leq \kappa \right \rangle $
of sub-binary Hausdorff trees with root
![]() $ 0 $
and
$ 0 $
and
![]() $ T_\alpha \subseteq \kappa $
of height at most
$ T_\alpha \subseteq \kappa $
of height at most
![]() $1+\alpha $
such that:
$1+\alpha $
such that:
-
(a)
-
(i)
 $ T_0=\{ 0 \} $
,
$ T_0=\{ 0 \} $
, -
(ii)
 $ T_{\alpha +1} $
is obtained from
$ T_{\alpha +1} $
is obtained from
 $ T_\alpha $
by inserting a new maximal element,
$ T_\alpha $
by inserting a new maximal element, -
(iii)
 $ T_\alpha =\bigcup _{\beta <\alpha }T_\beta $
if
$ T_\alpha =\bigcup _{\beta <\alpha }T_\beta $
if
 $ \alpha $
is a limit ordinal,
$ \alpha $
is a limit ordinal,
-
-
(b) for every distinct
 $ <_{T_\alpha } $
-comparable
$ <_{T_\alpha } $
-comparable
 $ u,v\in T_\alpha $
, the edge
$ u,v\in T_\alpha $
, the edge
 $ \{ u,v \} $
is claimed by Maker in the game.
$ \{ u,v \} $
is claimed by Maker in the game.
Suppose that
![]() $ \alpha =\beta +1 $
and
$ \alpha =\beta +1 $
and
![]() $ T_\beta $
is already defined. Maker picks the smallest ordinal
$ T_\beta $
is already defined. Maker picks the smallest ordinal
![]() $ v $
such that no edge incident with v is claimed and claims edge
$ v $
such that no edge incident with v is claimed and claims edge
![]() $ \{ 0, v \} $
. Then, for as long as she can, on each following turn she connects
$ \{ 0, v \} $
. Then, for as long as she can, on each following turn she connects
![]() $ v $
to vertices in
$ v $
to vertices in
![]() $ T_\beta $
in such a way that:
$ T_\beta $
in such a way that:
-
(1) she maintains that the current neighbourhood of
 $ v $
in her graph is a downward closed chain in
$ v $
in her graph is a downward closed chain in
 $ T_\beta $
,
$ T_\beta $
, -
(2) whenever she claims some
 $ \{ u,v \} $
, then Breaker has no edge between
$ \{ u,v \} $
, then Breaker has no edge between
 $ v $
and the subtree
$ v $
and the subtree
 $ T_{\beta , u} $
of
$ T_{\beta , u} $
of
 $ T_\beta $
rooted at
$ T_\beta $
rooted at
 $ u $
.
$ u $
.
Note that, at any step at which v has a largest Maker-neighbour in
![]() $T_\beta $
and this neighbour has two children in
$T_\beta $
and this neighbour has two children in
![]() $ T_\beta $
, she can proceed. Moreover, she can also proceed even if there is no such largest Maker-neighbour as long as there is some element of
$ T_\beta $
, she can proceed. Moreover, she can also proceed even if there is no such largest Maker-neighbour as long as there is some element of
![]() $T_{\beta }$
whose predecessors are precisely the Maker-neighbours of v in
$T_{\beta }$
whose predecessors are precisely the Maker-neighbours of v in
![]() $T_{\beta }$
. Thus, if Maker is unable to continue this process with
$T_{\beta }$
. Thus, if Maker is unable to continue this process with
![]() $ v $
, then either
$ v $
, then either
![]() $ v $
has a largest Maker-neighbour in
$ v $
has a largest Maker-neighbour in
![]() $ T_\beta $
which has at most one child or else there is no vertex in
$ T_\beta $
which has at most one child or else there is no vertex in
![]() $T_{\beta }$
with precisely the Maker-neighbours of u as its predecessors. In either case we can define
$T_{\beta }$
with precisely the Maker-neighbours of u as its predecessors. In either case we can define
![]() $ T_{\beta +1} $
by adding
$ T_{\beta +1} $
by adding
![]() $ v $
to
$ v $
to
![]() $ T_\beta $
with its current set of Maker-neighbours as its predecessors, and Maker starts a new phase with a new fresh vertex.
$ T_\beta $
with its current set of Maker-neighbours as its predecessors, and Maker starts a new phase with a new fresh vertex.
It is enough to show that there is a
![]() $ \kappa $
-branch
$ \kappa $
-branch
![]() $ B $
in
$ B $
in
![]() $ T_\kappa $
, because then
$ T_\kappa $
, because then
![]() $ G_M[B] $
is a copy of
$ G_M[B] $
is a copy of
![]() $ K_{\kappa } $
by (b). Since
$ K_{\kappa } $
by (b). Since
![]() $ \left |T_\kappa \right |=\kappa $
by (a), we can fix a
$ \left |T_\kappa \right |=\kappa $
by (a), we can fix a
![]() $ \kappa $
-complete free ultrafilter
$ \kappa $
-complete free ultrafilter
![]() $ \mathcal {U} $
on
$ \mathcal {U} $
on
![]() $ T_\kappa $
.
$ T_\kappa $
.
By transfinite recursion we build a
![]() $ \kappa $
-branch. Let
$ \kappa $
-branch. Let
![]() $ v_0:=0 $
. Suppose that there is an
$ v_0:=0 $
. Suppose that there is an
![]() $ \alpha <\kappa $
such that the
$ \alpha <\kappa $
such that the
![]() $ <_{T_\kappa } $
-increasing sequence
$ <_{T_\kappa } $
-increasing sequence
![]() $ \left \langle v_\beta : \beta <\alpha \right \rangle $
is already defined and for each
$ \left \langle v_\beta : \beta <\alpha \right \rangle $
is already defined and for each
![]() $ \beta <\alpha $
,
$ \beta <\alpha $
,
![]() $ T_{\kappa , v_\beta }\in \mathcal {U} $
. If
$ T_{\kappa , v_\beta }\in \mathcal {U} $
. If
![]() $ \alpha $
is a limit ordinal, then since
$ \alpha $
is a limit ordinal, then since
![]() $\bigcap _{\beta <\alpha }T_{v_\beta }\in \mathcal {U} $
by the
$\bigcap _{\beta <\alpha }T_{v_\beta }\in \mathcal {U} $
by the
![]() $ \kappa $
-completeness of
$ \kappa $
-completeness of
![]() $ \mathcal {U} $
, there is at least one vertex of T with all
$ \mathcal {U} $
, there is at least one vertex of T with all
![]() $v_{\beta }$
as predecessors. We define
$v_{\beta }$
as predecessors. We define
![]() $ v_\alpha $
to be the unique minimal such vertex, so that
$ v_\alpha $
to be the unique minimal such vertex, so that
![]() $ T_{v_\alpha }=\bigcap _{\beta <\alpha }T_{v_\beta }\in \mathcal {U} $
. If
$ T_{v_\alpha }=\bigcap _{\beta <\alpha }T_{v_\beta }\in \mathcal {U} $
. If
![]() $ \alpha =\beta +1 $
, then
$ \alpha =\beta +1 $
, then
![]() $ T_{\kappa , v_\beta }\in \mathcal {U} $
by assumption. Since
$ T_{\kappa , v_\beta }\in \mathcal {U} $
by assumption. Since
![]() $ T_\kappa $
is sub-binary,
$ T_\kappa $
is sub-binary,
![]() $ v_\beta $
has a unique child
$ v_\beta $
has a unique child
![]() $ v $
satisfying
$ v $
satisfying
![]() $ T_{\kappa , v}\in \mathcal {U} $
and we let
$ T_{\kappa , v}\in \mathcal {U} $
and we let
![]() $ v_{\beta +1}:=v $
. The recursion is done and
$ v_{\beta +1}:=v $
. The recursion is done and
![]() $\{ v_\alpha : \alpha <\kappa \} $
is clearly a
$\{ v_\alpha : \alpha <\kappa \} $
is clearly a
![]() $ \kappa $
-branch.
$ \kappa $
-branch.
We remark that this strategy is quite flexible and deals also with a number of variants of the Maker–Breaker game. For example, if Breaker is allowed
![]() $k<\omega $
moves for every move that Maker picks, simply take a sub-
$k<\omega $
moves for every move that Maker picks, simply take a sub-
![]() $(k+1)$
-regular Hausdorff tree, in which every node has at most
$(k+1)$
-regular Hausdorff tree, in which every node has at most
![]() $k+1$
children. Furthermore, if in addition Breaker is allowed to go first in every turn, simply weaken the Hausdorff assumption to the requirement that at most
$k+1$
children. Furthermore, if in addition Breaker is allowed to go first in every turn, simply weaken the Hausdorff assumption to the requirement that at most
![]() $k+1$
vertices at a limit level have the same set of predecessors.
$k+1$
vertices at a limit level have the same set of predecessors.
Since
![]() $ \omega _1 $
and
$ \omega _1 $
and
![]() $ \omega _2 $
are measurable cardinals under ZF+DC+AD [Reference Kanamori9, Theorems 28.2 and 28.6], the cases
$ \omega _2 $
are measurable cardinals under ZF+DC+AD [Reference Kanamori9, Theorems 28.2 and 28.6], the cases
![]() $ \kappa \in \{\omega , \omega _1 \} $
of Corollary 2.4/(2) and the cases
$ \kappa \in \{\omega , \omega _1 \} $
of Corollary 2.4/(2) and the cases
![]() $\kappa \in \{\omega _1, \omega _2\}$
of Proposition 3.5 together imply Theorem 1.3.
$\kappa \in \{\omega _1, \omega _2\}$
of Proposition 3.5 together imply Theorem 1.3.
3.3 Breaker may lose the
 $\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _1}, K_{\mathsf {club}})$
-game
$\mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _1}, K_{\mathsf {club}})$
-game
Proposition 3.6. Under ZF+DC+AD, Breaker does not have a winning strategy in the game
![]() $ \mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _1}, K_{\mathsf {club}}) $
.
$ \mathfrak {MB}(K_{\omega _1}, K_{\mathsf {club}}) $
.
Proof First of all, the club filter on
![]() $ \omega _1 $
is a countably complete free ultrafilter under ZF+DC+AD (this is explicit in the proof of [Reference Kanamori9, Theorem 28.2]). Furthermore, it is normal [Reference Dorais and Hathaway6, Proposition 4.1]. Thus for any 2-colouring of
$ \omega _1 $
is a countably complete free ultrafilter under ZF+DC+AD (this is explicit in the proof of [Reference Kanamori9, Theorem 28.2]). Furthermore, it is normal [Reference Dorais and Hathaway6, Proposition 4.1]. Thus for any 2-colouring of
![]() $ [\omega _1]^{2} $
there exists a colour with a monochromatic
$ [\omega _1]^{2} $
there exists a colour with a monochromatic
![]() $ K_{\mathsf {club}} $
(the standard proof of this for arbitrary normal ultrafilters uses only ZF, see [Reference Jech8, Theorem 10.22]). It follows that if Breaker successfully prevents Maker from building a
$ K_{\mathsf {club}} $
(the standard proof of this for arbitrary normal ultrafilters uses only ZF, see [Reference Jech8, Theorem 10.22]). It follows that if Breaker successfully prevents Maker from building a
![]() $ K_{\mathsf {club}} $
, then he necessarily builds a
$ K_{\mathsf {club}} $
, then he necessarily builds a
![]() $ K_{\mathsf {club}} $
himself.
$ K_{\mathsf {club}} $
himself.
Suppose for a contradiction that Breaker has a winning strategy. We shall show that Maker can “steal” this winning strategy. Indeed, Maker picks an arbitrary edge in turn
![]() $ 0 $
as well as in each limit turn while in successor turns she pretends to be Breaker and claims edges according to his winning strategy. This is a winning strategy for Maker, a contradiction.
$ 0 $
as well as in each limit turn while in successor turns she pretends to be Breaker and claims edges according to his winning strategy. This is a winning strategy for Maker, a contradiction.
Theorem 1.4 follows from the case
![]() $ \kappa =\omega $
of Corollary 2.4/(3) and Proposition 3.6.
$ \kappa =\omega $
of Corollary 2.4/(3) and Proposition 3.6.
Remark 3.7. The same strategy stealing argument shows that if
![]() $\kappa $
is a weakly compact cardinal, then Breaker does not have a winning strategy in the game
$\kappa $
is a weakly compact cardinal, then Breaker does not have a winning strategy in the game
![]() $ \mathfrak {MB}(K_{\kappa }, K_{\kappa }) $
.
$ \mathfrak {MB}(K_{\kappa }, K_{\kappa }) $
.
Remark 3.8. We did not really use the full power of AD, just some consequences that are weaker in the sense of consistency strength than AD itself. The axiom-system ZF+DC+“
![]() $\omega _1$
is measurable” is equiconsistent with ZFC+“there exists a measurable cardinal” (see [Reference Jech7]). The club filter being an ultrafilter is a strictly stronger assumption; for more details see page 3 of [Reference Dorais and Hathaway6].
$\omega _1$
is measurable” is equiconsistent with ZFC+“there exists a measurable cardinal” (see [Reference Jech7]). The club filter being an ultrafilter is a strictly stronger assumption; for more details see page 3 of [Reference Dorais and Hathaway6].
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Stefan Geschke, Zoltán Vidnyánszky, and Daniel Hathaway for the insightful discussions about the Axiom of determinacy. The third author would like to thank the generous support of the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation and NKFIH OTKA-129211.