Article contents
Development of solution-processed nanowire composites for opto-electronics
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 December 2016
Abstract
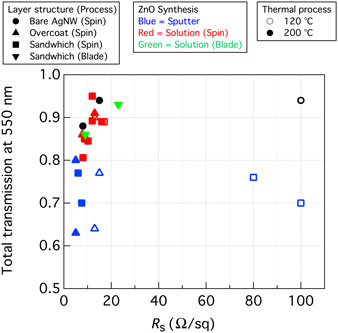
Silver nanowire-based contacts represent one of the major new directions in transparent contacts for opto-electronic devices with the added advantage that they can have Indium-Tin-Oxide-like properties at substantially reduced processing temperatures and without the use of vacuum-based processing. However, nanowires alone often do not adhere well to the substrate or other film interfaces; even after a relatively high-temperature anneal and unencapsulated nanowires show environmental degradation at high temperature and humidity. Here we report on the development of ZnO/Ag-nanowire composites that have sheet resistance below 10 Ω/sq and >90% transmittance from a solution-based process with process temperatures below 200 °C. These films have significant applications potential in photovoltaics and displays.
Information
- Type
- Functional Oxides Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
References
- 3
- Cited by

