Unhealthy diets play a central role in the onset of non-communicable disease. Approximately 11 % of disability-adjusted life years in New Zealand (NZ) are attributable to the effects of poor diets( 1 , Reference Lim, Vos and Flaxman 2 ). Even modest improvements in diet could have a major impact on health if they are adopted by much of the population( Reference Scarborough, Nnoaham and Clarke 3 , Reference Stefanogiannis, Lawes and Turley 4 ). One particular food group of concern is processed foods. Evidence indicates that higher levels of processing are related to decreasing healthiness of foods( Reference Monteiro, Levy and Claro 5 ). Nevertheless, sales of processed foods have increased rapidly; these foods currently account for approximately three-quarters of total world food sales (total $US 3·2 trillion in sales)( Reference Regmi and Gehlhar 6 ) and contribute between 40 % and 75 % of the energy and nutrients consumed in developed countries( Reference Slimani, Deharveng and Southgate 7 , Reference Monteiro 8 ).
Improving diets is a priority for public health, and effective and sustainable interventions are urgently needed. There is clear evidence showing that promotional campaigns are minimally effective( Reference Rekhy and McConchie 9 ) and that research should be looking into the design of the food environment to achieve healthier population diets( Reference Cohen 10 ). One of the most important food environments is the supermarket as this is the place where people in Western countries purchase most of their food( Reference Escaron, Meinen and Nitzke 11 ) (in NZ, 87 % of people shop at a supermarket at least once per week( Reference Murray 12 )).
Different aspects within supermarkets could influence consumer food choices, including the affordability of various foods( Reference Story, Kaphingst and Robinson-O’Brien 13 ). Different studies have indicated that unhealthier food is relatively cheaper compared with more nutrient-dense food; in particular, foods high in fat and sugar have been found to be cheaper than less energy-dense foods( Reference Drewnowski and Specter 14 – Reference Waterlander, de Haas and van Amstel 16 ). While there is some debate in the literature about this topic( Reference Lipsky 17 ), there is consensus that price may form a barrier to buying healthier food, particularly for people with a low socio-economic status( Reference Steenhuis, Waterlander and de Mul 18 ).
Accessibility and availability of less healthy food also influence consumer food purchasing decisions. Due to technological innovations and agricultural subsidies, food has become more available, varied and affordable( Reference Tillotson 19 ). However, our food system is strongly commercial and economically driven( Reference Pinstrup-Andersen 20 ). This commercial focus produces an over-supply of dietary energy including from low-nutrient crops such as sugar and corn( Reference Schafer Elinder, Lock and Blenkus 21 ). Moreover, many of the products available are in processed form and contain excessive salt, sweeteners, refined grains and oils( Reference Nugent 22 ). Evidence indicates that supermarkets in different developed countries display a large variety of processed foods high in sugars and fats and have more shelf space allocated to snack foods than to fresh fruit and vegetables( Reference Thornton, Cameron and McNaughton 23 ). In addition, global food manufacturers have a vested interest in the production and sale of ultra-processed foods because production costs are low and highly processed foods have a long shelf-life and a high retail value( Reference Stuckler, McKee and Ebrahim 24 ).
Monteiro et al. describe a three-level classification system to categorize processed foods based on the applied industrial processes: (i) unprocessed or minimally processed; (ii) culinary processed; and (iii) ultra-processed food products( Reference Monteiro, Levy and Claro 5 ). This classification system is used in the present study and is elaborated upon in the ‘Methods’ section.
The present study aims to use this classification to measure the packaged food environment in NZ supermarkets by examining the nutrient profiling score, price and product variety in relation to level of industrial processing. The study hypothesizes that foods with a higher level of industrial processes applied will be (i) less healthy, (ii) cheaper and (iii) more highly available compared with minimally processed foods.
Methods
Data sources
The NutriTrack database was used to examine the packaged food environment in NZ supermarkets. NutriTrack is an existing database developed by the University of Auckland to monitor the packaged food supply and identify opportunities for healthier reformulation of processed foods. Information is collected directly from all packaged supermarket products annually in four large NZ supermarkets in the Auckland region. In NZ, there is a duopoly in the retail market where the cooperatives Foodstuffs and Progressive Enterprises Ltd control over 90 % of the retail market( Reference Bava, Jaeger and Dawson 25 ). NutriTrack collects data from the four largest franchises within these two cooperatives, and then the largest store for each chain, providing the widest product range. The NutriTrack database includes brand and package information and all nutrients present on the mandatory Nutrition Information Panel( 26 ): energy (kJ), protein (g), carbohydrate (g), sugar (g) total fat (g), saturated fat (g) and sodium (mg). Products are categorized into a food categorization system used by the Global Food Monitoring Group( Reference Dunford, Webster and Metzler 27 ). Categories include, for example, beverages, dairy, eggs, fish and fish products.
For the present study, NutriTrack 2011 and 2013 databases were used. NutriTrack 2013 (the most recent available) was used to gain insight into brand variety. However, price information was not included in NutriTrack 2013 and thus NutriTrack 2011, which contains price information, was used to gain insight into the healthiness and price. NutriTrack 2011 contains data collected from two major supermarket stores on 6020 packaged foods categorized into thirteen food categories and NutriTrack 2013 contains data collected from four major supermarket stores on 13 406 products categorized into fifteen food categories.
Measures
Level of processing
A taxonomy developed by Monteiro et al. was used to categorize packaged foods into three levels of industrial processing: (i) unprocessed or minimally processed foods (group 1); (ii) processed culinary (group 2); and (iii) ultra-processed foods (group 3)( Reference Monteiro, Levy and Claro 5 ). The industrial processes applied to the products in group 1 do not substantially alter the foods, whereas the processes applied to group 3 result in products with no resemblance to the original foods. For example, portioning, drying and freezing are industrial processes included in group 1. Group 2 includes for example pressured and milled products; and salting, baking and (deep) frying are examples of industrial processes applied to products placed in group 3( Reference Monteiro, Levy and Claro 5 ). For some of the food sub-categories the classification was ambiguous, these were: cream, plain dairy milk, other milk, nuts and fruit, and some processed meat products. For example, the sub-category ‘other milk’ contained coconut milk (group 2) and flavoured milks (group 3), but had to be classified as an entire category into only one of these groups. As a rule, when classifying a food sub-category that was ambiguous a conservative approach was taken where the sub-category was placed into a more industrial processed food group (Table 1).
Table 1 Packaged food products subdivided into three levels of processing
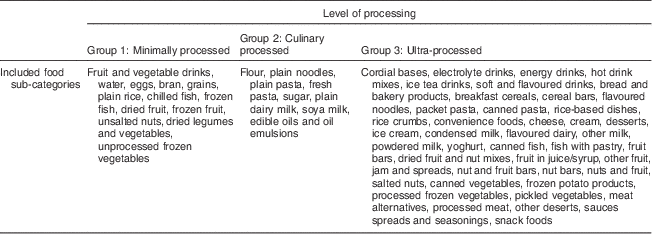
Price
Three price measures were calculated for each individual product to enable a comprehensive review of price: energy cost ($NZ/100 kJ), unit cost ($NZ/100 g or ml) and serving cost ($NZ/serving). We consider $NZ/serving to be the most relevant, since the serving size is a standardized measure that makes it easier to compare similar foods( 28 ).
Nutrient profiling score
The Food Standards Australia New Zealand Nutrient Profiling Scoring Criterion (NPSC)( 29 ) was calculated for all products in order to determine their healthiness. The NPSC system allocates products an overall score based on both ‘positive’ and ‘negative’ nutrients including: energy (kJ), saturated fat, sugars, sodium, fibre, protein, and % fruit, vegetable and nut content. The system is used to determine eligibility of foods to carry health claims in Australia and NZ. All foods and beverages are divided into three categories: category 1 includes beverages; category 2 includes any food not included in 1 or 3; and category 3 includes fats and oils. The scoring criteria differ for the three categories. Scores range between −10 and 28, with higher scores indicating a worse nutrient profile.
The NutriTrack 2011 data set did not contain all the required information to allocate the NPSC; fruit and vegetable percentage and (in the absence of a health claim) fibre content are not mandatory to list on NZ food products. Consequently, only 1518 of the 6020 products listed fibre on the Nutrition Information Panel. Indeed, two adaptions had to be made to the NPSC model( 26 ). First, since data on the fruit and vegetable percentage were missing, this component could not be used when calculating the NPSC. Second, since it can be expected that fibre is mostly listed in specific food categories (e.g. cereals), it was decided to exclude this from the NPSC to make the comparison between food categories more equitable. Sub-analysis revealed that this exclusion led to a slight increase in the mean NPSC from 3·6 to 5·9, meaning that the values used in our analysis will be slightly worse than the true NPSC.
Product and brand variety
All individual food products were categorized into three groups: (i) food manufacturer; (ii) brand; and (iii) sub-brand. The NutriTrack 2013 database contained data on sub-brand (brand or logo which is listed on the front of package of the product( Reference Vandevijvere and Swinburn 30 )) but an Internet search was required to determine whether these sub-brands were stand-alone brands or part of an overarching brand. For example, Woolworths Select and Woolworths Homebrand are different brands on the package, but both belong to the overarching brand Woolworths. Next, the site of the Ministry of Economic Development( 31 ) was used to identify the food manufacturers behind these brands. This website lists all manufacturers active in the NZ food and beverage market. All brands that were not stand-alone were allocated to the higher-level food manufacturer. These food manufacturers were a combination of national and global acting companies. To assess the size of the food manufacturers, the number of products available in our supermarket sample was counted (i.e. in the present paper, product availability refers to the number of unique products, not the shelf inventory).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using the statistical software package IBM SPSS Statistics version 22. Descriptive analyses were used to determine the number of unique products, energy costs, unit costs, serving costs and NPSC for the three levels of processing (groups 1, 2 and 3). An ANOVA F test was used to compare the NPSC, energy costs, unit costs and serving costs across processed food groups. Prior to this test, the homogeneity of variance was tested and when there was variance between the groups, the Brown–Forsythe test was used instead. Bonferroni and Games–Howell post hoc tests were used relatively when variance was equal and with non-equal variance to determine which groups differed significantly from each other. For this test, food categories were required to have products in at least two of the three processed food groups. Five categories met this condition: beverages, cereals, dairy, fish and fish products, and fruit and vegetables.
Next, the overall association between the NPSC and three price measures was explored using a linear regression model. Price was the dependent variable and the NPSC was the independent variable, adjusting for food category. These analyses were stratified by food category. Food categories containing <150 of the total 6020 products were considered too small to produce reliable estimates and were excluded. These categories were oils, eggs and other miscellaneous.
Sensitivity analysis was conducted to establish whether the classification of ambiguous food categories had any effect on results observed. In addition, analysis was repeated excluding beverages because their low energy density could impact observed associations between price and nutrient profiling scores( Reference Drewnowski 32 ).
Finally, the overall brand variety, brand variety within the different processed food groups and brand variety within different food categories was explored using descriptive analysis. Distinctions were made between food manufacturers, brands and sub-brands. For these analyses, the focus was on the food categories most likely to be adversely associated with non-communicable diseases, including ready meals, crisps and snacks, biscuits, chocolates and sweets, breakfast cereals and soft drinks( Reference Moodie, Stuckler and Monteiro 33 ).
Results
Descriptive data
The 2011 NutriTrack data set contained 6020 packaged food and beverage products with a mean NPSC score of 10·58 (sd 9·2). The mean energy cost was $NZ 1·17 (sd 7·2) per 100 kJ. The mean unit and serving costs were $NZ 1·77 (sd 1·6) per 100 g and $NZ 1·06 (sd 1·4) per serving, respectively).
Table 2 Nutrient profiling score and costs of 6020 packaged foods available for sale in New Zealand supermarkets in 2011
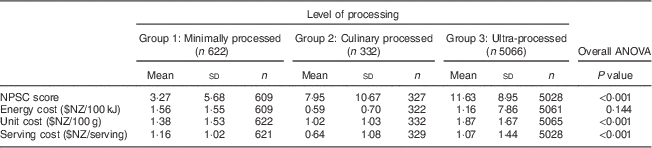
NPSC, Nutrient Profiling Scoring Criterion, is used to determine the healthiness of products and ranges between −5 and 40; higher scores indicate less healthy products.
NutriTrack 2013 contained data on 13406 packaged food products. The overall mean NPSC score of these products was 9·87 (sd 9·2).
Nutrient profiling score and price for different levels of processed food
Six hundred and twenty-two (10·3 %) packaged products were classified as minimally processed (group 1), 332 (5·5 %) as culinary processed (group 2) and 5066 (84·2 %) as ultra-processed foods (group 3). Table 2 shows the NPSC scores and costs for these three food groups.
The present study observed a difference in variance in NPSC scores between the three groups and therefore the Welch and Brown–Forsythe test was used, which supported the findings of the ANOVA in all cases. Results showed that the three processed food groups had statistically significantly different mean NPSC scores (P<0·001) and the post hoc Games–Howell test showed that the mean for each group differed significantly from the mean for both other groups (3× P<0·001). The mean NPSC score was the lowest (best nutrient profile) in the minimally processed group (3·27) and highest in the ultra-processed group (11·63).
No statistically significant differences were found in energy cost by level of processing (P=0·144). However, significant differences were observed in unit cost between all groups (3× P<0·050); the ultra-processed group had the highest unit cost ($NZ 1·87/100 g) and the culinary processed group had the lowest ($NZ 1·02/100 g). In addition, serving cost differed significantly between the minimally and culinary processed groups (P<0·001), and between the culinary and ultra-processed groups (P<0·001). The minimally processed group had the highest cost per serving with a mean of $NZ 1·16 (sd 1·02) and the culinary processed group had the lowest cost with a mean of $NZ 0·64 (sd 1·08) per serving (Table 2).
Differences in NPSC score and costs between the three levels of processing within five food categories are shown in Table 3. With the exception of fish and fish products and the culinary processed food category for cereals, the NPSC score was consistently higher (worse nutrient profile) for higher levels of processing. However, this difference was statistically significant only for beverages, cereals and dairy (3× P<0·001). In addition, within the fish and fish products and fruit and vegetables categories, the energy cost (P<0·001, P=0·517), unit cost (P<0·007, P<0·001) and serving cost (P<0·001, P<0·001) were consistently higher in the minimally processed food group (Table 3).
Table 3 Differences in energy, unit and serving costs according to level of processing across five food categories for 6020 packaged foods available for sale in New Zealand supermarkets in 2011
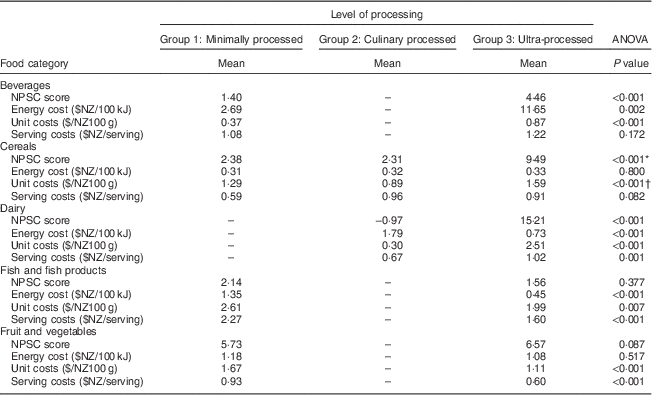
NPSC, Nutrient Profiling Scoring Criterion, is used to determine the healthiness of products and ranges between −5 and 40; higher scores indicate less healthy products.
* Post hoc Games–Howell showed that NPSC score differed significantly (P<0·050) between group 1 & 3 and group 2 & 3.
† Post hoc Games–Howell showed that unit cost differed significantly (P<0·050) between group 1 & 2 and group 2 & 3.
Association between nutrient profiling score and price
For all products combined, a significant linear relationship was found between NPSC score and all three price measures. However, all associations were weak: energy cost: B=−0·089, P<0·001, R 2=0·013; unit cost: B=0·071, P<0·001, R 2=0·163; serving cost: B=−0·027, P<0·001, R 2=0·031. For all three price measures, food category was found to be an effect modifier and thus analyses were also conducted separately for each food category. These results are shown in Table 4. Again, most associations (twenty-six out of thirty) were weak, although a moderate association was found for dairy, beverages and fish. For dairy, a negative association was observed between NPSC score and energy cost and a positive association with unit cost.
Table 4 Associations between nutrient profiling score (NPSC) and price by food category for 6020 packaged foods available for sale in New Zealand supermarkets in 2011
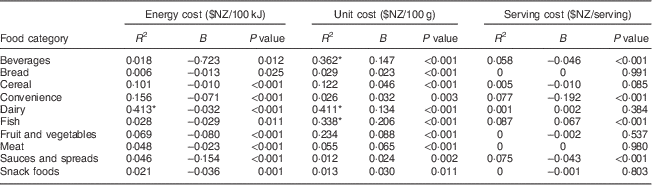
NPSC, Nutrient Profiling Scoring Criterion, is used to determine the healthiness of products.
* Moderate association between the nutrient profiling score and price.
Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analyses to explore the impact of ambiguous classifications of food categories revealed similar results to the differences in NPSC score and energy cost between the three groups. Further, analyses excluding beverages revealed similar results for the trend in NPSC score for the three different processed food groups. The analyses showed slightly different outcomes for the cost measures, but the directions of the associations stayed the same.
Product and brand variety
The NutriTrack 2013 database (13 406 products) was used to assess product variety. A total of thirty different food manufacturers were indicated as active in NZ, together producing 47·4 % (n 6351) of all packaged food available in supermarkets. The two biggest food manufacturers were Foodstuffs (1079 products) and Woolworths Limited (729 products). Together these food manufacturers produced 1808 products, accounting for 13·5 % of all packaged products available in supermarkets in NZ. The ten biggest food manufacturers produced 4707 products, accounting for 35·1 % of the products. When the study focused specifically only on ultra-processed foods, Foodstuffs (n 887) and Heinz (n 634) were the two single biggest food manufacturers producing 13·7 % of all ultra-processed foods available in NZ supermarkets. The ten biggest food manufacturers within ultra-processed foods together produced 36·9 % (n 4089) of ultra-processed foods.
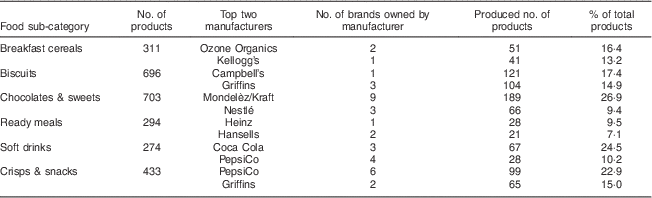
The largest product variety was observed for ultra-processed foods (11 085 products, 82·7 % of total). Our analysis revealed that these products were produced by a relatively small number of manufacturers (Table 5). More detail on the product range for a set of key product categories that are linked to non-communicable diseases, i.e. breakfast cereals, biscuits, chocolates and sweets, ready meals, soft drinks, and crisps and snacks(32), is provided in Table 5. For example, 311 breakfast cereal products were available, of which ninety-two (29·6 %) were produced by two food manufacturers, Ozone Organics and Kellogg’s. Likewise, we observed 703 varieties of chocolates and sweets (6·3 % of all ultra-processed foods); 255 of these (36·3 %) were produced by two food manufacturers, Mondelèz/Kraft and Nestlé. Mondelèz/Kraft produced these chocolates and sweets under nine different brands. Two hundred and seventy-four products were categorized as soft drinks and divided into two sub-categories: sugar-free (n 44) and sugar-sweetened (n 230). Ninety-five (34·7 %) soft drinks were products by two food manufacturers, Coco Cola and PepsiCo.
Table 5 Number of product varieties and manufacturers per food sub-category for 13 406 packaged foods available for sale in New Zealand supermarkets in 2013
Discussion
The present study aimed to map the packaged food environment in NZ supermarkets by examining the different levels of industrial food processing in relation to NPSC score, price and product variety. Our analyses showed a significant positive association between the level of industrial processing and NPSC score, indicating that ultra-processed foods had a worse nutrient profile than culinary processed foods, which in turn had a worse nutrient profile than minimally processed foods. These findings confirm our hypothesis that highly processed foods have a worse nutrient profile. A large majority (83 %) of packaged products were classified as ultra-processed and our study found that relatively few food manufacturers produced a large number of products and brands. These results show there is clear potential to improve product availability in supermarkets, in particular by reducing the large variety of very similar ultra-processed foods.
Our findings support those of Monteiro and colleagues, who suggest that diet quality decreases when purchases of ultra-processed food increase( Reference Monteiro, Levy and Claro 5 ). In the present study we found that the NPSC score was significantly worse for ultra-processed foods compared with their less processed counterparts. This finding was consistent across and within food categories.
The original UK model( Reference Rayner, Scarborough and Stockley 34 ) upon which the NPSC was based states that if beverages score 1 or more and if foods score 4 or more, then these are classified as ‘high in saturated fat, sodium or sugar’. The present study showed that, except for fish, for all food categories the mean NPSC score of ultra-processed foods clearly exceeded this value (beverages 4·46; cereals 9·49; dairy 15·21; fruit and vegetables 6·59). Since supermarkets are the most important point of food purchase( Reference Murray 12 ), the high availability of ultra-processed foods is a major concern.
A review by Glanz et al. showed that increased availability of unhealthier foods in supermarkets increases sales( Reference Glanz, Bader and Iyer 35 ) and already ultra-processed foods contribute at least 60 % of dietary intake in Western countries( Reference Moubarac, Martins and Claro 36 , Reference Slimani, Deharveng and Southgate 37 ). There are different interventions in the supermarket environment that could potentially reduce the consumption of these less healthy foods, including strategies focusing on the ‘4 P’s’ of the marketing mix: price, products, placement and promotion( Reference Glanz, Bader and Iyer 35 ). Promising strategies could be the reduction or relocation of unhealthier foods to less prominent shelf-space, the placement of healthier foods in more visible and accessible locations, reduction in promotion of high-fat, high-salt and high-sugar foods, and creating checkout aisles with healthier products( Reference Glanz, Bader and Iyer 35 ).
One aspect that could increase the attractiveness of ultra-processed foods is affordability. However, in contrast to our hypothesis, in the present study we found no clear patterns in the association between price (energy cost, unit cost or serving cost) and level of processing. Our study did find some patterns within specific food categories, where the energy, unit and serving costs were higher for minimally v. ultra-processed fish and fruit and vegetables. Likewise, our study did not find a strong association between the healthiness (NPSC) of products and their price. We did find some statistically significant associations for energy cost and serving cost, which were both negatively correlated with NPSC score, but these were very weak. This supports the findings by Ni Mhurchu and Ogra, who stated it is possible in NZ to improve diet quality with comparable but healthier products without also increasing the cost of the diet (e.g. moving from ultra-processed to minimally processed)( Reference Mhurchu and Ogra 38 ).
Many other studies in the literature, however, report that healthier foods tend to cost more( Reference Waterlander, de Haas and van Amstel 16 , 28 , Reference Maillot, Darmon and Darmon 39 ). A possible explanation for the difference in findings of our study compared with this previous work could be that they mostly used energy density to classify the healthiness of products( Reference Waterlander, de Haas and van Amstel 16 , 28 , Reference Maillot, Darmon and Darmon 39 ), while we used nutrient profiling. It can be argued that nutrient profiling is a better method, since it takes a more complete approach to the healthiness of food by looking not only at energy levels, but also at saturated fat, added sugars, salt levels and protein. However, not only the absolute price is important to consider, but also ‘the price of convenience’( Reference Brunner, Van der Horst and Siegrist 40 ). Ultra-processed foods are more convenient and require less preparation, cooking skills and time compared with less processed foods and people are prepared to pay for this( Reference Brunner, Van der Horst and Siegrist 40 ). Since our study did not observe significant absolute cost differences between minimally and ultra-processed foods, it can be argued that they still could be perceived cheaper in terms of value for money( Reference Brunner, Van der Horst and Siegrist 40 ).
The present study found that 35 % of all packaged foods available in NZ supermarkets were produced by the ten biggest food manufacturers. This is comparable to numbers from the USA showing that 32 % of the packaged food is produced by the ten biggest food manufacturers( Reference Stuckler, McKee and Ebrahim 24 ). Similar trends were observed within food categories. For example, our study observed that one manufacturer produced 189 (27 % of total) chocolates and sweets displayed through nine different brands. Furthermore, we found that a large number (n 1079, n 729) of food products were manufactured by the two largest supermarkets themselves (Foodstuffs and Progressive Enterprises Ltd). Together these supermarkets represent the largest food-producing manufacturers (14 % of all products), meaning that these two supermarkets do not only own 90 % of the market share, but also predominantly produce and sell their own products. These numbers suggest that there are strong incentives for manufacturers to produce many varieties of basically the same processed foods. Stuckler and colleagues gave three explanations for this phenomenon: low production costs, long shelf-life and high retail value( Reference Stuckler, McKee and Ebrahim 24 ).
To our knowledge the present study is the first that gives detailed insight into the availability, variety and healthiness of different processing levels of packaged foods available in supermarkets. However, there are some limitations that are important to consider. First, it is important to acknowledge the limitations of the three-tier taxonomy used to classify processed food products( Reference Monteiro, Levy and Claro 5 ). The processes making products eligible for inclusion in the ultra-processed food group were much broader than the processes for the minimally and culinary processed food groups. This could be a reason why the ultra-processed food group included substantially more products (n 5066) than the two other levels (n 662 and 332, respectively). However, the method of classification had been validated and used in other studies( Reference Moodie, Stuckler and Monteiro 33 , Reference Moubarac, Martins and Claro 36 , Reference Tavares, Fonseca and Garcia Rosa 41 ). To the best of our knowledge no other taxonomies exist to classify food by level of processing. Further, our sensitivity analyses, where fewer products were classified as ultra-processed, revealed similar results as the main analyses. Another limitation is that our study focused exclusively on packaged foods. Therefore it does not provide insight into the complete supermarket environment which also includes fresh produce (e.g. fresh fruits and vegetables, raw nuts, etc.) and thus is healthier than the supermarket environment presented here. However, our study does highlight how unhealthy most packaged foods available in supermarkets are. While the availability of more healthy foods is important, recent evidence shows that when both healthy and less healthy foods are highly available (as in supermarkets) this still has negative consequences for obesity( Reference Glanz, Bader and Iyer 35 ).
A strength of the current research was the use of the NutriTrack database. This database is unique in that it contains nutrient information on all packaged foods for sale in major NZ supermarkets, including brand details. Data are collected annually based on a published protocol( Reference Dunford, Webster and Metzler 27 ) and data collection is undertaken in the four biggest supermarket stores in the largest city in NZ. The use of the NPSC nutrient profiling model is another strength of our study. This is a rigorous method of assessing the healthiness of foods as it looks at both positive and negative nutrients. Unfortunately, we were not able to include all aspects of the NPSC score, such as fibre and % fruit, vegetable and nut, meaning that the true values might be healthier than the ones presented here. However, since this information was left out consistently, all products were affected equally, meaning that it likely did not affect reported differences between groups.
Finally, it is possible we might have misclassified some products in relation to their producing food manufacturers. However, the study used a quality database from the Ministry of Economic Development of NZ and most products were easy to track. In addition, the results are aligned with American data which gives us confidence that the results are valid.
Our study reveals there are clear opportunities to improve the packaged food environment in supermarkets, in particular with regard to the availability of ultra-processed foods. One strategy to achieve this is via voluntary industry codes( Reference Struben, Chan and Dube 42 ). A study by Stuben et al. showed that if food manufacturers were interested in improving the nutritional quality of their products, this could have lasting positive impacts on population BMI. However, that same study also revealed that these efforts would decrease their market share in low nutritional quality products in the long term, which explains the low interest of food manufacturers in reformulating their products( Reference Struben, Chan and Dube 42 ). Food manufacturer initiatives supported by governmental regulation are therefore expected to be more effective in creating a healthier food environment. To achieve this, governments should take a leading role( Reference Swinburn, Sacks and Hall 43 ).
Conclusion
The majority of packaged foods in NZ supermarkets are ultra-processed and these foods are also the least healthy. The present study found no significant price difference between ultra- and less processed foods, indicating ultra-processed foods might provide time-poor consumers with more value for money. There is a vast range of product and brand varieties of essentially the same product and these are produced by a relatively small number of manufacturers, including supermarket-owned brands. These findings highlight a clear need for improvement of the supermarket packaged food environment, where we should focus on displaying a smaller number of less healthy ultra-processed foods and more healthy products, and increase efforts to reformulate products to make them healthier.
Acknowledgements
Financial support: This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors. Conflict of interest: None. Authorship: C.M.L. designed and carried out the study, as well as conducted the data analyses and wrote the article. I.H.M.S. supervised the designing and carrying out of the study, as well as giving feedback on the writing. H.E. and C.N.M. gave permission to use the NutriTrack data set and both provided feedback on the article. W.E.W. formulated the research question and supervised the carrying out of the study, in addition to writing parts of the article. Ethics of human subject participation: Ethical approval was not required.







