No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Implicational Kleene algebra with domain and the substructural logic of partial correctness
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 March 2024
Abstract
We show that Kozen and Tiuryn’s substructural logic of partial correctness 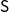 $\mathsf{S}$ embeds into the equational theory of Kleene algebra with domain,
$\mathsf{S}$ embeds into the equational theory of Kleene algebra with domain, 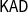 $\mathsf{KAD}$. We provide an implicational formulation of
$\mathsf{KAD}$. We provide an implicational formulation of 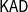 $\mathsf{KAD}$ which sets
$\mathsf{KAD}$ which sets 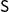 $\mathsf{S}$ in the context of implicational extensions of Kleene algebra.
$\mathsf{S}$ in the context of implicational extensions of Kleene algebra.
Information
- Type
- Special Issue: WoLLIC 2022
- Information
- Mathematical Structures in Computer Science , Volume 34 , Special Issue 7: WoLLIC 2022 , August 2024 , pp. 645 - 660
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
Bochman, A. and Gabbay, D. M. (2012). Sequential dynamic logic. Journal of Logic, Language and Information 21 (3) 279–298.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Buszkowski, W. (2006). On action logic: equational theories of action algebras. Journal of Logic and Computation 17 (1) 199–217.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Cohen, E., Kozen, D. and Smith, F. (1996). The complexity of Kleene algebra with tests. Technical Report TR96-1598, Computer Science Department, Cornell University.Google Scholar
Desharnais, J., Möller, B. and Struth, G. (2006). Kleene algebra with domain. ACM Transactions on Computational Logic 7 (4) 798–833.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Desharnais, J. and Struth, G. (2011). Internal axioms for domain semirings. Science of Computer Programming 76 (3) 181–203. Special issue on the Mathematics of Program Construction (MPC 2008).Google Scholar
Fischer, M. J. and Ladner, R. E. (1979). Propositional dynamic logic of regular programs. Journal of Computer and System Sciences 18 194–211.Google Scholar
Galatos, N., Jipsen, P., Kowalski, T. and Ono, H. (2007). Residuated Lattices: An Algebraic Glimpse at Substructural Logics, Elsevier, Amsterdam.Google Scholar
Groenendijk, J. and Stokhof, M. (1991). Dynamic predicate logic. Linguistics and Philosophy 14 (1) 39–100.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Harel, D., Kozen, D. and Tiuryn, J. (2000). Dynamic Logic, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Hollenberg, M. (1997). An equational axiomatization of dynamic negation and relational composition. Journal of Logic, Language and Information 6 (4) 381–401.Google Scholar
Jipsen, P. (2004). From semirings to residuated Kleene lattices. Studia Logica 76 (2) 291–303.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Kanazawa, M. (1993). Completeness and decidability of the mixed style of inference with composition. In: Dekker, P. and Stokhof, M. (eds.) Proceedings of the Ninth Amsterdam Colloquium, 377–390.Google Scholar
Kozen, D. (1994a). A completeness theorem for Kleene algebras and the algebra of regular events. Information and Computation 110 (2) 366–390.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Kozen, D. (1994b). On action algebras. In: Logic and Information Flow, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 78–88.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Kozen, D. (1997). Kleene algebra with tests. ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems 19 (3) 427–443.Google Scholar
Kozen, D. (2002). On the complexity of reasoning in Kleene algebra. Information and Computation 179 152–162.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Kozen, D. (2003). Automata on guarded strings and applications. Matématica Contemporânea 24 117–139.Google Scholar
Kozen, D. and Smith, F. (1997). Kleene algebra with tests: Completeness and decidability. In: van Dalen, D. and Bezem, M. (eds.) Computer Science Logic, Berlin, Heidelberg, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 244–259.Google Scholar
Kozen, D. and Tiuryn, J. (2003). Substructural logic and partial correctness. ACM Transactions on Computational Logic 4 (3) 355–378.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Kuznetsov, S. (2021). Action logic is undecidable. ACM Transactions on Computational Logic 22 (2) 1–26.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Palka, E. (2007). An infinitary sequent system for the equational theory of *-continuous action lattices. Fundamenta Informaticae 78 (2) 295–309.Google Scholar
Pratt, V. (1991). Action logic and pure induction. In: Logics in AI. European Workshop JELIA’90, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, September 10–14, 1990. Proceedings, Berlin etc., Springer-Verlag, 97–120.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Sedlár, I. (2023). On the complexity of Kleene algebra with domain. In: Glück, R., Santocanale, L. and Winter, M. (eds.) Relational and Algebraic Methods in Computer Science (RAMiCS 2023), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 13896, Cham, Springer, 208–223.Google Scholar
Sedlár, I. and Wannenburg, J. J. (2022). Embedding Kozen-Tiuryn logic into residuated one-sorted Kleene algebra with tests. In: Ciabattoni, A., Pimentel, E. and de Queiroz, R. J. G. B. (eds.) Logic, Language, Information, and Computation (WoLLIC 2022), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 13468, Cham, Springer International Publishing, 221–236.Google Scholar
van Benthem, J. (1995). Logic and the flow of information. In: Prawitz, D., Skyrms, B. and Westerstáhl, D. (eds.) Logic, Methodology and Philosophy of Science IX, Studies in Logic and the Foundations of Mathematics, vol. 134, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 693–724.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
van der Does, J., Groeneveld, W. and Veltman, F. (1997). An update on “might”. Journal of Logic, Language and Information 6 (4) 361–380.CrossRefGoogle Scholar


