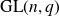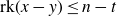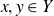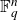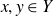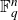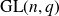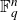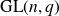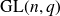1. Introduction and results
One of the most famous results in extremal set theory is the Erdős–Ko–Rado Theorem [
Reference Erdős, Ko and Rado9
]. In its strengthened version [
Reference Wilson27
] it states that, for all fixed k and t and all sufficiently large n, every t-intersecting family of k-subsets of
![]() $\{1,2,\dots,n\}$
has size at most
$\{1,2,\dots,n\}$
has size at most
![]() $\binom{n-t}{k-t}$
and equality holds if and only if there are t distinct points of
$\binom{n-t}{k-t}$
and equality holds if and only if there are t distinct points of
![]() $\{1,2,\dots,n\}$
contained in all members of the family.
$\{1,2,\dots,n\}$
contained in all members of the family.
There are several analogs of the Erdős–Ko–Rado Theorem (see [
Reference Godsil and Meagher13
], for example). Most notably, following important earlier work [
Reference Cameron and Ku5
,
Reference Frankl and Deza10
,
Reference Godsil and Meagher12
,
Reference Larose and Malvenuto18
], a corresponding result for the symmetric group
![]() $S_n$
was obtained by Ellis, Friedgut and Pilpel in a landmark paper [
Reference Ellis, Friedgut and Pilpel7
]. A subset Y of
$S_n$
was obtained by Ellis, Friedgut and Pilpel in a landmark paper [
Reference Ellis, Friedgut and Pilpel7
]. A subset Y of
![]() $S_n$
is t-intersecting if, for all
$S_n$
is t-intersecting if, for all
![]() $x,y\in Y$
, there exist distinct
$x,y\in Y$
, there exist distinct
![]() $i_1,i_2,\dots,i_t$
in
$i_1,i_2,\dots,i_t$
in
![]() $\{1,2,\dots,n\}$
such that
$\{1,2,\dots,n\}$
such that
![]() $x(i_k)=y(i_k)$
for all k. It was shown in [
Reference Ellis, Friedgut and Pilpel7
] that, for each fixed t and all sufficiently large n, every t-intersecting set in
$x(i_k)=y(i_k)$
for all k. It was shown in [
Reference Ellis, Friedgut and Pilpel7
] that, for each fixed t and all sufficiently large n, every t-intersecting set in
![]() $S_n$
has size at most
$S_n$
has size at most
![]() $(n-t)!$
and equality holds if and only if Y is a coset of the stabiliser of a t-tuple of distinct points in
$(n-t)!$
and equality holds if and only if Y is a coset of the stabiliser of a t-tuple of distinct points in
![]() $\{1,2,\dots,n\}$
.
$\{1,2,\dots,n\}$
.
In this paper we consider a q-analog of this problem, namely we study a corresponding problem for the finite general linear groups. Throughout this paper q is a fixed prime power and
![]() $G_n$
denotes the general linear group of degree n over the finite field
$G_n$
denotes the general linear group of degree n over the finite field
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q$
, namely the group of invertible
$\mathbb{F}_q$
, namely the group of invertible
![]() $n\times n$
matrices over
$n\times n$
matrices over
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q$
. We say that two elements
$\mathbb{F}_q$
. We say that two elements
![]() $x,y\in G_n$
are t-intersecting if there exist linearly independent elements
$x,y\in G_n$
are t-intersecting if there exist linearly independent elements
![]() $u_1,u_2,\dots,u_t$
in
$u_1,u_2,\dots,u_t$
in
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
such that
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
such that
![]() $xu_k=yu_k$
for all k. Equivalently
$xu_k=yu_k$
for all k. Equivalently
![]() $x,y\in G_n$
are t-intersecting if
$x,y\in G_n$
are t-intersecting if
![]() $\text{rk}(x-y)\le n-t$
. A subset Y of
$\text{rk}(x-y)\le n-t$
. A subset Y of
![]() $G_n$
is called t-intersecting if all pairs in
$G_n$
is called t-intersecting if all pairs in
![]() $Y\times Y$
are t-intersecting.
$Y\times Y$
are t-intersecting.
A coset of the stabiliser of a t-tuple of linearly independent elements of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
has the form
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
has the form
for some t-tuples
![]() $(u_1,u_2,\dots,u_t)$
and
$(u_1,u_2,\dots,u_t)$
and
![]() $(v_1,v_2,\dots,v_t)$
of linearly independent elements of
$(v_1,v_2,\dots,v_t)$
of linearly independent elements of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. We call such a coset a t-coset. It is plain that every t-coset is t-intersecting. Note that the size of a t-coset is
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. We call such a coset a t-coset. It is plain that every t-coset is t-intersecting. Note that the size of a t-coset is
 \begin{equation}\prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right). \end{equation}
\begin{equation}\prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right). \end{equation}
The t-cosets are however not the only t-intersecting sets of this size in
![]() $G_n$
, as the transpose of every t-intersecting set is t-intersecting.
$G_n$
, as the transpose of every t-intersecting set is t-intersecting.
We shall often identify a subset Y of
![]() $G_n$
with its characteristic vector
$G_n$
with its characteristic vector
![]() $1_Y\in\mathbb{C}(G_n)$
(where
$1_Y\in\mathbb{C}(G_n)$
(where
![]() $\mathbb{C}(G_n)$
is the vector space of functions from
$\mathbb{C}(G_n)$
is the vector space of functions from
![]() $G_n$
to
$G_n$
to
![]() $\mathbb{C}$
). It is well known (see [
Reference Ahanjideh and Ahanjideh2
] or [
Reference Ahmadi and Meagher3
], for example) that, since
$\mathbb{C}$
). It is well known (see [
Reference Ahanjideh and Ahanjideh2
] or [
Reference Ahmadi and Meagher3
], for example) that, since
![]() $G_n$
contains a Singer cycle as a regular subgroup, the size of every 1-intersecting set in
$G_n$
contains a Singer cycle as a regular subgroup, the size of every 1-intersecting set in
![]() $G_n$
is at most the expression given in (1·1) for
$G_n$
is at most the expression given in (1·1) for
![]() $t=1$
. Meagher and Razafimahatratra [
Reference Meagher and Razafimahatratra21
] have shown that, if Y is a 1-intersecting set of size
$t=1$
. Meagher and Razafimahatratra [
Reference Meagher and Razafimahatratra21
] have shown that, if Y is a 1-intersecting set of size
![]() $q^2-q$
in
$q^2-q$
in
![]() $G_2$
, then
$G_2$
, then
![]() $1_Y$
is in the span of the characteristic vectors of the 1-cosets. We prove a corresponding result for all t and n for which n is sufficiently large compared to t.
$1_Y$
is in the span of the characteristic vectors of the 1-cosets. We prove a corresponding result for all t and n for which n is sufficiently large compared to t.
Theorem 1·1. Let t be a positive integer and let Y be a t-intersecting set in
![]() $ G_n$
. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then
$ G_n$
. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then
 \begin{equation*}\lvert Y\rvert\le \prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\lvert Y\rvert\le \prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\end{equation*}
and, in case of equality,
![]() $1_Y$
is spanned by the characteristic vectors of t-cosets.
$1_Y$
is spanned by the characteristic vectors of t-cosets.
We also prove a result on cross-intersecting subsets of
![]() $G_n$
. Two subsets Y and Z are t-cross-intersecting if all pairs in
$G_n$
. Two subsets Y and Z are t-cross-intersecting if all pairs in
![]() $Y\times Z$
are t-intersecting.
$Y\times Z$
are t-intersecting.
Theorem 1·2. Let t be a positive integer and let Y and Z be t-cross-intersecting sets in
![]() $ G_n$
. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then
$ G_n$
. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then
 \begin{equation*}\sqrt{\lvert Y\rvert\cdot\lvert Z\rvert}\le \prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\sqrt{\lvert Y\rvert\cdot\lvert Z\rvert}\le \prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\end{equation*}
and, in case of equality,
![]() $1_Y$
and
$1_Y$
and
![]() $1_Z$
are spanned by the characteristic vectors of t-cosets.
$1_Z$
are spanned by the characteristic vectors of t-cosets.
Theorems 1·1 and 1·2 may be seen as q-analogs of [
Reference Ellis, Friedgut and Pilpel7
, theorems 5 and 6]. It seems plausible that corresponding q-analogs of [
Reference Ellis, Friedgut and Pilpel7
, theorems 3 and 4] also hold. In the case of t-intersecting sets, this means that the extremal t-intersecting sets in
![]() $G_n$
are the t-cosets and their transposes whenever n is sufficiently large compared to t. In fact, Ahanjideh [
Reference Ahanjideh1
] has shown that every 1-intersecting set in
$G_n$
are the t-cosets and their transposes whenever n is sufficiently large compared to t. In fact, Ahanjideh [
Reference Ahanjideh1
] has shown that every 1-intersecting set in
![]() $G_2$
of size
$G_2$
of size
![]() $q^2-q$
must be either a 1-coset or the transpose of a 1-coset. We therefore pose the following conjectures.
$q^2-q$
must be either a 1-coset or the transpose of a 1-coset. We therefore pose the following conjectures.
Conjecture 1·3. Let Y be a t-intersecting set in
![]() $G_n$
whose size meets the bound in Theorem 1·1. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then Y or
$G_n$
whose size meets the bound in Theorem 1·1. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then Y or
![]() $Y^T$
is a t-coset.
$Y^T$
is a t-coset.
Conjecture 1·4. Let Y and Z be t-cross-intersecting sets in
![]() $G_n$
whose sizes meet the bound in Theorem 1·2. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then
$G_n$
whose sizes meet the bound in Theorem 1·2. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then
![]() $Y=Z$
and Y or
$Y=Z$
and Y or
![]() $Y^T$
is a t-coset.
$Y^T$
is a t-coset.
A subset Y of the symmetric group
![]() $S_n$
is t-set-intersecting if, for all
$S_n$
is t-set-intersecting if, for all
![]() $x,y\in Y$
, there is a subset I of
$x,y\in Y$
, there is a subset I of
![]() $\{1,2,\dots,n\}$
containing t elements such that
$\{1,2,\dots,n\}$
containing t elements such that
![]() $x(I)=y(I)$
. It was shown in [
Reference Ellis6
] that, for each fixed t and all sufficiently large n, every t-set-intersecting set in
$x(I)=y(I)$
. It was shown in [
Reference Ellis6
] that, for each fixed t and all sufficiently large n, every t-set-intersecting set in
![]() $S_n$
has size at most
$S_n$
has size at most
![]() $t!(n-t)!$
and equality holds if and only if Y is a coset of the stabiliser of a subset of
$t!(n-t)!$
and equality holds if and only if Y is a coset of the stabiliser of a subset of
![]() $\{1,2,\dots,n\}$
containing t elements.
$\{1,2,\dots,n\}$
containing t elements.
We also obtain a q-analog of this result. We say that two elements
![]() $x,y\in G_n$
are t-space-intersecting if there exists a t-dimensional subspace U of
$x,y\in G_n$
are t-space-intersecting if there exists a t-dimensional subspace U of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
(or t-space for short) such that
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
(or t-space for short) such that
![]() $xU=yU$
. A subset Y of
$xU=yU$
. A subset Y of
![]() $G_n$
is called t-space-intersecting if all pairs in
$G_n$
is called t-space-intersecting if all pairs in
![]() $Y\times Y$
are t-space-intersecting. Of course in this context it would be more natural to replace
$Y\times Y$
are t-space-intersecting. Of course in this context it would be more natural to replace
![]() $G_n$
by the projective linear group
$G_n$
by the projective linear group
![]() $\text{PGL}(n,q)$
. However results for
$\text{PGL}(n,q)$
. However results for
![]() $G_n$
and for
$G_n$
and for
![]() $\text{PGL}(n,q)$
can be easily translated into each other and for consistency we prefer to work with
$\text{PGL}(n,q)$
can be easily translated into each other and for consistency we prefer to work with
![]() $G_n$
. A coset of the stabiliser in
$G_n$
. A coset of the stabiliser in
![]() $G_n$
of a t-space is clearly t-space-intersecting and has order
$G_n$
of a t-space is clearly t-space-intersecting and has order
 \begin{equation}\Bigg[\prod_{i=0}^{t-1}\left(q^t-q^i\right)\Bigg]\Bigg[\prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\Bigg]. \end{equation}
\begin{equation}\Bigg[\prod_{i=0}^{t-1}\left(q^t-q^i\right)\Bigg]\Bigg[\prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\Bigg]. \end{equation}
Note that again the transpose of a t-space-intersecting set is t-space-intersecting. The transpose of the stabiliser of a t-space is in fact the stabiliser of an
![]() $(n-t)$
-space, so the stabiliser of an
$(n-t)$
-space, so the stabiliser of an
![]() $(n-t)$
-space is an example of a t-space-intersecting set that has the same size as that of the stabiliser of a t-space.
$(n-t)$
-space is an example of a t-space-intersecting set that has the same size as that of the stabiliser of a t-space.
Using an argument involving a Singer cycle, similarly as that above, Meagher and Spiga [
Reference Meagher and Spiga22
] have shown that the size of every 1-space-intersecting set in
![]() $G_n$
is at most the expression given in (1·2) for
$G_n$
is at most the expression given in (1·2) for
![]() $t=1$
. We show that this is true for all t and all sufficiently large n.
$t=1$
. We show that this is true for all t and all sufficiently large n.
Theorem 1·5. Let t be a positive integer and let Y be a t-space-intersecting set in
![]() $G_n$
. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then
$G_n$
. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then
 \begin{equation*}\lvert Y\rvert\le \Bigg[\prod_{i=0}^{t-1}\left(q^t-q^i\right)\Bigg]\Bigg[\prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\Bigg]\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\lvert Y\rvert\le \Bigg[\prod_{i=0}^{t-1}\left(q^t-q^i\right)\Bigg]\Bigg[\prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\Bigg]\end{equation*}
and, in case of equality,
![]() $1_Y$
is spanned by the characteristic vectors of cosets of stabilisers of t-spaces.
$1_Y$
is spanned by the characteristic vectors of cosets of stabilisers of t-spaces.
Again, we have a corresponding result on cross-intersecting subsets of
![]() $G_n$
, in which we call two subsets Y and Z of
$G_n$
, in which we call two subsets Y and Z of
![]() $G_n$
t-space-cross-intersecting if all pairs in
$G_n$
t-space-cross-intersecting if all pairs in
![]() $Y\times Z$
are t-space-intersecting.
$Y\times Z$
are t-space-intersecting.
Theorem 1·6. Let t be a positive integer and let Y and Z be t-space-cross-intersecting sets in
![]() $ G_n$
. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then
$ G_n$
. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then
 \begin{equation*}\sqrt{\lvert Y\rvert\cdot\lvert Z\rvert}\le \Bigg[\prod_{i=0}^{t-1}\left(q^t-q^i\right)\Bigg]\Bigg[\prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\Bigg]\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\sqrt{\lvert Y\rvert\cdot\lvert Z\rvert}\le \Bigg[\prod_{i=0}^{t-1}\left(q^t-q^i\right)\Bigg]\Bigg[\prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\Bigg]\end{equation*}
and, in case of equality,
![]() $1_Y$
and
$1_Y$
and
![]() $1_Z$
are spanned by the characteristic vectors of cosets of stabilisers of t-spaces.
$1_Z$
are spanned by the characteristic vectors of cosets of stabilisers of t-spaces.
Meagher and Spiga [
Reference Meagher and Spiga22
] conjectured that the extremal 1-space-intersecting sets in
![]() $G_n$
must be cosets of the stabiliser of a 1-space or cosets of the stabiliser of an
$G_n$
must be cosets of the stabiliser of a 1-space or cosets of the stabiliser of an
![]() $(n-1)$
-space. This was proved by the same authors for
$(n-1)$
-space. This was proved by the same authors for
![]() $n=2$
[
Reference Meagher and Spiga22
] and
$n=2$
[
Reference Meagher and Spiga22
] and
![]() $n=3$
[
Reference Meagher and Spiga23
] and by Spiga for all
$n=3$
[
Reference Meagher and Spiga23
] and by Spiga for all
![]() $n\ge 4$
[
Reference Spiga25
]. We therefore pose the following conjectures.
$n\ge 4$
[
Reference Spiga25
]. We therefore pose the following conjectures.
Conjecture 1·7. Let Y be a t-space-intersecting set in
![]() $G_n$
whose size meets the bound in Theorem 1·5. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then Y is a coset of the stabiliser of a t-space or a coset of the stabiliser of an
$G_n$
whose size meets the bound in Theorem 1·5. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then Y is a coset of the stabiliser of a t-space or a coset of the stabiliser of an
![]() $(n-t)$
-space.
$(n-t)$
-space.
Conjecture 1·8. Let Y and Z be t-space-cross-intersecting sets in
![]() $G_n$
whose sizes meet the bound in Theorem 1·6. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then
$G_n$
whose sizes meet the bound in Theorem 1·6. If n is sufficiently large compared to t, then
![]() $Y=Z$
and Y is the stabiliser of a t-space or the stabiliser of an
$Y=Z$
and Y is the stabiliser of a t-space or the stabiliser of an
![]() $(n-t)$
-space.
$(n-t)$
-space.
Not surprisingly, as in [
Reference Ellis6
,
Reference Ellis, Friedgut and Pilpel7
], our proofs are based on eigenvalue techniques, in particular weighted versions of the Hoffman bound on independent sets in graphs, and crucially involve the representation theory of
![]() $G_n$
. We organise this paper as follows. In Section 2 we summarise relevant background on the representation theory of
$G_n$
. We organise this paper as follows. In Section 2 we summarise relevant background on the representation theory of
![]() $G_n$
. In Section 3 we recall versions of the Hoffman bound from [
Reference Ellis, Friedgut and Pilpel7
] and explain how they can be applied in our setting. In Section 4 we prepare some key steps of the proofs of our main results and in particular study properties of a matrix related to the character table of
$G_n$
. In Section 3 we recall versions of the Hoffman bound from [
Reference Ellis, Friedgut and Pilpel7
] and explain how they can be applied in our setting. In Section 4 we prepare some key steps of the proofs of our main results and in particular study properties of a matrix related to the character table of
![]() $G_n$
. Sections 5 and 6 contain the main arguments of our proofs of Theorems 1·1 and 1·2 and Theorems 1·5 and 1·6, respectively. In Section 7 we prove some auxiliary ingredients used in our proofs.
$G_n$
. Sections 5 and 6 contain the main arguments of our proofs of Theorems 1·1 and 1·2 and Theorems 1·5 and 1·6, respectively. In Section 7 we prove some auxiliary ingredients used in our proofs.
We close this introduction by noting that, after a first version of this paper was made publically available, Ellis, Kindler and Lifshitz [
Reference Ellis, Kindler and Lifshitz8
] independently proved a result that is slightly more general than Theorem 1·1 and also proved Conjecture 1·3. Their methods are completely different compared to ours and in particular make no use of the representation theory of
![]() $G_n$
.
$G_n$
.
2. The finite general linear groups
In this section we mostly recall some relevant facts about the conjugacy classes and the character theory of
![]() $ G_n$
.
$ G_n$
.
2·1. Partitions
An (integer) partition is a sequence
![]() $\lambda=(\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots)$
of nonnegative integers satisfying
$\lambda=(\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots)$
of nonnegative integers satisfying
![]() $\lambda_1\ge\lambda_2\ge\cdots$
. The set of partitions is denoted by Par. We often omit trailing zeros and write
$\lambda_1\ge\lambda_2\ge\cdots$
. The set of partitions is denoted by Par. We often omit trailing zeros and write
![]() $\lambda=(\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots,\lambda_k)$
if
$\lambda=(\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots,\lambda_k)$
if
![]() $\lambda_k>0$
and
$\lambda_k>0$
and
![]() $\lambda_{k+1}=0$
. The size of
$\lambda_{k+1}=0$
. The size of
![]() $(\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots)$
is defined to be
$(\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots)$
is defined to be
![]() $\lvert\lambda\rvert=\lambda_1+\lambda_2+\cdots$
. If
$\lvert\lambda\rvert=\lambda_1+\lambda_2+\cdots$
. If
![]() $\lvert\lambda\rvert=n$
, then we also say that
$\lvert\lambda\rvert=n$
, then we also say that
![]() $\lambda$
is a partition of n. We denote the unique partition of 0 by
$\lambda$
is a partition of n. We denote the unique partition of 0 by
![]() $\varnothing$
.
$\varnothing$
.
The Young diagram of a partition
![]() $(\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots,\lambda_k)$
of n is an array of n boxes with left-justified rows and top-justified columns, where row i contains
$(\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots,\lambda_k)$
of n is an array of n boxes with left-justified rows and top-justified columns, where row i contains
![]() $\lambda_i$
boxes. To each partition
$\lambda_i$
boxes. To each partition
![]() $\lambda$
belongs a conjugate partition
$\lambda$
belongs a conjugate partition
![]() $\lambda^{\prime}$
whose parts are the number of boxes in the columns of the Young diagram of
$\lambda^{\prime}$
whose parts are the number of boxes in the columns of the Young diagram of
![]() $\lambda$
. For two partitions
$\lambda$
. For two partitions
![]() $\lambda=(\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots)$
and
$\lambda=(\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots)$
and
![]() $\mu=(\mu_1,\mu_2,\dots)$
of the same size, we say that
$\mu=(\mu_1,\mu_2,\dots)$
of the same size, we say that
![]() $\lambda$
dominates
$\lambda$
dominates
![]() $\mu$
and write
$\mu$
and write
![]() $\lambda\unrhd\mu$
if
$\lambda\unrhd\mu$
if
 \begin{equation*}\sum_{i=1}^k\lambda_i\ge\sum_{i=1}^k\mu_i\quad \text{for each $k\ge 1$}.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\sum_{i=1}^k\lambda_i\ge\sum_{i=1}^k\mu_i\quad \text{for each $k\ge 1$}.\end{equation*}
This indeed defines a partial order on the set of partitions of a fixed size, which is called the dominance order.
2·2. Conjugacy classes
We shall now describe the conjugacy classes of
![]() $ G_n$
(see [
Reference Macdonald20
, chapter IV, section 3], for example). Let
$ G_n$
(see [
Reference Macdonald20
, chapter IV, section 3], for example). Let
![]() $\Phi$
be the set of monic irreducible polynomials in
$\Phi$
be the set of monic irreducible polynomials in
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q[X]$
distinct from X. For
$\mathbb{F}_q[X]$
distinct from X. For
![]() $a\in\mathbb{F}_q^*$
(where
$a\in\mathbb{F}_q^*$
(where
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^*$
is the multiplicative group of
$\mathbb{F}_q^*$
is the multiplicative group of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q$
), we shall often write a instead of
$\mathbb{F}_q$
), we shall often write a instead of
![]() $X-a$
when the meaning is clear from the context. We also write
$X-a$
when the meaning is clear from the context. We also write
![]() $\lvert f\rvert$
for the degree of
$\lvert f\rvert$
for the degree of
![]() $f\in\Phi$
. Let
$f\in\Phi$
. Let
![]() $\Lambda$
be the set of mappings
$\Lambda$
be the set of mappings
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\colon\Phi\to\text{Par}$
of finite support (with
$\underline{\lambda}\colon\Phi\to\text{Par}$
of finite support (with
![]() $\varnothing$
being the zero element in Par). We define the size of such a mapping to be
$\varnothing$
being the zero element in Par). We define the size of such a mapping to be
and put
![]() $\Lambda_n=\{\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda\,:\,\lVert\underline{\lambda}\rVert=n\}$
. The companion matrix of
$\Lambda_n=\{\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda\,:\,\lVert\underline{\lambda}\rVert=n\}$
. The companion matrix of
![]() $f\in\Phi$
with
$f\in\Phi$
with
![]() $f=X^d+f_{d-1}X^{d-1}+\cdots+f_1X+f_0$
is
$f=X^d+f_{d-1}X^{d-1}+\cdots+f_1X+f_0$
is
 \begin{equation*}C(f)=\begin{bmatrix} & \quad & \quad & \quad & \quad -f_0\\[4pt]1 & \quad & \quad & \quad & \quad -f_1\\[4pt] & \quad 1 & \quad & \quad & \quad -f_2\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad \ddots & \quad & \quad \vdots\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad & \quad 1 & \quad -f_{d-1}\\[4pt]\end{bmatrix}\in\mathbb{F}_q^{d\times d},\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}C(f)=\begin{bmatrix} & \quad & \quad & \quad & \quad -f_0\\[4pt]1 & \quad & \quad & \quad & \quad -f_1\\[4pt] & \quad 1 & \quad & \quad & \quad -f_2\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad \ddots & \quad & \quad \vdots\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad & \quad 1 & \quad -f_{d-1}\\[4pt]\end{bmatrix}\in\mathbb{F}_q^{d\times d},\end{equation*}
(where blanks are filled with zeros). For
![]() $f\in\Phi$
of degree d and a positive integer k, we write
$f\in\Phi$
of degree d and a positive integer k, we write
 \begin{equation*}C(f,k)=\begin{bmatrix}C(f) & \quad I & \quad & \quad & \quad \\[4pt] & \quad C(f) & \quad I & \quad & \quad \\[4pt]& \quad& \quad\ddots& \quad\ddots\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad & \quad \ddots & \quad I\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad & \quad & \quad C(f)\end{bmatrix}\in\mathbb{F}_q^{kd\times kd},\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}C(f,k)=\begin{bmatrix}C(f) & \quad I & \quad & \quad & \quad \\[4pt] & \quad C(f) & \quad I & \quad & \quad \\[4pt]& \quad& \quad\ddots& \quad\ddots\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad & \quad \ddots & \quad I\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad & \quad & \quad C(f)\end{bmatrix}\in\mathbb{F}_q^{kd\times kd},\end{equation*}
where I is an identity matrix of the appropriate size. For
![]() $f\in\Phi$
and
$f\in\Phi$
and
![]() $\sigma\in\text{Par}$
, we define
$\sigma\in\text{Par}$
, we define
![]() $C(f,\sigma)$
to be the block diagonal matrix of order
$C(f,\sigma)$
to be the block diagonal matrix of order
![]() $\lvert\sigma\rvert\cdot\lvert f\rvert$
with blocks
$\lvert\sigma\rvert\cdot\lvert f\rvert$
with blocks
![]() $C(f,\sigma_1),C(f,\sigma_2),\dots$
. Finally, with every
$C(f,\sigma_1),C(f,\sigma_2),\dots$
. Finally, with every
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Lambda_n$
we associate the block diagonal matrix
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Lambda_n$
we associate the block diagonal matrix
![]() $R_{\underline{\sigma}}$
of order n whose blocks are
$R_{\underline{\sigma}}$
of order n whose blocks are
![]() $C(f,\underline{\sigma}(f))$
, where f ranges through the support of
$C(f,\underline{\sigma}(f))$
, where f ranges through the support of
![]() $\underline{\sigma}$
. Then every element g of
$\underline{\sigma}$
. Then every element g of
![]() $ G_n$
is conjugate to exactly one matrix
$ G_n$
is conjugate to exactly one matrix
![]() $R_{\underline{\sigma}}$
for
$R_{\underline{\sigma}}$
for
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Lambda_n$
, which is called the Jordan canonical form of g. Hence
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Lambda_n$
, which is called the Jordan canonical form of g. Hence
![]() $\Lambda_n$
indexes the conjugacy classes of
$\Lambda_n$
indexes the conjugacy classes of
![]() $ G_n$
; we denote by
$ G_n$
; we denote by
![]() $C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
the conjugacy class containing
$C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
the conjugacy class containing
![]() $R_{\underline{\sigma}}$
. The following result gives an explicit expression for the number of elements in
$R_{\underline{\sigma}}$
. The following result gives an explicit expression for the number of elements in
![]() $C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
.
$C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
.
Lemma 2·1 ([
Reference Stanley26
, theorem 1·10·7]). For each
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Lambda_n$
, we have
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Lambda_n$
, we have
 \begin{equation*}\frac{\lvert G_n\rvert}{\lvert C_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert}=\prod_{f\in\Phi} \prod_{i=1}^{\lvert\underline{\sigma}(f)\rvert} \prod_{j=1}^{m_i(\underline{\sigma}(f))} q^{\lvert f\rvert\, s_i\left(\underline{\sigma}(f)^{\prime}\right)} \left(1-q^{-\lvert f\rvert\,j}\right),\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\frac{\lvert G_n\rvert}{\lvert C_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert}=\prod_{f\in\Phi} \prod_{i=1}^{\lvert\underline{\sigma}(f)\rvert} \prod_{j=1}^{m_i(\underline{\sigma}(f))} q^{\lvert f\rvert\, s_i\left(\underline{\sigma}(f)^{\prime}\right)} \left(1-q^{-\lvert f\rvert\,j}\right),\end{equation*}
where
![]() $m_i(\sigma)= \lvert\{j\ge 1\colon\sigma_j=i\}\rvert$
and
$m_i(\sigma)= \lvert\{j\ge 1\colon\sigma_j=i\}\rvert$
and
![]() $s_i(\sigma)=\sum_{j=1}^i \sigma_j$
for a partition
$s_i(\sigma)=\sum_{j=1}^i \sigma_j$
for a partition
![]() $\sigma$
.
$\sigma$
.
2·3. Parabolic induction
Recall that, given a finite group G, a subgroup H of G, and a class function
![]() $\phi$
on H, the induced class function
$\phi$
on H, the induced class function
![]() $\text{Ind}_H^G(\phi)$
on G is given by
$\text{Ind}_H^G(\phi)$
on G is given by
 \begin{equation}\text{Ind}_H^G(\phi)(g)=\frac{1}{\lvert H\rvert}\sum_{\substack{x\in G\\xgx^{-1}\in H}}\phi(xgx^{-1}). \end{equation}
\begin{equation}\text{Ind}_H^G(\phi)(g)=\frac{1}{\lvert H\rvert}\sum_{\substack{x\in G\\xgx^{-1}\in H}}\phi(xgx^{-1}). \end{equation}
The character theory of
![]() $ G_n$
crucially relies on the induction of characters from parabolic subgroups of
$ G_n$
crucially relies on the induction of characters from parabolic subgroups of
![]() $ G_n$
.
$ G_n$
.
A composition is much like a partition, except that the parts do not need to be nonincreasing. Let
![]() $\lambda=(\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots,\lambda_k)$
be a composition of n. Let
$\lambda=(\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots,\lambda_k)$
be a composition of n. Let
![]() $P_\lambda$
be the parabolic subgroup of
$P_\lambda$
be the parabolic subgroup of
![]() $ G_n$
consisting of block upper-triangular matrices with block sizes
$ G_n$
consisting of block upper-triangular matrices with block sizes
![]() $\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots,\lambda_k$
, namely
$\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots,\lambda_k$
, namely
 \begin{equation}P_\lambda=\left\{\begin{bmatrix}g_1 & \quad * & \quad \cdots & \quad *\\[4pt] & \quad g_2 & \quad \cdots & \quad *\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad \ddots & \quad \vdots\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad & \quad g_k\\[4pt]\end{bmatrix}:g_i\in G_{\lambda_i}\right\}.\end{equation}
\begin{equation}P_\lambda=\left\{\begin{bmatrix}g_1 & \quad * & \quad \cdots & \quad *\\[4pt] & \quad g_2 & \quad \cdots & \quad *\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad \ddots & \quad \vdots\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad & \quad g_k\\[4pt]\end{bmatrix}:g_i\in G_{\lambda_i}\right\}.\end{equation}
Let
![]() $\pi_i\,:\,P_\lambda\to G_{\lambda_i}$
be the mapping that projects to the ith diagonal block, so that
$\pi_i\,:\,P_\lambda\to G_{\lambda_i}$
be the mapping that projects to the ith diagonal block, so that
 \begin{equation}\pi_i\,:\,\begin{bmatrix}g_1 & \quad * & \quad \cdots & \quad *\\[4pt] & \quad g_2 & \quad \cdots & \quad *\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad \ddots & \quad \vdots\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad & \quad g_k\\[4pt]\end{bmatrix}\longmapsto g_i. \end{equation}
\begin{equation}\pi_i\,:\,\begin{bmatrix}g_1 & \quad * & \quad \cdots & \quad *\\[4pt] & \quad g_2 & \quad \cdots & \quad *\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad \ddots & \quad \vdots\\[4pt] & \quad & \quad & \quad g_k\\[4pt]\end{bmatrix}\longmapsto g_i. \end{equation}
Let
![]() $\phi_i$
be a class function on
$\phi_i$
be a class function on
![]() $G_{\lambda_i}$
. Then
$G_{\lambda_i}$
. Then
 \begin{equation*}\prod_{i=1}^k(\phi_i\circ \pi_i)\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\prod_{i=1}^k(\phi_i\circ \pi_i)\end{equation*}
is a class function on
![]() $P_\lambda$
. We define the product
$P_\lambda$
. We define the product
![]() $\phi_1\odot\phi_2\odot\cdots\odot\phi_k$
to be the induction of this class function to
$\phi_1\odot\phi_2\odot\cdots\odot\phi_k$
to be the induction of this class function to
![]() $ G_n$
, that is
$ G_n$
, that is
 \begin{equation}\bigodot_{i=1}^k\phi_i=\text{Ind}_{P_\lambda}^{ G_n}\left(\prod_{i=1}^k(\phi_i\circ \pi_i)\right). \end{equation}
\begin{equation}\bigodot_{i=1}^k\phi_i=\text{Ind}_{P_\lambda}^{ G_n}\left(\prod_{i=1}^k(\phi_i\circ \pi_i)\right). \end{equation}
2·4. Character theory of
 $ G_n$
$ G_n$
The complete set of complex irreducible characters has been obtained by Green [
Reference Green14
]. A good treatment of this topic is also contained in [
Reference Macdonald20
, chapter IV]. The complex irreducible representations were obtained by Gelfand [
Reference Gelfand11
] and the irreducible representations over fields of nondefining characteristic were obtained by James [
Reference James17
]. The approach of [
Reference James17
] is in fact very similar to the standard combinatorial approach to obtain the complex irreducible representations of the symmetric group (see [
Reference Sagan24
], for example) and we mostly follow [
Reference James17
] to recall some relevant background on the complex characters of
![]() $ G_n$
.
$ G_n$
.
The irreducible characters of
![]() $ G_n$
are naturally indexed by
$ G_n$
are naturally indexed by
![]() $\Lambda_n$
and, for
$\Lambda_n$
and, for
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n$
, we denote by
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n$
, we denote by
![]() $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
the corresponding irreducible character. We shall use the short-hand notation
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
the corresponding irreducible character. We shall use the short-hand notation
![]() $\chi^{f\mapsto\lambda}$
for
$\chi^{f\mapsto\lambda}$
for
![]() $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
if
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
if
![]() $\underline{\lambda}$
is supported only on
$\underline{\lambda}$
is supported only on
![]() $f\in\Phi$
and
$f\in\Phi$
and
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(f)=\lambda$
. These are typically called the primary irreducible characters of
$\underline{\lambda}(f)=\lambda$
. These are typically called the primary irreducible characters of
![]() $ G_n$
. It is well known (see [
Reference James17
, section 8], for example) that the irreducible characters of
$ G_n$
. It is well known (see [
Reference James17
, section 8], for example) that the irreducible characters of
![]() $ G_n$
satisfy
$ G_n$
satisfy
In order to construct the primary irreducible characters, James [
Reference James17
] constructs characters of
![]() $G_{dm}$
, denoted by
$G_{dm}$
, denoted by
![]() $\xi^{f\mapsto\mu}$
, where
$\xi^{f\mapsto\mu}$
, where
![]() $f\in\Phi$
has degree d and
$f\in\Phi$
has degree d and
![]() $\mu$
is a partition of m. Writing
$\mu$
is a partition of m. Writing
![]() $\mu=(\mu_1,\mu_2,\dots,\mu_k)$
, these characters satisfy [
Reference James17
, (6·2)]
$\mu=(\mu_1,\mu_2,\dots,\mu_k)$
, these characters satisfy [
Reference James17
, (6·2)]
 \begin{equation}\xi^{f\mapsto\mu}=\bigodot_{i=1}^k\xi^{f\mapsto(\mu_i)} \end{equation}
\begin{equation}\xi^{f\mapsto\mu}=\bigodot_{i=1}^k\xi^{f\mapsto(\mu_i)} \end{equation}
and [ Reference James17 , (7·19)]
where
![]() $\lambda$
ranges over the partitions of
$\lambda$
ranges over the partitions of
![]() $\lvert\mu\rvert$
and
$\lvert\mu\rvert$
and
![]() $K_{\lambda\mu}$
is a Kostka number, which equals the number of semistandard Young tableaux of shape
$K_{\lambda\mu}$
is a Kostka number, which equals the number of semistandard Young tableaux of shape
![]() $\lambda$
and content
$\lambda$
and content
![]() $\mu$
. It is well known (see [
Reference Sagan24
, section 2·11], for example) that the Kostka numbers satisfy
$\mu$
. It is well known (see [
Reference Sagan24
, section 2·11], for example) that the Kostka numbers satisfy
Conversely it is readily verified that there are integers
![]() $H_{\mu\lambda}$
satisfying$
$H_{\mu\lambda}$
satisfying$
and
(see [ Reference Macdonald20 , p. 105], for example).
Now, for
![]() $\underline{\mu}\in\Lambda_n$
, we define the characters
$\underline{\mu}\in\Lambda_n$
, we define the characters
We denote by
![]() $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}}$
and
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}}$
and
![]() $\xi^{\underline{\mu}}_{\underline{\sigma}}$
the characters
$\xi^{\underline{\mu}}_{\underline{\sigma}}$
the characters
![]() $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
and
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
and
![]() $\xi^{\underline{\mu}}$
, respectively, evaluated on the conjugacy class
$\xi^{\underline{\mu}}$
, respectively, evaluated on the conjugacy class
![]() $C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
.
$C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
.
We now express
![]() $\xi^{\underline{\mu}}$
and
$\xi^{\underline{\mu}}$
and
![]() $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
in terms of each other. To do so, we define the shape of
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
in terms of each other. To do so, we define the shape of
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n$
to be the mapping
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n$
to be the mapping
![]() $s\,:\,\Phi\to\mathbb{Z}$
given by
$s\,:\,\Phi\to\mathbb{Z}$
given by
![]() $s(f)=\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert$
for each
$s(f)=\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert$
for each
![]() $f\in\Phi$
. We write
$f\in\Phi$
. We write
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\sim\underline{\mu}$
if
$\underline{\lambda}\sim\underline{\mu}$
if
![]() $\underline{\lambda},\underline{\mu}\in\Lambda_n$
have the same shape. Then
$\underline{\lambda},\underline{\mu}\in\Lambda_n$
have the same shape. Then
![]() $\sim$
is an equivalence relation on
$\sim$
is an equivalence relation on
![]() $\Lambda_n$
. For
$\Lambda_n$
. For
![]() $\underline{\lambda},\underline{\mu}\in\Lambda_n$
with
$\underline{\lambda},\underline{\mu}\in\Lambda_n$
with
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\sim\underline{\mu}$
, write
$\underline{\lambda}\sim\underline{\mu}$
, write
 \begin{align*}K_{\underline{\lambda}\underline{\mu}}&=\prod_{f\in\Phi}K_{\underline{\lambda}(f)\underline{\mu}(f)},\\H_{\underline{\mu}\underline{\lambda}}&=\prod_{f\in\Phi}H_{\underline{\mu}(f)\underline{\lambda}(f)}.\end{align*}
\begin{align*}K_{\underline{\lambda}\underline{\mu}}&=\prod_{f\in\Phi}K_{\underline{\lambda}(f)\underline{\mu}(f)},\\H_{\underline{\mu}\underline{\lambda}}&=\prod_{f\in\Phi}H_{\underline{\mu}(f)\underline{\lambda}(f)}.\end{align*}
We then find that
An explicit expression for the degree
![]() $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)$
(where 1 is the identity of
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)$
(where 1 is the identity of
![]() $ G_n$
) of
$ G_n$
) of
![]() $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
is given by the so-called q-analog of the hook-length formula.
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
is given by the so-called q-analog of the hook-length formula.
Lemma 2·2 ([ Reference Green14 , theorem 14]). We have
 \begin{equation}\frac{1}{\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)}\;\prod_{i=1}^n(q^i-1)=\prod_{f\in\Phi}\frac{1}{q^{\lvert f\rvert b(\underline{\lambda}(f))}}\prod_{(i, j)\in\underline{\lambda}(f)}\left(q^{\lvert f\rvert h_{i, j}(\underline{\lambda}(f))}-1\right), \end{equation}
\begin{equation}\frac{1}{\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)}\;\prod_{i=1}^n(q^i-1)=\prod_{f\in\Phi}\frac{1}{q^{\lvert f\rvert b(\underline{\lambda}(f))}}\prod_{(i, j)\in\underline{\lambda}(f)}\left(q^{\lvert f\rvert h_{i, j}(\underline{\lambda}(f))}-1\right), \end{equation}
where, for each partition
![]() $\lambda=(\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots)$
,
$\lambda=(\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\dots)$
,
and
![]() $h_{i, j}(\lambda)$
is the hook length of
$h_{i, j}(\lambda)$
is the hook length of
![]() $\lambda$
at (i, j), namely
$\lambda$
at (i, j), namely
and the corresponding product over (i, j) is over all boxes of the Young diagram of
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(f)$
.
$\underline{\lambda}(f)$
.
It can be readily verified from Lemma 2·2 that the linear (degree-one) irreducible characters of
![]() $ G_n$
are precisely the primary characters
$ G_n$
are precisely the primary characters
![]() $\chi^{f\mapsto(n)}$
, where
$\chi^{f\mapsto(n)}$
, where
![]() $\lvert f\rvert=1$
. These are the only characters of
$\lvert f\rvert=1$
. These are the only characters of
![]() $ G_n$
that we shall need explicitly. Let
$ G_n$
that we shall need explicitly. Let
![]() $\alpha$
be a generator of the multiplicative group
$\alpha$
be a generator of the multiplicative group
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^*$
of
$\mathbb{F}_q^*$
of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q$
, let
$\mathbb{F}_q$
, let
![]() $\omega=\exp\!(2\pi \sqrt{-1}/(q-1))$
be a complex root of unity, and let
$\omega=\exp\!(2\pi \sqrt{-1}/(q-1))$
be a complex root of unity, and let
![]() $\theta\,:\,\mathbb{F}_q^*\to\mathbb{C}$
be the linear character of
$\theta\,:\,\mathbb{F}_q^*\to\mathbb{C}$
be the linear character of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^*$
given by
$\mathbb{F}_q^*$
given by
![]() $\theta\!\left(\alpha^i\right)=\omega^i$
. The following result is essentially given in [
Reference Green14
, pp. 415 and 444].
$\theta\!\left(\alpha^i\right)=\omega^i$
. The following result is essentially given in [
Reference Green14
, pp. 415 and 444].
Lemma 2·3 ([
Reference Green14
]). For all
![]() $g\in G_n$
, we have
$g\in G_n$
, we have
In particular
![]() $\chi^{X-1\mapsto(n)}$
is the trivial character.
$\chi^{X-1\mapsto(n)}$
is the trivial character.
In what follows we consider certain characters of
![]() $G_n$
related to the permutation character of
$G_n$
related to the permutation character of
![]() $G_n$
on the set of t-tuples of linearly independent elements of
$G_n$
on the set of t-tuples of linearly independent elements of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. For
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. For
![]() $t\leq n$
, let
$t\leq n$
, let
![]() $H_{n,t}$
be the stabiliser of a fixed t-tuple of linearly independent elements of
$H_{n,t}$
be the stabiliser of a fixed t-tuple of linearly independent elements of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. We define
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. We define
![]() $\zeta^{(t,i)}$
to be the character obtained by inducing the linear character
$\zeta^{(t,i)}$
to be the character obtained by inducing the linear character
to
![]() $ G_n$
. Then
$ G_n$
. Then
![]() $\zeta^{(t,0)}$
is the permutation character of
$\zeta^{(t,0)}$
is the permutation character of
![]() $ G_n$
on the set of t-tuples of linearly independent elements of
$ G_n$
on the set of t-tuples of linearly independent elements of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. These characters are related to each other in the following way.
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. These characters are related to each other in the following way.
Lemma 2·4. For each
![]() $g\in G_n$
, we have
$g\in G_n$
, we have
Proof. Since similar matrices have the same determinant, we find from (2·1) that
 \begin{align*}\zeta^{(t,i)}(g)&=\frac{1}{\lvert H_{n,t}\rvert}\sum_{\substack{x\in G_n\\xgx^{-1}\in H_{n,t}}}\theta\!\left(\det(xgx^{-1})^i\right)\\&=\frac{1}{\lvert H_{n,t}\rvert}\sum_{\substack{x\in G_n\\xgx^{-1}\in H_{n,t}}}\theta\!\left(\det(g)^i\right)\\&=\theta\!\left(\det(g)^i\right)\zeta^{(t,0)}(g).\end{align*}
\begin{align*}\zeta^{(t,i)}(g)&=\frac{1}{\lvert H_{n,t}\rvert}\sum_{\substack{x\in G_n\\xgx^{-1}\in H_{n,t}}}\theta\!\left(\det(xgx^{-1})^i\right)\\&=\frac{1}{\lvert H_{n,t}\rvert}\sum_{\substack{x\in G_n\\xgx^{-1}\in H_{n,t}}}\theta\!\left(\det(g)^i\right)\\&=\theta\!\left(\det(g)^i\right)\zeta^{(t,0)}(g).\end{align*}
We shall also need the following information about the decomposition of
![]() $\zeta^{(t,i)}$
into irreducible characters of
$\zeta^{(t,i)}$
into irreducible characters of
![]() $ G_n$
.
$ G_n$
.
Lemma 2·5. We have
where
![]() $m_{i,\underline{\lambda}}\ne 0$
if and only if
$m_{i,\underline{\lambda}}\ne 0$
if and only if
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)_1\ge n-t$
.
$\underline{\lambda}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)_1\ge n-t$
.
Proof. We may choose
![]() $H_{n,t}$
to be
$H_{n,t}$
to be
 \begin{equation*}H_{n,t}=\left\{\begin{bmatrix}I & \quad *\\[4pt] & \quad g\end{bmatrix}\,:\,g\in G_{n-t}\right\},\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}H_{n,t}=\left\{\begin{bmatrix}I & \quad *\\[4pt] & \quad g\end{bmatrix}\,:\,g\in G_{n-t}\right\},\end{equation*}
so that
![]() $H_{n,t}$
is a subgroup of the parabolic subgroup
$H_{n,t}$
is a subgroup of the parabolic subgroup
![]() $P_{(t,n-t)}$
given in (2·2). Let
$P_{(t,n-t)}$
given in (2·2). Let
![]() $\pi_1$
and
$\pi_1$
and
![]() $\pi_2$
be the projections onto the diagonal blocks of orders t and
$\pi_2$
be the projections onto the diagonal blocks of orders t and
![]() $n-t$
, respectively, as given in (2·3). Using Lemma 2·3, the character (2·15) can be written as
$n-t$
, respectively, as given in (2·3). Using Lemma 2·3, the character (2·15) can be written as
where 1 is the trivial character of the trivial subgroup of
![]() $G_t$
. By Frobenius reciprocity, 1 induces on
$G_t$
. By Frobenius reciprocity, 1 induces on
![]() $G_t$
to the character
$G_t$
to the character
Since
![]() $P_{(t,n-t)}/H_{n,t}\cong G_t$
, it is then readily verified that (2·16) induces on
$P_{(t,n-t)}/H_{n,t}\cong G_t$
, it is then readily verified that (2·16) induces on
![]() $P_{(t,n-t)}$
to the character
$P_{(t,n-t)}$
to the character
Hence, by transitivity of induction, we have
It is well known [
Reference Macdonald20
, chapter IV, section 4] that, for each fixed
![]() $f\in\Phi$
, characters
$f\in\Phi$
, characters
![]() $\chi^{f\mapsto \lambda}$
form an algebra with multiplication
$\chi^{f\mapsto \lambda}$
form an algebra with multiplication
![]() $\odot$
that is isomorphic to the algebra of symmetric functions and the images of the characters
$\odot$
that is isomorphic to the algebra of symmetric functions and the images of the characters
![]() $\chi^{f\mapsto \lambda}$
are the Schur functions. We then find from Pieri’s rule (see [
Reference Macdonald20
, chapter I, (5·16)], for example) that
$\chi^{f\mapsto \lambda}$
are the Schur functions. We then find from Pieri’s rule (see [
Reference Macdonald20
, chapter I, (5·16)], for example) that
where
![]() $\lambda$
runs through all partitions whose Young diagram is obtained from that of
$\lambda$
runs through all partitions whose Young diagram is obtained from that of
![]() $\kappa$
by adding
$\kappa$
by adding
![]() $n-t$
boxes, no two of which in the same column. Using (2·5) the statement of the lemma is then readily verified.
$n-t$
boxes, no two of which in the same column. Using (2·5) the statement of the lemma is then readily verified.
3. The Hoffman bound
Henceforth we use the following notation. For a field K and finite sets X and Y, we denote by K(X, Y) the set of
![]() $\lvert X\rvert\times\lvert Y\rvert$
matrices A with entries in K, where rows and columns are indexed by X and Y, respectively. For
$\lvert X\rvert\times\lvert Y\rvert$
matrices A with entries in K, where rows and columns are indexed by X and Y, respectively. For
![]() $x\in X$
and
$x\in X$
and
![]() $y\in Y$
, the (x, y)-entry of A is written as A(x, y). If
$y\in Y$
, the (x, y)-entry of A is written as A(x, y). If
![]() $\lvert Y\rvert=1$
, then we omit Y, so K(X) is the set of column vectors a indexed by X and, for
$\lvert Y\rvert=1$
, then we omit Y, so K(X) is the set of column vectors a indexed by X and, for
![]() $x\in X$
, the x-entry of a is written as a(x).
$x\in X$
, the x-entry of a is written as a(x).
The adjacency matrix of a graph
![]() $\Gamma=(X,E)$
is the matrix
$\Gamma=(X,E)$
is the matrix
![]() $A\in\mathbb{R}(X,X)$
given by
$A\in\mathbb{R}(X,X)$
given by
 \begin{equation*}A(x,y)=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $\{x,y\}\in E$}\\0 & \text{otherwise}.\end{cases}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}A(x,y)=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $\{x,y\}\in E$}\\0 & \text{otherwise}.\end{cases}\end{equation*}
Then A is a real symmetric matrix, which of course has an orthonormal system of
![]() $\lvert X\rvert$
eigenvectors forming a basis of
$\lvert X\rvert$
eigenvectors forming a basis of
![]() $\mathbb{R}(X)$
. All eigenvalues of A are real and referred to as the eigenvalues of
$\mathbb{R}(X)$
. All eigenvalues of A are real and referred to as the eigenvalues of
![]() $\Gamma$
. Note that, if
$\Gamma$
. Note that, if
![]() $\Gamma$
is d-regular, then d is an eigenvalue of
$\Gamma$
is d-regular, then d is an eigenvalue of
![]() $\Gamma$
and the all-ones vector is a corresponding eigenvector.
$\Gamma$
and the all-ones vector is a corresponding eigenvector.
Our starting point arises from the following generalised versions of the Hoffman bound [ Reference Haemers15 ], stated and proved by Ellis, Friedgut, and Pilpel [ Reference Ellis, Friedgut and Pilpel7 , section 2·4] in the following form.
Proposition 3·1. Let
![]() $\Gamma=(X,E)$
be a graph on n vertices. Suppose that
$\Gamma=(X,E)$
be a graph on n vertices. Suppose that
![]() $\Gamma_0,\Gamma_1,\dots,\Gamma_r$
are regular spanning subgraphs of
$\Gamma_0,\Gamma_1,\dots,\Gamma_r$
are regular spanning subgraphs of
![]() $\Gamma$
, all having
$\Gamma$
, all having
![]() $\{v_0,v_1,\dots,v_{n-1}\}$
as an orthonormal system of eigenvectors with
$\{v_0,v_1,\dots,v_{n-1}\}$
as an orthonormal system of eigenvectors with
![]() $v_0$
being the all-ones vector. Let
$v_0$
being the all-ones vector. Let
![]() $P_i(k)$
be the eigenvalue of
$P_i(k)$
be the eigenvalue of
![]() $v_k$
in
$v_k$
in
![]() $\Gamma_i$
. Let
$\Gamma_i$
. Let
![]() $w_0,w_1,\dots,w_r\in\mathbb{R}$
and write
$w_0,w_1,\dots,w_r\in\mathbb{R}$
and write
![]() $P(k)=\sum_{i=0}^rw_iP_i(k)$
.
$P(k)=\sum_{i=0}^rw_iP_i(k)$
.
-
(i) If
 $Y\subseteq X$
is an independent set in
$Y\subseteq X$
is an independent set in
 $\Gamma$
, thenwhere
$\Gamma$
, thenwhere \begin{equation*}\frac{\lvert Y\rvert}{\lvert X\rvert}\le \frac{\lvert P_{\min}\rvert}{P(0)+\lvert P_{\min}\rvert},\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\frac{\lvert Y\rvert}{\lvert X\rvert}\le \frac{\lvert P_{\min}\rvert}{P(0)+\lvert P_{\min}\rvert},\end{equation*}
 $P_{\min}=\min_{k\ne 0} P(k)$
. In case of equality we have
$P_{\min}=\min_{k\ne 0} P(k)$
. In case of equality we have \begin{equation*}1_Y\in\langle\{v_0\}\cup\{v_k\,:\,P(k)=P_{\min}\}\rangle.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}1_Y\in\langle\{v_0\}\cup\{v_k\,:\,P(k)=P_{\min}\}\rangle.\end{equation*}
-
(ii) If
 $Y, Z\subseteq X$
are such that there are no edges between Y and Z in
$Y, Z\subseteq X$
are such that there are no edges between Y and Z in
 $\Gamma$
, thenwhere
$\Gamma$
, thenwhere \[\sqrt{\frac{\lvert Y\rvert}{\lvert X\rvert}\,\frac{\lvert Z\rvert}{\lvert X\rvert}}\le \frac{P_{\max}}{P(0)+P_{\max}},\]
\[\sqrt{\frac{\lvert Y\rvert}{\lvert X\rvert}\,\frac{\lvert Z\rvert}{\lvert X\rvert}}\le \frac{P_{\max}}{P(0)+P_{\max}},\]
 $P_{\max}=\max_{k\ne 0}\lvert P(k)\rvert$
. In case of equality we have
$P_{\max}=\max_{k\ne 0}\lvert P(k)\rvert$
. In case of equality we have \begin{equation*}1_Y, 1_Z\in\langle\{v_0\}\cup\{v_k\,:\,\lvert P(k)\rvert =P_{\max}\}\rangle.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}1_Y, 1_Z\in\langle\{v_0\}\cup\{v_k\,:\,\lvert P(k)\rvert =P_{\max}\}\rangle.\end{equation*}
In order to study graphs induced by
![]() $ G_n$
and their eigenvalues, we shall bring the theory of association schemes into play. We refer to [
Reference Bannai and Ito4
] and [
Reference Godsil and Meagher13
] for background on association schemes. Every finite group gives rise to an association scheme (see [
Reference Bannai and Ito4
, section 2·7] or [
Reference Godsil and Meagher13
, section 3·3] for details). We shall recall relevant background about this association scheme and its symmetrisation for
$ G_n$
and their eigenvalues, we shall bring the theory of association schemes into play. We refer to [
Reference Bannai and Ito4
] and [
Reference Godsil and Meagher13
] for background on association schemes. Every finite group gives rise to an association scheme (see [
Reference Bannai and Ito4
, section 2·7] or [
Reference Godsil and Meagher13
, section 3·3] for details). We shall recall relevant background about this association scheme and its symmetrisation for
![]() $ G_n$
.
$ G_n$
.
For each
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Lambda_n$
, we define
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Lambda_n$
, we define
![]() $B_{\underline{\sigma}}=\mathbb{C}( G_n,G_n)$
by
$B_{\underline{\sigma}}=\mathbb{C}( G_n,G_n)$
by
 \begin{equation*}B_{\underline{\sigma}}(x,y)=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $x^{-1}y\in C_{\underline{\sigma}}$}\\0 & \text{otherwise}.\end{cases}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}B_{\underline{\sigma}}(x,y)=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $x^{-1}y\in C_{\underline{\sigma}}$}\\0 & \text{otherwise}.\end{cases}\end{equation*}
The vector space generated by
![]() $\{B_{\underline{\sigma}}\,:\,\underline{\sigma}\in\Lambda_n\}$
over the complex numbers turns out to be a commutative matrix algebra
$\{B_{\underline{\sigma}}\,:\,\underline{\sigma}\in\Lambda_n\}$
over the complex numbers turns out to be a commutative matrix algebra
![]() $\mathbb{A}$
, which contains the identity and the all-ones matrix and is closed under conjugate transposition. The collection of zero-one matrices
$\mathbb{A}$
, which contains the identity and the all-ones matrix and is closed under conjugate transposition. The collection of zero-one matrices
![]() $B_{\underline{\sigma}}$
therefore defines an association scheme. Since
$B_{\underline{\sigma}}$
therefore defines an association scheme. Since
![]() $\mathbb{A}$
is commutative, it can be simultaneously diagonalised and therefore there exists a basis
$\mathbb{A}$
is commutative, it can be simultaneously diagonalised and therefore there exists a basis
![]() $\{F_{\underline{\lambda}}\,:\,\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n\}$
of
$\{F_{\underline{\lambda}}\,:\,\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n\}$
of
![]() $\mathbb{A}$
consisting of primitive idempotent matrices. These matrices are given by [
Reference Bannai and Ito4
, theorem II·7·2]
$\mathbb{A}$
consisting of primitive idempotent matrices. These matrices are given by [
Reference Bannai and Ito4
, theorem II·7·2]
 \begin{equation}F_{\underline{\lambda}}\,=\frac{\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)}{\lvert G_n\rvert}\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Lambda_n}\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}}\,B_{\underline{\sigma}}. \end{equation}
\begin{equation}F_{\underline{\lambda}}\,=\frac{\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)}{\lvert G_n\rvert}\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Lambda_n}\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}}\,B_{\underline{\sigma}}. \end{equation}
Using the orthogonality of characters of the second kind, it is readily verified that
where
![]() $\overline{\chi}^{\underline{\lambda}}$
is the character of
$\overline{\chi}^{\underline{\lambda}}$
is the character of
![]() $ G_n$
whose values at
$ G_n$
whose values at
![]() $g\in G_n$
are the complex conjugates of
$g\in G_n$
are the complex conjugates of
![]() $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(g)$
.
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(g)$
.
For each
![]() $f\in\Phi$
, let
$f\in\Phi$
, let
![]() $f^*\in\Phi$
be its reciprocal polynomial, namely the monic polynomial whose roots (in an algebraic closure of
$f^*\in\Phi$
be its reciprocal polynomial, namely the monic polynomial whose roots (in an algebraic closure of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q$
) are precisely the inverses of the roots of f. For each
$\mathbb{F}_q$
) are precisely the inverses of the roots of f. For each
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n$
, define
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n$
, define
![]() $\underline{\lambda}^*$
to be the element of
$\underline{\lambda}^*$
to be the element of
![]() $\Lambda_n$
given by
$\Lambda_n$
given by
![]() $\underline{\lambda}^*(f)=\underline{\lambda}(f^*)$
for all
$\underline{\lambda}^*(f)=\underline{\lambda}(f^*)$
for all
![]() $f\in\Phi$
. We record the following lemma, in which we write
$f\in\Phi$
. We record the following lemma, in which we write
![]() $C^{-1}_{\underline{\sigma}}=\{g^{-1}\,:\,g\in C_{\underline{\sigma}}\}$
for
$C^{-1}_{\underline{\sigma}}=\{g^{-1}\,:\,g\in C_{\underline{\sigma}}\}$
for
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Lambda_n$
.
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Lambda_n$
.
Lemma 3·2. Let
![]() $\underline{\sigma},\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n$
. Then we have:
$\underline{\sigma},\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n$
. Then we have:
-
(i)
 $C_{\underline{\sigma}^*}=C_{\underline{\sigma}}^{-1}$
;
$C_{\underline{\sigma}^*}=C_{\underline{\sigma}}^{-1}$
; -
(ii)
 $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}^*}=\overline{\chi}^{\underline{\lambda}}$
;
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}^*}=\overline{\chi}^{\underline{\lambda}}$
; -
(iii)
 $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}^*}_{\underline{\sigma}}=\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}^*}$
.
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}^*}_{\underline{\sigma}}=\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}^*}$
.
Proof. Statement (i) is a basic fact in linear algebra, (ii) is essentially [ Reference James17 , (7·32)], and (iii) can be deduced from (i) and (ii).
Let
![]() $\Omega_n$
be the subset of
$\Omega_n$
be the subset of
![]() $\Lambda_n$
that contains all
$\Lambda_n$
that contains all
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n$
satisfying
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n$
satisfying
![]() $\underline{\lambda}=\underline{\lambda}^*$
and precisely one of
$\underline{\lambda}=\underline{\lambda}^*$
and precisely one of
![]() $\underline{\lambda}$
or
$\underline{\lambda}$
or
![]() $\underline{\lambda}^*$
for all
$\underline{\lambda}^*$
for all
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n$
satisfying
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n$
satisfying
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\ne\underline{\lambda}^*$
. For
$\underline{\lambda}\ne\underline{\lambda}^*$
. For
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
, we define the character
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
, we define the character
 \begin{equation*}\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}=\begin{cases}\chi^{\underline{\lambda}} & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}=\underline{\lambda}^*$}\\\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}+\chi^{\underline{\lambda}^*} & \text{otherwise},\end{cases}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}=\begin{cases}\chi^{\underline{\lambda}} & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}=\underline{\lambda}^*$}\\\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}+\chi^{\underline{\lambda}^*} & \text{otherwise},\end{cases}\end{equation*}
and, for
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n$
, we define
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n$
, we define
![]() $D_{\underline{\sigma}}=C_{\underline{\sigma}}\cup C_{\underline{\sigma}^*}$
. Lemma 3·2 implies that
$D_{\underline{\sigma}}=C_{\underline{\sigma}}\cup C_{\underline{\sigma}^*}$
. Lemma 3·2 implies that
![]() $\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
is constant on
$\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
is constant on
![]() $D_{\underline{\sigma}}$
. We write
$D_{\underline{\sigma}}$
. We write
For
![]() $\underline{\sigma},\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
, write
$\underline{\sigma},\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
, write
 \begin{equation}A_{\underline{\sigma}}=\begin{cases}B_{\underline{\sigma}} & \text{for $\underline{\sigma}=\underline{\sigma}^*$}\\B_{\underline{\sigma}}+B_{\underline{\sigma}^*} & \text{otherwise}\end{cases}\quad \text{and}\quad E_{\underline{\lambda}}=\begin{cases}F_{\underline{\lambda}} & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}=\underline{\lambda}^*$}\\F_{\underline{\lambda}}+F_{\underline{\lambda}^*} & \text{otherwise}.\end{cases}\end{equation}
\begin{equation}A_{\underline{\sigma}}=\begin{cases}B_{\underline{\sigma}} & \text{for $\underline{\sigma}=\underline{\sigma}^*$}\\B_{\underline{\sigma}}+B_{\underline{\sigma}^*} & \text{otherwise}\end{cases}\quad \text{and}\quad E_{\underline{\lambda}}=\begin{cases}F_{\underline{\lambda}} & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}=\underline{\lambda}^*$}\\F_{\underline{\lambda}}+F_{\underline{\lambda}^*} & \text{otherwise}.\end{cases}\end{equation}
Note that
![]() $A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
is symmetric, so all of its eigenvalues are real, and that
$A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
is symmetric, so all of its eigenvalues are real, and that
![]() $E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
has only real entries. Let
$E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
has only real entries. Let
![]() $V_{\underline{\lambda}}$
be the column span over the reals of
$V_{\underline{\lambda}}$
be the column span over the reals of
![]() $E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
and, for
$E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
and, for
![]() $\underline{\sigma},\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
, write
$\underline{\sigma},\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
, write
The following lemma, containing essentially standard results, will be crucial in the following.
Lemma 3·3. We have the following orthogonal direct sum decomposition
Moreover, for all
![]() $\underline{\sigma},\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
, every element of
$\underline{\sigma},\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
, every element of
![]() $V_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is an eigenvector of
$V_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is an eigenvector of
![]() $A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
and the corresponding eigenvalue is
$A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
and the corresponding eigenvalue is
![]() $P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)$
.
$P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)$
.
Proof. Since
![]() $F_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is a primitive idempotent in
$F_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is a primitive idempotent in
![]() $\mathbb{C}(G_n,G_n)$
for each
$\mathbb{C}(G_n,G_n)$
for each
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n$
, it is readily verified that
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n$
, it is readily verified that
![]() $E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is a primitive idempotent in
$E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is a primitive idempotent in
![]() $\mathbb{R}(G_n,G_n)$
for each
$\mathbb{R}(G_n,G_n)$
for each
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
. Therefore the
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
. Therefore the
![]() $E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
are pairwise orthogonal, namely we have
$E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
are pairwise orthogonal, namely we have
![]() $E_{\underline{\lambda}}E_{\underline{\mu}}=\delta_{\underline{\lambda}\underline{\mu}}E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
for all
$E_{\underline{\lambda}}E_{\underline{\mu}}=\delta_{\underline{\lambda}\underline{\mu}}E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
for all
![]() $\underline{\lambda},\underline{\mu}\in\Omega_n$
. Since
$\underline{\lambda},\underline{\mu}\in\Omega_n$
. Since
![]() $E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is idempotent,
$E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is idempotent,
![]() $\text{rk}(E_{\underline{\lambda}})$
is just the trace of
$\text{rk}(E_{\underline{\lambda}})$
is just the trace of
![]() $E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
. It follows from (3·1) that the trace of
$E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
. It follows from (3·1) that the trace of
![]() $F_{\underline{\lambda}}$
equals
$F_{\underline{\lambda}}$
equals
![]() $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)^2$
. Hence we have
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)^2$
. Hence we have
by standard properties of the degrees of irreducible characters. This proves the first statement. We have
![]() $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)=\chi^{\underline{\lambda}^*}(1)$
by Lemma 2·2, from which together with (3·2) and Lemma 3·2 it is readily verified that
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)=\chi^{\underline{\lambda}^*}(1)$
by Lemma 2·2, from which together with (3·2) and Lemma 3·2 it is readily verified that
Since the
![]() $E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
are pairwise orthogonal, we obtain the second statement.
$E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
are pairwise orthogonal, we obtain the second statement.
In fact the proof of Lemma 3·3 shows that
![]() $\{A_{\underline{\sigma}}\,:\,\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\}$
is a symmetric association scheme with primitive idempotents given by
$\{A_{\underline{\sigma}}\,:\,\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\}$
is a symmetric association scheme with primitive idempotents given by
![]() $\{E_{\underline{\lambda}}\,:\,\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\}$
. However we will not exploit this further.
$\{E_{\underline{\lambda}}\,:\,\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\}$
. However we will not exploit this further.
Note that
![]() $A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
is the adjacency matrix of a
$A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
is the adjacency matrix of a
![]() $\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert$
-regular graph for each
$\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert$
-regular graph for each
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n$
, except for
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n$
, except for
![]() $\underline{\sigma}$
given by
$\underline{\sigma}$
given by
![]() $\underline{\sigma}(1)=(1^n)$
, and that
$\underline{\sigma}(1)=(1^n)$
, and that
![]() $P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)=\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert$
if
$P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)=\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert$
if
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
is given by
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
is given by
![]() $X-1\mapsto (n)$
.
$X-1\mapsto (n)$
.
The strategy to prove Theorems 1·1 and 1·2 is as follows (Theorems 1·5 and 1·6 will be proved using slight modifications). We call an element
![]() $x\in G$
a t-derangement if there is no t-tuple of linearly independent elements of
$x\in G$
a t-derangement if there is no t-tuple of linearly independent elements of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
that is fixed by x. Equivalently
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
that is fixed by x. Equivalently
![]() $x\in G_n$
is a t-derangement if
$x\in G_n$
is a t-derangement if
![]() $\text{rk}(x-I)>n-t$
. It is readily verified that either all elements of
$\text{rk}(x-I)>n-t$
. It is readily verified that either all elements of
![]() $D_{\underline{\sigma}}$
are t-derangements or none of them. We wish to identify an appropriate subset
$D_{\underline{\sigma}}$
are t-derangements or none of them. We wish to identify an appropriate subset
![]() $\Sigma$
of
$\Sigma$
of
![]() $\Omega_n$
such that
$\Omega_n$
such that
![]() $D_{\underline{\sigma}}$
consists of t-derangements for all
$D_{\underline{\sigma}}$
consists of t-derangements for all
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma$
and then apply Proposition 3·1 to the graph
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma$
and then apply Proposition 3·1 to the graph
![]() $\Gamma$
with adjacency matrix
$\Gamma$
with adjacency matrix
![]() $\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma}A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
and
$\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma}A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
and
![]() $\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert$
-regular spanning subgraphs
$\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert$
-regular spanning subgraphs
![]() $\Gamma_{\underline{\sigma}}$
having adjacency matrix
$\Gamma_{\underline{\sigma}}$
having adjacency matrix
![]() $A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
for
$A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
for
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma$
. In view of Lemma 3·3, we wish to construct some
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma$
. In view of Lemma 3·3, we wish to construct some
![]() $w\in\mathbb{R}(\Sigma)$
such that both the minimum value and the negative of the second-largest absolute value over all
$w\in\mathbb{R}(\Sigma)$
such that both the minimum value and the negative of the second-largest absolute value over all
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
of
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
of
equals
and such that w is normalised in the sense that (3·6) equals 1 if
![]() $\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
is the trivial character (or equivalently
$\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
is the trivial character (or equivalently
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
is given by
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
is given by
![]() $X-1\mapsto (n)$
). This will ensure that Proposition 3·1 will give the bounds of Theorems 1·1 and 1·2.
$X-1\mapsto (n)$
). This will ensure that Proposition 3·1 will give the bounds of Theorems 1·1 and 1·2.
4. An invertible matrix
This section contains some key preparations for our main proofs. We first identify relevant conjugacy classes of
![]() $G_n$
whose elements are either t-derangements or do not fix a t-space. We then use these conjugacy classes to identify a matrix related to the character table of
$G_n$
whose elements are either t-derangements or do not fix a t-space. We then use these conjugacy classes to identify a matrix related to the character table of
![]() $G_n$
. A key step is to show that this matrix is invertible.
$G_n$
. A key step is to show that this matrix is invertible.
We call an element of
![]() $G_n$
regular elliptic if its characteristic polynomial is irreducible. The following lemma shows that regular elliptic elements in
$G_n$
regular elliptic if its characteristic polynomial is irreducible. The following lemma shows that regular elliptic elements in
![]() $ G_n$
play the role of an n-cycle in the symmetric group
$ G_n$
play the role of an n-cycle in the symmetric group
![]() $S_n$
.
$S_n$
.
Lemma 4·1 ([
Reference Lewis, Reiner and Stanton19
, proposition 4·4]). Each regular elliptic element of
![]() $ G_n$
fixes no proper nontrivial subspace of
$ G_n$
fixes no proper nontrivial subspace of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
.
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
.
Note that, for each
![]() $f\in\Phi$
of degree d, its companion matrix satisfies
$f\in\Phi$
of degree d, its companion matrix satisfies
![]() $\det\!\left(C_f\right)=({-}1)^df(0)$
. It is well known [
Reference Hansen and Mullen16
] that, for each
$\det\!\left(C_f\right)=({-}1)^df(0)$
. It is well known [
Reference Hansen and Mullen16
] that, for each
![]() $a\in\mathbb{F}_q^*$
, there exists an irreducible polynomial
$a\in\mathbb{F}_q^*$
, there exists an irreducible polynomial
![]() $f\in\mathbb{F}_q[x]$
of degree d such that
$f\in\mathbb{F}_q[x]$
of degree d such that
![]() $f(0)=a$
. Hence we can always find a polynomial in
$f(0)=a$
. Hence we can always find a polynomial in
![]() $\Phi$
with prescribed degree and prescribed nonzero determinant of its companion matrix. Also note that, for each
$\Phi$
with prescribed degree and prescribed nonzero determinant of its companion matrix. Also note that, for each
![]() $f\in\Phi$
, we have
$f\in\Phi$
, we have
![]() $f(0)f^*(0)=1$
and therefore
$f(0)f^*(0)=1$
and therefore
We now continue to use
![]() $\alpha$
to denote a fixed generator of
$\alpha$
to denote a fixed generator of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^*$
. For all integers
$\mathbb{F}_q^*$
. For all integers
![]() $\ell,j$
satisfying
$\ell,j$
satisfying
![]() $0\leq \ell<n$
and
$0\leq \ell<n$
and
![]() $0\leq j\leq q-2$
, we fix an irreducible polynomial
$0\leq j\leq q-2$
, we fix an irreducible polynomial
![]() $h_{\ell,j}\in\Phi$
of degree
$h_{\ell,j}\in\Phi$
of degree
![]() $n-\ell$
such that its companion matrix has determinant
$n-\ell$
such that its companion matrix has determinant
![]() $\alpha^j$
and such that
$\alpha^j$
and such that
![]() $h_{\ell,j}^*=h_{\ell,-j}$
. We define
$h_{\ell,j}^*=h_{\ell,-j}$
. We define
and
 \begin{equation*}\Sigma_\ell=\bigcup_{j=0}^{q-2}\Sigma_{\ell,j}\quad \text{and}\quad \Sigma_{\le t}=\bigcup_{\ell=0}^t\Sigma_\ell.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\Sigma_\ell=\bigcup_{j=0}^{q-2}\Sigma_{\ell,j}\quad \text{and}\quad \Sigma_{\le t}=\bigcup_{\ell=0}^t\Sigma_\ell.\end{equation*}
Note that, for each
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\le t-1}$
, the conjugacy class
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\le t-1}$
, the conjugacy class
![]() $C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
consists of elements that do not fix a t-space of
$C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
consists of elements that do not fix a t-space of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. In addition, for each
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. In addition, for each
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_t$
with the
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_t$
with the
![]() $q-1$
exceptions
$q-1$
exceptions
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_t$
satisfying
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_t$
satisfying
![]() $\underline{\sigma}(X-1)=(1^t)$
, the conjugacy class
$\underline{\sigma}(X-1)=(1^t)$
, the conjugacy class
![]() $C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
consists of elements that do not fix a t-space pointwise. Next we define
$C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
consists of elements that do not fix a t-space pointwise. Next we define
and
 \begin{equation*}\Pi_k=\bigcup_{i=0}^{q-2}\Pi_{k,i}\quad \text{and}\quad \Pi_{\le t}=\bigcup_{k=0}^t\Pi_k.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\Pi_k=\bigcup_{i=0}^{q-2}\Pi_{k,i}\quad \text{and}\quad \Pi_{\le t}=\bigcup_{k=0}^t\Pi_k.\end{equation*}
Note that, for
![]() $k<n/2$
, we have
$k<n/2$
, we have
![]() $\lvert\Pi_{k,i}\rvert=\lvert\Sigma_{k,i}\rvert$
and
$\lvert\Pi_{k,i}\rvert=\lvert\Sigma_{k,i}\rvert$
and
![]() $\lvert\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{k,i}\rvert=\lvert\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{k,i}\rvert$
.
$\lvert\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{k,i}\rvert=\lvert\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{k,i}\rvert$
.
We define
![]() $Q\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n,\Omega_n)$
by
$Q\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n,\Omega_n)$
by
and let
![]() $Q_t$
be the restriction of Q to
$Q_t$
be the restriction of Q to
![]() $\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{\le t},\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t})$
. We emphasise that
$\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{\le t},\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t})$
. We emphasise that
![]() $Q_t$
is a square matrix. A key step in our proof is the following proposition.
$Q_t$
is a square matrix. A key step in our proof is the following proposition.
Proposition 4·2. For
![]() $n>2t$
, the matrix
$n>2t$
, the matrix
![]() $Q_t$
has full rank and is independent of n.
$Q_t$
has full rank and is independent of n.
In the remainder of this section we essentially only prove Proposition 4·2. The reader who is interested in maintaining the flow of the proof of our main results may wish to skip to the next section at first reading.
We define
![]() $R\in\mathbb{C}(\Lambda_n,\Lambda_n)$
by
$R\in\mathbb{C}(\Lambda_n,\Lambda_n)$
by
and let
![]() $R_t$
be the restriction of R to
$R_t$
be the restriction of R to
![]() $\mathbb{C}(\Pi_{\le t},\Sigma_{\le t})$
. We shall prove a counterpart of Proposition 4·2 for the matrix
$\mathbb{C}(\Pi_{\le t},\Sigma_{\le t})$
. We shall prove a counterpart of Proposition 4·2 for the matrix
![]() $R_t$
.
$R_t$
.
Proposition 4·3. For
![]() $n>2t$
, the matrix
$n>2t$
, the matrix
![]() $R_t$
has full rank and is independent of n.
$R_t$
has full rank and is independent of n.
Note that
![]() $Q_t$
is obtained from
$Q_t$
is obtained from
![]() $R_t$
by first applying elementary row operations, then deleting some rows, and then (in view of (3·3)) deleting duplicate columns. Hence Proposition 4·2 follows from Proposition 4·3.
$R_t$
by first applying elementary row operations, then deleting some rows, and then (in view of (3·3)) deleting duplicate columns. Hence Proposition 4·2 follows from Proposition 4·3.
We now prove Proposition 4·3. We let
![]() $S\in\mathbb{C}(\Lambda_n,\Lambda_n)$
be the matrix defined by
$S\in\mathbb{C}(\Lambda_n,\Lambda_n)$
be the matrix defined by
and let
![]() $S_t$
be the restriction of S to
$S_t$
be the restriction of S to
![]() $\mathbb{C}(\Pi_{\le t},\Sigma_{\le t})$
. Now recall the equivalence relation
$\mathbb{C}(\Pi_{\le t},\Sigma_{\le t})$
. Now recall the equivalence relation
![]() $\sim$
on
$\sim$
on
![]() $\Lambda_n$
and the numbers
$\Lambda_n$
and the numbers
![]() $K_{\underline{\lambda}\underline{\mu}}$
from Section 2·4. Define
$K_{\underline{\lambda}\underline{\mu}}$
from Section 2·4. Define
![]() $T\in\mathbb{C}(\Lambda_n,\Lambda_n)$
by
$T\in\mathbb{C}(\Lambda_n,\Lambda_n)$
by
 \begin{equation*}T(\underline{\mu},\underline{\lambda})=\begin{cases}K_{\underline{\lambda}\underline{\mu}} & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}\sim\underline{\mu}$}\\[4pt]0 & \text{otherwise}\end{cases}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}T(\underline{\mu},\underline{\lambda})=\begin{cases}K_{\underline{\lambda}\underline{\mu}} & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}\sim\underline{\mu}$}\\[4pt]0 & \text{otherwise}\end{cases}\end{equation*}
and let
![]() $T_t$
be the restriction of T to
$T_t$
be the restriction of T to
![]() $\mathbb{C}(\Pi_{\le t},\Pi_{\le t})$
. We first prove the following.
$\mathbb{C}(\Pi_{\le t},\Pi_{\le t})$
. We first prove the following.
Lemma 4·4.
-
(i) We have
 $S=TR$
and T has full rank.
$S=TR$
and T has full rank. -
(ii) For
 $n>2t$
, we have
$n>2t$
, we have
 $S_t=T_tR_t$
and
$S_t=T_tR_t$
and
 $T_t$
has full rank and is independent of n.
$T_t$
has full rank and is independent of n.
Proof. From (2·12) we have
![]() $S=TR$
and T is block diagonal, where the blocks are induced by the equivalence classes under
$S=TR$
and T is block diagonal, where the blocks are induced by the equivalence classes under
![]() $\sim$
. Each diagonal block corresponds to one equivalence class. If
$\sim$
. Each diagonal block corresponds to one equivalence class. If
![]() $s\,:\,\Phi\to\mathbb{Z}$
is the shape of such an equivalence class, then the corresponding block can be written as a Kronecker product
$s\,:\,\Phi\to\mathbb{Z}$
is the shape of such an equivalence class, then the corresponding block can be written as a Kronecker product
where
![]() $K^{(m)}\in\mathbb{C}(\text{Par}_m,\text{Par}_m)$
is a Kostka matrix given by
$K^{(m)}\in\mathbb{C}(\text{Par}_m,\text{Par}_m)$
is a Kostka matrix given by
![]() $K^{(m)}(\mu,\lambda)=K_{\lambda\mu}$
with the convention
$K^{(m)}(\mu,\lambda)=K_{\lambda\mu}$
with the convention
![]() $K^{(0)}=(1)$
and
$K^{(0)}=(1)$
and
![]() $\text{Par}_m$
is the set of partitions of m. By (2·8) the Kostka matrices are invertible. Hence T is a block-diagonal matrix whose blocks are Kronecker products of matrices of full rank and so T itself has full rank. This proves (i).
$\text{Par}_m$
is the set of partitions of m. By (2·8) the Kostka matrices are invertible. Hence T is a block-diagonal matrix whose blocks are Kronecker products of matrices of full rank and so T itself has full rank. This proves (i).
From (2·8) we find that
![]() $S_t=T_tR_t$
. Note that
$S_t=T_tR_t$
. Note that
![]() $T_t$
is still block diagonal with one diagonal block for each equivalence class of
$T_t$
is still block diagonal with one diagonal block for each equivalence class of
![]() $\Lambda_n$
under
$\Lambda_n$
under
![]() $\sim$
whose shape
$\sim$
whose shape
![]() $s\,:\,\Phi\to\mathbb{Z}$
satisfies
$s\,:\,\Phi\to\mathbb{Z}$
satisfies
![]() $s\!\left(\alpha^i\right)\ge n-t$
for some i. The corresponding block can be written as
$s\!\left(\alpha^i\right)\ge n-t$
for some i. The corresponding block can be written as
where
![]() $\tilde K^{(s\!\left(\alpha^i\right))}$
is the matrix
$\tilde K^{(s\!\left(\alpha^i\right))}$
is the matrix
![]() $K^{(s\!\left(\alpha^i\right))}$
restricted to partitions
$K^{(s\!\left(\alpha^i\right))}$
restricted to partitions
![]() $\lambda$
of
$\lambda$
of
![]() $s\!\left(\alpha^i\right)$
satisfying
$s\!\left(\alpha^i\right)$
satisfying
From (2·8) we find that, after a suitable ordering of rows and columns, all matrices occuring in the Kronecker product (4·2) are upper-triangular with ones on the diagonal. Again
![]() $T_t$
is a block-diagonal matrix whose blocks are Kronecker products of matrices of full rank and so
$T_t$
is a block-diagonal matrix whose blocks are Kronecker products of matrices of full rank and so
![]() $T_t$
itself has full rank.
$T_t$
itself has full rank.
From the proof of [
Reference Ellis, Friedgut and Pilpel7
, theorem 20] we know that
![]() $\tilde K^{(s\!\left(\alpha^i\right))}$
is independent of n. Moreover all other matrices occuring in the Kronecker product (4·2) are also independent of n. Hence
$\tilde K^{(s\!\left(\alpha^i\right))}$
is independent of n. Moreover all other matrices occuring in the Kronecker product (4·2) are also independent of n. Hence
![]() $T_t$
itself is also independent of n. This proves (ii).
$T_t$
itself is also independent of n. This proves (ii).
Next we shall show that the matrix
![]() $S_t$
has full rank. Recall that, for a composition
$S_t$
has full rank. Recall that, for a composition
![]() $\lambda$
, we denote by
$\lambda$
, we denote by
![]() $P_{\lambda}$
the parabolic subgroup of
$P_{\lambda}$
the parabolic subgroup of
![]() $G_{\lvert\lambda\rvert}$
given in (2·2). We start with the following lemma.
$G_{\lvert\lambda\rvert}$
given in (2·2). We start with the following lemma.
Lemma 4·5. Let m and n be positive integers satisfying
![]() $m<n$
and let
$m<n$
and let
![]() $\phi$
and
$\phi$
and
![]() $\psi$
be class functions of
$\psi$
be class functions of
![]() $G_m$
and
$G_m$
and
![]() $G_n$
, respectively. Let
$G_n$
, respectively. Let
![]() $\pi_1\,:\,P_{(m,n)}\to G_m$
and
$\pi_1\,:\,P_{(m,n)}\to G_m$
and
![]() $\pi_2\,:\,P_{(m,n)}\to G_n$
be the natural projections onto the corresponding diagonal blocks. Let
$\pi_2\,:\,P_{(m,n)}\to G_n$
be the natural projections onto the corresponding diagonal blocks. Let
![]() $g\in P_{(m,n)}$
be such that
$g\in P_{(m,n)}$
be such that
![]() $\pi_2(g)$
is regular elliptic. Then we have
$\pi_2(g)$
is regular elliptic. Then we have
Proof. From (2·4) we have
 \begin{equation}(\phi\odot \psi)(g)=\frac{1}{\lvert P_{(m,n)}\rvert}\sum_{\substack{x\in G_{m+n}\\xgx^{-1}\in P_{(m,n)}}}\phi\!\left(\pi_1\!\left(xgx^{-1}\right)\right)\psi\!\left(\pi_2\!\left(xgx^{-1}\right)\right). \end{equation}
\begin{equation}(\phi\odot \psi)(g)=\frac{1}{\lvert P_{(m,n)}\rvert}\sum_{\substack{x\in G_{m+n}\\xgx^{-1}\in P_{(m,n)}}}\phi\!\left(\pi_1\!\left(xgx^{-1}\right)\right)\psi\!\left(\pi_2\!\left(xgx^{-1}\right)\right). \end{equation}
Since
![]() $\pi_2(g)$
is regular elliptic and
$\pi_2(g)$
is regular elliptic and
![]() $m<n$
, we find from Lemma 4·1 that g stabilises a unique m-dimensional subspace U of
$m<n$
, we find from Lemma 4·1 that g stabilises a unique m-dimensional subspace U of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^{m+n}$
. Hence the number of
$\mathbb{F}_q^{m+n}$
. Hence the number of
![]() $x\in G_{m+n}$
such that
$x\in G_{m+n}$
such that
![]() $xgx^{-1}\in P_{(m,n)}$
is the number of ordered bases
$xgx^{-1}\in P_{(m,n)}$
is the number of ordered bases
![]() $\{u_1,\dots,u_m,w_1,\dots,w_n\}$
of
$\{u_1,\dots,u_m,w_1,\dots,w_n\}$
of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^{m+n}$
such that
$\mathbb{F}_q^{m+n}$
such that
![]() $\{u_1,\dots,u_m\}$
spans U. This number equals
$\{u_1,\dots,u_m\}$
spans U. This number equals
![]() $\lvert P_{(m,n)}\rvert$
. Since
$\lvert P_{(m,n)}\rvert$
. Since
![]() $xgx^{-1}\in P_{(m,n)}$
for each
$xgx^{-1}\in P_{(m,n)}$
for each
![]() $x\in P_{(m,n)}$
, we conclude that
$x\in P_{(m,n)}$
, we conclude that
Since
![]() $\pi_i(xgx^{-1})$
is conjugate to
$\pi_i(xgx^{-1})$
is conjugate to
![]() $\pi_i(g)$
for each
$\pi_i(g)$
for each
![]() $i\in\{1,2\}$
and each
$i\in\{1,2\}$
and each
![]() $x\in P_{(m,n)}$
, the statement of the lemma follows from (4·3).
$x\in P_{(m,n)}$
, the statement of the lemma follows from (4·3).
We use Lemma 4·5 to prove the following lemma on the structure of the matrix S.
Lemma 4·6. Let
![]() $k,\ell$
be integers satisfying
$k,\ell$
be integers satisfying
![]() $0\leq k,\ell<n/2$
and let
$0\leq k,\ell<n/2$
and let
![]() $\underline{\mu}\in\Pi_{k,i}$
and
$\underline{\mu}\in\Pi_{k,i}$
and
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\ell,j}$
. If
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\ell,j}$
. If
![]() $k>\ell$
, then we have
$k>\ell$
, then we have
![]() $\xi^{\underline{\mu}}_{\underline{\sigma}}=0$
. For
$\xi^{\underline{\mu}}_{\underline{\sigma}}=0$
. For
![]() $k\leq \ell$
, let
$k\leq \ell$
, let
![]() $\nu$
be the partition obtained from
$\nu$
be the partition obtained from
![]() $\underline{\mu}(X-\alpha^i)$
by replacing the part
$\underline{\mu}(X-\alpha^i)$
by replacing the part
![]() $n-k$
by
$n-k$
by
![]() $\ell-k$
and define
$\ell-k$
and define
![]() $\underline{\nu},\underline{\tau}\in\Lambda_\ell$
by
$\underline{\nu},\underline{\tau}\in\Lambda_\ell$
by
 \begin{equation*}\underline{\nu}(f)=\begin{cases}\nu & \text{for $f=X-\alpha^i$}\\\underline{\mu}(f) & \text{otherwise}\end{cases}\quad \text{and}\quad \underline{\tau}(f)=\begin{cases}\varnothing & \text{for $f=h_{\ell,j}$}\\\underline{\sigma}(f) & \text{otherwise}.\end{cases}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\underline{\nu}(f)=\begin{cases}\nu & \text{for $f=X-\alpha^i$}\\\underline{\mu}(f) & \text{otherwise}\end{cases}\quad \text{and}\quad \underline{\tau}(f)=\begin{cases}\varnothing & \text{for $f=h_{\ell,j}$}\\\underline{\sigma}(f) & \text{otherwise}.\end{cases}\end{equation*}
If
![]() $k\leq \ell$
, then we have
$k\leq \ell$
, then we have
![]() $\xi^{\underline{\mu}}_{\underline{\sigma}}=\xi^{\underline{\nu}}_{\underline{\tau}}\,\omega^{ij}$
.
$\xi^{\underline{\mu}}_{\underline{\sigma}}=\xi^{\underline{\nu}}_{\underline{\tau}}\,\omega^{ij}$
.
Proof. Let
![]() $g\in C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
. Define
$g\in C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
. Define
![]() $\underline{\kappa}\in\Lambda_k$
by
$\underline{\kappa}\in\Lambda_k$
by
 \begin{equation*}\underline{\kappa}(f)=\begin{cases}\left(\underline{\mu}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)_2,\underline{\mu}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)_3,\dots\right) & \text{for $f=X-\alpha^i$}\\[4pt]\underline{\mu}(f) & \text{otherwise},\end{cases}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\underline{\kappa}(f)=\begin{cases}\left(\underline{\mu}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)_2,\underline{\mu}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)_3,\dots\right) & \text{for $f=X-\alpha^i$}\\[4pt]\underline{\mu}(f) & \text{otherwise},\end{cases}\end{equation*}
For
![]() $\xi^{\underline{\mu}}(g)$
to be nonzero, g must be conjugate to an element of
$\xi^{\underline{\mu}}(g)$
to be nonzero, g must be conjugate to an element of
![]() $P_{(k,n-k)}$
. Each such element fixes a k-dimensional subspace of
$P_{(k,n-k)}$
. Each such element fixes a k-dimensional subspace of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. If
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. If
![]() $k>\ell$
, then by Lemma 4·1, g fixes no k-dimensional subspace of
$k>\ell$
, then by Lemma 4·1, g fixes no k-dimensional subspace of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
and hence
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
and hence
![]() $\xi^{\underline{\mu}}(g)=0$
.
$\xi^{\underline{\mu}}(g)=0$
.
Henceforth assume that
![]() $k\leq \ell$
. We shall frequently use
$k\leq \ell$
. We shall frequently use
![]() $\xi^{f\mapsto (m)}=\chi^{f\mapsto (m)}$
, which follows from (2·7) and (2·8). Since
$\xi^{f\mapsto (m)}=\chi^{f\mapsto (m)}$
, which follows from (2·7) and (2·8). Since
![]() $k\leq \ell$
we have
$k\leq \ell$
we have
Write
 \begin{equation*}E=\bigcup_{\substack{\underline{\rho}\in\Lambda_{n-k}\\\underline{\rho}(h_{\ell,j})=(1)}} C_{\underline{\rho}}.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}E=\bigcup_{\substack{\underline{\rho}\in\Lambda_{n-k}\\\underline{\rho}(h_{\ell,j})=(1)}} C_{\underline{\rho}}.\end{equation*}
We claim that
Indeed, each
![]() $e\in E$
is conjugate to an element of
$e\in E$
is conjugate to an element of
![]() $P_{(\ell-k,n-\ell)}$
with blocks
$P_{(\ell-k,n-\ell)}$
with blocks
![]() $e_1\in G_{\ell-k}$
and
$e_1\in G_{\ell-k}$
and
![]() $e_2\in G_{n-\ell}$
on the main diagonal, where
$e_2\in G_{n-\ell}$
on the main diagonal, where
![]() $e_2$
is regular elliptic. Hence we find from Lemma 2·3 that, for each
$e_2$
is regular elliptic. Hence we find from Lemma 2·3 that, for each
![]() $e\in E$
, the left-hand side of (4·6) equals
$e\in E$
, the left-hand side of (4·6) equals
 \begin{align*}\theta\!\left(\det(e)^i\right)&=\theta\!\left(\det(e_1)^i\right)\cdot \theta\!\left(\det(e_2)^i\right)\\&=\xi^{X-\alpha^i\mapsto (\ell-k)}(e_1)\cdot \xi^{X-\alpha^i\mapsto (n-\ell)}(e_2),\end{align*}
\begin{align*}\theta\!\left(\det(e)^i\right)&=\theta\!\left(\det(e_1)^i\right)\cdot \theta\!\left(\det(e_2)^i\right)\\&=\xi^{X-\alpha^i\mapsto (\ell-k)}(e_1)\cdot \xi^{X-\alpha^i\mapsto (n-\ell)}(e_2),\end{align*}
which by Lemma 4·5 equals the right hand side of (4·6). From (4·4) we have
 \begin{equation*}\xi^{\underline{\mu}}(g)=\frac{1}{\lvert P_{(k,n-k)}\rvert}\sum_{\substack{x\in G_n\\xgx^{-1}\in P_{(k,n-k)}}}\xi^{\underline{\kappa}}\!\left(\pi_1\!\left(xgx^{-1}\right)\right)\xi^{X-\alpha^i\mapsto (n-k)}\left(\pi_2\!\left(xgx^{-1}\right)\right),\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\xi^{\underline{\mu}}(g)=\frac{1}{\lvert P_{(k,n-k)}\rvert}\sum_{\substack{x\in G_n\\xgx^{-1}\in P_{(k,n-k)}}}\xi^{\underline{\kappa}}\!\left(\pi_1\!\left(xgx^{-1}\right)\right)\xi^{X-\alpha^i\mapsto (n-k)}\left(\pi_2\!\left(xgx^{-1}\right)\right),\end{equation*}
where
![]() $\pi_1\,:\,P_{(k,n-k)}\to G_{k}$
and
$\pi_1\,:\,P_{(k,n-k)}\to G_{k}$
and
![]() $\pi_2\,:\,P_{(k,n-k)}\to G_{n-k}$
are the natural projections onto the diagonal blocks. Since
$\pi_2\,:\,P_{(k,n-k)}\to G_{n-k}$
are the natural projections onto the diagonal blocks. Since
![]() $k,\ell<n/2$
, Lemma 4·1 implies that each
$k,\ell<n/2$
, Lemma 4·1 implies that each
![]() $\pi_2(xgx^{-1})$
occuring in the summation is forced to lie inside E. Hence by subsequent applications of (4·4), (4·6), and (4·5) we then find that
$\pi_2(xgx^{-1})$
occuring in the summation is forced to lie inside E. Hence by subsequent applications of (4·4), (4·6), and (4·5) we then find that
 \begin{align*}\xi^{\underline{\mu}}(g)&=\left(\xi^{\underline{\kappa}}\odot \xi^{X-\alpha^i\mapsto (n-k)}\right)(g)\\&=\left(\xi^{\underline{\kappa}}\odot\xi^{X-\alpha^i\mapsto (\ell-k)}\odot \xi^{X-\alpha^i\mapsto (n-\ell)}\right)(g)\\&=\left(\xi^{\underline{\nu}}\odot \xi^{X-\alpha^i\mapsto (n-\ell)}\right)(g).\end{align*}
\begin{align*}\xi^{\underline{\mu}}(g)&=\left(\xi^{\underline{\kappa}}\odot \xi^{X-\alpha^i\mapsto (n-k)}\right)(g)\\&=\left(\xi^{\underline{\kappa}}\odot\xi^{X-\alpha^i\mapsto (\ell-k)}\odot \xi^{X-\alpha^i\mapsto (n-\ell)}\right)(g)\\&=\left(\xi^{\underline{\nu}}\odot \xi^{X-\alpha^i\mapsto (n-\ell)}\right)(g).\end{align*}
Without loss of generality, we may assume that
![]() $g\in P_{(\ell,n-\ell)}$
and that the diagonal blocks of g are
$g\in P_{(\ell,n-\ell)}$
and that the diagonal blocks of g are
![]() $g_1$
and
$g_1$
and
![]() $g_2$
, where
$g_2$
, where
![]() $g_1\in C_{\underline{\tau}}$
and
$g_1\in C_{\underline{\tau}}$
and
![]() $g_2$
is the companion matrix of
$g_2$
is the companion matrix of
![]() $h_{\ell,j}$
. Since
$h_{\ell,j}$
. Since
![]() $g_2$
is regular elliptic, we may apply Lemma 4·5 once more to obtain
$g_2$
is regular elliptic, we may apply Lemma 4·5 once more to obtain
Since
![]() $g_1\in C_{\underline{\tau}}$
, we have
$g_1\in C_{\underline{\tau}}$
, we have
![]() $\xi^{\underline{\nu}}(g_1)=\xi^{\underline{\nu}}_{\underline{\tau}}$
, and since
$\xi^{\underline{\nu}}(g_1)=\xi^{\underline{\nu}}_{\underline{\tau}}$
, and since
![]() $g_2$
is the companion matrix of
$g_2$
is the companion matrix of
![]() $h_{\ell,j}$
, we find from Lemma 2·3 that
$h_{\ell,j}$
, we find from Lemma 2·3 that
Hence we obtain
![]() $\xi^{\underline{\mu}}(g)=\xi^{\underline{\nu}}_{\underline{\tau}}\,\omega^{ij}$
, as required.
$\xi^{\underline{\mu}}(g)=\xi^{\underline{\nu}}_{\underline{\tau}}\,\omega^{ij}$
, as required.
We can now prove the required property of the matrix
![]() $S_t$
.
$S_t$
.
Lemma 4·7. For
![]() $n>2t$
, the matrix
$n>2t$
, the matrix
![]() $S_t$
has full rank and is independent of n.
$S_t$
has full rank and is independent of n.
Proof. To indicate dependence on n, write
![]() $S^{(n)}$
for the matrix S given in (4·1) and
$S^{(n)}$
for the matrix S given in (4·1) and
![]() $S^{(n)}_t$
for the corresponding restricted matrix
$S^{(n)}_t$
for the corresponding restricted matrix
![]() $S_t$
. Let
$S_t$
. Let
![]() $n>2t$
. From Lemma 4·6 we find that all entries in
$n>2t$
. From Lemma 4·6 we find that all entries in
![]() $S^{(n)}_t$
are independent of n, which proves the second statement of the lemma.
$S^{(n)}_t$
are independent of n, which proves the second statement of the lemma.
To show that
![]() $S^{(n)}_t$
is invertible, we view
$S^{(n)}_t$
is invertible, we view
![]() $S^{(n)}_t$
as a block matrix, where the blocks are indexed by
$S^{(n)}_t$
as a block matrix, where the blocks are indexed by
![]() $\Pi_k$
and
$\Pi_k$
and
![]() $\Sigma_\ell$
for
$\Sigma_\ell$
for
![]() $k,\ell\in\{0,1,\dots,t\}$
. Let
$k,\ell\in\{0,1,\dots,t\}$
. Let
![]() $B_{k,\ell}$
be the block corresponding to
$B_{k,\ell}$
be the block corresponding to
![]() $\Pi_k$
and
$\Pi_k$
and
![]() $\Sigma_\ell$
. Lemma 4·6 implies that
$\Sigma_\ell$
. Lemma 4·6 implies that
![]() $B_{k,\ell}$
is zero for
$B_{k,\ell}$
is zero for
![]() $k>\ell$
and, for
$k>\ell$
and, for
![]() $0\leq k\leq t$
, the block
$0\leq k\leq t$
, the block
![]() $B_{kk}$
is the Kronecker product of
$B_{kk}$
is the Kronecker product of
![]() $S^{(k)}$
and the Vandermonde matrix
$S^{(k)}$
and the Vandermonde matrix
![]() $(\omega^{ij})_{0\leq i, j\leq q-2}$
. Since the character table of irreducible characters of every finite group is invertible, Lemma 4·4 implies that
$(\omega^{ij})_{0\leq i, j\leq q-2}$
. Since the character table of irreducible characters of every finite group is invertible, Lemma 4·4 implies that
![]() $S^{(k)}$
is invertible and so
$S^{(k)}$
is invertible and so
![]() $B_{kk}$
is invertible. Hence
$B_{kk}$
is invertible. Hence
![]() $S^{(n)}_t$
is block upper-triangular and all diagonal blocks are invertible. Therefore
$S^{(n)}_t$
is block upper-triangular and all diagonal blocks are invertible. Therefore
![]() $S^{(n)}_t$
itself is invertible.
$S^{(n)}_t$
itself is invertible.
Finally, by combining Lemmas 4·4 and 4·7, we obtain a proof of Proposition 4·3.
5. Proof of Theorems 1·1 and 1·2
Now recall the definition (3·5) of the eigenvalues
![]() $P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)$
and the definition (3·7) of the prescribed extremal eigenvalue
$P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)$
and the definition (3·7) of the prescribed extremal eigenvalue
![]() $\eta$
. As a first step in constructing the required weight function w occuring in (3·6), we prove the following result.
$\eta$
. As a first step in constructing the required weight function w occuring in (3·6), we prove the following result.
Proposition 5·1. Let n and t be positive integers satisfying
![]() $n>2t$
. Then there exists
$n>2t$
. Then there exists
![]() $w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t})$
such that
$w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t})$
such that
![]() $w(\underline{\sigma})=0$
for
$w(\underline{\sigma})=0$
for
![]() $\underline{\sigma}(1)=(1^t)$
and
$\underline{\sigma}(1)=(1^t)$
and
 \begin{equation}\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}w(\underline{\sigma})P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{0,0}$}\\\eta & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{k,0}$ and $1\leq k\leq t$}\\0 & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{k,i}$ and $0\leq k\leq t$ and $1\leq i\leq q-2$}\end{cases} \end{equation}
\begin{equation}\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}w(\underline{\sigma})P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{0,0}$}\\\eta & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{k,0}$ and $1\leq k\leq t$}\\0 & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{k,i}$ and $0\leq k\leq t$ and $1\leq i\leq q-2$}\end{cases} \end{equation}
and
for some constant
![]() $\gamma_t$
depending only on t.
$\gamma_t$
depending only on t.
Proof. From Proposition 4·2 we know that
![]() $Q_t$
has full rank. In view of (3·5) there exists a unique
$Q_t$
has full rank. In view of (3·5) there exists a unique
![]() $w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t})$
satisfying (5·1).
$w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t})$
satisfying (5·1).
We now show that
![]() $w(\underline{\sigma})=0$
for the
$w(\underline{\sigma})=0$
for the
![]() $\lfloor q/2\rfloor+1$
elements
$\lfloor q/2\rfloor+1$
elements
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}$
satisfying
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}$
satisfying
![]() $\underline{\sigma}(1)=(1^t)$
. Without loss of generality we may assume that
$\underline{\sigma}(1)=(1^t)$
. Without loss of generality we may assume that
![]() $\Omega_n$
contains
$\Omega_n$
contains
![]() $X-\alpha^i$
and
$X-\alpha^i$
and
![]() $h_{t,j}$
for all
$h_{t,j}$
for all
![]() $i, j=0,1,\dots,\lfloor q/2\rfloor$
. Accordingly we define
$i, j=0,1,\dots,\lfloor q/2\rfloor$
. Accordingly we define
![]() $\underline{\sigma}_j\in\Sigma_{t,j}$
by
$\underline{\sigma}_j\in\Sigma_{t,j}$
by
![]() $\underline{\sigma}_j(1)=(1^t)$
for
$\underline{\sigma}_j(1)=(1^t)$
for
![]() $j=0,1,\dots,\lfloor q/2\rfloor$
. Recall the definition of the character
$j=0,1,\dots,\lfloor q/2\rfloor$
. Recall the definition of the character
![]() $\zeta^{(t,i)}$
from Section 2·4 and write
$\zeta^{(t,i)}$
from Section 2·4 and write
![]() $\zeta^{(t,i)}_{\underline{\sigma}}$
for this character evaluated on the conjugacy class
$\zeta^{(t,i)}_{\underline{\sigma}}$
for this character evaluated on the conjugacy class
![]() $C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
. We evaluate the sum
$C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
. We evaluate the sum
in two ways. Since
![]() $\zeta^{(t,0)}$
is the permutation character on the set of t-tuples of linearly independent elements of
$\zeta^{(t,0)}$
is the permutation character on the set of t-tuples of linearly independent elements of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
, we find by Lemma 2·4 that the summand in (5·3) is nonzero only when the elements of
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
, we find by Lemma 2·4 that the summand in (5·3) is nonzero only when the elements of
![]() $C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
fix a t-tuple of linearly independent elements of
$C_{\underline{\sigma}}$
fix a t-tuple of linearly independent elements of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
, hence only when
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
, hence only when
![]() $\underline{\sigma}=\underline{\sigma}_j$
for some j. By the definition of
$\underline{\sigma}=\underline{\sigma}_j$
for some j. By the definition of
![]() $\underline{\sigma}_j$
, each element in
$\underline{\sigma}_j$
, each element in
![]() $C_{\underline{\sigma}_j}$
has determinant
$C_{\underline{\sigma}_j}$
has determinant
![]() $\alpha^j$
. Hence by applying Lemma 2·4 twice we obtain
$\alpha^j$
. Hence by applying Lemma 2·4 twice we obtain
and therefore
 \begin{equation}S_i=2\zeta^{(t,0)}_{\underline{\sigma}_0}\sum_{j=0}^{\lfloor q/2\rfloor}w\!\left(\underline{\sigma}_j\right)\,\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}_j}\rvert\,\cos\bigg(\frac{2\pi ij}{q-1}\bigg). \end{equation}
\begin{equation}S_i=2\zeta^{(t,0)}_{\underline{\sigma}_0}\sum_{j=0}^{\lfloor q/2\rfloor}w\!\left(\underline{\sigma}_j\right)\,\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}_j}\rvert\,\cos\bigg(\frac{2\pi ij}{q-1}\bigg). \end{equation}
On the other hand, since
![]() $\zeta^{(t,i)}+\zeta^{(t,-i)}$
is a real-valued class function, we find from Lemma 3·2 that it is a linear combination of
$\zeta^{(t,i)}+\zeta^{(t,-i)}$
is a real-valued class function, we find from Lemma 3·2 that it is a linear combination of
![]() $\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
for
$\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
for
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
. Hence by Lemma 2·5 there exists numbers
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
. Hence by Lemma 2·5 there exists numbers
![]() $n_{i,\underline{\lambda}}$
such that
$n_{i,\underline{\lambda}}$
such that
 \begin{equation*}\zeta^{(t,i)}_{\underline{\sigma}}+\zeta^{(t,-i)}_{\underline{\sigma}}=\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\\\underline{\lambda}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)_1\ge n-t}}n_{i,\underline{\lambda}}\,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\zeta^{(t,i)}_{\underline{\sigma}}+\zeta^{(t,-i)}_{\underline{\sigma}}=\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\\\underline{\lambda}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)_1\ge n-t}}n_{i,\underline{\lambda}}\,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}}\end{equation*}
and hence
 \begin{equation}S_i=\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\\\underline{\lambda}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)_1\ge n-t}}n_{i,\underline{\lambda}}\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}w(\underline{\sigma})\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert\,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}}. \end{equation}
\begin{equation}S_i=\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\\\underline{\lambda}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)_1\ge n-t}}n_{i,\underline{\lambda}}\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}w(\underline{\sigma})\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert\,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}}. \end{equation}
Since (5·1) holds, we conclude that
![]() $S_i=0$
for each i satisfying
$S_i=0$
for each i satisfying
![]() $1\leq i\leq \lfloor q/2\rfloor$
. Since
$1\leq i\leq \lfloor q/2\rfloor$
. Since
![]() $\zeta^{(t,0)}$
is a permutation character, it contains the trivial character with multiplicity 1 (this can be seen by Frobenius reciprocity, for example). Hence we have
$\zeta^{(t,0)}$
is a permutation character, it contains the trivial character with multiplicity 1 (this can be seen by Frobenius reciprocity, for example). Hence we have
![]() $n_{0,\underline{\lambda}}=2$
for
$n_{0,\underline{\lambda}}=2$
for
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
satisfying
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
satisfying
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n)$
. We therefore find from (5·5) and (5·1) that
$\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n)$
. We therefore find from (5·5) and (5·1) that
 \begin{equation*}S_0=2+\eta\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\\n-t\leq \underline{\lambda}(1)_1<n}}n_{0,\underline{\lambda}}\,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)=2+2\eta\left(\zeta^{(t,0)}(1)-1\right).\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}S_0=2+\eta\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\\n-t\leq \underline{\lambda}(1)_1<n}}n_{0,\underline{\lambda}}\,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)=2+2\eta\left(\zeta^{(t,0)}(1)-1\right).\end{equation*}
Since
![]() $\zeta^{(t,0)}(1)$
equals the number of t-tuples of linearly independent elements of
$\zeta^{(t,0)}(1)$
equals the number of t-tuples of linearly independent elements of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
, we have
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
, we have
Therefore
![]() $S_0=0$
and so
$S_0=0$
and so
![]() $S_i=0$
for each i satisfying
$S_i=0$
for each i satisfying
![]() $0\leq i\leq \lfloor q/2\rfloor$
. Since each element of
$0\leq i\leq \lfloor q/2\rfloor$
. Since each element of
![]() $C_{\underline{\sigma}_0}$
fixes a t-tuple of linearly independent elements of
$C_{\underline{\sigma}_0}$
fixes a t-tuple of linearly independent elements of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
, we have
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
, we have
![]() $\zeta^{(t,0)}_{\underline{\sigma}_0}\ne 0$
. Thus (5·4) implies
$\zeta^{(t,0)}_{\underline{\sigma}_0}\ne 0$
. Thus (5·4) implies
 \begin{equation*}\sum_{j=0}^{\lfloor q/2\rfloor}w\!\left(\underline{\sigma}_j\right)\,\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}_j}\rvert\,\,\cos\bigg(\frac{2\pi ij}{q-1}\bigg)=0\quad \text{for each} \, i \, \text{satisfying $0\leq i\leq \lfloor q/2\rfloor$}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\sum_{j=0}^{\lfloor q/2\rfloor}w\!\left(\underline{\sigma}_j\right)\,\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}_j}\rvert\,\,\cos\bigg(\frac{2\pi ij}{q-1}\bigg)=0\quad \text{for each} \, i \, \text{satisfying $0\leq i\leq \lfloor q/2\rfloor$}\end{equation*}
and it is readily verified, using that
![]() $(\omega^{ij})_{0\leq i, j<q-1}$
is a Vandermonde matrix, that this in turn implies that
$(\omega^{ij})_{0\leq i, j<q-1}$
is a Vandermonde matrix, that this in turn implies that
![]() $w\!\left(\underline{\sigma}_j\right)=0$
for all j satisfying
$w\!\left(\underline{\sigma}_j\right)=0$
for all j satisfying
![]() $0\leq j\leq \lfloor q/2\rfloor$
, as required.
$0\leq j\leq \lfloor q/2\rfloor$
, as required.
Now, for each
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
satisfying
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
satisfying
![]() $n-t\leq \underline{\lambda}(1)_1<n$
, we find from Lemma 2·5 that
$n-t\leq \underline{\lambda}(1)_1<n$
, we find from Lemma 2·5 that
using (5·6). Since
![]() $\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)=\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)=1$
for
$\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)=\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)=1$
for
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Pi_{0,0}$
, we conclude from (5·1) that
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Pi_{0,0}$
, we conclude from (5·1) that
 \begin{equation*}\Bigg\lvert\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}w(\underline{\sigma})\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert\,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}}\Bigg\rvert\le 1 \quad \text{for each $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{\le t}$}.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\Bigg\lvert\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}w(\underline{\sigma})\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert\,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}}\Bigg\rvert\le 1 \quad \text{for each $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{\le t}$}.\end{equation*}
By Lemma 4·2 all entries of
![]() $Q_t$
(which are precisely the values of
$Q_t$
(which are precisely the values of
![]() $\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}}$
occuring in the sum) are independent of n and so are uniformly bounded by some value only depending on t. The same also holds for the inverse of
$\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}}$
occuring in the sum) are independent of n and so are uniformly bounded by some value only depending on t. The same also holds for the inverse of
![]() $Q_t$
, which establishes (5·2).
$Q_t$
, which establishes (5·2).
In what follows we treat the remaining eigenvalues.
Lemma 5·2. Let n and t be positive integers satisfying
![]() $n>2t$
and let
$n>2t$
and let
![]() $w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t})$
be such that
$w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t})$
be such that
for some constant
![]() $\gamma_t$
depending only on t. Then
$\gamma_t$
depending only on t. Then
 \begin{equation*}\Bigg\lvert\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}w(\underline{\sigma})P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)\Bigg\rvert \lt \lvert\eta\rvert\quad \text{for all $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\setminus\Pi_{\le t}$},\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\Bigg\lvert\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}w(\underline{\sigma})P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)\Bigg\rvert \lt \lvert\eta\rvert\quad \text{for all $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\setminus\Pi_{\le t}$},\end{equation*}
provided that n is sufficiently large compared to t.
In the proof of the lemma we use the usual scalar product on class functions of
![]() $G_n$
, which is given by
$G_n$
, which is given by
where
![]() $\chi,\psi$
are class functions of
$\chi,\psi$
are class functions of
![]() $G_n$
.
$G_n$
.
Proof of Lemma 5·2. By the definition (3·5) of
![]() $P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)$
and (3·3) we have
$P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)$
and (3·3) we have
Since
![]() $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
is irreducible, we have
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}$
is irreducible, we have
![]() $\langle\psi^{\underline{\lambda}},\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}\rangle=1$
or 2 and therefore we obtain, by an application of the Cauchy–Schwarz inequality,
$\langle\psi^{\underline{\lambda}},\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}\rangle=1$
or 2 and therefore we obtain, by an application of the Cauchy–Schwarz inequality,
 \begin{equation*}\big\lvert\big\langle\psi^{\underline{\lambda}},1_{D_{\underline{\sigma}}}\big\rangle\big\rvert\le \sqrt{2\,\big\langle1_{D_{\underline{\sigma}}},1_{D_{\underline{\sigma}}}\big\rangle}=\sqrt\frac{2\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert}{\lvert G_n\rvert}.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\big\lvert\big\langle\psi^{\underline{\lambda}},1_{D_{\underline{\sigma}}}\big\rangle\big\rvert\le \sqrt{2\,\big\langle1_{D_{\underline{\sigma}}},1_{D_{\underline{\sigma}}}\big\rangle}=\sqrt\frac{2\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert}{\lvert G_n\rvert}.\end{equation*}
From (5·8) and our hypothesis on w we then find that
 \begin{align*}\Bigg\lvert\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}w(\underline{\sigma})P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)\Bigg\rvert&\le \sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}\lvert w(\underline{\sigma})\rvert\,\lvert P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)\rvert\\[4pt]&\le\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}\frac{\gamma_t}{\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert}\,\frac{\lvert G_n\rvert}{\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)}\sqrt{\frac{2\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert}{\lvert G_n\rvert}}\\[4pt]&\le\frac{\gamma_t\,\lvert\Sigma_{\le t}\rvert}{\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)}\max_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}\sqrt{\frac{2\lvert G_n\rvert}{\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert}}\\[4pt]&\le\frac{\gamma_t\,\lvert\Sigma_{\le t}\rvert}{\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)}\max_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\le t}}\sqrt{\frac{2\lvert G_n\rvert}{\lvert C_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert}}.\end{align*}
\begin{align*}\Bigg\lvert\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}w(\underline{\sigma})P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)\Bigg\rvert&\le \sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}\lvert w(\underline{\sigma})\rvert\,\lvert P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)\rvert\\[4pt]&\le\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}\frac{\gamma_t}{\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert}\,\frac{\lvert G_n\rvert}{\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)}\sqrt{\frac{2\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert}{\lvert G_n\rvert}}\\[4pt]&\le\frac{\gamma_t\,\lvert\Sigma_{\le t}\rvert}{\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)}\max_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}\sqrt{\frac{2\lvert G_n\rvert}{\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert}}\\[4pt]&\le\frac{\gamma_t\,\lvert\Sigma_{\le t}\rvert}{\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)}\max_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\le t}}\sqrt{\frac{2\lvert G_n\rvert}{\lvert C_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert}}.\end{align*}
Note that
![]() $\lvert\Sigma_{\le t}\rvert$
is independent of n. Using Lemmas 7·1 and 7·2, to be stated and proved in Section 7, we find that there is a constant
$\lvert\Sigma_{\le t}\rvert$
is independent of n. Using Lemmas 7·1 and 7·2, to be stated and proved in Section 7, we find that there is a constant
![]() $\gamma^{\prime}_t$
, depending only on t, such that
$\gamma^{\prime}_t$
, depending only on t, such that
 \begin{equation*}\Bigg\lvert\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}w(\underline{\sigma})P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)\Bigg\rvert\le \frac{\gamma^{\prime}_t}{q^{n/2}}\,\frac{1}{q^{nt}}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\Bigg\lvert\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}}w(\underline{\sigma})P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)\Bigg\rvert\le \frac{\gamma^{\prime}_t}{q^{n/2}}\,\frac{1}{q^{nt}}\end{equation*}
for all
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\setminus\Pi_{\le t}$
and all sufficiently large n. The right-hand side is certainly strictly smaller than
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\setminus\Pi_{\le t}$
and all sufficiently large n. The right-hand side is certainly strictly smaller than
![]() $1/q^{nt}$
for all sufficiently large n and the proof is completed by noting that
$1/q^{nt}$
for all sufficiently large n and the proof is completed by noting that
![]() $\lvert\eta\rvert>1/q^{nt}$
.
$\lvert\eta\rvert>1/q^{nt}$
.
Recall that
![]() $V_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is the column span of
$V_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is the column span of
![]() $E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
. Define
$E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
. Define
 \begin{equation*}U_t=\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\\\underline{\lambda}(1)_1\ge n-t}} V_{\underline{\lambda}}.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}U_t=\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\\\underline{\lambda}(1)_1\ge n-t}} V_{\underline{\lambda}}.\end{equation*}
Now we obtain the following.
Theorem 5·3. Let t be a positive integer. Then, for all sufficiently large n, the following holds:
-
(i) every t-intersecting set Y in
 $ G_n$
satisfiesand, in case of equality, we have
$ G_n$
satisfiesand, in case of equality, we have \begin{equation*}\lvert Y\rvert\le \prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\lvert Y\rvert\le \prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\end{equation*}
 $1_Y\in U_t$
;
$1_Y\in U_t$
;
-
(ii) every pair of t-cross-intersecting sets Y, Z in
 $ G_n$
satisfiesand, in case of equality, we have
$ G_n$
satisfiesand, in case of equality, we have \[\sqrt{\lvert Y\rvert\cdot\lvert Z\rvert}\le \prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\]
\[\sqrt{\lvert Y\rvert\cdot\lvert Z\rvert}\le \prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\]
 $1_Y,1_Z\in U_t$
.
$1_Y,1_Z\in U_t$
.
Proof. As explained at the end of Section 3, we apply Proposition 3·1 to the graph with adjacency matrix
 \begin{equation*}\sum_{\substack{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}\\\underline{\sigma}(1)\ne (1^t)}}A_{\underline{\sigma}}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\sum_{\substack{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}\\\underline{\sigma}(1)\ne (1^t)}}A_{\underline{\sigma}}\end{equation*}
and the
![]() $\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert$
-regular spanning subgraphs with adjacency matrix
$\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert$
-regular spanning subgraphs with adjacency matrix
![]() $A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
for those
$A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
for those
![]() $\underline{\sigma}$
occuring in the above set union. Since none of the elements in
$\underline{\sigma}$
occuring in the above set union. Since none of the elements in
![]() $D_{\underline{\sigma}}$
for such
$D_{\underline{\sigma}}$
for such
![]() $\underline{\sigma}$
fix a t-space pointwise, every t-intersecting set in
$\underline{\sigma}$
fix a t-space pointwise, every t-intersecting set in
![]() $G_n$
is an independent set in this graph. Recall from Lemma 3·3 that every element of
$G_n$
is an independent set in this graph. Recall from Lemma 3·3 that every element of
![]() $V_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is an eigenvector of
$V_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is an eigenvector of
![]() $A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
with eigenvalue
$A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
with eigenvalue
![]() $P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)$
. Let
$P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)$
. Let
![]() $w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t})$
be the vector given by Proposition 5·1 and write
$w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t})$
be the vector given by Proposition 5·1 and write
 \begin{equation*}P(\underline{\lambda})=\sum_{\substack{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}\\\underline{\sigma}(1)\ne (1^t)}}w(\underline{\sigma})P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right).\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}P(\underline{\lambda})=\sum_{\substack{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t}\\\underline{\sigma}(1)\ne (1^t)}}w(\underline{\sigma})P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right).\end{equation*}
Proposition 5·1 and Lemma 5·2 imply that, for all sufficiently large n, we have
 \begin{equation*}P(\underline{\lambda})=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}(1)_1=n$}\\\eta & \text{for $n-t\leq \underline{\lambda}(1)_1<n$}\\\end{cases}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}P(\underline{\lambda})=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}(1)_1=n$}\\\eta & \text{for $n-t\leq \underline{\lambda}(1)_1<n$}\\\end{cases}\end{equation*}
and
![]() $\lvert P(\underline{\lambda})\rvert<\lvert\eta\rvert$
for
$\lvert P(\underline{\lambda})\rvert<\lvert\eta\rvert$
for
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(1)_1<n-t$
. Hence, writing
$\underline{\lambda}(1)_1<n-t$
. Hence, writing
![]() $\underline{\lambda}_0$
for
$\underline{\lambda}_0$
for
![]() $X-1\mapsto (n)$
, we have
$X-1\mapsto (n)$
, we have
![]() $P(\underline{\lambda}_0)=1$
and
$P(\underline{\lambda}_0)=1$
and
Then the required result follows from Proposition 3·1 and the decomposition of
![]() $\mathbb{R}(G_n)$
given in Lemma 3·3.
$\mathbb{R}(G_n)$
given in Lemma 3·3.
Our proof of Theorems 1·1 and 1·2 is completed by the following result.
Theorem 5·4.
![]() $U_t$
is spanned by the characteristic vectors of t-cosets.
$U_t$
is spanned by the characteristic vectors of t-cosets.
Proof. Let
![]() $\mathcal{A}_t$
be the set of t-tuples of linearly independent elements of
$\mathcal{A}_t$
be the set of t-tuples of linearly independent elements of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. Define the incidence matrix
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. Define the incidence matrix
![]() $M_t\in\mathbb{C}( G_n,\mathcal{A}_t\times\mathcal{A}_t)$
of elements of
$M_t\in\mathbb{C}( G_n,\mathcal{A}_t\times\mathcal{A}_t)$
of elements of
![]() $ G_n$
versus t-cosets by
$ G_n$
versus t-cosets by
 \begin{equation*}M_t(x,(u,v))=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $xu=v$}\\0 & \text{otherwise},\end{cases}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}M_t(x,(u,v))=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $xu=v$}\\0 & \text{otherwise},\end{cases}\end{equation*}
so that the columns of
![]() $M_t$
are precisely the characteristic vectors of the t-cosets. Let
$M_t$
are precisely the characteristic vectors of the t-cosets. Let
![]() $\zeta^t=\zeta^{(t,0)}$
be the permutation character of the set of t-tuples of linearly independent elements of
$\zeta^t=\zeta^{(t,0)}$
be the permutation character of the set of t-tuples of linearly independent elements of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
and define
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
and define
![]() $C_t\in\mathbb{C}( G_n, G_n)$
by
$C_t\in\mathbb{C}( G_n, G_n)$
by
Denoting by
![]() $\unicode{x1D7D9}_{xu=v}$
the indicator of the event that
$\unicode{x1D7D9}_{xu=v}$
the indicator of the event that
![]() $x\in G_n$
maps u to v, we have
$x\in G_n$
maps u to v, we have
 \begin{align*}\left(M_tM_t^T\right)(x,y)&=\sum_{u,v}M_t(x,(u,v))M_t(y,(u,v))\\&=\sum_{u,v}\unicode{x1D7D9}_{xu=v}\unicode{x1D7D9}_{yu=v}\\&=\sum_{u}\unicode{x1D7D9}_{xu=yu}\\&=\sum_{u}\unicode{x1D7D9}_{x^{-1}yu=u}\\&=\zeta^t\left(x^{-1}y\right)=C_t(x,y).\end{align*}
\begin{align*}\left(M_tM_t^T\right)(x,y)&=\sum_{u,v}M_t(x,(u,v))M_t(y,(u,v))\\&=\sum_{u,v}\unicode{x1D7D9}_{xu=v}\unicode{x1D7D9}_{yu=v}\\&=\sum_{u}\unicode{x1D7D9}_{xu=yu}\\&=\sum_{u}\unicode{x1D7D9}_{x^{-1}yu=u}\\&=\zeta^t\left(x^{-1}y\right)=C_t(x,y).\end{align*}
Hence we have
![]() $C_t=M_tM_t^T$
and so the column span of
$C_t=M_tM_t^T$
and so the column span of
![]() $C_t$
equals the column span of
$C_t$
equals the column span of
![]() $M_t$
or equivalently the span of the characteristic vectors of the t-cosets.
$M_t$
or equivalently the span of the characteristic vectors of the t-cosets.
From Lemma 2·5 we have
 \begin{equation*}\zeta^t=\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n\\\underline{\lambda}(1)_1\ge n-t}} m_{\underline{\lambda}}\,\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\zeta^t=\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n\\\underline{\lambda}(1)_1\ge n-t}} m_{\underline{\lambda}}\,\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}\end{equation*}
for some integers
![]() $m_{\underline{\lambda}}$
satisfying
$m_{\underline{\lambda}}$
satisfying
![]() $m_{\underline{\lambda}}\ne 0$
for each
$m_{\underline{\lambda}}\ne 0$
for each
![]() $\underline{\lambda}$
occuring in the summation. Since
$\underline{\lambda}$
occuring in the summation. Since
![]() $\zeta^t$
is real-valued, we find by Lemma 3·2 that
$\zeta^t$
is real-valued, we find by Lemma 3·2 that
![]() $m_{\underline{\lambda}^*}=m_{\underline{\lambda}}$
and therefore have
$m_{\underline{\lambda}^*}=m_{\underline{\lambda}}$
and therefore have
 \begin{equation}\zeta^t=\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\\\underline{\lambda}(1)_1\ge n-t}} m_{\underline{\lambda}}\,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}. \end{equation}
\begin{equation}\zeta^t=\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\\\underline{\lambda}(1)_1\ge n-t}} m_{\underline{\lambda}}\,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}. \end{equation}
Lemma 2·2 implies that
![]() $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)=\chi^{\underline{\lambda}^*}(1)$
. We therefore obtain from (3·4) and (3·1) that
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)=\chi^{\underline{\lambda}^*}(1)$
. We therefore obtain from (3·4) and (3·1) that
and thus find from (5·9) that
 \begin{equation}C_t=\lvert G_n\rvert\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n\\\underline{\lambda}(1)_1\ge n-t}}\frac{m_{\underline{\lambda}}}{\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)}\,E_{\underline{\lambda}}. \end{equation}
\begin{equation}C_t=\lvert G_n\rvert\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n\\\underline{\lambda}(1)_1\ge n-t}}\frac{m_{\underline{\lambda}}}{\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)}\,E_{\underline{\lambda}}. \end{equation}
Hence the column span of
![]() $C_t$
is contained in
$C_t$
is contained in
![]() $U_t$
. Conversely, let v be a column of
$U_t$
. Conversely, let v be a column of
![]() $E_{\underline{\kappa}}$
for some
$E_{\underline{\kappa}}$
for some
![]() $\underline{\kappa}\in\Omega_n$
satisfying
$\underline{\kappa}\in\Omega_n$
satisfying
![]() $\underline{\kappa}(1)_1\ge n-t$
. Since
$\underline{\kappa}(1)_1\ge n-t$
. Since
![]() $E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is idempotent, we have
$E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is idempotent, we have
![]() $E_{\underline{\lambda}}v=v$
for
$E_{\underline{\lambda}}v=v$
for
![]() $\underline{\kappa}=\underline{\lambda}$
and Lemma 3·3 implies
$\underline{\kappa}=\underline{\lambda}$
and Lemma 3·3 implies
![]() $E_{\underline{\lambda}}v=0$
for
$E_{\underline{\lambda}}v=0$
for
![]() $\underline{\kappa}\ne \underline{\lambda}$
. Hence from (5·10) we find that
$\underline{\kappa}\ne \underline{\lambda}$
. Hence from (5·10) we find that
and, since
![]() $m_{\underline{\kappa}}\ne 0$
, we conclude that v is in the column span of
$m_{\underline{\kappa}}\ne 0$
, we conclude that v is in the column span of
![]() $C_t$
. This completes the proof.
$C_t$
. This completes the proof.
6. Proof of Theorems 1·5 and 1·6
Our proofs of Theorems 1·5 and 1·6 follow along similar lines as those in the previous section and therefore our proofs will be less detailed.
Since the parabolic subgroup
![]() $P_{(t,n-t)}$
is the stabiliser of a t-space of
$P_{(t,n-t)}$
is the stabiliser of a t-space of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
, the character
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
, the character
![]() $\xi^{X-1\mapsto (n-t,t)}$
is the permutation character of the set of t-spaces of
$\xi^{X-1\mapsto (n-t,t)}$
is the permutation character of the set of t-spaces of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. From (2·7) we obtain its decomposition
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. From (2·7) we obtain its decomposition
 \begin{equation}\xi^{X-1\mapsto (n-t,t)}=\sum_{s=0}^t\chi^{X-1\mapsto (n-s,s)}. \end{equation}
\begin{equation}\xi^{X-1\mapsto (n-t,t)}=\sum_{s=0}^t\chi^{X-1\mapsto (n-s,s)}. \end{equation}
Let
![]() $\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{k}}_q$
denote the q-binomial coefficient, which counts the number of k-spaces of
$\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{k}}_q$
denote the q-binomial coefficient, which counts the number of k-spaces of
![]() $\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. Then we have
$\mathbb{F}_q^n$
. Then we have
and so (6·1) implies that
Also note that
![]() $\psi^{X-1\mapsto \lambda}=\chi^{X-1\mapsto \lambda}$
for all partitions
$\psi^{X-1\mapsto \lambda}=\chi^{X-1\mapsto \lambda}$
for all partitions
![]() $\lambda$
. Throughout this section, we define
$\lambda$
. Throughout this section, we define
which will be our prescribed extremal eigenvalue.
We begin with the following counterpart of Proposition 5·1.
Proposition 6·1. Let n and t be positive integers satisfying
![]() $n>2t$
. Then there exists
$n>2t$
. Then there exists
![]() $w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t-1})$
such that
$w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t-1})$
such that
 \begin{equation}\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n \cap \Sigma_{\le t-1}} w(\underline{\sigma}) P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n)$},\\\varepsilon & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n-s,s)$ with $1\leq s\leq t$},\\0 & \text{for $\underline{\lambda} \in \Omega_n \cap \Pi_{\le t-1}$, where}\\&\quad \, \underline{\lambda}(1)\ne (n-s,s) \text{with} \, 0 \, \leq s\leq t-1\end{cases} \end{equation}
\begin{equation}\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n \cap \Sigma_{\le t-1}} w(\underline{\sigma}) P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n)$},\\\varepsilon & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n-s,s)$ with $1\leq s\leq t$},\\0 & \text{for $\underline{\lambda} \in \Omega_n \cap \Pi_{\le t-1}$, where}\\&\quad \, \underline{\lambda}(1)\ne (n-s,s) \text{with} \, 0 \, \leq s\leq t-1\end{cases} \end{equation}
and
for some constant
![]() $\gamma_t$
depending only on t.
$\gamma_t$
depending only on t.
Proof. From Lemma 4·2 we know that
![]() $Q_{t-1}$
has full rank. In view of (3·5) there exists a unique
$Q_{t-1}$
has full rank. In view of (3·5) there exists a unique
![]() $w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t-1})$
satisfying (6·4) except for
$w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t-1})$
satisfying (6·4) except for
![]() $\underline{\lambda}$
of the form
$\underline{\lambda}$
of the form
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n-t,t)$
.
$\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n-t,t)$
.
Next we show that (6·4) also holds when
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n-t,t)$
. By Lemma 4·6 we have
$\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n-t,t)$
. By Lemma 4·6 we have
![]() $\xi^{X-1\mapsto (n-t,t)}_{\underline{\sigma}}=0$
for each
$\xi^{X-1\mapsto (n-t,t)}_{\underline{\sigma}}=0$
for each
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\le t-1}$
. Hence we have
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\le t-1}$
. Hence we have
 \begin{align}0&=\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n \cap \Sigma_{\le t-1}} w(\underline{\sigma}) \lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert\xi^{X-1\mapsto (n-t,t)}_{\underline{\sigma}} \nonumber\\&=\sum_{s=0}^t\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n \cap \Sigma_{\le t-1}} w(\underline{\sigma}) \lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert\chi^{X-1\mapsto (n-s,s)}_{\underline{\sigma}}, \end{align}
\begin{align}0&=\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n \cap \Sigma_{\le t-1}} w(\underline{\sigma}) \lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert\xi^{X-1\mapsto (n-t,t)}_{\underline{\sigma}} \nonumber\\&=\sum_{s=0}^t\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n \cap \Sigma_{\le t-1}} w(\underline{\sigma}) \lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert\chi^{X-1\mapsto (n-s,s)}_{\underline{\sigma}}, \end{align}
using (6·1). Since (6·4) holds with the only exception
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n-t,t)$
, the inner sum equals 1 for
$\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n-t,t)$
, the inner sum equals 1 for
![]() $s=0$
and
$s=0$
and
![]() $\varepsilon\,\chi^{X-1\mapsto (n-s,s)}(1)$
for each s satisfying
$\varepsilon\,\chi^{X-1\mapsto (n-s,s)}(1)$
for each s satisfying
![]() $1\leq s\leq t-1$
. Assuming that this is true also for
$1\leq s\leq t-1$
. Assuming that this is true also for
![]() $s=t$
and using (6·3), the right-hand side of (6·6) is indeed
$s=t$
and using (6·3), the right-hand side of (6·6) is indeed
 \begin{equation*}1+\varepsilon\,\sum_{s=1}^t\bigg(\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{s}}_q-\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{s-1}}_q\bigg)=1+\varepsilon\,\bigg(\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{t}}_q-1\bigg)=0.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}1+\varepsilon\,\sum_{s=1}^t\bigg(\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{s}}_q-\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{s-1}}_q\bigg)=1+\varepsilon\,\bigg(\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{t}}_q-1\bigg)=0.\end{equation*}
Hence (6·4) also holds when
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n-t,t)$
.
$\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n-t,t)$
.
It remains to prove (6·5). For each s satisfying
![]() $1\leq s\leq t$
, we find from (6·1) that
$1\leq s\leq t$
, we find from (6·1) that
using (6·2). Since
![]() $\chi^{X-1\mapsto (n)}(1)=1$
, we conclude from (6·4) that
$\chi^{X-1\mapsto (n)}(1)=1$
, we conclude from (6·4) that
 \begin{equation*}\Bigg\lvert\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t-1}}w(\underline{\sigma})\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert\,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}}\Bigg\rvert\le 1 \quad \text{for each $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{\le t-1}$}.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\Bigg\lvert\sum_{\underline{\sigma}\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t-1}}w(\underline{\sigma})\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert\,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}_{\underline{\sigma}}\Bigg\rvert\le 1 \quad \text{for each $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{\le t-1}$}.\end{equation*}
By Lemma 4·2 all entries of
![]() $Q_{t-1}$
are independent of n and so are uniformly bounded by some value only depending on t. The same also holds for the inverse of
$Q_{t-1}$
are independent of n and so are uniformly bounded by some value only depending on t. The same also holds for the inverse of
![]() $Q_t$
, which establishes (6·5).
$Q_t$
, which establishes (6·5).
The bound (6·5) and Lemma 5·2 ensure that the right-hand side of (6·4) is small in modulus for each
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\setminus\Pi_t$
. It therefore remains to deal with the case that
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\setminus\Pi_t$
. It therefore remains to deal with the case that
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\cap\Pi_t$
except for
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\cap\Pi_t$
except for
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
given by
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n$
given by
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n-t,t)$
, which is the subject of the following lemma.
$\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n-t,t)$
, which is the subject of the following lemma.
Lemma 6·2. Let
![]() $w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t-1})$
be given in Proposition 6·1 (so that
$w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t-1})$
be given in Proposition 6·1 (so that
![]() $n>2t$
). Then, for all
$n>2t$
). Then, for all
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in \Omega_n\cap \Pi_t$
with
$\underline{\lambda}\in \Omega_n\cap \Pi_t$
with
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(1)\ne (n-t,t)$
, we have
$\underline{\lambda}(1)\ne (n-t,t)$
, we have
 \begin{align*}\bigg\lvert\sum_{\underline{\sigma} \in \Omega_n \cap \Sigma_{\le t-1}} w(\underline{\sigma}) P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)\bigg\rvert<\lvert\varepsilon\rvert,\end{align*}
\begin{align*}\bigg\lvert\sum_{\underline{\sigma} \in \Omega_n \cap \Sigma_{\le t-1}} w(\underline{\sigma}) P\!\left(\underline{\lambda},\underline{\sigma}\right)\bigg\rvert<\lvert\varepsilon\rvert,\end{align*}
provided that n is sufficiently large compared to t.
Proof. By slight abuse of notation, we view w as an element of
![]() $\mathbb{R}(G_n)$
by setting
$\mathbb{R}(G_n)$
by setting
![]() $w(x)=0$
if
$w(x)=0$
if
![]() $x\not\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t-1}$
and
$x\not\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t-1}$
and
![]() $w(x)=w(\underline{\sigma})$
if
$w(x)=w(\underline{\sigma})$
if
![]() $x\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t-1}$
and
$x\in\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t-1}$
and
![]() $x\in D_{\underline{\sigma}}$
. Recalling the scalar product on class functions of
$x\in D_{\underline{\sigma}}$
. Recalling the scalar product on class functions of
![]() $G_n$
from (5·7), the statement of the lemma is equivalent to
$G_n$
from (5·7), the statement of the lemma is equivalent to
for all
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in \Omega_n\cap \Pi_t$
with
$\underline{\lambda}\in \Omega_n\cap \Pi_t$
with
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(1)\ne (n-t,t)$
, provided that n is sufficiently large compared to t.
$\underline{\lambda}(1)\ne (n-t,t)$
, provided that n is sufficiently large compared to t.
Pick
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\cap \Pi_t$
such that
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\cap \Pi_t$
such that
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(1)\ne(n-t,t)$
. Then
$\underline{\lambda}(1)\ne(n-t,t)$
. Then
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)_1=n-t$
for some i. First assume that
$\underline{\lambda}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)_1=n-t$
for some i. First assume that
![]() $\lvert\underline{\lambda}(1)\rvert\ne n$
. Denoting by
$\lvert\underline{\lambda}(1)\rvert\ne n$
. Denoting by
![]() $\text{Re}\ x$
the real part of a complex number x, we find from Lemma 3·2 and (2·13) that
$\text{Re}\ x$
the real part of a complex number x, we find from Lemma 3·2 and (2·13) that
 \begin{equation*}\frac{1}{2}\big\lvert\big\langle w,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}\big\rangle\big\rvert\le \lvert\text{Re}\;\langle w,\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}\rangle\rvert=\bigg\lvert\sum_{\underline{\mu}\sim\underline{\lambda}}H_{\underline{\mu}\underline{\lambda}}\,\text{Re}\;\big\langle w,\xi^{\underline{\mu}}\big\rangle\bigg\rvert.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\frac{1}{2}\big\lvert\big\langle w,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}\big\rangle\big\rvert\le \lvert\text{Re}\;\langle w,\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}\rangle\rvert=\bigg\lvert\sum_{\underline{\mu}\sim\underline{\lambda}}H_{\underline{\mu}\underline{\lambda}}\,\text{Re}\;\big\langle w,\xi^{\underline{\mu}}\big\rangle\bigg\rvert.\end{equation*}
Lemma 4·6 implies that
![]() $\xi^{\underline{\mu}}_{\underline{\sigma}}=0$
for each
$\xi^{\underline{\mu}}_{\underline{\sigma}}=0$
for each
![]() $\underline{\mu}\not\in\Pi_{\le t-1}$
and each
$\underline{\mu}\not\in\Pi_{\le t-1}$
and each
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\le t-1}$
. For
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\le t-1}$
. For
![]() $\underline{\mu}\in\Lambda_n$
, we have
$\underline{\mu}\in\Lambda_n$
, we have
By (2·8), the summation can be taken over all
![]() $\underline{\kappa}$
such that
$\underline{\kappa}$
such that
![]() $\underline{\kappa}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)\unrhd\underline{\mu}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)$
. Hence if
$\underline{\kappa}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)\unrhd\underline{\mu}\!\left(\alpha^i\right)$
. Hence if
![]() $\mu\in\Pi_{\le t-1}$
, then
$\mu\in\Pi_{\le t-1}$
, then
![]() $\underline{\kappa}\in\Pi_{\le t-1}$
. By the assumed properties of w given in Proposition 6·1, we have
$\underline{\kappa}\in\Pi_{\le t-1}$
. By the assumed properties of w given in Proposition 6·1, we have
![]() $\langle w,\psi^{\underline{\kappa}}\rangle=0$
for each
$\langle w,\psi^{\underline{\kappa}}\rangle=0$
for each
![]() $\underline{\kappa}\in\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{\le t-1}$
satisfying
$\underline{\kappa}\in\Omega_n\cap\Pi_{\le t-1}$
satisfying
![]() $\lvert\underline{\kappa}(1)\rvert\ne n$
. Since
$\lvert\underline{\kappa}(1)\rvert\ne n$
. Since
![]() $\lvert\underline{\lambda}(1)\rvert\ne n$
we conclude that
$\lvert\underline{\lambda}(1)\rvert\ne n$
we conclude that
![]() $\langle w,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}\rangle=0$
.
$\langle w,\psi^{\underline{\lambda}}\rangle=0$
.
Now assume that
![]() $\lvert\underline{\lambda}(1)\rvert=n$
and write
$\lvert\underline{\lambda}(1)\rvert=n$
and write
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(1)=\lambda$
. From (2·9) and (2·10) we have
$\underline{\lambda}(1)=\lambda$
. From (2·9) and (2·10) we have
 \begin{equation*}\big\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto\lambda}\big\rangle=\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda\\\mu_1>n-t}}H_{\mu\lambda}\,\big\langle w,\xi^{X-1\mapsto\mu}\big\rangle,\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\big\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto\lambda}\big\rangle=\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda\\\mu_1>n-t}}H_{\mu\lambda}\,\big\langle w,\xi^{X-1\mapsto\mu}\big\rangle,\end{equation*}
since by Lemma 4·6 in the case
![]() $\mu_1=n-t$
we have
$\mu_1=n-t$
we have
![]() $\xi^{X-1\mapsto\mu}_{\underline{\sigma}}=0$
for each
$\xi^{X-1\mapsto\mu}_{\underline{\sigma}}=0$
for each
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\le t-1}$
. From (2·7) and (2·8) we then find that$
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\le t-1}$
. From (2·7) and (2·8) we then find that$
 \begin{align}\big\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto\lambda}\big\rangle&=\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda\\\mu_1>n-t}}H_{\mu\lambda}\,\sum_{\kappa\unrhd\mu}K_{\kappa\mu}\,\big\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto\kappa}\big\rangle\nonumber \\&=\frac{1}{\lvert G_n\rvert}\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda\\\mu_1>n-t}}H_{\mu\lambda}+\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda\\\mu_1>n-t}}H_{\mu\lambda}\sum_{(n)\rhd\kappa\unrhd\mu}K_{\kappa\mu}\,\big\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto\kappa}\big\rangle, \end{align}
\begin{align}\big\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto\lambda}\big\rangle&=\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda\\\mu_1>n-t}}H_{\mu\lambda}\,\sum_{\kappa\unrhd\mu}K_{\kappa\mu}\,\big\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto\kappa}\big\rangle\nonumber \\&=\frac{1}{\lvert G_n\rvert}\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda\\\mu_1>n-t}}H_{\mu\lambda}+\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda\\\mu_1>n-t}}H_{\mu\lambda}\sum_{(n)\rhd\kappa\unrhd\mu}K_{\kappa\mu}\,\big\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto\kappa}\big\rangle, \end{align}
using that
![]() $\lvert G_n\rvert\,\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto (n)}\rangle=1$
by the assumed properties of w given in Proposition 6·1 and
$\lvert G_n\rvert\,\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto (n)}\rangle=1$
by the assumed properties of w given in Proposition 6·1 and
![]() $K_{(n)\mu}=1$
for each partition
$K_{(n)\mu}=1$
for each partition
![]() $\mu$
of n. We first show that the first sum is zero. We have
$\mu$
of n. We first show that the first sum is zero. We have
 \begin{equation}\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda\\\mu_1>n-t}}H_{\mu\lambda}=\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda}}K_{(n)\mu}H_{\mu\lambda}-\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda}}K_{(n-t,t)\mu}H_{\mu\lambda}, \end{equation}
\begin{equation}\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda\\\mu_1>n-t}}H_{\mu\lambda}=\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda}}K_{(n)\mu}H_{\mu\lambda}-\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda}}K_{(n-t,t)\mu}H_{\mu\lambda}, \end{equation}
using that
![]() $\lambda_1=n-t$
and that, for each partition
$\lambda_1=n-t$
and that, for each partition
![]() $\mu$
of n, we have
$\mu$
of n, we have
 \begin{equation*}K_{(n-t,t)\mu}=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $\mu_1=n-t$}\\0 & \text{for $\mu_1>n-t$}.\end{cases}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}K_{(n-t,t)\mu}=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $\mu_1=n-t$}\\0 & \text{for $\mu_1>n-t$}.\end{cases}\end{equation*}
It is readily verified that
Since
![]() $\lambda$
is neither (n) nor
$\lambda$
is neither (n) nor
![]() $(n-t,t)$
, we conclude that (6·9) equals zero. Hence (6·8) becomes
$(n-t,t)$
, we conclude that (6·9) equals zero. Hence (6·8) becomes
 \begin{equation}\big\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto\lambda}\big\rangle=\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda\\\mu_1>n-t}}H_{\mu\lambda}\sum_{(n)\rhd\kappa\unrhd\mu}K_{\kappa\mu}\,\big\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto\kappa}\big\rangle .\end{equation}
\begin{equation}\big\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto\lambda}\big\rangle=\sum_{\substack{\mu\unrhd\lambda\\\mu_1>n-t}}H_{\mu\lambda}\sum_{(n)\rhd\kappa\unrhd\mu}K_{\kappa\mu}\,\big\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto\kappa}\big\rangle .\end{equation}
By the assumed properties of w given in Proposition 6·1, the inner summand is nonzero only when
![]() $\kappa=(n-s,s)$
for some s satisfying
$\kappa=(n-s,s)$
for some s satisfying
![]() $1\leq s\leq t-1$
. In particular, for
$1\leq s\leq t-1$
. In particular, for
![]() $\kappa$
of this form, Proposition 6·1 and (6·3) give
$\kappa$
of this form, Proposition 6·1 and (6·3) give
 \begin{equation*}\lvert G_n\rvert\,\big\lvert\big\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto \kappa}\big\rangle\big\rvert=\frac{\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{s}}_q-\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{s-1}}_q}{\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{t}}_q-1}\le \frac{\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{t-1}}_q}{\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{t}}_q}=\frac{q^t-1}{q^{n-t+1}-1}\le \frac{q^{2t-1}}{q^n}.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\lvert G_n\rvert\,\big\lvert\big\langle w,\psi^{X-1\mapsto \kappa}\big\rangle\big\rvert=\frac{\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{s}}_q-\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{s-1}}_q}{\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{t}}_q-1}\le \frac{\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{t-1}}_q}{\genfrac{[}{]}{0pt}{}{{n}}{{t}}_q}=\frac{q^t-1}{q^{n-t+1}-1}\le \frac{q^{2t-1}}{q^n}.\end{equation*}
By Lemma 4·4 the Kostka numbers
![]() $K_{\kappa\mu}$
occuring in (6·11) are independent of n and it is readily verified from (6·10) that the numbers
$K_{\kappa\mu}$
occuring in (6·11) are independent of n and it is readily verified from (6·10) that the numbers
![]() $H_{\mu\lambda}$
occuring in (6·11) are also independent of n. Moreover the number of summands in (6·11) is also independent of n. From Lemma 7·2, to be stated and proved in Section 7, we have
$H_{\mu\lambda}$
occuring in (6·11) are also independent of n. Moreover the number of summands in (6·11) is also independent of n. From Lemma 7·2, to be stated and proved in Section 7, we have
![]() $\psi^{X-1\mapsto\lambda}(1)\ge \delta_{t-1}\,q^{nt}$
for some constant
$\psi^{X-1\mapsto\lambda}(1)\ge \delta_{t-1}\,q^{nt}$
for some constant
![]() $\delta_{t-1}$
only depending on t. Hence there is a constant
$\delta_{t-1}$
only depending on t. Hence there is a constant
![]() $c_t$
, depending only on t, such that
$c_t$
, depending only on t, such that
Since
![]() $\lvert\varepsilon\rvert>1/q^{nt}$
, this shows that (6·7) holds provided that n is sufficiently large compared to t.
$\lvert\varepsilon\rvert>1/q^{nt}$
, this shows that (6·7) holds provided that n is sufficiently large compared to t.
Recall that
![]() $V_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is the column span of
$V_{\underline{\lambda}}$
is the column span of
![]() $E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
. Define
$E_{\underline{\lambda}}$
. Define
 \begin{equation*}W_t=\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\\\underline{\lambda}(1)\unrhd (n-t,t)}} V_{\underline{\lambda}}.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}W_t=\sum_{\substack{\underline{\lambda}\in\Omega_n\\\underline{\lambda}(1)\unrhd (n-t,t)}} V_{\underline{\lambda}}.\end{equation*}
Now we obtain the following.
Theorem 6·3. Let t be a positive integer. Then, for all sufficiently large n, the following holds:
(i) every t-space-intersecting set Y in
![]() $ G_n$
satisfies
$ G_n$
satisfies
 \begin{equation*}\lvert Y\rvert\le \Bigg[\prod_{i=0}^{t-1}\left(q^t-q^i\right)\Bigg]\Bigg[\prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\Bigg]\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\lvert Y\rvert\le \Bigg[\prod_{i=0}^{t-1}\left(q^t-q^i\right)\Bigg]\Bigg[\prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\Bigg]\end{equation*}
and, in case of equality, we have
![]() $1_Y\in W_t$
;
$1_Y\in W_t$
;
(ii) every pair of t-space-cross-intersecting sets Y, Z in
![]() $ G_n$
satisfies
$ G_n$
satisfies
 \begin{equation*}\sqrt{\lvert Y\rvert\cdot\lvert Z\rvert}\le \Bigg[\prod_{i=0}^{t-1}\left(q^t-q^i\right)\Bigg]\Bigg[\prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\Bigg]\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\sqrt{\lvert Y\rvert\cdot\lvert Z\rvert}\le \Bigg[\prod_{i=0}^{t-1}\left(q^t-q^i\right)\Bigg]\Bigg[\prod_{i=t}^{n-1}\left(q^n-q^i\right)\Bigg]\end{equation*}
and, in case of equality, we have
![]() $1_Y,1_Z\in W_t$
.
$1_Y,1_Z\in W_t$
.
Proof. We apply Proposition 3·1 to the graph with adjacency matrix
and the
![]() $\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert$
-regular spanning subgraphs with adjacency matrix
$\lvert D_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert$
-regular spanning subgraphs with adjacency matrix
![]() $A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
for those
$A_{\underline{\sigma}}$
for those
![]() $\underline{\sigma}$
occuring in the above set union. Every t-space-intersecting set in
$\underline{\sigma}$
occuring in the above set union. Every t-space-intersecting set in
![]() $G_n$
is an independent set in this graph. Let
$G_n$
is an independent set in this graph. Let
![]() $w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t-1})$
be given by Proposition 6·1 and write
$w\in\mathbb{R}(\Omega_n\cap\Sigma_{\le t-1})$
be given by Proposition 6·1 and write
Proposition 6·1 and Lemmas 5·2 and 6·2 imply that, for all sufficiently large n, we have
 \begin{equation*}P(\underline{\lambda})=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n)$}\\\varepsilon & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n-s,s)$ with $1\leq s\leq t$}\\\end{cases}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}P(\underline{\lambda})=\begin{cases}1 & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n)$}\\\varepsilon & \text{for $\underline{\lambda}(1)=(n-s,s)$ with $1\leq s\leq t$}\\\end{cases}\end{equation*}
and
![]() $\lvert P(\underline{\lambda})\rvert<\lvert\varepsilon\rvert$
for
$\lvert P(\underline{\lambda})\rvert<\lvert\varepsilon\rvert$
for
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(1)\ne (n-s,s)$
with some s satisfying
$\underline{\lambda}(1)\ne (n-s,s)$
with some s satisfying
![]() $0\leq s\leq t$
. Hence, writing
$0\leq s\leq t$
. Hence, writing
![]() $\underline{\lambda}_0$
for
$\underline{\lambda}_0$
for
![]() $X-1\mapsto (n)$
, we have
$X-1\mapsto (n)$
, we have
![]() $P(\underline{\lambda}_0)=1$
and
$P(\underline{\lambda}_0)=1$
and
Then the required result follows from Proposition 3·1 and the decomposition of
![]() $\mathbb{R}(G_n)$
given in Lemma 3·3.
$\mathbb{R}(G_n)$
given in Lemma 3·3.
Our proof of Theorems 1·5 and 1·6 is completed by the following result.
Theorem 6·4.
![]() $W_t$
is spanned by the characteristic vectors of cosets of stabilisers of t-spaces.
$W_t$
is spanned by the characteristic vectors of cosets of stabilisers of t-spaces.
Proof. The proof is almost identical to that of Theorem 5·4 with
![]() $\mathcal{A}_t$
replaced by the set of t-spaces and
$\mathcal{A}_t$
replaced by the set of t-spaces and
![]() $\zeta^t$
replaced by the permutation character
$\zeta^t$
replaced by the permutation character
![]() $\xi^{X-1\mapsto(n-t,t)}$
of t-spaces and the decomposition of
$\xi^{X-1\mapsto(n-t,t)}$
of t-spaces and the decomposition of
![]() $\zeta^t$
replaced by the decomposition given in (6·1).
$\zeta^t$
replaced by the decomposition given in (6·1).
7. Estimates on conjugacy class sizes and character degrees
In this section we provide bounds on the size of certain conjugacy classes and degrees of certain irreducible characters of
![]() $ G_n$
, which are used in the proof of Lemma 5·2.
$ G_n$
, which are used in the proof of Lemma 5·2.
Lemma 7·1. Let n and t be positive integers satisfying
![]() $n>2t$
and let
$n>2t$
and let
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\le t}$
. Then we have
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\le t}$
. Then we have
Proof. From Lemma 2·1 we find that (with the same notation as in Lemma 2·1)
 \begin{equation}\frac{\lvert G_n\rvert}{\lvert C_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert}\le\prod_{f\in\Phi} \prod_{i=1}^{\lvert\underline{\sigma}(f)\rvert} q^{\lvert f\rvert\, s_i\left(\underline{\sigma}(f)^{\prime}\right)\,m_i(\underline{\sigma}(f))}. \end{equation}
\begin{equation}\frac{\lvert G_n\rvert}{\lvert C_{\underline{\sigma}}\rvert}\le\prod_{f\in\Phi} \prod_{i=1}^{\lvert\underline{\sigma}(f)\rvert} q^{\lvert f\rvert\, s_i\left(\underline{\sigma}(f)^{\prime}\right)\,m_i(\underline{\sigma}(f))}. \end{equation}
Since
![]() $\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\le t}$
and
$\underline{\sigma}\in\Sigma_{\le t}$
and
![]() $t<n/2$
, there is exactly one polynomial
$t<n/2$
, there is exactly one polynomial
![]() $h\in\Phi$
of degree at least
$h\in\Phi$
of degree at least
![]() $n-t$
in the support of
$n-t$
in the support of
![]() $\underline{\sigma}$
. This polynomial must satisfy
$\underline{\sigma}$
. This polynomial must satisfy
![]() $\underline{\sigma}(h)=(1)$
and the corresponding factor in (7·1) is at most
$\underline{\sigma}(h)=(1)$
and the corresponding factor in (7·1) is at most
![]() $q^n$
. There are at most t other polynomials in the support of
$q^n$
. There are at most t other polynomials in the support of
![]() $\underline{\sigma}$
. Each such polynomial f has degree at most t and satisfies
$\underline{\sigma}$
. Each such polynomial f has degree at most t and satisfies
![]() $\lvert\underline{\sigma}(f)\rvert\le t$
and hence the corresponding factor in (7·1) has a crude upper bound of
$\lvert\underline{\sigma}(f)\rvert\le t$
and hence the corresponding factor in (7·1) has a crude upper bound of
![]() $q^{t^4}$
. As there are at most t such factors, the proof is completed.
$q^{t^4}$
. As there are at most t such factors, the proof is completed.
Lemma 7·2. Let t be a positive integer. Then there is a constant
![]() $\delta_t$
such that, for all sufficiently large n and for all
$\delta_t$
such that, for all sufficiently large n and for all
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n\setminus \Pi_{\le t}$
, we have
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n\setminus \Pi_{\le t}$
, we have
Proof. Let
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n\setminus \Pi_{\le t}$
. Using elementary calculus we find that
$\underline{\lambda}\in\Lambda_n\setminus \Pi_{\le t}$
. Using elementary calculus we find that
and therefore
 \begin{equation*}\frac{\prod_{i=1}^n(q^i-1)}{q^{\frac{1}{2}n(n+1)}}=\prod_{i=1}^n\bigg(1-\frac{1}{q^i}\bigg)\ge \prod_{i=1}^n\bigg(1-\frac{1}{2^i}\bigg)\ge \prod_{i=1}^n4^{-1/2^i}\ge\prod_{i=1}^\infty4^{-1/2^i}=\frac{1}{4}.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\frac{\prod_{i=1}^n(q^i-1)}{q^{\frac{1}{2}n(n+1)}}=\prod_{i=1}^n\bigg(1-\frac{1}{q^i}\bigg)\ge \prod_{i=1}^n\bigg(1-\frac{1}{2^i}\bigg)\ge \prod_{i=1}^n4^{-1/2^i}\ge\prod_{i=1}^\infty4^{-1/2^i}=\frac{1}{4}.\end{equation*}
Substitute into (2·14) of Lemma 2·2 to give
where
 \begin{align*}N(\underline{\lambda})&=\sum_{f\in\Phi}\lvert f\rvert\sum_{(i, j)\in\underline{\lambda}(f)}h_{i, j}(\underline{\lambda}(f)),\\M(\underline{\lambda})&=\sum_{f\in\Phi}\lvert f\rvert\,b(\underline{\lambda}(f))\end{align*}
\begin{align*}N(\underline{\lambda})&=\sum_{f\in\Phi}\lvert f\rvert\sum_{(i, j)\in\underline{\lambda}(f)}h_{i, j}(\underline{\lambda}(f)),\\M(\underline{\lambda})&=\sum_{f\in\Phi}\lvert f\rvert\,b(\underline{\lambda}(f))\end{align*}
and b and
![]() $h_{i, j}$
are as in Lemma 2·2. Note that for each partition
$h_{i, j}$
are as in Lemma 2·2. Note that for each partition
![]() $\lambda$
, we have
$\lambda$
, we have
 \begin{equation}\sum_{(i, j)\in\lambda}h_{i, j}(\lambda)\le \sum_{k=1}^{\lvert\lambda\rvert}k=\frac{1}{2}\lvert\lambda\rvert(\lvert\lambda\rvert+1). \end{equation}
\begin{equation}\sum_{(i, j)\in\lambda}h_{i, j}(\lambda)\le \sum_{k=1}^{\lvert\lambda\rvert}k=\frac{1}{2}\lvert\lambda\rvert(\lvert\lambda\rvert+1). \end{equation}
First assume that there exists a polynomial
![]() $h\in\Phi$
such that
$h\in\Phi$
such that
![]() $\lvert h\rvert=1$
and
$\lvert h\rvert=1$
and
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(h)^{\prime}_1\ge n-t$
. In this case we have
$\underline{\lambda}(h)^{\prime}_1\ge n-t$
. In this case we have
 \begin{equation*}M(\underline{\lambda})\ge b(\underline{\lambda}(h))\ge \sum_{k=1}^{n-t-1}k=\frac{1}{2}(n-t)(n-t-1)\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}M(\underline{\lambda})\ge b(\underline{\lambda}(h))\ge \sum_{k=1}^{n-t-1}k=\frac{1}{2}(n-t)(n-t-1)\end{equation*}
and by (7·3)
 \begin{align*}N(\underline{\lambda})&\le \frac{1}{2}\sum_{f\in\Phi}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert(\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert+1)\\&\le \frac{n+1}{2}\sum_{f\in\Phi}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert\\&=\frac{n(n+1)}{2}.\end{align*}
\begin{align*}N(\underline{\lambda})&\le \frac{1}{2}\sum_{f\in\Phi}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert(\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert+1)\\&\le \frac{n+1}{2}\sum_{f\in\Phi}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert\\&=\frac{n(n+1)}{2}.\end{align*}
Therefore (7·2) implies that
so that we have
![]() $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)\ge q^{n(t+1)}$
for all sufficiently large n by very crude estimates.
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)\ge q^{n(t+1)}$
for all sufficiently large n by very crude estimates.
Hence we can assume that
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(f)^{\prime}_1\leq n-t-1$
and
$\underline{\lambda}(f)^{\prime}_1\leq n-t-1$
and
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(f)_1\leq n-t-1$
for all
$\underline{\lambda}(f)_1\leq n-t-1$
for all
![]() $f\in\Phi$
satisfying
$f\in\Phi$
satisfying
![]() $\lvert f\rvert=1$
. Note that the second assumption is implied by the hypothesis
$\lvert f\rvert=1$
. Note that the second assumption is implied by the hypothesis
![]() $\underline{\lambda}\not\in\Pi_{\le t}$
. In what follows we use the trivial bound
$\underline{\lambda}\not\in\Pi_{\le t}$
. In what follows we use the trivial bound
![]() $M(\underline{\lambda})\ge 0$
. We distinguish two cases.
$M(\underline{\lambda})\ge 0$
. We distinguish two cases.
In the first case we assume that
![]() $\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert\le n-t-1$
for all
$\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert\le n-t-1$
for all
![]() $f\in\Phi$
satisfying
$f\in\Phi$
satisfying
![]() $\lvert f\rvert=1$
. Let
$\lvert f\rvert=1$
. Let
![]() $\ell$
be the maximum of
$\ell$
be the maximum of
![]() $\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert$
over all
$\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert$
over all
![]() $f\in\Phi$
satisfying
$f\in\Phi$
satisfying
![]() $\lvert f\rvert=1$
, hence
$\lvert f\rvert=1$
, hence
![]() $\ell\leq n-t-1$
. By (7·3) we have
$\ell\leq n-t-1$
. By (7·3) we have
 \begin{align*}N(\underline{\lambda})&\le\frac{1}{2}\sum_{f\in\Phi}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert(\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert+1)\\&=\frac{n}{2}+\frac{1}{2}\sum_{f\in\Phi}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert^2.\end{align*}
\begin{align*}N(\underline{\lambda})&\le\frac{1}{2}\sum_{f\in\Phi}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert(\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert+1)\\&=\frac{n}{2}+\frac{1}{2}\sum_{f\in\Phi}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert^2.\end{align*}
If
![]() $\ell\leq n/2$
, then we have
$\ell\leq n/2$
, then we have
![]() $\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert\le n/2$
for all
$\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert\le n/2$
for all
![]() $f\in\Phi$
and so
$f\in\Phi$
and so
![]() $N(\underline{\lambda})\le n^2/4+n/2$
. From (7·2) we then find that
$N(\underline{\lambda})\le n^2/4+n/2$
. From (7·2) we then find that
![]() $\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)\ge q^{n(t+1)}$
for all sufficiently large n, again by very crude estimates. If
$\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)\ge q^{n(t+1)}$
for all sufficiently large n, again by very crude estimates. If
![]() $\ell>n/2$
, then
$\ell>n/2$
, then
 \begin{align*}N(\underline{\lambda})&\le \frac{1}{2}\left(n+\ell^2+(n-\ell)^2\right)\\&\le \frac{1}{2}\left(n+(n-t-1)^2+(t+1)^2\right)\\&=\frac{n^2+n}{2}-n(t+1)+(t+1)^2,\end{align*}
\begin{align*}N(\underline{\lambda})&\le \frac{1}{2}\left(n+\ell^2+(n-\ell)^2\right)\\&\le \frac{1}{2}\left(n+(n-t-1)^2+(t+1)^2\right)\\&=\frac{n^2+n}{2}-n(t+1)+(t+1)^2,\end{align*}
where we have used that
![]() $x^2+(n-x)^2$
is increasing for
$x^2+(n-x)^2$
is increasing for
![]() $x\ge n/2$
. Hence in this case we obtain
$x\ge n/2$
. Hence in this case we obtain
![]() $1/\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)\le 4q^{-n(t+1)+(t+1)^2}$
by (7·2).
$1/\chi^{\underline{\lambda}}(1)\le 4q^{-n(t+1)+(t+1)^2}$
by (7·2).
In the remaining case we assume that there exists
![]() $h\in\Phi$
such that
$h\in\Phi$
such that
![]() $\lvert h\rvert=1$
and
$\lvert h\rvert=1$
and
![]() $\lvert\underline{\lambda}(h)\rvert\ge n-t$
. Recall that we also assume that
$\lvert\underline{\lambda}(h)\rvert\ge n-t$
. Recall that we also assume that
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(h)_1\leq n-t-1$
and
$\underline{\lambda}(h)_1\leq n-t-1$
and
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(h)^{\prime}_1\leq n-t-1$
. Since
$\underline{\lambda}(h)^{\prime}_1\leq n-t-1$
. Since
![]() $N(\underline{\lambda})$
depends only on the hook lengths of
$N(\underline{\lambda})$
depends only on the hook lengths of
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(f)$
for
$\underline{\lambda}(f)$
for
![]() $f\in\Phi$
, we may replace
$f\in\Phi$
, we may replace
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(h)$
by its conjugate
$\underline{\lambda}(h)$
by its conjugate
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(h)^{\prime}$
. Assuming that n is sufficiently large, namely
$\underline{\lambda}(h)^{\prime}$
. Assuming that n is sufficiently large, namely
![]() $n\ge (t+2)^2$
, we have
$n\ge (t+2)^2$
, we have
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(h)_1\ge t+2$
or
$\underline{\lambda}(h)_1\ge t+2$
or
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(h)^{\prime}_1\ge t+2$
and we assume without loss of generality that
$\underline{\lambda}(h)^{\prime}_1\ge t+2$
and we assume without loss of generality that
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(h)_1\ge t+2$
. Write
$\underline{\lambda}(h)_1\ge t+2$
. Write
![]() $\underline{\lambda}(h)_1=n-r$
, so that our assumptions imply
$\underline{\lambda}(h)_1=n-r$
, so that our assumptions imply
![]() $t+1\leq r\leq n-t-2$
. Then, writing
$t+1\leq r\leq n-t-2$
. Then, writing
![]() $s=\lvert\underline{\lambda}(h)\rvert$
, there exist nonnegative integers
$s=\lvert\underline{\lambda}(h)\rvert$
, there exist nonnegative integers
![]() $c_j$
satisfying
$c_j$
satisfying
 \begin{equation*}\sum_{j=1}^{n-r}h_{1j}(\underline{\lambda}(h))=\sum_{j=1}^{n-r}(j+c_j),\quad \text{where}\quad \sum_{j=1}^{n-r}c_j=s-(n-r).\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\sum_{j=1}^{n-r}h_{1j}(\underline{\lambda}(h))=\sum_{j=1}^{n-r}(j+c_j),\quad \text{where}\quad \sum_{j=1}^{n-r}c_j=s-(n-r).\end{equation*}
Hence
 \begin{equation*}\sum_{j=1}^{n-r}h_{1j}(\underline{\lambda}(h))=\binom{n-r+1}{2}+(s-n+r).\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\sum_{j=1}^{n-r}h_{1j}(\underline{\lambda}(h))=\binom{n-r+1}{2}+(s-n+r).\end{equation*}
Application of (7·3) with
![]() $\lambda=(\underline{\lambda}(h)_2,\underline{\lambda}(h)_3,\dots)$
gives
$\lambda=(\underline{\lambda}(h)_2,\underline{\lambda}(h)_3,\dots)$
gives
 \begin{align*}\sum_{(i, j)\in\underline{\lambda}(h)}h_{i, j}(\underline{\lambda}(h))&\le \binom{s-n+r+1}{2}+\binom{n-r+1}{2}+(s-n+r)\\&=\frac{s^2}{2}+\frac{3s}{2}+n^2-sn-n+r(r-(2n-s-1))\\&\le \frac{s^2}{2}+\frac{3s}{2}+n^2-sn-n+(t+1)((t+1)-(2n-s-1)),\end{align*}
\begin{align*}\sum_{(i, j)\in\underline{\lambda}(h)}h_{i, j}(\underline{\lambda}(h))&\le \binom{s-n+r+1}{2}+\binom{n-r+1}{2}+(s-n+r)\\&=\frac{s^2}{2}+\frac{3s}{2}+n^2-sn-n+r(r-(2n-s-1))\\&\le \frac{s^2}{2}+\frac{3s}{2}+n^2-sn-n+(t+1)((t+1)-(2n-s-1)),\end{align*}
since the term depending on r is maximised for
![]() $r=t+1$
over the interval
$r=t+1$
over the interval
![]() $[t+1,n-t-2]$
. This last expression equals
$[t+1,n-t-2]$
. This last expression equals
The second summand is increasing for
![]() $s\ge n-t$
and so is at most
$s\ge n-t$
and so is at most
![]() $\frac{1}{2}n(n-2(n-t-2))$
. Hence we obtain
$\frac{1}{2}n(n-2(n-t-2))$
. Hence we obtain
 \begin{equation*}\sum_{(i, j)\in\underline{\lambda}(h)}h_{i, j}(\underline{\lambda}(h))\le \frac{s}{2}+\frac{n^2}{2}-n(t+1)+(t+1)(t+2).\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\sum_{(i, j)\in\underline{\lambda}(h)}h_{i, j}(\underline{\lambda}(h))\le \frac{s}{2}+\frac{n^2}{2}-n(t+1)+(t+1)(t+2).\end{equation*}
Invoking (7·3) once more, we obtain
 \begin{equation*}N(\underline{\lambda})\le \sum_{(i, j)\in\underline{\lambda}(h)}h_{ij}+\frac{1}{2}\sum_{\substack{f\in\Phi\\f\ne h}}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert(\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert+1).\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}N(\underline{\lambda})\le \sum_{(i, j)\in\underline{\lambda}(h)}h_{ij}+\frac{1}{2}\sum_{\substack{f\in\Phi\\f\ne h}}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert(\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert+1).\end{equation*}
We have
 \begin{equation*}\frac{s}{2}+\frac{1}{2}\sum_{\substack{f\in\Phi\\f\ne h}}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert=\frac{1}{2}\sum_{f\in\Phi}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert=\frac{n}{2}\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\frac{s}{2}+\frac{1}{2}\sum_{\substack{f\in\Phi\\f\ne h}}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert=\frac{1}{2}\sum_{f\in\Phi}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert=\frac{n}{2}\end{equation*}
and
 \begin{equation*}\frac{1}{2}\sum_{\substack{f\in\Phi\\f\ne h}}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert^2\leq \frac{1}{2}\left(\sum_{\substack{f\in\Phi\\f\ne h}}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert\right)^2\leq \frac{t^2}{2}.\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}\frac{1}{2}\sum_{\substack{f\in\Phi\\f\ne h}}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert^2\leq \frac{1}{2}\left(\sum_{\substack{f\in\Phi\\f\ne h}}\lvert f\rvert\lvert\underline{\lambda}(f)\rvert\right)^2\leq \frac{t^2}{2}.\end{equation*}
Collecting all terms, we find that
From (7·2) we then obtain
which completes the proof.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) – Project number 459964179.