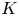1. Introduction
1.1 Double nested Hilbert scheme of points
Let ![]() $X$ be a quasi-projective scheme over
$X$ be a quasi-projective scheme over ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}$. We denote by
${{\mathbb {C}}}$. We denote by ![]() $X^{[n]}$ the Hilbert scheme of
$X^{[n]}$ the Hilbert scheme of ![]() $n$ points on
$n$ points on ![]() $X$, which parametrizes zero-dimensional closed subschemes
$X$, which parametrizes zero-dimensional closed subschemes ![]() $Z\subset X$ of length
$Z\subset X$ of length ![]() $n$. Given a tuple of non-decreasing integers
$n$. Given a tuple of non-decreasing integers ![]() $\mathbf {n}=(n_0 \leq \cdots \leq n_d)$, the nested Hilbert scheme of points
$\mathbf {n}=(n_0 \leq \cdots \leq n_d)$, the nested Hilbert scheme of points ![]() $X^{[\mathbf {n}]}$ parametrizes flags of zero-dimensional subschemes
$X^{[\mathbf {n}]}$ parametrizes flags of zero-dimensional subschemes ![]() $(Z_0\subset \cdots \subset Z_d)$ of
$(Z_0\subset \cdots \subset Z_d)$ of ![]() $X$, where each
$X$, where each ![]() $Z_i$ has length
$Z_i$ has length ![]() $n_i$. The scheme structure of these moduli spaces has been intensively studied in the literature; see, for example, [Reference CheahChe98].
$n_i$. The scheme structure of these moduli spaces has been intensively studied in the literature; see, for example, [Reference CheahChe98].
We propose a variation of this moduli space, by parametrizing flags of subschemes nesting in two directions. Let ![]() $\lambda$ be a Young diagram and
$\lambda$ be a Young diagram and ![]() $\mathbf {n}_\lambda =(n_\Box )_{\Box \in \lambda }$ a reversed plane partition, that is a labelling of
$\mathbf {n}_\lambda =(n_\Box )_{\Box \in \lambda }$ a reversed plane partition, that is a labelling of ![]() $\lambda$ by non-negative integers non-decreasing in rows and columns. We denote by
$\lambda$ by non-negative integers non-decreasing in rows and columns. We denote by ![]() $X^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ the double nested Hilbert scheme of points, the moduli space parametrizing flags of zero-dimensional closed subschemes
$X^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ the double nested Hilbert scheme of points, the moduli space parametrizing flags of zero-dimensional closed subschemes ![]() $(Z_\Box )_{\Box \in \lambda }\subset X$
$(Z_\Box )_{\Box \in \lambda }\subset X$

where each ![]() $Z_\Box$ has length
$Z_\Box$ has length ![]() $n_\Box$. If
$n_\Box$. If ![]() $\lambda$ is a horizontal or vertical Young diagram, the nesting is linear and we recover the usual nested Hilbert scheme of points.
$\lambda$ is a horizontal or vertical Young diagram, the nesting is linear and we recover the usual nested Hilbert scheme of points.
The scheme structure of these moduli spaces is interesting already in dimension one, for a smooth curve ![]() $C$. Cheah proved [Reference CheahChe98] that the nested Hilbert scheme
$C$. Cheah proved [Reference CheahChe98] that the nested Hilbert scheme ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}]}$ is smooth, being isomorphic to a product of symmetric powers of
$C^{[\mathbf {n}]}$ is smooth, being isomorphic to a product of symmetric powers of ![]() $C$ via a Hilbert–Chow-type morphism. However, as soon as we allow double nestings,
$C$ via a Hilbert–Chow-type morphism. However, as soon as we allow double nestings, ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ can have several irreducible components (see Example 2.6), therefore failing to be smooth.
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ can have several irreducible components (see Example 2.6), therefore failing to be smooth.
Our first result is a closed formula for the generating series of topological Euler characteristic of ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ in terms of the hook-lengths
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ in terms of the hook-lengths ![]() $h(\Box )$ of
$h(\Box )$ of ![]() $\lambda$.
$\lambda$.
Theorem 1.1 (Theorem 2.11)
Let ![]() $C$ be a smooth quasi-projective curve and
$C$ be a smooth quasi-projective curve and ![]() $\lambda$ a Young diagram. Then
$\lambda$ a Young diagram. Then
This is achieved by exploiting the power structure on the Grothendieck ring of varieties ![]() $K_0(\operatorname {Var}_{{{\mathbb {C}}}})$, by which we reduce to the combinatorial problem of counting the number of reversed plane partitions of a given Young diagram, which was solved by Stanley [Reference StanleySta71] and Hillman and Grassl [Reference Hillman and GrasslHG76]. Motivic analogues of this formula are studied in [Reference Monavari and RicolfiMR22].
$K_0(\operatorname {Var}_{{{\mathbb {C}}}})$, by which we reduce to the combinatorial problem of counting the number of reversed plane partitions of a given Young diagram, which was solved by Stanley [Reference StanleySta71] and Hillman and Grassl [Reference Hillman and GrasslHG76]. Motivic analogues of this formula are studied in [Reference Monavari and RicolfiMR22].
1.2 Virtual fundamental class
The double nested Hilbert scheme ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ is in general singular, making it hard to perform intersection theory. To remedy this, we show that
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ is in general singular, making it hard to perform intersection theory. To remedy this, we show that ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ admits a perfect obstruction theory in the sense of Behrend and Fantechi [Reference Behrend and FantechiBF97] and Li and Tian [Reference Li and TianLT98]. In fact, we can (globally!) realize
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ admits a perfect obstruction theory in the sense of Behrend and Fantechi [Reference Behrend and FantechiBF97] and Li and Tian [Reference Li and TianLT98]. In fact, we can (globally!) realize ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ as the zero locus of a section of a vector bundle over a smooth ambient space.
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ as the zero locus of a section of a vector bundle over a smooth ambient space.
Theorem 1.2 (Theorem 2.8)
Let ![]() $C$ be an irreducible smooth quasi-projective curve. There exists a section
$C$ be an irreducible smooth quasi-projective curve. There exists a section ![]() $s$ of a vector bundle
$s$ of a vector bundle ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}$ over a smooth scheme
${{\mathcal {E}}}$ over a smooth scheme ![]() $A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }$ such that
$A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }$ such that

By this construction ![]() $C^{[ \mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ naturally admits a perfect obstruction theory (see Example 2.7) and, in particular, carries a virtual fundamental class
$C^{[ \mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ naturally admits a perfect obstruction theory (see Example 2.7) and, in particular, carries a virtual fundamental class ![]() $[C^{[ \mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}]^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$, which recovers the usual fundamental class in the case where the nesting is linear. We pause a moment to explain this construction in the easiest interesting example, that is for the reversed plane partition
$[C^{[ \mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}]^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$, which recovers the usual fundamental class in the case where the nesting is linear. We pause a moment to explain this construction in the easiest interesting example, that is for the reversed plane partition

The embedding in the smooth ambient space is
 \begin{align*} C^{[ \mathbf{n}_\lambda]}&\hookrightarrow A_{C,\mathbf{n}_{\lambda}}:=C^{[n_{00}]}\times C^{[n_{10}-n_{00}]}\times C^{[n_{11}-n_{01}]}\times C^{[n_{01}-n_{00}]}\times C^{[n_{11}-n_{10}]},\\ (Z_{00}, Z_{01}, Z_{10}, Z_{11})&\mapsto (Z_{00}, Z_{10}-Z_{00},Z_{11}-Z_{01},Z_{01}-Z_{00},Z_{11}-Z_{10}). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} C^{[ \mathbf{n}_\lambda]}&\hookrightarrow A_{C,\mathbf{n}_{\lambda}}:=C^{[n_{00}]}\times C^{[n_{10}-n_{00}]}\times C^{[n_{11}-n_{01}]}\times C^{[n_{01}-n_{00}]}\times C^{[n_{11}-n_{10}]},\\ (Z_{00}, Z_{01}, Z_{10}, Z_{11})&\mapsto (Z_{00}, Z_{10}-Z_{00},Z_{11}-Z_{01},Z_{01}-Z_{00},Z_{11}-Z_{10}). \end{align*}
In other words, ![]() $A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}$ records the subscheme in position
$A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}$ records the subscheme in position ![]() $(0,0)$ and all possible vertical and horizontal differences of subschemes, where sum and difference are well-defined by seeing the closed subschemes
$(0,0)$ and all possible vertical and horizontal differences of subschemes, where sum and difference are well-defined by seeing the closed subschemes ![]() $Z_{ij}$ as divisors on
$Z_{ij}$ as divisors on ![]() $C$. At the level of closed points, the image of the embedding is given by all
$C$. At the level of closed points, the image of the embedding is given by all ![]() $(Z_{00}, X_1, X_2,Y_1 , Y_2)\in A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}$ such that
$(Z_{00}, X_1, X_2,Y_1 , Y_2)\in A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}$ such that ![]() $X_1+Y_2=Y_1+X_2$, again as divisors. Note that
$X_1+Y_2=Y_1+X_2$, again as divisors. Note that ![]() $X_1+Y_2$ and
$X_1+Y_2$ and ![]() $Y_1+X_2$ are effective divisors of the same degree, therefore they are equal if and only if one is contained into the other, say
$Y_1+X_2$ are effective divisors of the same degree, therefore they are equal if and only if one is contained into the other, say ![]() $X_1+Y_2\subset Y_1+X_2$.
$X_1+Y_2\subset Y_1+X_2$.
This relation is encoded into a section of a vector bundle ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}$, as we now explain. Denote by
${{\mathcal {E}}}$, as we now explain. Denote by ![]() ${{\mathcal {X}}}_1, {{\mathcal {X}}}_2, {{\mathcal {Y}}}_1, {{\mathcal {Y}}}_2$ the universal divisors on
${{\mathcal {X}}}_1, {{\mathcal {X}}}_2, {{\mathcal {Y}}}_1, {{\mathcal {Y}}}_2$ the universal divisors on ![]() $A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}\times C$ and set
$A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}\times C$ and set
 \begin{align*} \Gamma^{1}&={{\mathcal{Y}}}_{1}+{{\mathcal{X}}}_{2},\\ \Gamma^{2}&={{\mathcal{X}}}_{1}+{{\mathcal{Y}}}_{2}. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \Gamma^{1}&={{\mathcal{Y}}}_{1}+{{\mathcal{X}}}_{2},\\ \Gamma^{2}&={{\mathcal{X}}}_{1}+{{\mathcal{Y}}}_{2}. \end{align*}
The vector bundle ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is defined as
${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is defined as
where ![]() $\pi :A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}\times C\to A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}$ is the projection. The section
$\pi :A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}\times C\to A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}$ is the projection. The section ![]() $s$ of
$s$ of ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is that induced, via
${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is that induced, via ![]() $\pi _*$, by the section of
$\pi _*$, by the section of ![]() $\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}\times C}(\Gamma ^{1})$ which vanishes on
$\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}\times C}(\Gamma ^{1})$ which vanishes on ![]() $\Gamma ^{1}$ and then restricted to
$\Gamma ^{1}$ and then restricted to ![]() $\Gamma ^{2}$.
$\Gamma ^{2}$.
1.3 Stable pair invariants of local curves
Let ![]() $C$ be a smooth projective curve and
$C$ be a smooth projective curve and ![]() $L_1, L_2$ two line bundles over
$L_1, L_2$ two line bundles over ![]() $C$. We denote by local curve the total space
$C$. We denote by local curve the total space ![]() $X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ with its natural
$X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ with its natural ![]() $\mathbf {T}=({{\mathbb {C}}}^{*})^{2}$-action on the fibers.
$\mathbf {T}=({{\mathbb {C}}}^{*})^{2}$-action on the fibers.
For ![]() $d> 0$ and
$d> 0$ and ![]() $n\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$, we denote by
$n\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$, we denote by ![]() $P_X=P_n(X, d[C])$ the moduli space of stable pairs
$P_X=P_n(X, d[C])$ the moduli space of stable pairs ![]() $[\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X\xrightarrow {s} F]\in \operatorname {D^{b}} (X)$ with curve class
$[\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X\xrightarrow {s} F]\in \operatorname {D^{b}} (X)$ with curve class ![]() $d[C]$ and
$d[C]$ and ![]() $\chi (F)=n$. The moduli space
$\chi (F)=n$. The moduli space ![]() $P_X$ has a perfect obstruction theory [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09a], but is, in general, non-proper. Still, the
$P_X$ has a perfect obstruction theory [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09a], but is, in general, non-proper. Still, the ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-action on
$\mathbf {T}$-action on ![]() $X$ induces one on
$X$ induces one on ![]() $P_X$ with proper
$P_X$ with proper ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus ![]() $P_X^{\mathbf {T}}$, therefore we can define invariants via Graber–Pandharipande virtual localization [Reference Graber and PandharipandeGP99]
$P_X^{\mathbf {T}}$, therefore we can define invariants via Graber–Pandharipande virtual localization [Reference Graber and PandharipandeGP99]
where ![]() $s_1,s_2$ are the generators of the
$s_1,s_2$ are the generators of the ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant cohomology of a point and
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant cohomology of a point and ![]() $N^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ is the virtual normal bundle. We denote its generating series by
$N^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ is the virtual normal bundle. We denote its generating series by
Pandharipande and Pixton extensively studied stable pair theory on local curves [Reference Pandharipande and PixtonPP13, Reference Pandharipande and PixtonPP12] using degeneration techniques and relative invariants, focusing on the rationality of the generating series, including the case of descendent insertions. The novelty of this paper is the different approach which only relies on the Graber–Pandharipande localization, without degenerating the curve ![]() $C$, and the virtual structure constructed on the double nested Hilbert schemes
$C$, and the virtual structure constructed on the double nested Hilbert schemes ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$. This is in particular useful to address the
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$. This is in particular useful to address the ![]() $K$-theoretic generalizations of stable pair invariants (cf. § 1.8).
$K$-theoretic generalizations of stable pair invariants (cf. § 1.8).
Our main result is that the generating series ![]() $\mathsf {PT}_d(X;q)$ of such invariants is controlled by some universal series and determine them under the anti-diagonal restriction
$\mathsf {PT}_d(X;q)$ of such invariants is controlled by some universal series and determine them under the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$.
$s_1+s_2=0$.
Theorem 1.3 (Theorems 8.2 and 8.1)
There are universal series ![]() $A_{\lambda }(q), B_\lambda (q), C_\lambda (q)\in {{\mathbb {Q}}}(s_1,s_2)[\![ q]\!]$ such that
$A_{\lambda }(q), B_\lambda (q), C_\lambda (q)\in {{\mathbb {Q}}}(s_1,s_2)[\![ q]\!]$ such that
where ![]() $\bar {\lambda }$ is the conjugate partition of
$\bar {\lambda }$ is the conjugate partition of ![]() $\lambda$,
$\lambda$, ![]() $n(\lambda )=\sum _{i=0}^{l(\lambda )}i\cdot \lambda _{i}$ and
$n(\lambda )=\sum _{i=0}^{l(\lambda )}i\cdot \lambda _{i}$ and ![]() $g=g(C)$. Moreover, under the anti-diagonal restriction
$g=g(C)$. Moreover, under the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$
$s_1+s_2=0$
 \begin{align*} A_{\lambda}(q,s_1,-s_1)&=(-s_1^{2})^{|\lambda|}\cdot \prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{2},\\ B_{\lambda}(-q,s_1,-s_1)&=(-1)^{n(\lambda)}\cdot s_1^{-|\lambda|} \cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{-1}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)}),\\ C_{\lambda}(-q,s_1,-s_1)&=(-1)^{n(\bar{\lambda})} \cdot (-s_1)^{-|\lambda|}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{-1} \cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)}). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} A_{\lambda}(q,s_1,-s_1)&=(-s_1^{2})^{|\lambda|}\cdot \prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{2},\\ B_{\lambda}(-q,s_1,-s_1)&=(-1)^{n(\lambda)}\cdot s_1^{-|\lambda|} \cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{-1}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)}),\\ C_{\lambda}(-q,s_1,-s_1)&=(-1)^{n(\bar{\lambda})} \cdot (-s_1)^{-|\lambda|}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{-1} \cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)}). \end{align*}We now sketch the main steps required in proving Theorem 1.3.
1.4 Proof of the main theorem
The connected components of the ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus ![]() $P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf {T}}$ are double nested Hilbert schemes of points
$P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf {T}}$ are double nested Hilbert schemes of points ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, for suitable reversed plane partitions
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, for suitable reversed plane partitions ![]() $\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ and Young diagram
$\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ and Young diagram ![]() $\lambda$. In fact, pushing forward via
$\lambda$. In fact, pushing forward via ![]() $X\to C$ a
$X\to C$ a ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed stable pair
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed stable pair ![]() $[\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X\xrightarrow {s}F]$, corresponds a decomposition
$[\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X\xrightarrow {s}F]$, corresponds a decomposition ![]() $\bigoplus _{(i,j)\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}^{2}}[\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_C\xrightarrow {s_{ij}} F_{ij}]$ on
$\bigoplus _{(i,j)\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}^{2}}[\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_C\xrightarrow {s_{ij}} F_{ij}]$ on ![]() $C$, where every
$C$, where every ![]() $F_{ij}$ is a line bundle with section
$F_{ij}$ is a line bundle with section ![]() $s_{ij}$. These data produce divisors
$s_{ij}$. These data produce divisors ![]() $Z_{ij}\subset C$ satisfying the nesting conditions dictated by
$Z_{ij}\subset C$ satisfying the nesting conditions dictated by ![]() $\lambda$, in other words an element of
$\lambda$, in other words an element of ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$.
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$.
On each connected component, there is an induced virtual fundamental class ![]() $[C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}]^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{\mathsf {PT}}$, coming from the deformation of stable pairs. This virtual cycle coincides with that constructed by the zero-locus construction of Theorem 1.2. By determining the class in
$[C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}]^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{\mathsf {PT}}$, coming from the deformation of stable pairs. This virtual cycle coincides with that constructed by the zero-locus construction of Theorem 1.2. By determining the class in ![]() $K$-theory of the virtual normal bundle, stable pair invariants on
$K$-theory of the virtual normal bundle, stable pair invariants on ![]() $X$ are reduced to (
$X$ are reduced to (![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant) virtual intersection numbers on
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant) virtual intersection numbers on ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, namely
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, namely
The generating series of these invariants, for every fixed Young diagram ![]() $\lambda$, is controlled by three universal series (Theorem 5.1)
$\lambda$, is controlled by three universal series (Theorem 5.1)
 \[ \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}) =A_{\lambda}^{g-1}\cdot B_{\lambda}^{\deg L_1}\cdot C_{\lambda}^{\deg L_2}\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(s_1,s_2)[\![ q ]\!]. \]
\[ \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}) =A_{\lambda}^{g-1}\cdot B_{\lambda}^{\deg L_1}\cdot C_{\lambda}^{\deg L_2}\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(s_1,s_2)[\![ q ]\!]. \]
This universal structure is proven by following the strategy of [Reference Ellingsrud, Göttsche and LehnEGL01]. In fact, these invariants are multiplicative on triples of the form ![]() $(C, L_1, L_2)=(C'\sqcup C'', L'_1\oplus L''_1, L'_2\oplus L''_2)$ and are polynomial in the Chern numbers of
$(C, L_1, L_2)=(C'\sqcup C'', L'_1\oplus L''_1, L'_2\oplus L''_2)$ and are polynomial in the Chern numbers of ![]() $(C, L_1, L_2)$. The latter is obtained by pushing the virtual intersection number to
$(C, L_1, L_2)$. The latter is obtained by pushing the virtual intersection number to ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ on the smooth ambient space
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ on the smooth ambient space ![]() $A_{C, \mathbf {n}_\lambda }$, a product of symmetric powers of
$A_{C, \mathbf {n}_\lambda }$, a product of symmetric powers of ![]() $C$, and later to a product of Jacobians
$C$, and later to a product of Jacobians ![]() $\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{n_i}(C)$, where the integrand is a polynomial on well-behaved cohomology classes.
$\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{n_i}(C)$, where the integrand is a polynomial on well-behaved cohomology classes.
By the universal structure any computation is reduced to a basis of the three-dimensional ![]() ${{\mathbb {Q}}}$-vector space of Chern numbers of triples
${{\mathbb {Q}}}$-vector space of Chern numbers of triples ![]() $(C, L_1, L_2)$. A simple basis consists of the Chern numbers of
$(C, L_1, L_2)$. A simple basis consists of the Chern numbers of ![]() $({{\mathbb {P}}}^{1},\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}, \operatorname {\mathcal {O}})$ and any two
$({{\mathbb {P}}}^{1},\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}, \operatorname {\mathcal {O}})$ and any two ![]() $({{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}, L_1, L_2)$ with
$({{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}, L_1, L_2)$ with ![]() $L_1\otimes L_2 =K_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$. In both cases, the invariants are explicitly determined under the anti-diagonal restriction
$L_1\otimes L_2 =K_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$. In both cases, the invariants are explicitly determined under the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$ by further applying the virtual localization formula.
$s_1+s_2=0$ by further applying the virtual localization formula.
1.5 Toric computations
The ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on ![]() ${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ canonically lifts to the double nested Hilbert scheme
${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ canonically lifts to the double nested Hilbert scheme ![]() ${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, with only finitely many
${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, with only finitely many ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed points, therefore we can further
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed points, therefore we can further ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-localize the invariants (1.1) to obtain
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-localize the invariants (1.1) to obtain
 \[ \int_{[{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}) =\bigg(\sum_{{\underline{Z}}\in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda], {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}}e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(-T^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{\underline{Z}}-N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}, L_1,L_2, {\underline{Z}} }) \bigg)\bigg|_{s_3=0}, \]
\[ \int_{[{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}) =\bigg(\sum_{{\underline{Z}}\in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda], {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}}e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(-T^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{\underline{Z}}-N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}, L_1,L_2, {\underline{Z}} }) \bigg)\bigg|_{s_3=0}, \]
where ![]() $s_3$ is the generator of the
$s_3$ is the generator of the ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-equivariant cohomology of a point and
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-equivariant cohomology of a point and ![]() $T^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{\underline {Z}}$ is the virtual tangent bundle of
$T^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{\underline {Z}}$ is the virtual tangent bundle of ![]() ${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ at the fixed point
${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ at the fixed point ![]() ${\underline {Z}}$.
${\underline {Z}}$.
Under the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$, this translates the computation of the invariants into a purely combinatorial problem, which we explicitly solve in the trivial vector bundle case
$s_1+s_2=0$, this translates the computation of the invariants into a purely combinatorial problem, which we explicitly solve in the trivial vector bundle case ![]() $L_1=L_2=\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$ and in the Calabi–Yau case
$L_1=L_2=\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$ and in the Calabi–Yau case ![]() $L_1\otimes L_2=K_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$. A few remarks are in order. In the trivial vector bundle case, the solution is equivalent to the vanishing
$L_1\otimes L_2=K_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$. A few remarks are in order. In the trivial vector bundle case, the solution is equivalent to the vanishing
for every reversed plane partition of positive size ![]() $|\mathbf {n}_\lambda |>0$. This relies on the vanishing
$|\mathbf {n}_\lambda |>0$. This relies on the vanishing ![]() $e^{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}(-T^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{\underline {Z}} - N^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1},L_1,L_2, {\underline {Z}} })=0$, which comes from a simple vanishing property of the topological vertex in stable pair theory proved in [Reference Maulik, Pandharipande and ThomasMPT10].
$e^{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}(-T^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{\underline {Z}} - N^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1},L_1,L_2, {\underline {Z}} })=0$, which comes from a simple vanishing property of the topological vertex in stable pair theory proved in [Reference Maulik, Pandharipande and ThomasMPT10].
In the Calabi–Yau case, the invariants turn out to be topological, under the anti-diagonal restriction.
Theorem 1.4 (Theorem 7.3)
Let ![]() $X$ be Calabi–Yau. Then the generating series of the invariants (1.1) after the restriction
$X$ be Calabi–Yau. Then the generating series of the invariants (1.1) after the restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$ coincides, up to a sign, with the generating series of the topological Euler characteristic
$s_1+s_2=0$ coincides, up to a sign, with the generating series of the topological Euler characteristic
 \[ \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|}\cdot \bigg( \int_{[{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}, L_1, L_2})\bigg)\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0} =(-1)^{\deg L_1(c_\lambda+|\lambda|)+ |\lambda|}\cdot \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}(-q)^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} e({{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}), \]
\[ \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|}\cdot \bigg( \int_{[{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}, L_1, L_2})\bigg)\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0} =(-1)^{\deg L_1(c_\lambda+|\lambda|)+ |\lambda|}\cdot \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}(-q)^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} e({{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}), \]
where ![]() $c_\lambda =\sum _{(i,j)\in \lambda }(j-i)$.
$c_\lambda =\sum _{(i,j)\in \lambda }(j-i)$.
This happens as, under the anti-diagonal restriction, each ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed point
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed point ![]() ${\underline {Z}}$ contributes with a sign
${\underline {Z}}$ contributes with a sign
which is independent of ![]() ${\underline {Z}}$ and the invariants amount to a (signed) count of the
${\underline {Z}}$ and the invariants amount to a (signed) count of the ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed points. It is not a priori clear how to obtain the same sign through the vertex formalism for stable pairs developed by Pandharipande and Thomas (PT) [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09b].
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed points. It is not a priori clear how to obtain the same sign through the vertex formalism for stable pairs developed by Pandharipande and Thomas (PT) [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09b].
Nevertheless, the topological nature of the invariants in the Calabi–Yau case is not surprising also for a non-toric curve ![]() $C$. If
$C$. If ![]() $X$ is Calabi–Yau and
$X$ is Calabi–Yau and ![]() $P_n(X, d[C])$ is proper, which happens only in rare cases, the anti-diagonal restriction would compute its virtual Euler characteristic and Behrend's weighted Euler characteristic, which is a purely motivic invariant of a scheme with a symmetric perfect obstruction theory [Reference BehrendBeh09].
$P_n(X, d[C])$ is proper, which happens only in rare cases, the anti-diagonal restriction would compute its virtual Euler characteristic and Behrend's weighted Euler characteristic, which is a purely motivic invariant of a scheme with a symmetric perfect obstruction theory [Reference BehrendBeh09].
1.6 Gromov–Witten/stable pairs correspondence
In the seminal work [Reference Maulik, Nekrasov, Okounkov and PandharipandeMNOP06a], a conjectural correspondence, known as the Maulik–Nekrasov– Okounkov–Pandharipande (MNOP) conjecture, between Gromov–Witten (GW) invariants and Donaldson–Thomas (DT) invariants of projective threefolds is formulated, proven for toric varieties in [Reference Maulik, Nekrasov, Okounkov and PandharipandeMNOP06a, Reference Maulik, Nekrasov, Okounkov and PandharipandeMNOP06b, Reference Maulik, Oblomkov, Okounkov and PandharipandeMOOP11] for primary insertions. By defining the GW/DT invariants via equivariant residues, the conjecture has been extended to local curves in [Reference Bryan and PandharipandeBP08] and proven by combining the results of [Reference Bryan and PandharipandeBP08, Reference Okounkov and PandharipandeOP10].
Stable pair invariants were later introduced by Pandharipande and Thomas [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09a] to give a more natural geometric interpretation of the MNOP conjecture through the DT/PT correspondence proved by Toda and Bridgeland in [Reference TodaTod10, Reference BridgelandBri11] using wall-crossing and Hall algebra techniques. The GW/stable pairs correspondence has been subsequently extended to include descendent insertions and to quasi-projective varieties whenever invariants can be defined through virtual localization. The correspondence had been confirmed by Pandharipande and Pixton for Calabi–Yau and Fano complete intersections in product of projective spaces and toric varieties [Reference Pandharipande and PixtonPP17, Reference Pandharipande and PixtonPP14] and had been recently addressed in [Reference Oblomkov, Okounkov and PandharipandeOOP20]. See [Reference PandharipandePan18] for a complete survey on the subject.
1.7 The local GW theory of curves
For ![]() $X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ a local curve, let
$X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ a local curve, let ![]() $\overline {M}^{\bullet }_h(X, d[C])$ denote the moduli space of stable maps (with possibly disconnected domain) of genus
$\overline {M}^{\bullet }_h(X, d[C])$ denote the moduli space of stable maps (with possibly disconnected domain) of genus ![]() $h$ and degree
$h$ and degree ![]() $d[C]$. Define the partition function of GW invariants of
$d[C]$. Define the partition function of GW invariants of ![]() $X$ (with a shifted exponent)
$X$ (with a shifted exponent)
 \begin{align*} &\mathsf{GW}_d(g|\deg L_1, \deg L_2;u)\\ &\quad =u^{2-2g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2} \sum_{h\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}u^{2h-2}\int_{[ \overline{M}^{\bullet}_h(X, d[C])^{\mathbf{T}}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}\frac{1}{e^{\mathbf{T}}(N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})}\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(s_1, s_2)( ( u ) ), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &\mathsf{GW}_d(g|\deg L_1, \deg L_2;u)\\ &\quad =u^{2-2g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2} \sum_{h\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}u^{2h-2}\int_{[ \overline{M}^{\bullet}_h(X, d[C])^{\mathbf{T}}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}\frac{1}{e^{\mathbf{T}}(N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})}\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(s_1, s_2)( ( u ) ), \end{align*}
where the dependence is only on the genus ![]() $g=g(C)$, the degrees of the line bundles and the degree
$g=g(C)$, the degrees of the line bundles and the degree ![]() $d$. The GW theory of local curves had been solved by Bryan and Pandharipande [Reference Bryan and PandharipandeBP08, Theorem 7.1] using a topological quantum field theory approach. Moreover they deduced an explicit closed formula for the partition function under the anti-diagonal restriction
$d$. The GW theory of local curves had been solved by Bryan and Pandharipande [Reference Bryan and PandharipandeBP08, Theorem 7.1] using a topological quantum field theory approach. Moreover they deduced an explicit closed formula for the partition function under the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$.
$s_1+s_2=0$.
Theorem 1.5 (Bryan–Pandharipande)
The partition function of GW invariants satisfies
 \begin{align*} \mathsf{GW}_{d}(g|\deg L_1,\deg L_2;u)|_{s_1+s_2=0}&=(-1)^{d(g-1-\deg L_2)} s_1^{d(2g-2-\deg L_1-\deg L_2)}\\ &\quad \cdot\sum_{\lambda\vdash d} Q^{({1}/{2})c_\lambda(\deg L_1- \deg L_2)}\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{2g-2-\deg L_1- \deg L_2}\\ &\quad \cdot i^{-\deg L_1-\deg L_2}(Q^{{h(\Box)}/{2}} -Q^{-{h(\Box)}/{2}})^{\deg L_1+\deg L_2}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \mathsf{GW}_{d}(g|\deg L_1,\deg L_2;u)|_{s_1+s_2=0}&=(-1)^{d(g-1-\deg L_2)} s_1^{d(2g-2-\deg L_1-\deg L_2)}\\ &\quad \cdot\sum_{\lambda\vdash d} Q^{({1}/{2})c_\lambda(\deg L_1- \deg L_2)}\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{2g-2-\deg L_1- \deg L_2}\\ &\quad \cdot i^{-\deg L_1-\deg L_2}(Q^{{h(\Box)}/{2}} -Q^{-{h(\Box)}/{2}})^{\deg L_1+\deg L_2}, \end{align*}
where we set ![]() $Q=e^{i u}$ and
$Q=e^{i u}$ and ![]() $i=\sqrt {-1}$.
$i=\sqrt {-1}$.
With this explicit expression it is immediate to check the GW/stable pairs correspondence under the anti-diagonal restriction.
Corollary 1.6 (Corollary 8.3)
Let ![]() $X$ be a local curve. Under the anti-diagonal restriction
$X$ be a local curve. Under the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$ the GW/stable pair correspondence holds
$s_1+s_2=0$ the GW/stable pair correspondence holds
after the change of variable ![]() $q=-e^{iu}$.
$q=-e^{iu}$.
1.8  $K$-theoretic refinement
$K$-theoretic refinement
The ![]() $K$-theoretic refinement of DT theory and stable pair theory have attracted much attention recently, both in mathematics and string theory: see, for example, [Reference ThomasTho20, Reference AfganiAfg20, Reference ArbesfeldArb21, Reference Fasola, Monavari and RicolfiFMR21] for Calabi–Yau threefolds, [Reference NekrasovNek20, Reference Nekrasov and PiazzalungaNP19, Reference Cao, Kool and MonavariCKM22a] for Calabi–Yau fourfolds and [Reference Nekrasov and OkounkovNO16, Reference OkounkovOko17, Reference Kononov, Okounkov and OsinenkoKOO21, Reference OkounkovOko19] for local curves.
$K$-theoretic refinement of DT theory and stable pair theory have attracted much attention recently, both in mathematics and string theory: see, for example, [Reference ThomasTho20, Reference AfganiAfg20, Reference ArbesfeldArb21, Reference Fasola, Monavari and RicolfiFMR21] for Calabi–Yau threefolds, [Reference NekrasovNek20, Reference Nekrasov and PiazzalungaNP19, Reference Cao, Kool and MonavariCKM22a] for Calabi–Yau fourfolds and [Reference Nekrasov and OkounkovNO16, Reference OkounkovOko17, Reference Kononov, Okounkov and OsinenkoKOO21, Reference OkounkovOko19] for local curves.
A scheme ![]() $X$ with a perfect obstruction theory is endowed not only with a virtual fundamental class, but also with a virtual structure sheaf
$X$ with a perfect obstruction theory is endowed not only with a virtual fundamental class, but also with a virtual structure sheaf ![]() $\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_X\in K_0(X)$. If
$\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_X\in K_0(X)$. If ![]() $X$ is proper,
$X$ is proper, ![]() $K$-theoretic invariants are simply of the form
$K$-theoretic invariants are simply of the form
where ![]() $V\in K_0(X)$. If
$V\in K_0(X)$. If ![]() $X$ is a local curve the moduli space of stable pairs
$X$ is a local curve the moduli space of stable pairs ![]() $P_X$ is, in general, not proper and
$P_X$ is, in general, not proper and ![]() $K$-theoretic stable pair invariants are defined by virtual localization [Reference Fantechi and GöttscheFG10] on the proper
$K$-theoretic stable pair invariants are defined by virtual localization [Reference Fantechi and GöttscheFG10] on the proper ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus ![]() $P_X^{\mathbf {T}}$, that is one set
$P_X^{\mathbf {T}}$, that is one set
 \[ \chi(P_X, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{P_X}\otimes V):= \chi\bigg(P_X^{\mathbf{T}}, \frac{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}\otimes V|_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}}{\Lambda^{\bullet} N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} \bigg)\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1, \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2). \]
\[ \chi(P_X, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{P_X}\otimes V):= \chi\bigg(P_X^{\mathbf{T}}, \frac{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}\otimes V|_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}}{\Lambda^{\bullet} N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} \bigg)\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1, \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2). \]
In § 9 we show that, also in the ![]() $K$-theoretic setting, the invariants are controlled by universal series.
$K$-theoretic setting, the invariants are controlled by universal series.
The naive generalization of cohomological invariants is for ![]() $V=\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X$, that is no insertions. However, we learn from Nekrasov and Okounkov [Reference Nekrasov and OkounkovNO16] that it is more natural to consider the twisted virtual structure sheaf
$V=\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X$, that is no insertions. However, we learn from Nekrasov and Okounkov [Reference Nekrasov and OkounkovNO16] that it is more natural to consider the twisted virtual structure sheaf
where ![]() $K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}^{1/2}$ is a square rootFootnote 1 of the virtual canonical bundle. Denote by
$K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}^{1/2}$ is a square rootFootnote 1 of the virtual canonical bundle. Denote by ![]() $\mathsf {PT}^{\hat {K}}_d(X;q)$ the generating series of
$\mathsf {PT}^{\hat {K}}_d(X;q)$ the generating series of ![]() $K$-theoretic invariants with
$K$-theoretic invariants with ![]() $V=K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}^{1/2}$.
$V=K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}^{1/2}$.
Theorem 1.7 (Corollary 9.5)
There exist universal series
such that
Moreover, the universal series are explicitly computed under ![]() $\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2=1$.
$\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2=1$.
We are not aware of a ![]() $K$-theoretic GW refinement for which a refined GW/stable pairs correspondence holds.
$K$-theoretic GW refinement for which a refined GW/stable pairs correspondence holds.
Conventions
All schemes are separated and of finite type over ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}$. We let
${{\mathbb {C}}}$. We let ![]() $K^{0}(X)$ be the
$K^{0}(X)$ be the ![]() $K$-group of vector bundles on
$K$-group of vector bundles on ![]() $X$. When
$X$. When ![]() $X$ carries an action by an algebraic torus
$X$ carries an action by an algebraic torus ![]() $\mathbf {T}$, we let
$\mathbf {T}$, we let ![]() $K^{0}_\mathbf {T}(X)$ be the
$K^{0}_\mathbf {T}(X)$ be the ![]() $K$-group of
$K$-group of ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant vector bundles on
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant vector bundles on ![]() $X$. Similarly, we let
$X$. Similarly, we let ![]() $K_0(X)$ denote the
$K_0(X)$ denote the ![]() $K$-group of coherent sheaves on
$K$-group of coherent sheaves on ![]() $X$, and we let
$X$, and we let ![]() $K_0^{\mathbf {T}}(X)$ be the
$K_0^{\mathbf {T}}(X)$ be the ![]() $K$-group of (the abelian category of)
$K$-group of (the abelian category of) ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant coherent sheaves on
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant coherent sheaves on ![]() $X$. When
$X$. When ![]() $X$ is smooth, the natural
$X$ is smooth, the natural ![]() ${{\mathbb {Z}}}$-linear map
${{\mathbb {Z}}}$-linear map ![]() $K^{0}(X) \to K_0(X)$, respectively
$K^{0}(X) \to K_0(X)$, respectively ![]() $K^{0}_{\mathbf {T}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$-linear map
$K^{0}_{\mathbf {T}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$-linear map ![]() $K^{0}_{\mathbf {T}}(X) \to K_0^{\mathbf {T}}(X)$, is an isomorphism. Chow groups
$K^{0}_{\mathbf {T}}(X) \to K_0^{\mathbf {T}}(X)$, is an isomorphism. Chow groups ![]() $A^{\ast } (X)$ and cohomology groups
$A^{\ast } (X)$ and cohomology groups ![]() $H^{\ast }(X)$ are taken with rational coefficients. We use
$H^{\ast }(X)$ are taken with rational coefficients. We use ![]() $(\cdot )^{\vee }$ for the derived dual of complexes and
$(\cdot )^{\vee }$ for the derived dual of complexes and ![]() $(\cdot )^{*}$ for the (underived) dual of coherent sheaves. For clarity of exposition, we suppress various pullback maps, whenever they are clear from the context.
$(\cdot )^{*}$ for the (underived) dual of coherent sheaves. For clarity of exposition, we suppress various pullback maps, whenever they are clear from the context.
2. Double nested Hilbert schemes
2.1 Young diagrams
By definition, a partition ![]() $\lambda$ of
$\lambda$ of ![]() $d\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}_{\geq 0}$ is a finite sequence of positive integers
$d\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}_{\geq 0}$ is a finite sequence of positive integers
where
The number of parts of ![]() $\lambda$ is called the length of
$\lambda$ is called the length of ![]() $\lambda$ and is denoted by
$\lambda$ and is denoted by ![]() $l(\lambda )$. A partition
$l(\lambda )$. A partition ![]() $\lambda$ can be equivalently described by its associated Young diagram, which is the collection of
$\lambda$ can be equivalently described by its associated Young diagram, which is the collection of ![]() $d$ boxes in
$d$ boxes in ![]() ${{\mathbb {Z}}}^{2}$ located at
${{\mathbb {Z}}}^{2}$ located at ![]() $(i,j)$ where
$(i,j)$ where ![]() $0\leq j< \lambda _{i}$.Footnote 2
$0\leq j< \lambda _{i}$.Footnote 2
Given a partition ![]() $\lambda$, a reversed plane partition
$\lambda$, a reversed plane partition ![]() $\mathbf {n}_\lambda =(n_{\Box })_{\Box \in \lambda }\in \mathbb {Z}_{\geq 0}$ is a collection of non-negative integers such that
$\mathbf {n}_\lambda =(n_{\Box })_{\Box \in \lambda }\in \mathbb {Z}_{\geq 0}$ is a collection of non-negative integers such that ![]() $n_{\Box }\leq n_{\Box '}$ for any
$n_{\Box }\leq n_{\Box '}$ for any ![]() $\Box,\Box '\in \lambda$ such that
$\Box,\Box '\in \lambda$ such that ![]() $\Box \leq \Box '$.Footnote 3 In other words, a reversed plane partition is a Young diagram labelled with non-negative integers which are non-decreasing in rows and columns (Figure 1). The size of a reversed plane partition is
$\Box \leq \Box '$.Footnote 3 In other words, a reversed plane partition is a Young diagram labelled with non-negative integers which are non-decreasing in rows and columns (Figure 1). The size of a reversed plane partition is
The conjugate partition ![]() $\bar{\lambda}$ is obtained by reflecting the Young diagram of
$\bar{\lambda}$ is obtained by reflecting the Young diagram of ![]() $\lambda$ about the
$\lambda$ about the ![]() $i=j$ line.
$i=j$ line.

Figure 1. On the left, a Young diagram of size 8. On the right, a reversed plane partition of size 14.
In the paper we require the following standard quantities. Given a box in the Young diagram ![]() $\box \in \lambda$, define the content
$\box \in \lambda$, define the content ![]() $c(\Box )=j-i$ and the hooklength
$c(\Box )=j-i$ and the hooklength ![]() $h(\Box )=\lambda _{i}+\bar {\lambda }_{j}-i-j-1$. The total content
$h(\Box )=\lambda _{i}+\bar {\lambda }_{j}-i-j-1$. The total content
satisfies the following identities (cf. [Reference MacdonaldMac95, p. 11]):
where
 \[ n(\lambda)=\sum_{i=0}^{l(\lambda)}i\cdot\lambda_{i}. \]
\[ n(\lambda)=\sum_{i=0}^{l(\lambda)}i\cdot\lambda_{i}. \]
For any Young diagram ![]() $\lambda$ there is an associated graph, where any box of
$\lambda$ there is an associated graph, where any box of ![]() $\lambda$ corresponds to a vertex and any face common to two boxes correspond to an edge connecting the corresponding vertices (Figure 2). A square of this graph is a circuit made of four different edges.
$\lambda$ corresponds to a vertex and any face common to two boxes correspond to an edge connecting the corresponding vertices (Figure 2). A square of this graph is a circuit made of four different edges.
Lemma 2.1 Let ![]() $\lambda$ be a Young diagram and denote by
$\lambda$ be a Young diagram and denote by ![]() $V$,
$V$,![]() $E$ and
$E$ and ![]() $Q$ the number of vertices, edges and squares of the associated graph, respectively. Then
$Q$ the number of vertices, edges and squares of the associated graph, respectively. Then

Figure 2. A Young diagram and its associated graph, with eight vertices, nine edges and two squares.
Proof. We prove the claim by induction on the size of ![]() $\lambda$. If
$\lambda$. If ![]() $|\lambda |=1$, this is clear. Suppose it holds for all
$|\lambda |=1$, this is clear. Suppose it holds for all ![]() $\lambda$ with
$\lambda$ with ![]() $|\lambda |\leq n-1$. Then we construct
$|\lambda |\leq n-1$. Then we construct ![]() $\lambda$ of size
$\lambda$ of size ![]() $n$ by adding a box with lattice coordinates
$n$ by adding a box with lattice coordinates ![]() $(i,j)$ to a Young diagram
$(i,j)$ to a Young diagram ![]() $\tilde {\lambda }$ of size
$\tilde {\lambda }$ of size ![]() $n-1$. There are two possibilities: either one of
$n-1$. There are two possibilities: either one of ![]() $i,j$ is zero, so we added one vertex and one edge, or both
$i,j$ is zero, so we added one vertex and one edge, or both ![]() $i,j$ are non-zero, so we added one vertex, one square and two edges. In both cases the claim is proved.
$i,j$ are non-zero, so we added one vertex, one square and two edges. In both cases the claim is proved.
2.2 Double nested Hilbert schemes
Let ![]() $X$ be a projective scheme and
$X$ be a projective scheme and ![]() $\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}(1)$ a fixed ample line bundle. The Hilbert polynomial of a closed subscheme
$\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}(1)$ a fixed ample line bundle. The Hilbert polynomial of a closed subscheme ![]() $Y\subset X$ is defined by
$Y\subset X$ is defined by
Given a polynomial ![]() $p(m)$, the Hilbert scheme is the moduli space parametrizing closed subschemes
$p(m)$, the Hilbert scheme is the moduli space parametrizing closed subschemes ![]() $Y\subset X$ with Hilbert polynomial
$Y\subset X$ with Hilbert polynomial ![]() $p(m)$, which is representable by a projective scheme (e.g. by [Reference GrothendieckGro61]). We consider here a more general situation, where we replace closed subschemes by flags of closed subschemes, satisfying certain nesting conditions dictated by Young diagrams.
$p(m)$, which is representable by a projective scheme (e.g. by [Reference GrothendieckGro61]). We consider here a more general situation, where we replace closed subschemes by flags of closed subschemes, satisfying certain nesting conditions dictated by Young diagrams.
Let ![]() $\lambda$ be a Young diagram and
$\lambda$ be a Young diagram and ![]() $\mathbf {p}_\lambda =(p_{\Box })_{\Box \in \lambda }\in \mathbb {Z}[x]$ be a collection of polynomials indexed by
$\mathbf {p}_\lambda =(p_{\Box })_{\Box \in \lambda }\in \mathbb {Z}[x]$ be a collection of polynomials indexed by ![]() $\lambda$. If all
$\lambda$. If all ![]() $p_{\Box }$ are non-negative integers which are non-decreasing in rows and columns,
$p_{\Box }$ are non-negative integers which are non-decreasing in rows and columns, ![]() $\mathbf {p}_\lambda =\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ is a reversed plane partition.
$\mathbf {p}_\lambda =\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ is a reversed plane partition.
Definition 2.2 Let ![]() $X$ be a projective scheme and
$X$ be a projective scheme and ![]() $\mathbf {p}_\lambda$ as previously. The double nested Hilbert functor of
$\mathbf {p}_\lambda$ as previously. The double nested Hilbert functor of ![]() $X$ of type
$X$ of type ![]() $\mathbf {p}_\lambda$ is the moduli functor
$\mathbf {p}_\lambda$ is the moduli functor
Remark 2.3 If ![]() $|\lambda |=1$ we recover the classical Hilbert scheme, whereas if
$|\lambda |=1$ we recover the classical Hilbert scheme, whereas if ![]() $\lambda$ is a horizontal (or vertical) Young diagram we recover the nested Hilbert scheme, already widely studied in the literature.
$\lambda$ is a horizontal (or vertical) Young diagram we recover the nested Hilbert scheme, already widely studied in the literature.
Proposition 2.4 Let ![]() $X$ be a projective scheme and
$X$ be a projective scheme and ![]() $\mathbf {p}_\lambda$ as previously. Then
$\mathbf {p}_\lambda$ as previously. Then ![]() ${\underline {\operatorname {Hilb}}}^{\mathbf {p}_{\lambda }}(X)$ is representable by a projective scheme
${\underline {\operatorname {Hilb}}}^{\mathbf {p}_{\lambda }}(X)$ is representable by a projective scheme ![]() $\operatorname {Hilb}^{\mathbf {p}_{\lambda }}(X)$, which we call the double nested Hilbert scheme.
$\operatorname {Hilb}^{\mathbf {p}_{\lambda }}(X)$, which we call the double nested Hilbert scheme.
Proof. We prove our claim in the case ![]() $\mathbf {p}_{\lambda }$ is
$\mathbf {p}_{\lambda }$ is

as the general case will follow by an analogous reasoning. There are forgetful maps between nested Hilbert functors
 \begin{align*} &{\underline{\operatorname{Hilb}}}^{[p_{00}, p_{01},p_{11}]}(X)\to {\underline{\operatorname{Hilb}}}^{[p_{00},p_{11}]}(X),\\ &{\underline{\operatorname{Hilb}}}^{[p_{00}, p_{10},p_{11}]}(X)\to {\underline{\operatorname{Hilb}}}^{[p_{00},p_{11}]}(X), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &{\underline{\operatorname{Hilb}}}^{[p_{00}, p_{01},p_{11}]}(X)\to {\underline{\operatorname{Hilb}}}^{[p_{00},p_{11}]}(X),\\ &{\underline{\operatorname{Hilb}}}^{[p_{00}, p_{10},p_{11}]}(X)\to {\underline{\operatorname{Hilb}}}^{[p_{00},p_{11}]}(X), \end{align*}which forget the second subscheme of the corresponding flag. Consider their fiber product

There is an obvious morphism of functors
which is easily checked to be an isomorphism by comparing each flat family of flags over every scheme ![]() $T$. We conclude by the fact that the nested Hilbert functors (and their fiber products) are representable by a projective scheme by [Reference SernesiSer06, Theorem 4.5.1].
$T$. We conclude by the fact that the nested Hilbert functors (and their fiber products) are representable by a projective scheme by [Reference SernesiSer06, Theorem 4.5.1].
Thanks to representability, double nested Hilbert schemes are equipped with universal subschemes, for any ![]() $\Box \in \lambda$,
$\Box \in \lambda$,
such that the fiber over a point ![]() ${\underline {Z}}=(Z_\Box )_{\Box \in \lambda }\in \operatorname {Hilb}^{\mathbf {p}_{\lambda }}(X)$ is
${\underline {Z}}=(Z_\Box )_{\Box \in \lambda }\in \operatorname {Hilb}^{\mathbf {p}_{\lambda }}(X)$ is
Remark 2.5 If ![]() $\mathbf {p}_{\lambda }=\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }$, Definition 2.2 generalizes to
$\mathbf {p}_{\lambda }=\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }$, Definition 2.2 generalizes to ![]() $X$ quasi-projective. In fact, let
$X$ quasi-projective. In fact, let ![]() $X\subset \overline {X}$ be any compactification of
$X\subset \overline {X}$ be any compactification of ![]() $X$. We define the double nested Hilbert scheme points as the open subscheme
$X$. We define the double nested Hilbert scheme points as the open subscheme
consisting of the zero-dimensional subschemes supported on ![]() $X\subset \overline {X}$.
$X\subset \overline {X}$.
Double nested Hilbert schemes of points are rarely smooth varieties. Some smooth examples consist of:
(i)
 $|\lambda |=1$,
$|\lambda |=1$,  $X$ a smooth quasi-projective curve or surface (see, e.g., [Reference NakajimaNak99]);
$X$ a smooth quasi-projective curve or surface (see, e.g., [Reference NakajimaNak99]);(ii)
 $\lambda$ a vertical/horizontal Young diagram,
$\lambda$ a vertical/horizontal Young diagram,  $X$ a smooth quasi-projective curve (see, e.g., [Reference CheahChe98]).
$X$ a smooth quasi-projective curve (see, e.g., [Reference CheahChe98]).
In general, ![]() $X^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ is singular even for
$X^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ is singular even for ![]() $X$ a smooth quasi-projective curve.
$X$ a smooth quasi-projective curve.
Example 2.6 Let ![]() $C$ be a smooth curve and consider the reversed plane partition
$C$ be a smooth curve and consider the reversed plane partition ![]() $\mathbf {n}_\lambda$
$\mathbf {n}_\lambda$

There are two types of flags of divisors, of the form

where ![]() $P,Q\in C$. Therefore, its reduced scheme structure consists of two irreducible components
$P,Q\in C$. Therefore, its reduced scheme structure consists of two irreducible components ![]() $C\times C\cup C\times C$, intersecting at the diagonals of
$C\times C\cup C\times C$, intersecting at the diagonals of ![]() $C\times C$.
$C\times C$.
Singularities make it hard to perform intersection theory on ![]() $X^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$. To remedy this we construct, in special cases, virtual fundamental classes in
$X^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$. To remedy this we construct, in special cases, virtual fundamental classes in ![]() $A_*(X^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$. We briefly recall the language of perfect obstruction theories of Behrend and Fantechi [Reference Behrend and FantechiBF97] and Li and Tian [Reference Li and TianLT98].
$A_*(X^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$. We briefly recall the language of perfect obstruction theories of Behrend and Fantechi [Reference Behrend and FantechiBF97] and Li and Tian [Reference Li and TianLT98].
2.3 Perfect obstruction theories
A perfect obstruction theory on a scheme ![]() $X$ is the datum of a morphism
$X$ is the datum of a morphism
in ![]() $\mathbf {D}^{[-1,0]}(X)$, where
$\mathbf {D}^{[-1,0]}(X)$, where ![]() ${{\mathbb {E}}}$ is a perfect complex of perfect amplitude contained in
${{\mathbb {E}}}$ is a perfect complex of perfect amplitude contained in ![]() $[-1,0]$, such that
$[-1,0]$, such that ![]() $h^{0}(\phi )$ is an isomorphism and
$h^{0}(\phi )$ is an isomorphism and ![]() $h^{-1}(\phi )$ is surjective. Here,
$h^{-1}(\phi )$ is surjective. Here, ![]() ${{\mathbb {L}}}_X = \tau _{\geq -1}L_X^{\bullet }$ is the cut-off at
${{\mathbb {L}}}_X = \tau _{\geq -1}L_X^{\bullet }$ is the cut-off at ![]() $-1$ of the full cotangent complex
$-1$ of the full cotangent complex ![]() $L_X^{\bullet } \in \mathbf {D}^{[-\infty,0]}(X)$. A perfect obstruction theory is called symmetric (see [Reference Behrend and FantechiBF08]) if there exists an isomorphism
$L_X^{\bullet } \in \mathbf {D}^{[-\infty,0]}(X)$. A perfect obstruction theory is called symmetric (see [Reference Behrend and FantechiBF08]) if there exists an isomorphism ![]() $\theta \colon {{\mathbb {E}}} \xrightarrow {\sim } {{\mathbb {E}}}^{\vee }[1]$ such that
$\theta \colon {{\mathbb {E}}} \xrightarrow {\sim } {{\mathbb {E}}}^{\vee }[1]$ such that ![]() $\theta = \theta ^{\vee }[1]$. The virtual dimension of
$\theta = \theta ^{\vee }[1]$. The virtual dimension of ![]() $X$ with respect to
$X$ with respect to ![]() $({{\mathbb {E}}},\phi )$ is the integer
$({{\mathbb {E}}},\phi )$ is the integer ![]() $\operatorname {vd} = \operatorname {rk} {{\mathbb {E}}}$. This is just
$\operatorname {vd} = \operatorname {rk} {{\mathbb {E}}}$. This is just ![]() $\operatorname {rk} E^{0} - \operatorname {rk} E^{-1}$ if one can write
$\operatorname {rk} E^{0} - \operatorname {rk} E^{-1}$ if one can write ![]() ${{\mathbb {E}}} = [E^{-1}\to E^{0}]$.
${{\mathbb {E}}} = [E^{-1}\to E^{0}]$.
A perfect obstruction theory determines a cone
Letting ![]() $\iota \colon X \hookrightarrow E_1$ be the zero section of the vector bundle
$\iota \colon X \hookrightarrow E_1$ be the zero section of the vector bundle ![]() $E_1$, the induced virtual fundamental class on
$E_1$, the induced virtual fundamental class on ![]() $X$ is the refined intersection
$X$ is the refined intersection
By a result of Siebert [Reference SiebertSie04, Theorem 4.6], the virtual fundamental class depends only on the ![]() $K$-theory class of
$K$-theory class of ![]() ${{\mathbb {E}}}$.
${{\mathbb {E}}}$.
Example 2.7 Let ![]() $\iota : Z=Z(s)\hookrightarrow A$ be the zero locus of a section
$\iota : Z=Z(s)\hookrightarrow A$ be the zero locus of a section ![]() $s\in \Gamma (A,{{\mathcal {E}}})$, where
$s\in \Gamma (A,{{\mathcal {E}}})$, where ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is a vector bundle over a smooth quasi-projective variety
${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is a vector bundle over a smooth quasi-projective variety ![]() $A$. Then there exists an induced perfect obstruction theory on
$A$. Then there exists an induced perfect obstruction theory on ![]() $Z$
$Z$

in ![]() $\mathbf {D}^{[-1,0]}(Z)$, where we represented the truncated cotangent complex by means of the exterior derivative
$\mathbf {D}^{[-1,0]}(Z)$, where we represented the truncated cotangent complex by means of the exterior derivative ![]() $\mathrm {d}$ constructed out of the ideal sheaf
$\mathrm {d}$ constructed out of the ideal sheaf ![]() ${{\mathcal {I}}} \subset \operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{Z}$ of the inclusion
${{\mathcal {I}}} \subset \operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{Z}$ of the inclusion ![]() $Z \hookrightarrow A$. Moreover,
$Z \hookrightarrow A$. Moreover,
where ![]() $e(\cdot )$ denotes the Euler class.
$e(\cdot )$ denotes the Euler class.
2.4 Points on curves
Let ![]() $C$ be an irreducible smooth quasi-projective curve and
$C$ be an irreducible smooth quasi-projective curve and ![]() $\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }$ a reversed plane partition. In this section we show that
$\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }$ a reversed plane partition. In this section we show that ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }]}$ is the zero locus of a section of a vector bundle over a smooth ambient space, and therefore admits a perfect obstruction theory as in Example 2.7.
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }]}$ is the zero locus of a section of a vector bundle over a smooth ambient space, and therefore admits a perfect obstruction theory as in Example 2.7.
We define
 \begin{align*} A_{C,\mathbf{n}_{\lambda}}=C^{[n_{00}]}\times \prod_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}} C^{[n_{ij}-n_{i-1,j}]} \times \prod_{\substack{(l,k)\in \lambda\\ k\geq 1}} C^{[n_{lk}-n_{l,k-1}]}. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} A_{C,\mathbf{n}_{\lambda}}=C^{[n_{00}]}\times \prod_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}} C^{[n_{ij}-n_{i-1,j}]} \times \prod_{\substack{(l,k)\in \lambda\\ k\geq 1}} C^{[n_{lk}-n_{l,k-1}]}. \end{align*}
As ![]() $C^{[n]}\cong C^{(n)}$ is a symmetric product via the Hilbert–Chow morphism,
$C^{[n]}\cong C^{(n)}$ is a symmetric product via the Hilbert–Chow morphism, ![]() $A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}$ is a smooth quasi-projective variety of dimension
$A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}$ is a smooth quasi-projective variety of dimension
 \[ \dim(A_{C,\mathbf{n}_{\lambda}})=n_{00}+\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}}(n_{ij}-n_{i-1,j})+\sum_{\substack{(l,k)\in \lambda\\ k\geq 1}}(n_{lk}-n_{l,k-1}). \]
\[ \dim(A_{C,\mathbf{n}_{\lambda}})=n_{00}+\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}}(n_{ij}-n_{i-1,j})+\sum_{\substack{(l,k)\in \lambda\\ k\geq 1}}(n_{lk}-n_{l,k-1}). \]
To ease the notation, we denote its elements by ![]() $\underline {Z}=((Z_{00}, X_{ij},Y_{lk}))_{ij,lk}\in A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}$, where
$\underline {Z}=((Z_{00}, X_{ij},Y_{lk}))_{ij,lk}\in A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}$, where ![]() $Z_{00}\subset C$ is a divisor of length
$Z_{00}\subset C$ is a divisor of length ![]() $n_{00}$ and
$n_{00}$ and ![]() $X_{ij}\subset C$ (respectively,
$X_{ij}\subset C$ (respectively, ![]() $Y_{lk}\subset C$) is a divisor of length
$Y_{lk}\subset C$) is a divisor of length ![]() $n_{ij}-n_{i-1,j}$ (respectively,
$n_{ij}-n_{i-1,j}$ (respectively, ![]() $n_{lk}-n_{l,k-1}$).
$n_{lk}-n_{l,k-1}$).
Here ![]() $A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}$ comes equipped with universal divisors, which we denote by
$A_{C,\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }}$ comes equipped with universal divisors, which we denote by
with fibers are
For every ![]() $(i,j)\in \lambda$ with
$(i,j)\in \lambda$ with ![]() $i,j\geq 1$ define the universal effective divisors
$i,j\geq 1$ define the universal effective divisors
Theorem 2.8 Let ![]() $C$ be an irreducible smooth quasi-projective curve,
$C$ be an irreducible smooth quasi-projective curve, ![]() $\pi :C\times A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }\to A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }$ be the natural projection and define the vector bundle
$\pi :C\times A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }\to A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }$ be the natural projection and define the vector bundle
 \begin{align*} {{\mathcal{E}}}= \bigoplus_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Gamma^{2}_{ij} }(\Gamma^{1}_{ij}). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} {{\mathcal{E}}}= \bigoplus_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Gamma^{2}_{ij} }(\Gamma^{1}_{ij}). \end{align*}
Then there exists a section ![]() $s$ of
$s$ of ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}$ whose zero set is isomorphic to
${{\mathcal {E}}}$ whose zero set is isomorphic to ![]() $C^{[ \mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$
$C^{[ \mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$

Proof. Note that ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is a vector bundle, as by cohomology and base change all higher direct images vanish
${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is a vector bundle, as by cohomology and base change all higher direct images vanish
There is a closed immersion
given on closed points ![]() $(Z_{ij})_{(i,j)\in \lambda }\in C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ as
$(Z_{ij})_{(i,j)\in \lambda }\in C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ as
Define sections ![]() $\tilde {s}_{ij}\in H^{0}(C\times A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }, \operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{\Gamma ^{2}_{ij} }(\Gamma ^{1}_{ij}) )$ as the composition
$\tilde {s}_{ij}\in H^{0}(C\times A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }, \operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{\Gamma ^{2}_{ij} }(\Gamma ^{1}_{ij}) )$ as the composition
where ![]() $s'_{ij}$ is the section vanishing on
$s'_{ij}$ is the section vanishing on ![]() $\Gamma ^{1}_{ij}$ whereas the second morphism is the restriction along
$\Gamma ^{1}_{ij}$ whereas the second morphism is the restriction along ![]() $j:\Gamma ^{2}_{ij}\to A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }\times C$; in other words,
$j:\Gamma ^{2}_{ij}\to A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }\times C$; in other words, ![]() $\tilde {s}_{ij}=j_*j^{*} s'_{ij}$. The sections
$\tilde {s}_{ij}=j_*j^{*} s'_{ij}$. The sections ![]() $\tilde {s}_{ij}$ induce sections
$\tilde {s}_{ij}$ induce sections ![]() $s_{ij}=\pi _* \tilde {s}_{ij}$ of
$s_{ij}=\pi _* \tilde {s}_{ij}$ of ![]() $\pi _* \operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{\Gamma ^{2}_{ij} }(\Gamma ^{1}_{ij})$ and we set
$\pi _* \operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{\Gamma ^{2}_{ij} }(\Gamma ^{1}_{ij})$ and we set ![]() $s=(s_{ij})_{ij}\in H^{0}(A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda },{{\mathcal {E}}})$. We claim that
$s=(s_{ij})_{ij}\in H^{0}(A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda },{{\mathcal {E}}})$. We claim that
To prove it, we follow the strategy of [Reference Cao and KoolCK18, Proposition 2.4]. For ![]() $(i,j)\in \lambda$ with
$(i,j)\in \lambda$ with ![]() $i,j\geq 1$, consider the universal divisors
$i,j\geq 1$, consider the universal divisors

Let ![]() $\underline {Z}_T=(Z^{T}_{00}, X^{T}_{ij},Y^{T}_{lk})_{ij,lk}$ be any
$\underline {Z}_T=(Z^{T}_{00}, X^{T}_{ij},Y^{T}_{lk})_{ij,lk}$ be any ![]() $T$-flat family with corresponding classifying morphism
$T$-flat family with corresponding classifying morphism ![]() $f:T\to A_{C, \mathbf {n}_\lambda }$, where
$f:T\to A_{C, \mathbf {n}_\lambda }$, where ![]() $Z^{T}_{00}, X^{T}_{ij},Y^{T}_{lk}\subset T\times C$ have zero-dimensional fibers of appropriate length. Consider the commutative diagram
$Z^{T}_{00}, X^{T}_{ij},Y^{T}_{lk}\subset T\times C$ have zero-dimensional fibers of appropriate length. Consider the commutative diagram

where ![]() $\Gamma ^{1,T}_{ij},\Gamma ^{2,T}_{ij}$ are the pullbacks of the universal divisors
$\Gamma ^{1,T}_{ij},\Gamma ^{2,T}_{ij}$ are the pullbacks of the universal divisors ![]() $\Gamma ^{1}_{ij},\Gamma ^{2}_{ij}$ along
$\Gamma ^{1}_{ij},\Gamma ^{2}_{ij}$ along ![]() $f\times \operatorname {id}_C$. To prove the claim it suffices to show that
$f\times \operatorname {id}_C$. To prove the claim it suffices to show that ![]() $\underline {Z}_T$ is a
$\underline {Z}_T$ is a ![]() $T$-point of
$T$-point of ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ if and only if
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ if and only if ![]() $f$ factors through
$f$ factors through ![]() $Z(s)$.
$Z(s)$.
Now ![]() $\underline {Z}_T$ is a
$\underline {Z}_T$ is a ![]() $T$-point of
$T$-point of ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ if and only if
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ if and only if ![]() $\Gamma ^{2,T}_{ij} =\Gamma ^{1,T}_{ij}$ for all
$\Gamma ^{2,T}_{ij} =\Gamma ^{1,T}_{ij}$ for all ![]() $(i,j)\in \lambda$ such that
$(i,j)\in \lambda$ such that ![]() $(i,j)\geq 1$. Note that the inclusion
$(i,j)\geq 1$. Note that the inclusion ![]() $\Gamma ^{2,T}_{ij} \subset \Gamma ^{1,T}_{ij}$ is enough to have the equality, as all fibers are divisors in
$\Gamma ^{2,T}_{ij} \subset \Gamma ^{1,T}_{ij}$ is enough to have the equality, as all fibers are divisors in ![]() $C$ of the same degree.
$C$ of the same degree.
On the other hand, we have that ![]() $f$ factors through
$f$ factors through ![]() $Z(s)$ if and only if
$Z(s)$ if and only if ![]() $f^{*}s$ is the zero section of
$f^{*}s$ is the zero section of ![]() $f^{*}{{\mathcal {E}}}$, i.e. if
$f^{*}{{\mathcal {E}}}$, i.e. if ![]() $f^{*}s_{ij}=0$ for all
$f^{*}s_{ij}=0$ for all ![]() $(i,j)\in \lambda$ such that
$(i,j)\in \lambda$ such that ![]() $(i,j)\geq 1$. Repeatedly applying flat base change, we obtain
$(i,j)\geq 1$. Repeatedly applying flat base change, we obtain
Therefore, ![]() $f^{*}s_{ij}$ is the zero section if and only if
$f^{*}s_{ij}$ is the zero section if and only if ![]() $\Gamma ^{2,T}_{ij} \subset \Gamma ^{1,T}_{ij}$ as required.
$\Gamma ^{2,T}_{ij} \subset \Gamma ^{1,T}_{ij}$ as required.
Thanks to Theorem 2.8, ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ falls in the situation of Example 2.7 and we obtain a virtual fundamental class.
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ falls in the situation of Example 2.7 and we obtain a virtual fundamental class.
Corollary 2.9 Let ![]() $C$ be a smooth quasi-projective curve and
$C$ be a smooth quasi-projective curve and ![]() $\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ a reversed plane partition. Then
$\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ a reversed plane partition. Then ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ has a perfect obstruction theory
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ has a perfect obstruction theory
In particular, there exists a virtual fundamental class
2.5 Topological Euler characteristic
Recall that we can view Euler characteristic weighted by a constructible function as a Lebesgue integral, where the measurable sets are constructible sets, measurable functions are constructible functions and the measure of a set is given by its Euler characteristic (cf. [Reference Bryan and KoolBK19, § 2]). In this language we have
for any constructible set ![]() $X$. The following lemma is reminiscent of the existence of a power structure on the Grothendieck ring of varieties.
$X$. The following lemma is reminiscent of the existence of a power structure on the Grothendieck ring of varieties.
Lemma 2.10 [Reference Bryan and KoolBK19, Lemma 32]
Let ![]() $B$ be a scheme of finite type over
$B$ be a scheme of finite type over ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}$ and
${{\mathbb {C}}}$ and ![]() $e(B)$ its topological Euler characteristic. Let
$e(B)$ its topological Euler characteristic. Let ![]() $g:{{\mathbb {Z}}}_{\geq 0}\to {{\mathbb {Z}}}( (p) )$ be any function with
$g:{{\mathbb {Z}}}_{\geq 0}\to {{\mathbb {Z}}}( (p) )$ be any function with ![]() $g(0)=1$. Let
$g(0)=1$. Let ![]() $G: \operatorname {Sym}^{n} B\to {{\mathbb {Z}}}( (p) )$ be the constructible function defined by
$G: \operatorname {Sym}^{n} B\to {{\mathbb {Z}}}( (p) )$ be the constructible function defined by
for all ![]() $\mathbf {ax}=\sum _i a_ix_i\in \operatorname {Sym}^{n} B$, where
$\mathbf {ax}=\sum _i a_ix_i\in \operatorname {Sym}^{n} B$, where ![]() $x_i\in B$ are distinct closed points. Then
$x_i\in B$ are distinct closed points. Then
 \[ \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}q^{n} \int_{\operatorname{Sym}^{n} B}G\cdot de= \bigg(\sum_{a=0}^{\infty} g(a)q^{a}\bigg)^{e(B)}. \]
\[ \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}q^{n} \int_{\operatorname{Sym}^{n} B}G\cdot de= \bigg(\sum_{a=0}^{\infty} g(a)q^{a}\bigg)^{e(B)}. \]Using Lemma 2.10 we compute the topological Euler characteristic of double nested Hilbert schemes of points of any quasi-projective smooth curve.
Theorem 2.11 Let ![]() $C$ be a smooth quasi-projective curve and
$C$ be a smooth quasi-projective curve and ![]() $\lambda$ a Young diagram. Then
$\lambda$ a Young diagram. Then
Proof. Consider the constructible map
defined, for ![]() $\underline {Z}=(Z_{\Box })_{\Box \in \lambda }\in C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, by
$\underline {Z}=(Z_{\Box })_{\Box \in \lambda }\in C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, by
In other words, ![]() $\rho$ just forgets the distribution and the nesting of the divisor
$\rho$ just forgets the distribution and the nesting of the divisor ![]() $\sum _{\Box \in \lambda }Z_{\Box }$ among all
$\sum _{\Box \in \lambda }Z_{\Box }$ among all ![]() $\Box \in \lambda$.
$\Box \in \lambda$.
Let ![]() $\mathbf {ax}=\sum _{i}a_ix_i\in \operatorname {Sym}^{n} C$, with
$\mathbf {ax}=\sum _{i}a_ix_i\in \operatorname {Sym}^{n} C$, with ![]() $x_i$ different to each other. The fiber
$x_i$ different to each other. The fiber ![]() $\rho _n^{-1}(\mathbf {ax})$ is clearly zero-dimensional and satisfies
$\rho _n^{-1}(\mathbf {ax})$ is clearly zero-dimensional and satisfies
In particular, the Euler characteristic of the fiber ![]() $\rho _n(nx)$ does not depend on the point
$\rho _n(nx)$ does not depend on the point ![]() $x\in C$ and counts the number of reversed plane partition of size
$x\in C$ and counts the number of reversed plane partition of size ![]() $n$ and underlying Young diagram
$n$ and underlying Young diagram ![]() $\lambda$
$\lambda$
Now consider
 \[ \int_{\bigsqcup_{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|=n} C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]} }1\cdot de=\int_{\operatorname{Sym}^{n} C}{\rho_n}_*1\cdot de, \]
\[ \int_{\bigsqcup_{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|=n} C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]} }1\cdot de=\int_{\operatorname{Sym}^{n} C}{\rho_n}_*1\cdot de, \]
where for any ![]() $\mathbf {ax}\in \operatorname {Sym}^{n} C$ with
$\mathbf {ax}\in \operatorname {Sym}^{n} C$ with ![]() $x_i$ different to each other, using (2.3) and (2.4)
$x_i$ different to each other, using (2.3) and (2.4)
 \begin{align*} {\rho_n}_* 1(\mathbf{ax})&=e(\rho_n^{-1}(\mathbf{ax}))\\ &= \prod_i \sum_{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|=a_i}1. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} {\rho_n}_* 1(\mathbf{ax})&=e(\rho_n^{-1}(\mathbf{ax}))\\ &= \prod_i \sum_{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|=a_i}1. \end{align*}
Now, ![]() $g(a)=\sum _{|\mathbf {n}_\lambda |=a}1$ and
$g(a)=\sum _{|\mathbf {n}_\lambda |=a}1$ and ![]() $G(\mathbf {ax} )={\rho _n}_* 1(\mathbf {ax})$ satisfy the hypotheses of Lemma 2.10 and therefore
$G(\mathbf {ax} )={\rho _n}_* 1(\mathbf {ax})$ satisfy the hypotheses of Lemma 2.10 and therefore
 \begin{align*} \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\sum_{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|=n} e(C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]})q^{n}&= \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} q^{n} \int_{\bigsqcup_{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|=n} C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]} }1\cdot de \\ &= \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} q^{n} \int_{\operatorname{Sym}^{n} C}{\rho_n}_*1\cdot de\\ &= \bigg(\sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \sum_{|\mathbf{n}_{\lambda}|=n}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \bigg)^{e(C)}. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\sum_{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|=n} e(C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]})q^{n}&= \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} q^{n} \int_{\bigsqcup_{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|=n} C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]} }1\cdot de \\ &= \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} q^{n} \int_{\operatorname{Sym}^{n} C}{\rho_n}_*1\cdot de\\ &= \bigg(\sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \sum_{|\mathbf{n}_{\lambda}|=n}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \bigg)^{e(C)}. \end{align*}A closed formula for the generating series of reversed plane partitions was given by Stanley [Reference StanleySta71, Proposition 18.3] and by Hillman and Grassl [Reference Hillman and GrasslHG76, Theorem 1] using hook-lengths
 \[ \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \sum_{|\mathbf{n}_{\lambda}|=n}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} =\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)})^{-1}, \]
\[ \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \sum_{|\mathbf{n}_{\lambda}|=n}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} =\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)})^{-1}, \]by which we conclude the proof.
2.6 Double nesting of divisors
We conclude this section with a generalization of the zero-locus construction of Theorem 2.8.
Let ![]() $X$ be a smooth projective variety of dimension
$X$ be a smooth projective variety of dimension ![]() $d$ and
$d$ and ![]() $\boldsymbol {\beta }_\lambda =(\beta _\Box )_{\Box \in \lambda }$ be a collection of homology classes
$\boldsymbol {\beta }_\lambda =(\beta _\Box )_{\Box \in \lambda }$ be a collection of homology classes ![]() $\beta _\Box \in H_{n-2}(X,{{\mathbb {Z}}})$. Denote by
$\beta _\Box \in H_{n-2}(X,{{\mathbb {Z}}})$. Denote by ![]() $H_{\boldsymbol {\beta }_\lambda }$ the double nested Hilbert scheme of effective divisors on
$H_{\boldsymbol {\beta }_\lambda }$ the double nested Hilbert scheme of effective divisors on ![]() $X$, which parametrizes flags of divisors
$X$, which parametrizes flags of divisors ![]() $(Z_{\Box })_{\Box \in \lambda }\subset X$ satisfying the nesting condition dictated by
$(Z_{\Box })_{\Box \in \lambda }\subset X$ satisfying the nesting condition dictated by ![]() $\boldsymbol {\beta }_\lambda$. Denote by
$\boldsymbol {\beta }_\lambda$. Denote by
 \begin{align*} A_{X,\boldsymbol{\beta}_{\lambda}}=H_{\beta_{00}}\times \prod_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}}H_{\beta_{ij}- \beta_{i-1,j}}\times \prod_{\substack{(l,k)\in \lambda\\ k\geq 1}} H_{\beta_{lk}-\beta_{l,k-1}}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} A_{X,\boldsymbol{\beta}_{\lambda}}=H_{\beta_{00}}\times \prod_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}}H_{\beta_{ij}- \beta_{i-1,j}}\times \prod_{\substack{(l,k)\in \lambda\\ k\geq 1}} H_{\beta_{lk}-\beta_{l,k-1}}, \end{align*}
where ![]() $H_\beta$ is the usual Hilbert scheme of divisors on
$H_\beta$ is the usual Hilbert scheme of divisors on ![]() $X$ of class
$X$ of class ![]() $\beta$. Analogously to § 2.4,
$\beta$. Analogously to § 2.4, ![]() $A_{X,\boldsymbol {\beta }_{\lambda }}$ comes equipped with universal (Cartier) divisors
$A_{X,\boldsymbol {\beta }_{\lambda }}$ comes equipped with universal (Cartier) divisors ![]() ${{\mathcal {Z}}}_{00}, {{\mathcal {X}}}_{ij},{{\mathcal {Y}}}_{lk}\subset X\times A_{X,\boldsymbol {\beta }_{\lambda }}$ and for every
${{\mathcal {Z}}}_{00}, {{\mathcal {X}}}_{ij},{{\mathcal {Y}}}_{lk}\subset X\times A_{X,\boldsymbol {\beta }_{\lambda }}$ and for every ![]() $(i,j)\in \lambda$ with
$(i,j)\in \lambda$ with ![]() $i,j\geq 1$ we define the universal effective divisors
$i,j\geq 1$ we define the universal effective divisors
Define the coherent sheaf
 \begin{align*} {{\mathcal{E}}}= \bigoplus_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}\pi_* \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Gamma^{2}_{ij} }(\Gamma^{1}_{ij}), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} {{\mathcal{E}}}= \bigoplus_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}\pi_* \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Gamma^{2}_{ij} }(\Gamma^{1}_{ij}), \end{align*}
where ![]() $\pi :X\times A_{X,\boldsymbol {\beta }_{\lambda }}\to A_{X,\boldsymbol {\beta }_{\lambda }}$ is the natural projection. Under some extra assumptions on
$\pi :X\times A_{X,\boldsymbol {\beta }_{\lambda }}\to A_{X,\boldsymbol {\beta }_{\lambda }}$ is the natural projection. Under some extra assumptions on ![]() $X$ and
$X$ and ![]() $\boldsymbol {\beta }_{\lambda }$ Theorem 2.8 generalizes.
$\boldsymbol {\beta }_{\lambda }$ Theorem 2.8 generalizes.
Proposition 2.12 Assume that ![]() $A_{X,\boldsymbol {\beta }_{\lambda }}$ is smooth and
$A_{X,\boldsymbol {\beta }_{\lambda }}$ is smooth and ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is a vector bundle. Then there exists a section
${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is a vector bundle. Then there exists a section ![]() $s$ of
$s$ of ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}$ such that
${{\mathcal {E}}}$ such that

In particular, ![]() $H_{\boldsymbol {\beta }_\lambda }$ has a perfect obstruction theory.
$H_{\boldsymbol {\beta }_\lambda }$ has a perfect obstruction theory.
Corollary 2.13 Let ![]() $X={{\mathbb {P}}}^{n_1}\times \cdots \times {{\mathbb {P}}}^{n_s}$. Then there exists a virtual fundamental class
$X={{\mathbb {P}}}^{n_1}\times \cdots \times {{\mathbb {P}}}^{n_s}$. Then there exists a virtual fundamental class ![]() $[H_{\boldsymbol {\beta }_\lambda }]^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}\in A_*( H_{\boldsymbol {\beta }_\lambda })$.
$[H_{\boldsymbol {\beta }_\lambda }]^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}\in A_*( H_{\boldsymbol {\beta }_\lambda })$.
Proof. The smoothness of ![]() $A_{X,\boldsymbol {\beta }_{\lambda }}$ follows by the smoothness of
$A_{X,\boldsymbol {\beta }_{\lambda }}$ follows by the smoothness of ![]() $H_{\beta }\cong {{\mathbb {P}}}(H^{0}(X,\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X( \beta )))$ for every
$H_{\beta }\cong {{\mathbb {P}}}(H^{0}(X,\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X( \beta )))$ for every ![]() $\beta \in H_{n-2}(X,{{\mathbb {Z}}})$. Let
$\beta \in H_{n-2}(X,{{\mathbb {Z}}})$. Let ![]() $D_1, D_2$ be two effective divisors on
$D_1, D_2$ be two effective divisors on ![]() $X$ such that
$X$ such that ![]() $[D_1]=[D_2]\in H_{n-2}(X,{{\mathbb {Z}}})$; in particular,
$[D_1]=[D_2]\in H_{n-2}(X,{{\mathbb {Z}}})$; in particular, ![]() $D_1,D_2$ are linearly equivalent. Combining the long exact sequence in cohomology of the short exact sequence
$D_1,D_2$ are linearly equivalent. Combining the long exact sequence in cohomology of the short exact sequence
and the vanishings
 \begin{gather*} H^{k}(X, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}(D_1))=0, \quad k=1, \ldots, \dim X -1,\\ H^{k}(X, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}(D_1-D_2))=0, \quad k=2,\ldots \dim X, \end{gather*}
\begin{gather*} H^{k}(X, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}(D_1))=0, \quad k=1, \ldots, \dim X -1,\\ H^{k}(X, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}(D_1-D_2))=0, \quad k=2,\ldots \dim X, \end{gather*}
yields that ![]() $H^{k}(X, \operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{D_2 }(D_1))=0$ for
$H^{k}(X, \operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{D_2 }(D_1))=0$ for ![]() $k\geq 1$; cohomology and base change implies that
$k\geq 1$; cohomology and base change implies that ![]() $\mathbf {R}^{k}\pi _*\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{\Gamma ^{2}_{ij} }(\Gamma ^{1}_{ij})=0$ for
$\mathbf {R}^{k}\pi _*\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{\Gamma ^{2}_{ij} }(\Gamma ^{1}_{ij})=0$ for ![]() $k\geq 1$. Finally, We have that, if
$k\geq 1$. Finally, We have that, if ![]() $\dim X\geq 2$,
$\dim X\geq 2$,
which depends only on the degree ![]() $[D_1]=[D_2]\in H_2(X, {{\mathbb {Z}}})$ and implies that the dimension of the fibers of
$[D_1]=[D_2]\in H_2(X, {{\mathbb {Z}}})$ and implies that the dimension of the fibers of ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is constant, thus
${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is constant, thus ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is a vector bundle.
${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is a vector bundle.
3. Moduli space of stable pairs
3.1 Moduli space of stable pairs
Moduli spaces of stable pairs were introduced by Pandharipande and Thomas [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09a] in order to give a geometric interpretation of the MNOP conjectures [Reference Maulik, Nekrasov, Okounkov and PandharipandeMNOP06a], through the DT/PT correspondence proved by Toda (for Euler characteristic) and Bridgeland in [Reference TodaTod10, Reference BridgelandBri11] using wall-crossing and Hall algebra techniques.
For a smooth quasi-projective threefold ![]() $X$, a curve class
$X$, a curve class ![]() $\beta \in H_2(X, {{\mathbb {Z}}})$ and
$\beta \in H_2(X, {{\mathbb {Z}}})$ and ![]() $n\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$, we define
$n\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$, we define ![]() $P_{n}(X,\beta )$ to be the moduli space of pairs
$P_{n}(X,\beta )$ to be the moduli space of pairs
in the derived category of ![]() $X$ where
$X$ where ![]() $F$ is a pure one-dimensional sheaf with proper support
$F$ is a pure one-dimensional sheaf with proper support ![]() $[\mathrm {supp}( F)]=\beta$ with
$[\mathrm {supp}( F)]=\beta$ with ![]() $\chi (F)=n$ and
$\chi (F)=n$ and ![]() $s$ is a section with zero-dimensional cokernel.
$s$ is a section with zero-dimensional cokernel.
By the work of Huybrechts and Thomas [Reference Huybrechts and ThomasHT10], the Atiyah class gives a perfect obstruction theory on ![]() $P_n(X,\beta )$
$P_n(X,\beta )$
where ![]() $(\cdot )_0$ denotes the trace-free part,
$(\cdot )_0$ denotes the trace-free part, ![]() $\pi :X\times P_n(X,\beta )\to P_n(X,\beta )$ is the canonical projection and
$\pi :X\times P_n(X,\beta )\to P_n(X,\beta )$ is the canonical projection and ![]() ${{\mathbb {I}}}^{\bullet }=[\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}\to {{\mathbb {F}}}]$ is the universal stable pair on
${{\mathbb {I}}}^{\bullet }=[\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}\to {{\mathbb {F}}}]$ is the universal stable pair on ![]() $X\times P_n(X,\beta )$.
$X\times P_n(X,\beta )$.
If ![]() $X$ is projective, the perfect obstruction theory induces a virtual fundamental class
$X$ is projective, the perfect obstruction theory induces a virtual fundamental class ![]() $[ P_n(X,\beta )]^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}\in A_*(P_n(X,\beta ))$ and one defines stable pair (or PT) invariants by integrating cohomology classes
$[ P_n(X,\beta )]^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}\in A_*(P_n(X,\beta ))$ and one defines stable pair (or PT) invariants by integrating cohomology classes ![]() $\gamma \in H^{*}(P_{n}(X,\beta ), {{\mathbb {Z}}})$ against the virtual fundamental class
$\gamma \in H^{*}(P_{n}(X,\beta ), {{\mathbb {Z}}})$ against the virtual fundamental class
We focus here in the case of ![]() $X$ a local curve, i.e.
$X$ a local curve, i.e. ![]() $X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ the total space of the direct sum of two line bundles
$X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ the total space of the direct sum of two line bundles ![]() $L_1, L_2$ on a smooth projective curve
$L_1, L_2$ on a smooth projective curve ![]() $C$ and
$C$ and ![]() $\beta =d[C]\in H_2(X,{{\mathbb {Z}}})\cong H_2(C,{{\mathbb {Z}}})$ a multiple of the zero section of
$\beta =d[C]\in H_2(X,{{\mathbb {Z}}})\cong H_2(C,{{\mathbb {Z}}})$ a multiple of the zero section of ![]() $X\to C$.
$X\to C$.
Here ![]() $X$ is a smooth quasi-projective threefold, therefore the moduli space of stable pairs
$X$ is a smooth quasi-projective threefold, therefore the moduli space of stable pairs ![]() $P_n(X,\beta )$ is hardly ever a proper scheme and one cannot define invariants as in (3.2). Nevertheless, the algebraic torus
$P_n(X,\beta )$ is hardly ever a proper scheme and one cannot define invariants as in (3.2). Nevertheless, the algebraic torus ![]() $\mathbf {T}=({{\mathbb {C}}}^{*})^{2}$ acts on
$\mathbf {T}=({{\mathbb {C}}}^{*})^{2}$ acts on ![]() $X$ by scaling the fibers and the action naturally lifts to
$X$ by scaling the fibers and the action naturally lifts to ![]() $P_n(X,d[C])$, making the perfect obstruction theory naturally
$P_n(X,d[C])$, making the perfect obstruction theory naturally ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant by [Reference RicolfiRic21, Example 4.6]. Moreover, the
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant by [Reference RicolfiRic21, Example 4.6]. Moreover, the ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus ![]() $P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf {T}}$ is proper (cf. Proposition 3.1), therefore by Graber and Pandharipande [Reference Graber and PandharipandeGP99] there is naturally an induced perfect obstruction theory on
$P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf {T}}$ is proper (cf. Proposition 3.1), therefore by Graber and Pandharipande [Reference Graber and PandharipandeGP99] there is naturally an induced perfect obstruction theory on ![]() $P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf {T}}$ and a virtual fundamental class
$P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf {T}}$ and a virtual fundamental class ![]() $[P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf {T}}]^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}\in A_*(P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf {T}})$. We define
$[P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf {T}}]^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}\in A_*(P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf {T}})$. We define ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant stable pair invariants by the Graber–Pandharipande virtual localization formula
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant stable pair invariants by the Graber–Pandharipande virtual localization formula
where ![]() $s_1, s_2$ are the generators of
$s_1, s_2$ are the generators of ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant cohomology and the virtual normal bundle
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant cohomology and the virtual normal bundle
is the ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-moving part of the restriction of the dual of the perfect obstruction theory. Stable pair invariants with descendent insertions on local curves have been studied in [Reference Pandharipande and PixtonPP12, Reference Pandharipande and PixtonPP13, Reference OblomkovObl19].
$\mathbf {T}$-moving part of the restriction of the dual of the perfect obstruction theory. Stable pair invariants with descendent insertions on local curves have been studied in [Reference Pandharipande and PixtonPP12, Reference Pandharipande and PixtonPP13, Reference OblomkovObl19].
3.2 Torus representations and their weights
Let ![]() $\mathbf {T} = ({{\mathbb {C}}}^{*})^{g}$ be an algebraic torus, with character lattice
$\mathbf {T} = ({{\mathbb {C}}}^{*})^{g}$ be an algebraic torus, with character lattice ![]() $\hat {\mathbf {T}} = \operatorname {Hom}(\mathbf {T},{{\mathbb {C}}}^{\ast }) \cong {{\mathbb {Z}}}^{g}$. Let
$\hat {\mathbf {T}} = \operatorname {Hom}(\mathbf {T},{{\mathbb {C}}}^{\ast }) \cong {{\mathbb {Z}}}^{g}$. Let ![]() $K^{0}_{\mathbf {T}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$ be the
$K^{0}_{\mathbf {T}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$ be the ![]() $K$-group of the category of
$K$-group of the category of ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-representations. Any finite-dimensional
$\mathbf {T}$-representations. Any finite-dimensional ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-representation
$\mathbf {T}$-representation ![]() $V$ splits as a sum of one-dimensional representations called the weights of
$V$ splits as a sum of one-dimensional representations called the weights of ![]() $V$. Each weight corresponds to a character
$V$. Each weight corresponds to a character ![]() $\mu \in \hat {\mathbf {T}}$ and, in turn, each character corresponds to a monomial
$\mu \in \hat {\mathbf {T}}$ and, in turn, each character corresponds to a monomial ![]() $\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu } = \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1^{\mu _1}\cdots \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_g^{\mu _g}$ in the coordinates of
$\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu } = \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1^{\mu _1}\cdots \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_g^{\mu _g}$ in the coordinates of ![]() $\mathbf {T}$. The map
$\mathbf {T}$. The map
sending the class of a ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-representation to its decomposition into weight spaces is a ring isomorphism, where tensor product on the left corresponds to the natural multiplication on the right. We therefore sometimes identify a (virtual)
$\mathbf {T}$-representation to its decomposition into weight spaces is a ring isomorphism, where tensor product on the left corresponds to the natural multiplication on the right. We therefore sometimes identify a (virtual) ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-representation with its character.
$\mathbf {T}$-representation with its character.
If ![]() $X$ is a scheme with a trivial
$X$ is a scheme with a trivial ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-action, every
$\mathbf {T}$-action, every ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant coherent sheaf on
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant coherent sheaf on ![]() $X$ decomposes as
$X$ decomposes as ![]() $F=\bigoplus _{\mu \in \hat {\mathbf {T}}}F_\mu \otimes \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu }$.
$F=\bigoplus _{\mu \in \hat {\mathbf {T}}}F_\mu \otimes \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu }$.
3.3 The fixed locus
In this section we prove that the ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus ![]() $P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf {T}}$ is a disjoint union of double nested Hilbert schemes of points
$P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf {T}}$ is a disjoint union of double nested Hilbert schemes of points ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, for suitable reversed plane partitions
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, for suitable reversed plane partitions ![]() $\mathbf {n}_\lambda$, where
$\mathbf {n}_\lambda$, where ![]() $\lambda$ are Young diagram of size
$\lambda$ are Young diagram of size ![]() $|\lambda |=d$. Our strategy is similar to Kool and Thomas [Reference Kool and ThomasKT17, § 4] for local surfaces.
$|\lambda |=d$. Our strategy is similar to Kool and Thomas [Reference Kool and ThomasKT17, § 4] for local surfaces.
Given a ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant coherent sheaf on
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant coherent sheaf on ![]() $X$, its pushdown along
$X$, its pushdown along ![]() $p:X\to C$ decomposes into weight spaces (e.g. by [Reference HartshorneHar77, Exercises II.5.17 and II.5.18])
$p:X\to C$ decomposes into weight spaces (e.g. by [Reference HartshorneHar77, Exercises II.5.17 and II.5.18])
where ![]() $F_{ij}$ is a coherent sheaf on
$F_{ij}$ is a coherent sheaf on ![]() $C$. For example,
$C$. For example,
As ![]() $p$ is affine, the pushdown does not lose any information, and we recover the
$p$ is affine, the pushdown does not lose any information, and we recover the ![]() $\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X$-module structure of
$\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X$-module structure of ![]() $F$ by the
$F$ by the ![]() $p_*\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X$-action that
$p_*\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X$-action that ![]() $p_*F$ carries. This is generated by the action of the
$p_*F$ carries. This is generated by the action of the ![]() $-1$ pieces
$-1$ pieces ![]() $L_1^{-1}\otimes \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1^{-1},L_2^{-1}\otimes \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2^{-1}$, so we find that the
$L_1^{-1}\otimes \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1^{-1},L_2^{-1}\otimes \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2^{-1}$, so we find that the ![]() $\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X$-module structure is determined by the maps
$\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X$-module structure is determined by the maps
 \begin{equation} \begin{aligned} & \bigg(\bigoplus_{i,j}F_{ij}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j} \bigg)\otimes L_1^{-1}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-1}\to \bigoplus_{i,j}F_{ij} \otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j},\\ & \bigg(\bigoplus_{i,j}F_{ij}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j} \bigg)\otimes L_2^{-1}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{-1}\to \bigoplus_{i,j}F_{ij}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j}, \end{aligned} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \begin{aligned} & \bigg(\bigoplus_{i,j}F_{ij}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j} \bigg)\otimes L_1^{-1}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-1}\to \bigoplus_{i,j}F_{ij} \otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j},\\ & \bigg(\bigoplus_{i,j}F_{ij}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j} \bigg)\otimes L_2^{-1}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{-1}\to \bigoplus_{i,j}F_{ij}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j}, \end{aligned} \end{equation}
which commute with both the actions of ![]() $\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_C$ and
$\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_C$ and ![]() $\mathbf {T}$. In other words, (3.5) are
$\mathbf {T}$. In other words, (3.5) are ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant maps of
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant maps of ![]() $\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_C$-modules. By
$\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_C$-modules. By ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariance, they are sums of maps
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariance, they are sums of maps
 \begin{equation} \begin{aligned} & F_{ij}\otimes L_1^{-1}\to F_{i-1,j},\\ & F_{ij}\otimes L_2^{-1}\to F_{i,j-1}. \end{aligned} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \begin{aligned} & F_{ij}\otimes L_1^{-1}\to F_{i-1,j},\\ & F_{ij}\otimes L_2^{-1}\to F_{i,j-1}. \end{aligned} \end{equation}
Now let ![]() $(F,s)\in P_n(X, d[C])^{\mathbf {T}}$ be a
$(F,s)\in P_n(X, d[C])^{\mathbf {T}}$ be a ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed stable pair. Then
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed stable pair. Then ![]() $s$ is a
$s$ is a ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant section of a
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant section of a ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant coherent sheaf
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant coherent sheaf ![]() $F$ on
$F$ on ![]() $X$. Applying
$X$. Applying ![]() $p_*$ to
$p_*$ to ![]() $\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X\xrightarrow {s} F$ gives a graded map which commutes with the maps (3.6). Writing
$\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_X\xrightarrow {s} F$ gives a graded map which commutes with the maps (3.6). Writing
we find that the ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed stable pair
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed stable pair ![]() $(F,s)$ on
$(F,s)$ on ![]() $X$ is equivalent to the following data of sheaves and commuting maps on
$X$ is equivalent to the following data of sheaves and commuting maps on ![]() $C$.
$C$.

By the purity of ![]() $F$, each
$F$, each ![]() $G_{ij}$ is either zero or a pure one-dimensional coherent sheaf on
$G_{ij}$ is either zero or a pure one-dimensional coherent sheaf on ![]() $C$, and the ‘vertical’ maps are generically isomorphisms. In particular, for every
$C$, and the ‘vertical’ maps are generically isomorphisms. In particular, for every ![]() $(i,j)$ such that either
$(i,j)$ such that either ![]() $i<0$ or
$i<0$ or ![]() $j<0$, it follows that
$j<0$, it follows that ![]() $G_{ij}$ is zero-dimensional and therefore vanishes by the purity assumption. Moreover, if
$G_{ij}$ is zero-dimensional and therefore vanishes by the purity assumption. Moreover, if ![]() $G_{ij}$ is non-zero, it is a rank-one torsion-free sheaf on a smooth curve, that is a line bundle on
$G_{ij}$ is non-zero, it is a rank-one torsion-free sheaf on a smooth curve, that is a line bundle on ![]() $C$ (with a section). Finally, any
$C$ (with a section). Finally, any ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant stable pair on
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant stable pair on ![]() $X$ is set-theoretically supported on
$X$ is set-theoretically supported on ![]() $C$, thus is properly supported on
$C$, thus is properly supported on ![]() $X$ and only finitely many
$X$ and only finitely many ![]() $G_{ij}$ can be non-zero. This results in a diagram of the following shape.
$G_{ij}$ can be non-zero. This results in a diagram of the following shape.

where ![]() $Z_{ij}$ are divisors on
$Z_{ij}$ are divisors on ![]() $C$ and all ‘horizontal’ maps are injections of line bundles. Therefore, a
$C$ and all ‘horizontal’ maps are injections of line bundles. Therefore, a ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed stable pair
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed stable pair ![]() $(F,s)$ is equivalent to a nesting of divisors
$(F,s)$ is equivalent to a nesting of divisors

where the nesting is dictated by a Young diagram ![]() $\lambda$. This results into a point of the double nested Hilbert scheme
$\lambda$. This results into a point of the double nested Hilbert scheme ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, where by Riemann–Roch
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, where by Riemann–Roch
where for a Young diagram ![]() $\lambda$ and
$\lambda$ and ![]() $g,k_1, k_2\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$ we define
$g,k_1, k_2\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$ we define
 \begin{align} \mathbf{f}_{\lambda,g}(k_1,k_2)&=\sum_{(i,j)\in \lambda}(1-g-i\cdot k_1-j\cdot k_2 )\nonumber\\ &=|\lambda|(1-g)-k_1\cdot n(\lambda)-k_2\cdot n(\bar{\lambda}). \end{align}
\begin{align} \mathbf{f}_{\lambda,g}(k_1,k_2)&=\sum_{(i,j)\in \lambda}(1-g-i\cdot k_1-j\cdot k_2 )\nonumber\\ &=|\lambda|(1-g)-k_1\cdot n(\lambda)-k_2\cdot n(\bar{\lambda}). \end{align}
Conversely, any nesting of divisors as in (3.9) corresponds to a diagram of sheaves as in (3.8), which corresponds to a ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed stable pair on
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed stable pair on ![]() $X$. Therefore, we have a bijection of sets
$X$. Therefore, we have a bijection of sets
where the disjoint union is over all Young diagrams ![]() $\lambda$ of size
$\lambda$ of size ![]() $d$ and all reversed plane partitions
$d$ and all reversed plane partitions ![]() $\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ satisfying
$\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ satisfying ![]() $n=|\mathbf {n}_\lambda |+ \mathbf {f}_{\lambda,g}( \deg L_1, \deg L_2)$. We mimic [Reference Kool and ThomasKT17, Proposition 4.1] to prove that the above bijection on sets is an isomorphism of schemes.
$n=|\mathbf {n}_\lambda |+ \mathbf {f}_{\lambda,g}( \deg L_1, \deg L_2)$. We mimic [Reference Kool and ThomasKT17, Proposition 4.1] to prove that the above bijection on sets is an isomorphism of schemes.
Proposition 3.1 There exists an isomorphism of schemes
where the disjoint union is over all Young diagrams ![]() $\lambda$ of size
$\lambda$ of size ![]() $d$ and all reversed plane partitions
$d$ and all reversed plane partitions ![]() $\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ satisfying
$\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ satisfying
In particular, ![]() $P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf {T}}$ is proper.
$P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf {T}}$ is proper.
Proof. Let ![]() $B$ be any (connected) scheme over
$B$ be any (connected) scheme over ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}$. We need to adapt the construction of this section to a
${{\mathbb {C}}}$. We need to adapt the construction of this section to a ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed stable pair on
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed stable pair on ![]() $X\times B$, flat over
$X\times B$, flat over ![]() $B$. Pushing down by the affine map
$B$. Pushing down by the affine map ![]() $p:X\times B\to C\times B$ gives a graded sheaf
$p:X\times B\to C\times B$ gives a graded sheaf ![]() $\bigoplus _{i,j}F_{ij}$ on
$\bigoplus _{i,j}F_{ij}$ on ![]() $C\times B$, flat over
$C\times B$, flat over ![]() $B$ (therefore so are all its weight spaces
$B$ (therefore so are all its weight spaces ![]() $F_{ij}$). The original sheaf
$F_{ij}$). The original sheaf ![]() $F$ on
$F$ on ![]() $X\times B$ can be reconstructed from the maps (3.6). Therefore, a
$X\times B$ can be reconstructed from the maps (3.6). Therefore, a ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed pair
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed pair ![]() $(F,s)$ on
$(F,s)$ on ![]() $X\times B$, flat over
$X\times B$, flat over ![]() $B$, is equivalent to the data (3.7), with each
$B$, is equivalent to the data (3.7), with each ![]() $G_{ij}$ on
$G_{ij}$ on ![]() $C\times B$, flat over
$C\times B$, flat over ![]() $B$.
$B$.
If ![]() $(F,s)$ is a stable pair, over each closed fiber
$(F,s)$ is a stable pair, over each closed fiber ![]() $C\times \{b\}$, where
$C\times \{b\}$, where ![]() $b\in B$, we showed that each (non-zero)
$b\in B$, we showed that each (non-zero) ![]() $G_{ij}$ is a line bundle. By [Reference Huybrechts and LehnHL10, Lemma 2.1.7], this shows that each (non-zero)
$G_{ij}$ is a line bundle. By [Reference Huybrechts and LehnHL10, Lemma 2.1.7], this shows that each (non-zero) ![]() $G_{ij}$ is a line bundle on
$G_{ij}$ is a line bundle on ![]() $C\times B$. Together with its non-zero section, this defines divisors
$C\times B$. Together with its non-zero section, this defines divisors ![]() $Z_{ij}\subset C\times B$, flat over
$Z_{ij}\subset C\times B$, flat over ![]() $B$, satisfying the nesting condition of (3.9), which yields a
$B$, satisfying the nesting condition of (3.9), which yields a ![]() $B$-point
$B$-point ![]() $B\to \bigsqcup _{\mathbf {n}_\lambda } C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$. Conversely, any
$B\to \bigsqcup _{\mathbf {n}_\lambda } C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$. Conversely, any ![]() $B$-point
$B$-point ![]() $B\to \bigsqcup _{\mathbf {n}_\lambda } C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ defines a diagram (3.8), equivalent to a
$B\to \bigsqcup _{\mathbf {n}_\lambda } C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ defines a diagram (3.8), equivalent to a ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed stable pair
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed stable pair ![]() $(F,s)$ on
$(F,s)$ on ![]() $X\times B$, flat over
$X\times B$, flat over ![]() $B$.
$B$.
As a corollary, we compute the generating series of the topological Euler characteristic of the moduli space of stable pairs on a local curve.
Corollary 3.2 Let ![]() $C$ be a smooth projective curve of genus
$C$ be a smooth projective curve of genus ![]() $g$,
$g$, ![]() $L_1,L_2$ line bundle on
$L_1,L_2$ line bundle on ![]() $C$ and set
$C$ and set ![]() $X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$. Then, for any
$X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$. Then, for any ![]() $d> 0$, we have
$d> 0$, we have
Proof. The topological Euler characteristic of a ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-scheme is the same of its
$\mathbf {T}$-scheme is the same of its ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus, therefore
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus, therefore
 \begin{align*} \sum_{n\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}e(P_n(X,d[C]))\cdot q^{n}&=\sum_{n\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}e(P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf{T}})\cdot q^{n}\\ &= \sum_{n\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}\sum_{|\lambda|=d}\sum_{\substack{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|=n-\\\mathbf{f}_{\lambda,g}( \deg L_1, \deg L_2)}}q^{n}\cdot e(C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]})\\ &= \sum_{|\lambda|=d}q^{\mathbf{f}_{\lambda,g}( \deg L_1, \deg L_2)} \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda} q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|}\cdot e(C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]})\\ &= \sum_{|\lambda|=d}q^{\mathbf{f}_{\lambda,g}( \deg L_1, \deg L_2)}\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)})^{2g-2}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \sum_{n\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}e(P_n(X,d[C]))\cdot q^{n}&=\sum_{n\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}e(P_n(X,d[C])^{\mathbf{T}})\cdot q^{n}\\ &= \sum_{n\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}\sum_{|\lambda|=d}\sum_{\substack{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|=n-\\\mathbf{f}_{\lambda,g}( \deg L_1, \deg L_2)}}q^{n}\cdot e(C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]})\\ &= \sum_{|\lambda|=d}q^{\mathbf{f}_{\lambda,g}( \deg L_1, \deg L_2)} \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda} q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|}\cdot e(C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]})\\ &= \sum_{|\lambda|=d}q^{\mathbf{f}_{\lambda,g}( \deg L_1, \deg L_2)}\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)})^{2g-2}, \end{align*}where in the second line we applied Proposition 3.1 and in the last line we applied Theorem 2.11.
4.  $K$-theory class of the perfect obstruction theory
$K$-theory class of the perfect obstruction theory
Let ![]() $C$ be an irreducible smooth projective curve. On each connected component
$C$ be an irreducible smooth projective curve. On each connected component ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}\subset P_{n}(X,\beta )^{\mathbf {T}}$ of the
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}\subset P_{n}(X,\beta )^{\mathbf {T}}$ of the ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus there exists and induced virtual fundamental class
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus there exists and induced virtual fundamental class ![]() $[C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}]_{\mathrm {PT}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ coming from the perfect obstruction theory (3.1). We show in this section that
$[C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}]_{\mathrm {PT}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ coming from the perfect obstruction theory (3.1). We show in this section that ![]() $[C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}]_{\mathrm {PT}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ agrees with the virtual fundamental class constructed in Corollary 2.9 and compute the class in
$[C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}]_{\mathrm {PT}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ agrees with the virtual fundamental class constructed in Corollary 2.9 and compute the class in ![]() $K$-theory of the virtual normal bundle
$K$-theory of the virtual normal bundle ![]() $N^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$.
$N^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$.
We start by describing the class in ![]() $K$-theory of (the restriction of) the perfect obstruction theory
$K$-theory of (the restriction of) the perfect obstruction theory ![]() ${{\mathbb {E}}}\in K^{\mathbf {T}}_0(C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$. To ease readability we omit various pullbacks whenever they are clear from the context. Recall the following identities in
${{\mathbb {E}}}\in K^{\mathbf {T}}_0(C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$. To ease readability we omit various pullbacks whenever they are clear from the context. Recall the following identities in ![]() $K$-theory:
$K$-theory:
 \begin{align*} &{{\mathbb{E}}}=-\mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om({{\mathbb{I}}}, {{\mathbb{I}}} )^{\vee}_0\in K_0^{\mathbf{T}}(P_{n}(X,\beta)^{\mathbf{T}}),\\ &{{\mathbb{F}}}=\sum_{(i,j)\in \lambda}i_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{ij}) \otimes L_1^{-i}\otimes L_2^{-j}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{-j} \in K_0^{\mathbf{T}}(X\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]} ),\\ &{{\mathbb{I}}}=\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{X\times P_{n}(X,\beta)^{\mathbf{T}}}-{{\mathbb{F}}}\in K_0^{\mathbf{T}}(X\times P_{n}(X,\beta)^{\mathbf{T}}), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &{{\mathbb{E}}}=-\mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om({{\mathbb{I}}}, {{\mathbb{I}}} )^{\vee}_0\in K_0^{\mathbf{T}}(P_{n}(X,\beta)^{\mathbf{T}}),\\ &{{\mathbb{F}}}=\sum_{(i,j)\in \lambda}i_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{ij}) \otimes L_1^{-i}\otimes L_2^{-j}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{-j} \in K_0^{\mathbf{T}}(X\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]} ),\\ &{{\mathbb{I}}}=\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{X\times P_{n}(X,\beta)^{\mathbf{T}}}-{{\mathbb{F}}}\in K_0^{\mathbf{T}}(X\times P_{n}(X,\beta)^{\mathbf{T}}), \end{align*}where the various maps fit in the following diagram.

Again, to ease notation, we keep denoting ![]() $i\times \operatorname {id}_{C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}},p\times \operatorname {id}_{C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}}$ by
$i\times \operatorname {id}_{C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}},p\times \operatorname {id}_{C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}}$ by ![]() $i,p$ and by
$i,p$ and by ![]() $\pi$ the composition
$\pi$ the composition ![]() $\pi \circ i$. We compute
$\pi \circ i$. We compute
where in the second equality we applied Grothendieck dualityFootnote 4 and the projection formula and ![]() $K_X=K_C\otimes L_1^{-1}\otimes L_2^{-1}$. Define
$K_X=K_C\otimes L_1^{-1}\otimes L_2^{-1}$. Define ![]() $\Lambda ^{\bullet }(V)=\sum _{i=0}^{\operatorname {rk} V}(-1)^{i}\Lambda ^{i} V$ for a locally free sheaf
$\Lambda ^{\bullet }(V)=\sum _{i=0}^{\operatorname {rk} V}(-1)^{i}\Lambda ^{i} V$ for a locally free sheaf ![]() $V$ and extend it by linearity to any class in
$V$ and extend it by linearity to any class in ![]() $K^{0}_\mathbf {T}(C)$. By [Reference Chriss and GinzburgCG10, Lemma 5.4.9], for every
$K^{0}_\mathbf {T}(C)$. By [Reference Chriss and GinzburgCG10, Lemma 5.4.9], for every ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant coherent sheaf
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant coherent sheaf ![]() ${{\mathcal {F}}}\in K^{\mathbf {T}}_0(C)$, we have
${{\mathcal {F}}}\in K^{\mathbf {T}}_0(C)$, we have
where ![]() $N_{C/X}=L_1\otimes \mathfrak {t}_1\oplus L_2\otimes \mathfrak {t}_2$ is the
$N_{C/X}=L_1\otimes \mathfrak {t}_1\oplus L_2\otimes \mathfrak {t}_2$ is the ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant normal bundle of
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant normal bundle of ![]() $i:C\to X$; an analogous statement holds for
$i:C\to X$; an analogous statement holds for ![]() $i:C\times C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}\to X\times C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$. Therefore,
$i:C\times C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}\to X\times C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$. Therefore,
 \begin{align*} &\mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om( {{\mathbb{F}}},{{\mathbb{F}}})\\ &\quad =\sum_{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om_X( i_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{ij}),i_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{lk})\otimes L_1^{i-l}L_2^{j-k} )\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k}\\ &\quad =\sum_{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om_C( \mathbf{L}i^{*}i_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{ij}),\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{lk})\otimes L_1^{i-l}L_2^{j-k} )\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k}\\ &\quad =\sum_{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda}\mathbf{R}\pi_*((\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}-L_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1-L_2\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2+ L_1 L_2\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{lk}-{{\mathcal{Z}}}_{ij})\otimes L_1^{i-l}L_2^{j-k} )\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k} ), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &\mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om( {{\mathbb{F}}},{{\mathbb{F}}})\\ &\quad =\sum_{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om_X( i_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{ij}),i_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{lk})\otimes L_1^{i-l}L_2^{j-k} )\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k}\\ &\quad =\sum_{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om_C( \mathbf{L}i^{*}i_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{ij}),\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{lk})\otimes L_1^{i-l}L_2^{j-k} )\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k}\\ &\quad =\sum_{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda}\mathbf{R}\pi_*((\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}-L_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1-L_2\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2+ L_1 L_2\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{lk}-{{\mathcal{Z}}}_{ij})\otimes L_1^{i-l}L_2^{j-k} )\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k} ), \end{align*}
where in the second line we used adjunction in the derived category. To simplify the notation, for any ![]() $(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda$ set
$(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda$ set ![]() $\Delta _{ij;lk}={{\mathcal {Z}}}_{lk}-{{\mathcal {Z}}}_{ij}$, which is an effective divisor if
$\Delta _{ij;lk}={{\mathcal {Z}}}_{lk}-{{\mathcal {Z}}}_{ij}$, which is an effective divisor if ![]() $(i,j)\leq (l,k)$. Putting this all together we have the following identity in
$(i,j)\leq (l,k)$. Putting this all together we have the following identity in ![]() $K_0^{\mathbf {T}}(C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$:
$K_0^{\mathbf {T}}(C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$:
 \begin{align} {{\mathbb{E}}}^{\vee}&=\sum_{(i,j)\in \lambda}\mathbf{R}\pi_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{ij}) \otimes L_1^{-i} L_2^{-j}) \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{-j}\nonumber\\ &\quad -\sum_{(i,j)\in \lambda}(\mathbf{R}\pi_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{ij}) \otimes K_X\otimes L_1^{-i} L_2^{-j} \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{-j}))^{\vee} \otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2\nonumber\\ &\quad -\sum_{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda}\mathbf{R}\pi_*((\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}-L_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1 -L_2\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2+ L_1L_2\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)(\Delta_{ij;lk})\otimes L_1^{i-l}L_2^{j-k}) \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k} ). \end{align}
\begin{align} {{\mathbb{E}}}^{\vee}&=\sum_{(i,j)\in \lambda}\mathbf{R}\pi_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{ij}) \otimes L_1^{-i} L_2^{-j}) \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{-j}\nonumber\\ &\quad -\sum_{(i,j)\in \lambda}(\mathbf{R}\pi_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{ij}) \otimes K_X\otimes L_1^{-i} L_2^{-j} \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{-j}))^{\vee} \otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2\nonumber\\ &\quad -\sum_{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda}\mathbf{R}\pi_*((\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}-L_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1 -L_2\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2+ L_1L_2\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)(\Delta_{ij;lk})\otimes L_1^{i-l}L_2^{j-k}) \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k} ). \end{align}Theorem 4.1 There is an identity of virtual fundamental classes
where the class on the left-hand-side is induced by (3.1) by Graber–Pandharipande localization and that on the right-hand side is constructed in Corollary 2.9.
Proof. By a result of Siebert [Reference SiebertSie04, Theorem 4.6] any two virtual fundamental classes coincide if the classes in ![]() $K$-theory of their perfect obstruction theory agree. The class in
$K$-theory of their perfect obstruction theory agree. The class in ![]() $K$-theory of the dual of the induced PT perfect obstruction theory is the
$K$-theory of the dual of the induced PT perfect obstruction theory is the ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed part of
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed part of ![]() ${{\mathbb {E}}}^{\vee }$ by [Reference Graber and PandharipandeGP99, Proposition 1]
${{\mathbb {E}}}^{\vee }$ by [Reference Graber and PandharipandeGP99, Proposition 1]
 \begin{align} ({{\mathbb{E}}}^{\vee})^{\mathsf{fix}}&=\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00})- \sum_{(i,j)\in \lambda}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}} +\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}(\Delta_{i-1,j;ij})\nonumber\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq 1}}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}(\Delta_{i,j-1;ij}) -\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}(\Delta_{i -1,j-1;ij}). \end{align}
\begin{align} ({{\mathbb{E}}}^{\vee})^{\mathsf{fix}}&=\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00})- \sum_{(i,j)\in \lambda}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}} +\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}(\Delta_{i-1,j;ij})\nonumber\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq 1}}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}(\Delta_{i,j-1;ij}) -\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}(\Delta_{i -1,j-1;ij}). \end{align}
We explained in § 2.1 how to associate a graph with any Young diagram ![]() $\lambda$. Note that boxes
$\lambda$. Note that boxes ![]() $(i,j)\in \lambda$ are in bijection with the vertices
$(i,j)\in \lambda$ are in bijection with the vertices ![]() $V$, boxes
$V$, boxes ![]() $(i,j)\in \lambda$, such that
$(i,j)\in \lambda$, such that ![]() $i\geq 1$ (respectively,
$i\geq 1$ (respectively, ![]() $j\geq 1$) are in bijection with vertical (respectively, horizontal) edges
$j\geq 1$) are in bijection with vertical (respectively, horizontal) edges ![]() $E$ and boxes
$E$ and boxes ![]() $(i,j)\in \lambda$, such that
$(i,j)\in \lambda$, such that ![]() $i,j\geq 1$ are in bijection with squares
$i,j\geq 1$ are in bijection with squares ![]() $Q$ of the associated graph. By Lemma 2.1
$Q$ of the associated graph. By Lemma 2.1
From the universal exact sequences
whenever ![]() $\Delta _{ij,lk}$ is an effective divisor, we deduce the identity in
$\Delta _{ij,lk}$ is an effective divisor, we deduce the identity in ![]() $K$-theory
$K$-theory
and similarly for ![]() ${{\mathcal {Z}}}_{00}$ replaced by
${{\mathcal {Z}}}_{00}$ replaced by ![]() $\Delta _{ij;lk}$. Substituting (4.5) in (4.2) and noting that
$\Delta _{ij;lk}$. Substituting (4.5) in (4.2) and noting that
we obtain
 \begin{align*} ({{\mathbb{E}}}^{\vee})^{\mathsf{fix}}&=\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00}) +\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i-1, j;ij}}(\Delta_{i-1,j;ij})\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq 1}}\mathbf{R} \pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i,j-1;ij}}(\Delta_{i,j-1;ij}) -\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i-1, j-1;ij}}(\Delta_{i-1,j-1;ij}). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} ({{\mathbb{E}}}^{\vee})^{\mathsf{fix}}&=\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00}) +\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i-1, j;ij}}(\Delta_{i-1,j;ij})\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq 1}}\mathbf{R} \pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i,j-1;ij}}(\Delta_{i,j-1;ij}) -\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}\mathbf{R}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i-1, j-1;ij}}(\Delta_{i-1,j-1;ij}). \end{align*}
Moreover, in the expression above, all higher direct images ![]() $\mathbf {R}^{k}\pi _*$ vanish for
$\mathbf {R}^{k}\pi _*$ vanish for ![]() $k> 0$ by cohomology and base change, therefore
$k> 0$ by cohomology and base change, therefore
 \begin{align*} ({{\mathbb{E}}}^{\vee})^{\mathsf{fix}}&=\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00})+\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq~1}}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i-1,j;ij}}(\Delta_{i-1,j;ij})\nonumber\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq~1}}\pi_* \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i,j-1;ij}}(\Delta_{i,j-1;ij}) -\sum_{\substack{(i,j) \in \lambda\\ i,j\geq~1}}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i-1,j-1;ij}}(\Delta_{i-1,j-1;ij}). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} ({{\mathbb{E}}}^{\vee})^{\mathsf{fix}}&=\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00})+\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq~1}}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i-1,j;ij}}(\Delta_{i-1,j;ij})\nonumber\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq~1}}\pi_* \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i,j-1;ij}}(\Delta_{i,j-1;ij}) -\sum_{\substack{(i,j) \in \lambda\\ i,j\geq~1}}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i-1,j-1;ij}}(\Delta_{i-1,j-1;ij}). \end{align*}
We finally show that this is precisely the same class in ![]() $K$-theory as
$K$-theory as
where ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}\to A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }$ is the vector bundle constructed in Theorem 2.8. In fact, in the notation of § 2.4, we have
${{\mathcal {E}}}\to A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }$ is the vector bundle constructed in Theorem 2.8. In fact, in the notation of § 2.4, we have
 \begin{align*} {{\mathcal{X}}}_{ij}|_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}\times C}&=\Delta_{i-1,j;ij}, \quad i\geq 1,\\ {{\mathcal{Y}}}_{ij}|_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}\times C}&=\Delta_{i,j-1;ij}, \quad j\geq 1,\\ \Gamma^{1}_{ij}|_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}\times C}&= \Gamma^{2}_{ij}|_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}\times C}=\Delta_{i-1,j-1;ij}, \quad i,j\geq 1. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} {{\mathcal{X}}}_{ij}|_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}\times C}&=\Delta_{i-1,j;ij}, \quad i\geq 1,\\ {{\mathcal{Y}}}_{ij}|_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}\times C}&=\Delta_{i,j-1;ij}, \quad j\geq 1,\\ \Gamma^{1}_{ij}|_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}\times C}&= \Gamma^{2}_{ij}|_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}\times C}=\Delta_{i-1,j-1;ij}, \quad i,j\geq 1. \end{align*}Moreover, the explicit description of the tangent bundle of the Hilbert scheme of points on a smooth curve in terms of its universal subscheme [Reference Arbarello, Cornalba, Griffiths and HarrisACGH85, Lemma IV.2.3] yields
 \begin{align*} T_{A_{C,\mathbf{n}_\lambda}}=\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00}) \oplus\bigoplus_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}} \pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{{\mathcal{X}}}_{ij}}({{\mathcal{X}}}_{ij})\oplus\bigoplus_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq 1}}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{{\mathcal{Y}}}_{ij}}({{\mathcal{Y}}}_{ij}), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} T_{A_{C,\mathbf{n}_\lambda}}=\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00}) \oplus\bigoplus_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}} \pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{{\mathcal{X}}}_{ij}}({{\mathcal{X}}}_{ij})\oplus\bigoplus_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq 1}}\pi_*\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{{\mathcal{Y}}}_{ij}}({{\mathcal{Y}}}_{ij}), \end{align*}by which we conclude that
In virtue of Theorem 4.1, we now denote by ![]() $T_{C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ the class in
$T_{C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ the class in ![]() $K$-theory of the dual of the perfect obstruction theory (2.2) and that induced by the fixed part of (3.1), which we showed to agree.
$K$-theory of the dual of the perfect obstruction theory (2.2) and that induced by the fixed part of (3.1), which we showed to agree.
In order to compute stable pair invariants (3.3) one needs to express the virtual normal bundle (3.4) in terms of ![]() $K$-theoretic classes which are easier to handle. For instance, we could express
$K$-theoretic classes which are easier to handle. For instance, we could express ![]() $N^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ in terms of pullbacks of the line bundles
$N^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ in terms of pullbacks of the line bundles ![]() $L_1,L_2, K_C$ and the universal divisors
$L_1,L_2, K_C$ and the universal divisors ![]() $\Delta _{ij;lk}$, but that would lead to cumbersome expressions difficult to manipulate.
$\Delta _{ij;lk}$, but that would lead to cumbersome expressions difficult to manipulate.
Example 4.2 As a concrete example, we compute the weight space of ![]() ${{\mathbb {E}}}^{\vee }$ relative to the character
${{\mathbb {E}}}^{\vee }$ relative to the character ![]() $\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2$, which we denote by
$\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2$, which we denote by ![]() ${{\mathbb {E}}}_{\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2}^{\vee }$.
${{\mathbb {E}}}_{\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2}^{\vee }$.
An application of Grothendieck duality and projection formula on ![]() $\pi : C\times C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}\to C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ yields
$\pi : C\times C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}\to C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ yields
for any divisor ![]() $\Delta \subset C\times C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ and any line bundle
$\Delta \subset C\times C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ and any line bundle ![]() $L$ on
$L$ on ![]() $C$. As in the proof of Theorem 4.1, combining (4.3), (4.4), (4.6), the identity
$C$. As in the proof of Theorem 4.1, combining (4.3), (4.4), (4.6), the identity ![]() $K_X=K_C\otimes L_1^{-1}\otimes L^{-1}_2$ and some vanishing of higher direct images yields
$K_X=K_C\otimes L_1^{-1}\otimes L^{-1}_2$ and some vanishing of higher direct images yields
 \begin{align*} {{\mathbb{E}}}_{\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2}^{\vee}&=-(\pi_*(K_X\otimes\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00})))^{\vee}- \sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}}(\pi_*(K_X \otimes\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i-1,j;ij}}(\Delta_{i-1,j;ij})))^{\vee}\\ &\quad -\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq 1}}(\pi_*(K_X\otimes \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i,j-1;ij}}(\Delta_{i,j-1;ij})))^{\vee} +\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}(\pi_*(K_X\otimes \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i-1,j-1;ij}}(\Delta_{i-1,j-1;ij})))^{\vee}. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} {{\mathbb{E}}}_{\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2}^{\vee}&=-(\pi_*(K_X\otimes\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{00})))^{\vee}- \sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}}(\pi_*(K_X \otimes\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i-1,j;ij}}(\Delta_{i-1,j;ij})))^{\vee}\\ &\quad -\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq 1}}(\pi_*(K_X\otimes \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i,j-1;ij}}(\Delta_{i,j-1;ij})))^{\vee} +\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}(\pi_*(K_X\otimes \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{\Delta_{i-1,j-1;ij}}(\Delta_{i-1,j-1;ij})))^{\vee}. \end{align*} The situation notably simplifies if we impose ![]() $X$ to be Calabi–Yau.
$X$ to be Calabi–Yau.
Proposition 4.3 If ![]() $X$ is Calabi–Yau, we have an identity
$X$ is Calabi–Yau, we have an identity
where ![]() $\Omega,\Omega ^{\vee }\in K^{0}_\mathbf {T}( C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$ have no weight spaces corresponding to the characters
$\Omega,\Omega ^{\vee }\in K^{0}_\mathbf {T}( C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$ have no weight spaces corresponding to the characters ![]() $(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2)^{0}, \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2$.
$(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2)^{0}, \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2$.
Proof. If ![]() $X$ is Calabi–Yau, the perfect obstruction theory (3.1) satisfies
$X$ is Calabi–Yau, the perfect obstruction theory (3.1) satisfies
by ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant Serre duality. Setting
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant Serre duality. Setting ![]() ${{\mathbb {E}}}^{\vee }=W_+-W_-$, where
${{\mathbb {E}}}^{\vee }=W_+-W_-$, where ![]() $W_+, W_-\in K^{0}_\mathbf {T}( C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$ are classes of
$W_+, W_-\in K^{0}_\mathbf {T}( C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$ are classes of ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant vector bundles, (4.7) implies that
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant vector bundles, (4.7) implies that
We have that ![]() $({{\mathbb {E}}}^{\vee })^{\mathsf {fix}}=T^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}}$, therefore
$({{\mathbb {E}}}^{\vee })^{\mathsf {fix}}=T^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}}$, therefore
which concludes the argument.
Remark 4.4 A simple computation shows that we could take ![]() $\Omega$ to be of the form
$\Omega$ to be of the form
 \begin{align*} \Omega&=\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (0,0)}}\mathbf{R} \pi_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{ij}) \otimes L_1^{-i} L_2^{-j}) \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{-j}\\ &\quad -\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (l,k)\\(i,j) \neq (l+1,k+1)}}\mathbf{R}\pi_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}(\Delta_{ij;lk})\otimes L_1^{i-l} L_2^{j-k} )\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k}\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (l-1,k)\\(i,j) \neq (l,k+1)}}\mathbf{R}\pi_* ( \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}(\Delta_{ij;lk})\otimes L_1^{i -l+1}L_2^{j-k} )\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l+1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k}. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \Omega&=\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (0,0)}}\mathbf{R} \pi_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{ij}) \otimes L_1^{-i} L_2^{-j}) \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{-j}\\ &\quad -\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (l,k)\\(i,j) \neq (l+1,k+1)}}\mathbf{R}\pi_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}(\Delta_{ij;lk})\otimes L_1^{i-l} L_2^{j-k} )\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k}\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (l-1,k)\\(i,j) \neq (l,k+1)}}\mathbf{R}\pi_* ( \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}(\Delta_{ij;lk})\otimes L_1^{i -l+1}L_2^{j-k} )\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l+1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k}. \end{align*}
All other choices ![]() $\tilde {\Omega }$ must be of the form
$\tilde {\Omega }$ must be of the form
for any ![]() $A\in K^{0}_\mathbf {T}( C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$ having no weight spaces corresponding to the characters
$A\in K^{0}_\mathbf {T}( C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$ having no weight spaces corresponding to the characters ![]() $(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2)^{0}, \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2$. In particular, this implies that the parity of
$(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2)^{0}, \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2$. In particular, this implies that the parity of ![]() $\operatorname {rk} \Omega$ is independent by the choice of
$\operatorname {rk} \Omega$ is independent by the choice of ![]() $\Omega$.
$\Omega$.
5. Universality
5.1 Universal expression
In the previous sections, given a triple ![]() $(C,L_1,L_2)$ with
$(C,L_1,L_2)$ with ![]() $C$ an irreducible smooth projective curve and
$C$ an irreducible smooth projective curve and ![]() $L_1, L_2$ line bundles on
$L_1, L_2$ line bundles on ![]() $C$, we reduced stable pair invariants (with no insertions) of
$C$, we reduced stable pair invariants (with no insertions) of ![]() $\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ to the computation of
$\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ to the computation of
where ![]() $\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ is a reversed plane partition and the virtual normal bundle
$\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ is a reversed plane partition and the virtual normal bundle ![]() $N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ is the
$N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ is the ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-moving part of the class in
$\mathbf {T}$-moving part of the class in ![]() $K$-theory (4.1).
$K$-theory (4.1).
We state our main results, describing the generating series of (5.1) in terms of three universal functions exploiting the universality techniques used in [Reference Ellingsrud, Göttsche and LehnEGL01, Theorem 4.2] for surfaces. Furthermore, we find explicit expressions for these universal series under the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$.
$s_1+s_2=0$.
Theorem 5.1 Let ![]() $C$ be a genus
$C$ be a genus ![]() $g$ smooth irreducible projective curve and
$g$ smooth irreducible projective curve and ![]() $L_1, L_2$ line bundles over
$L_1, L_2$ line bundles over ![]() $C$. We have an identity
$C$. We have an identity
 \[ \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}) =A_{\lambda}^{g-1}\cdot B_{\lambda}^{\deg L_1}\cdot C_{\lambda}^{\deg L_2}\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(s_1,s_2)[\![ q ]\!], \]
\[ \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}) =A_{\lambda}^{g-1}\cdot B_{\lambda}^{\deg L_1}\cdot C_{\lambda}^{\deg L_2}\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(s_1,s_2)[\![ q ]\!], \]
where ![]() $A_{\lambda },B_{\lambda },C_{\lambda }\in {{\mathbb {Q}}}(s_1,s_2)[\![ q ]\!]$ are fixed universal series for
$A_{\lambda },B_{\lambda },C_{\lambda }\in {{\mathbb {Q}}}(s_1,s_2)[\![ q ]\!]$ are fixed universal series for ![]() $i=1,2,3$ which only depend on
$i=1,2,3$ which only depend on ![]() $\lambda$. Moreover,
$\lambda$. Moreover,
Proof. The proof is similar to [Reference Ellingsrud, Göttsche and LehnEGL01, Theorem 4.2]. Consider the map
given by
 \[ Z(C,L_1, L_2)= C_{g,\deg L_1\deg L_2}^{-1}\cdot\sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}), \]
\[ Z(C,L_1, L_2)= C_{g,\deg L_1\deg L_2}^{-1}\cdot\sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}), \]
where ![]() $C_{g,\deg L_1\deg L_2}$ is the leading term of the generating series of the integrals (5.1).
$C_{g,\deg L_1\deg L_2}$ is the leading term of the generating series of the integrals (5.1).
By Proposition 5.2 the integral (5.1) is multiplicative and by Corollary 5.4 it is a polynomial on ![]() $g, \deg L_1, \deg L_2$. This implies that
$g, \deg L_1, \deg L_2$. This implies that ![]() $Z$ factors through
$Z$ factors through
where ![]() $\gamma (C,L_1, L_2)=(g-1, \deg L_1, \deg L_2)$ and
$\gamma (C,L_1, L_2)=(g-1, \deg L_1, \deg L_2)$ and ![]() $Z'$ is a linear map.
$Z'$ is a linear map.
A basis of ![]() ${{\mathbb {Q}}}^{3}$ is given by the images
${{\mathbb {Q}}}^{3}$ is given by the images
and the image of a generic triple ![]() $(C,L_1,L_2)$ can be written as
$(C,L_1,L_2)$ can be written as
We conclude that
which gives the universal series we were looking for. The second claim just follows by interchanging the role of ![]() $L_1$ and
$L_1$ and ![]() $L_2$.
$L_2$.
We devote the remainder of § 5 to prove the multiplicativity and polynomiality of (5.1). In § 6 we compute the leading term of the generating series of (5.1), whereas in § 7 we explicitly compute the integral (5.1) in the toric case under the anti-diagonal restriction. These computations will lead to the proof of the second part of the main Theorem 1.3 (see Theorem 8.1).
5.2 Multiplicativity
We now show that the integral (5.1) is multiplicative. First, note that if ![]() $C=C'\sqcup C''$ is a smooth projective curve with two connected components, the construction of Theorem 2.8 does not directly work and we need to adjust it to define a virtual fundamental class.
$C=C'\sqcup C''$ is a smooth projective curve with two connected components, the construction of Theorem 2.8 does not directly work and we need to adjust it to define a virtual fundamental class.
For any reversed plane partition ![]() $\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ there is an induced stratification
$\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ there is an induced stratification
We set
which is a smooth projective variety. Let ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}_{C',\mathbf {n}'_\lambda },{{\mathcal {E}}}_{C'',\mathbf {n}''_\lambda }$ denote the vector bundles over
${{\mathcal {E}}}_{C',\mathbf {n}'_\lambda },{{\mathcal {E}}}_{C'',\mathbf {n}''_\lambda }$ denote the vector bundles over ![]() $A_{C',\mathbf {n}'_\lambda },A_{C'',\mathbf {n}''_\lambda }$ of Theorem 2.8. We define a vector bundle
$A_{C',\mathbf {n}'_\lambda },A_{C'',\mathbf {n}''_\lambda }$ of Theorem 2.8. We define a vector bundle ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }$ over
${{\mathcal {E}}}_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }$ over ![]() $A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }$ by declaring its restriction to any connected component
$A_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }$ by declaring its restriction to any connected component ![]() $A_{C',\mathbf {n}'_\lambda }\times A_{C'',\mathbf {n}''_\lambda }$ to be
$A_{C',\mathbf {n}'_\lambda }\times A_{C'',\mathbf {n}''_\lambda }$ to be
By Theorem 2.8, there exists a section ![]() $s$ of
$s$ of ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }$ such that
${{\mathcal {E}}}_{C,\mathbf {n}_\lambda }$ such that
and, therefore, an induced virtual fundamental class ![]() $[C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}]^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ satisfying
$[C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}]^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ satisfying
By iterating this construction, there exists a natural virtual fundamental class on ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ for any smooth projective curve
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ for any smooth projective curve ![]() $C$ (with any number of connected components).
$C$ (with any number of connected components).
Proposition 5.2 Let ![]() $(C,L_1,L_2)$ be a triple where
$(C,L_1,L_2)$ be a triple where ![]() $C=C'\sqcup C''$ and
$C=C'\sqcup C''$ and ![]() $L_i=L'_i\oplus L''_i$ for
$L_i=L'_i\oplus L''_i$ for ![]() $i=1,2$, where
$i=1,2$, where ![]() $L'_i$ are line bundles on
$L'_i$ are line bundles on ![]() $C'$ and
$C'$ and ![]() $L''_i$ are line bundles on
$L''_i$ are line bundles on ![]() $C''$. Then
$C''$. Then
 \begin{align*} &\sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})\nonumber\\ &\quad = \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[C'^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C', L'_1,L'_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}) \cdot \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[C''^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C'',L''_1, L''_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &\sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})\nonumber\\ &\quad = \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[C'^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C', L'_1,L'_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}) \cdot \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[C''^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C'',L''_1, L''_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}). \end{align*}Proof. Let ![]() $\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ be a fixed reversed plane partition. We claim that the restriction of the virtual normal bundle to the connected component
$\mathbf {n}_\lambda$ be a fixed reversed plane partition. We claim that the restriction of the virtual normal bundle to the connected component ![]() $C'^{[\mathbf {n}'_\lambda ]}\times C''^{[\mathbf {n}''_\lambda ]}\subset C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ decomposes as
$C'^{[\mathbf {n}'_\lambda ]}\times C''^{[\mathbf {n}''_\lambda ]}\subset C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ decomposes as
In fact, ![]() $N^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{C,L_1,L_2}$ is a linear combination of
$N^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{C,L_1,L_2}$ is a linear combination of ![]() $K$-theoretic classes of the form
$K$-theoretic classes of the form
where ![]() $\Delta$ is a
$\Delta$ is a ![]() ${{\mathbb {Z}}}$-linear combination of the universal divisors
${{\mathbb {Z}}}$-linear combination of the universal divisors ![]() ${{\mathcal {Z}}}_{ij}$ on
${{\mathcal {Z}}}_{ij}$ on ![]() $C\times C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$,
$C\times C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, ![]() $a,b\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$ and
$a,b\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$ and ![]() $\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu }$ is a
$\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu }$ is a ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-character and note that
$\mathbf {T}$-character and note that
Consider the induced stratification
Denote by ![]() $\Delta ', \Delta ''$ the corresponding universal divisor on
$\Delta ', \Delta ''$ the corresponding universal divisor on ![]() $C'\times C'^{[\mathbf {n}'_\lambda ]}, C''\times C''^{[\mathbf {n}''_\lambda ]}$ and consider the projection maps
$C'\times C'^{[\mathbf {n}'_\lambda ]}, C''\times C''^{[\mathbf {n}''_\lambda ]}$ and consider the projection maps
 \begin{align*} q_1: C' \times C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]}\times C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]} &\to C' \times C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]},\\ q_2: C'' \times C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]}\times C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]} &\to C'' \times C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]}. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} q_1: C' \times C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]}\times C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]} &\to C' \times C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]},\\ q_2: C'' \times C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]}\times C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]} &\to C'' \times C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]}. \end{align*}
On every component ![]() $(C'\sqcup C'') \times C'^{[\mathbf {n}'_\lambda ]}\times C''^{[\mathbf {n}''_\lambda ]}$ we have
$(C'\sqcup C'') \times C'^{[\mathbf {n}'_\lambda ]}\times C''^{[\mathbf {n}''_\lambda ]}$ we have
and, similarly,
 \begin{align*} &\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}(\Delta)\otimes L_1^{a} L_2^{b}|_{(C'\sqcup C'') \times C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]} \times C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]}}\\ &\quad =q_1^{*}(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C'\times C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]}}(\Delta') \otimes {L'_1}^{a} {L'_2}^{b})\oplus q_2^{*}(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C'' \times C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]}}(\Delta'')\otimes {L''_1}^{a} {L''_2}^{b}). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}(\Delta)\otimes L_1^{a} L_2^{b}|_{(C'\sqcup C'') \times C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]} \times C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]}}\\ &\quad =q_1^{*}(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C'\times C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]}}(\Delta') \otimes {L'_1}^{a} {L'_2}^{b})\oplus q_2^{*}(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C'' \times C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]}}(\Delta'')\otimes {L''_1}^{a} {L''_2}^{b}). \end{align*}Consider the following cartesian diagram given by the natural projections.

Flat base change yields
and analogously for ![]() $C''$, which implies
$C''$, which implies
 \begin{align*} &\mathbf{R}\pi_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}(\Delta) \otimes L_1^{a}L_2^{b})\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{\mu}|_{ C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]} \times C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]}}\\ &\quad = \mathbf{R}{\pi_1}_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C'\times C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]}}(\Delta') \otimes {L'_1}^{a}{L'_2}^{b})\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{\mu}\boxplus \mathbf{R}{\pi_2}_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C''\times C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]}}(\Delta'') \otimes {L''_1}^{a} {L''_2}^{b})\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{\mu}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &\mathbf{R}\pi_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C\times C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}(\Delta) \otimes L_1^{a}L_2^{b})\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{\mu}|_{ C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]} \times C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]}}\\ &\quad = \mathbf{R}{\pi_1}_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C'\times C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]}}(\Delta') \otimes {L'_1}^{a}{L'_2}^{b})\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{\mu}\boxplus \mathbf{R}{\pi_2}_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C''\times C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]}}(\Delta'') \otimes {L''_1}^{a} {L''_2}^{b})\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{\mu}, \end{align*}and proves the claim (5.3). Combining (5.2) and (5.3) yields
 \[ \int_{[C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}) = \sum_{\mathbf{n}'_\lambda+\mathbf{n}''_\lambda= \mathbf{n}_\lambda}\int_{[C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C',L'_1,L'_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})\cdot \int_{[C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C'',L''_1,L''_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}), \]
\[ \int_{[C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}) = \sum_{\mathbf{n}'_\lambda+\mathbf{n}''_\lambda= \mathbf{n}_\lambda}\int_{[C'^{[\mathbf{n}'_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C',L'_1,L'_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})\cdot \int_{[C''^{[\mathbf{n}''_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C'',L''_1,L''_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}), \]which concludes the proof.
5.3 Chern numbers dependence
We now show that the integral 5.1 is a polynomial in the Chern numbers of the triple ![]() $(C, L_1, L_2)$. Our strategy is to express the integral on a product of Picard varieties
$(C, L_1, L_2)$. Our strategy is to express the integral on a product of Picard varieties ![]() $\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{n}(C)$, via the Abel–Jacobi map, where the integrand is a polynomial expression on tautological classes. Through this section, we follow the notation as in [Reference Arbarello, Cornalba, Griffiths and HarrisACGH85, § VIII.2] and [Reference Kool and ThomasKT17, §§ 9, 10.1].
$\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{n}(C)$, via the Abel–Jacobi map, where the integrand is a polynomial expression on tautological classes. Through this section, we follow the notation as in [Reference Arbarello, Cornalba, Griffiths and HarrisACGH85, § VIII.2] and [Reference Kool and ThomasKT17, §§ 9, 10.1].
5.3.1 Tautological integrals on  $\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{n}(C)$
$\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{n}(C)$
Let ![]() $C$ be a smooth curve of genus
$C$ be a smooth curve of genus ![]() $g$. If
$g$. If ![]() $n> 2g-2$, the Abel–Jacobi map
$n> 2g-2$, the Abel–Jacobi map
 \begin{align*} \operatorname{AJ}:C^{(n)}&\to \mathop{\rm Pic}\nolimits^{n}(C)\\ Z&\to [\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_C(Z)] \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \operatorname{AJ}:C^{(n)}&\to \mathop{\rm Pic}\nolimits^{n}(C)\\ Z&\to [\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_C(Z)] \end{align*}is a projective bundle. In fact, consider the diagram

and a Poincaré line bundle ![]() ${{\mathcal {P}}}$ on
${{\mathcal {P}}}$ on ![]() $\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{n}(C)\times C$, normalized by fixing
$\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{n}(C)\times C$, normalized by fixing
for a certain ![]() $c\in C$. Then
$c\in C$. Then
The universal divisor ![]() ${{\mathcal {Z}}}\subset C^{(n)}\times C$ satisfies [Reference Kool and ThomasKT17, (67)]
${{\mathcal {Z}}}\subset C^{(n)}\times C$ satisfies [Reference Kool and ThomasKT17, (67)]
and we denote the first Chern class of the latter by
Now consider the product of Abel–Jacobi maps
where each ![]() $n_i> 2g-2$. We denote by
$n_i> 2g-2$. We denote by ![]() ${{\mathcal {P}}}_i$ (the pullback of) the Poincaré line bundle on
${{\mathcal {P}}}_i$ (the pullback of) the Poincaré line bundle on ![]() $\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{n_i}(C)\times C$, each normalized at a point
$\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{n_i}(C)\times C$, each normalized at a point ![]() $c_i\in C$, and by
$c_i\in C$, and by ![]() $\omega _i$ the first Chern classes of the tautological bundles on
$\omega _i$ the first Chern classes of the tautological bundles on ![]() $C^{(n_i)}$. Finally, we denote by
$C^{(n_i)}$. Finally, we denote by ![]() ${{\mathcal {Z}}}_i\subset C^{(n_i)}\times C$ the universal divisors and by
${{\mathcal {Z}}}_i\subset C^{(n_i)}\times C$ the universal divisors and by ![]() ${{\mathcal {I}}}_i$ (the pullback of) their ideal sheaves, which in this case are line bundles.
${{\mathcal {I}}}_i$ (the pullback of) their ideal sheaves, which in this case are line bundles.
We are interested in studying integrals of the form
where ![]() $f$ is a polynomial in the Chern classes of the
$f$ is a polynomial in the Chern classes of the ![]() $K$-theoretic classes
$K$-theoretic classes
 \[ \mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{I}}}_i,\bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{I}}}_j\otimes L_k\bigg), \]
\[ \mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{I}}}_i,\bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{I}}}_j\otimes L_k\bigg), \]
![]() $L_k$ are line bundles on
$L_k$ are line bundles on ![]() $C$ and
$C$ and ![]() $I,J$ are families of indices (possibly with repetitions).
$I,J$ are families of indices (possibly with repetitions).
We assume now that ![]() $n_i\gg 0$ for all
$n_i\gg 0$ for all ![]() $i=1,\ldots, s$. Applying the projection formula and flat base change yields
$i=1,\ldots, s$. Applying the projection formula and flat base change yields
 \begin{align*} &\mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{I}}}_i,\bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{I}}}_j\otimes L_k\bigg)\\ &\quad = \mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}(\operatorname{AJ}\times \operatorname{id})^{*}{{\mathcal{P}}}_i^{*}\otimes \pi^{*}\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C^{(n_i)}}(-1),\bigotimes_{j\in J}(\operatorname{AJ}\times \operatorname{id})^{*}{{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*}\otimes \pi^{*}\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C^{(n_j)}}(-1)\otimes L_k\bigg)\\ &\quad = {{\mathcal{F}}}\otimes\mathbf{R}\pi_*\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}(\operatorname{AJ}\times \operatorname{id})^{*}{{\mathcal{P}}}_i\otimes\bigotimes_{j\in J}(\operatorname{AJ}\times \operatorname{id})^{*}{{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*}\otimes L_k \bigg)\\ &\quad = {{\mathcal{F}}}\otimes \operatorname{AJ}^{*}\mathbf{R}\overline{\pi}_*\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{P}}}_i\otimes\bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*}\otimes L_k \bigg), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &\mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{I}}}_i,\bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{I}}}_j\otimes L_k\bigg)\\ &\quad = \mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}(\operatorname{AJ}\times \operatorname{id})^{*}{{\mathcal{P}}}_i^{*}\otimes \pi^{*}\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C^{(n_i)}}(-1),\bigotimes_{j\in J}(\operatorname{AJ}\times \operatorname{id})^{*}{{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*}\otimes \pi^{*}\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C^{(n_j)}}(-1)\otimes L_k\bigg)\\ &\quad = {{\mathcal{F}}}\otimes\mathbf{R}\pi_*\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}(\operatorname{AJ}\times \operatorname{id})^{*}{{\mathcal{P}}}_i\otimes\bigotimes_{j\in J}(\operatorname{AJ}\times \operatorname{id})^{*}{{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*}\otimes L_k \bigg)\\ &\quad = {{\mathcal{F}}}\otimes \operatorname{AJ}^{*}\mathbf{R}\overline{\pi}_*\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{P}}}_i\otimes\bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*}\otimes L_k \bigg), \end{align*}
where ![]() ${{\mathcal {F}}}=\bigotimes _{i\in I}\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{C^{(n_i)}}(1)\otimes \bigotimes _{j\in J} \operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{C^{(n_j)}}(-1)$. The Chern classes of the last expression are a linear combination of
${{\mathcal {F}}}=\bigotimes _{i\in I}\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{C^{(n_i)}}(1)\otimes \bigotimes _{j\in J} \operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{C^{(n_j)}}(-1)$. The Chern classes of the last expression are a linear combination of
 \[ \prod_{i=1}^{s}\omega_i^{m_i}\cdot \operatorname{AJ}^{*}{{\mathrm{ch}}}_l\bigg(\mathbf{R}\overline{\pi}_* \bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{P}}}_i\otimes\bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*}\otimes L_k \bigg)\bigg), \]
\[ \prod_{i=1}^{s}\omega_i^{m_i}\cdot \operatorname{AJ}^{*}{{\mathrm{ch}}}_l\bigg(\mathbf{R}\overline{\pi}_* \bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{P}}}_i\otimes\bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*}\otimes L_k \bigg)\bigg), \]
where ![]() ${{\mathrm {ch}}}$ denotes the Chern character for certain
${{\mathrm {ch}}}$ denotes the Chern character for certain ![]() $m_i\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}_{\geq 0}$. Integrating this class yields
$m_i\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}_{\geq 0}$. Integrating this class yields
 \begin{align*} &\int_{C^{(n_1)}\times \cdots\times C^{(n_s)}} \prod_{i=1}^{s}\omega_i^{m_i}\cdot \operatorname{AJ}^{*}{{\mathrm{ch}}}_l\bigg(\mathbf{R}\overline{\pi}_* \bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{P}}}_i\otimes\bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*}\otimes L_k \bigg)\bigg)\\ &\quad = \int_{\mathop{\rm Pic}\nolimits^{n_1}(C)\times \cdots\times \mathop{\rm Pic}\nolimits^{n_s}(C)}\operatorname{AJ}_* \prod_{i=1}^{s}\omega_i^{m_i}\cdot {{\mathrm{ch}}}_l \bigg(\mathbf{R}\overline{\pi}_*\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{P}}}_i\otimes \bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*}\otimes L_k \bigg)\bigg). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &\int_{C^{(n_1)}\times \cdots\times C^{(n_s)}} \prod_{i=1}^{s}\omega_i^{m_i}\cdot \operatorname{AJ}^{*}{{\mathrm{ch}}}_l\bigg(\mathbf{R}\overline{\pi}_* \bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{P}}}_i\otimes\bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*}\otimes L_k \bigg)\bigg)\\ &\quad = \int_{\mathop{\rm Pic}\nolimits^{n_1}(C)\times \cdots\times \mathop{\rm Pic}\nolimits^{n_s}(C)}\operatorname{AJ}_* \prod_{i=1}^{s}\omega_i^{m_i}\cdot {{\mathrm{ch}}}_l \bigg(\mathbf{R}\overline{\pi}_*\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{P}}}_i\otimes \bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*}\otimes L_k \bigg)\bigg). \end{align*}
Using a standard identity [Reference FultonFul98, § 3.1] we can express the pushforward ![]() $\operatorname {AJ}_*\omega _i^{m_i}$ in terms of Segre classes (and, therefore, Chern characters) of
$\operatorname {AJ}_*\omega _i^{m_i}$ in terms of Segre classes (and, therefore, Chern characters) of ![]() $\overline {\pi }_*{{\mathcal {P}}}_i$. These Chern characters appearing in the integral are computed by Grothendieck–Riemann–Roch:
$\overline {\pi }_*{{\mathcal {P}}}_i$. These Chern characters appearing in the integral are computed by Grothendieck–Riemann–Roch:
 \[ {{\mathrm{ch}}}\bigg(\mathbf{R}\overline{\pi}_*\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{P}}}_i\otimes \bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*}\otimes L_k \bigg)\bigg)=\overline{\pi}_* \bigg(\prod_{i\in I}{{\mathrm{ch}}}({{\mathcal{P}}}_i)\prod_{j\in J}{{\mathrm{ch}}}({{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*})\cdot e^{c_1(L_k)}\cdot {{\mathrm{td}}}(T_C) \bigg). \]
\[ {{\mathrm{ch}}}\bigg(\mathbf{R}\overline{\pi}_*\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{P}}}_i\otimes \bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*}\otimes L_k \bigg)\bigg)=\overline{\pi}_* \bigg(\prod_{i\in I}{{\mathrm{ch}}}({{\mathcal{P}}}_i)\prod_{j\in J}{{\mathrm{ch}}}({{\mathcal{P}}}_j^{*})\cdot e^{c_1(L_k)}\cdot {{\mathrm{td}}}(T_C) \bigg). \]The Chern character of the Poincaré line bundle is (cf. [Reference Arbarello, Cornalba, Griffiths and HarrisACGH85, p. 335])
Here, in the decomposition
we have
 \begin{align*} &[c_i]\in H^{2}(C),\\ &\theta_i\in H^{2}(\mathop{\rm Pic}\nolimits^{n_i}(C)),\\ &\gamma_i=[\Delta]^{1,1}\in H^{1}(C)\otimes H^{1}(C)\cong H^{1}(\mathop{\rm Pic}\nolimits^{n_i}(C))\otimes H^{1}(C), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &[c_i]\in H^{2}(C),\\ &\theta_i\in H^{2}(\mathop{\rm Pic}\nolimits^{n_i}(C)),\\ &\gamma_i=[\Delta]^{1,1}\in H^{1}(C)\otimes H^{1}(C)\cong H^{1}(\mathop{\rm Pic}\nolimits^{n_i}(C))\otimes H^{1}(C), \end{align*}
where ![]() $\Delta \subset C\times C$ is the diagonal and
$\Delta \subset C\times C$ is the diagonal and ![]() $\theta _i$ is the theta divisor. All of this results in
$\theta _i$ is the theta divisor. All of this results in
where ![]() $\tilde {f}$ is a polynomial in the classes
$\tilde {f}$ is a polynomial in the classes
5.3.2 Extension to all  $n$
$n$
In the previous section we assumed that all ![]() $n_i> 2g-2$; we now explain how to remove this assumption, following closely [Reference Kool and ThomasKT17, § 10.1].
$n_i> 2g-2$; we now explain how to remove this assumption, following closely [Reference Kool and ThomasKT17, § 10.1].
Let ![]() $n\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}_{\geq 0}$ and
$n\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}_{\geq 0}$ and ![]() $N>2g-2$. Then
$N>2g-2$. Then ![]() $C^{(N)}\cong {{\mathbb {P}}}(\overline {\pi }_*{{\mathcal {P}}})$, where
$C^{(N)}\cong {{\mathbb {P}}}(\overline {\pi }_*{{\mathcal {P}}})$, where ![]() ${{\mathcal {P}}}$ is the Poincaré line bundle on
${{\mathcal {P}}}$ is the Poincaré line bundle on ![]() $\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{N}(C)\times C$ normalized at
$\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{N}(C)\times C$ normalized at ![]() $c\in C$. We can embed
$c\in C$. We can embed ![]() $C^{(n)}$ in
$C^{(n)}$ in ![]() $C^{(N)}$ as the zero section of a vector bundle
$C^{(N)}$ as the zero section of a vector bundle

by sending ![]() $Z\mapsto Z+(N-n)c$, where
$Z\mapsto Z+(N-n)c$, where ![]() ${{\mathcal {W}}}\subset C^{(N)}\times C$ is the universal divisor and
${{\mathcal {W}}}\subset C^{(N)}\times C$ is the universal divisor and ![]() $(N-n)c\subset C$ is an Artinian thickened point. Moreover, the section is regular, therefore
$(N-n)c\subset C$ is an Artinian thickened point. Moreover, the section is regular, therefore
where ![]() ${{\mathcal {G}}}= \pi _*\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}({{\mathcal {W}}})|_{C^{(N)}\times (N-n)c}$. Finally, if we denote by
${{\mathcal {G}}}= \pi _*\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}({{\mathcal {W}}})|_{C^{(N)}\times (N-n)c}$. Finally, if we denote by ![]() ${{\mathcal {Z}}}\subset C^{(n)}\times C$ the universal divisor, we have that
${{\mathcal {Z}}}\subset C^{(n)}\times C$ the universal divisor, we have that ![]() $(\iota \times \operatorname {id})^{*}{{\mathcal {W}}}={{\mathcal {Z}}}((N-n)c)$.
$(\iota \times \operatorname {id})^{*}{{\mathcal {W}}}={{\mathcal {Z}}}((N-n)c)$.
Recall that we are interested in the integrals (5.4). Choose ![]() $N_i> 2g-2$, denote by
$N_i> 2g-2$, denote by ![]() ${{\mathcal {I}}}'_i$ the universal ideal sheaves of the universal divisors
${{\mathcal {I}}}'_i$ the universal ideal sheaves of the universal divisors ![]() ${{\mathcal {W}}}_i$ on
${{\mathcal {W}}}_i$ on ![]() $C^{(N_1)}\times \cdots \times C^{(N_s)}\times C$ and by
$C^{(N_1)}\times \cdots \times C^{(N_s)}\times C$ and by ![]() $\pi '$ the projection map. By base change we can write
$\pi '$ the projection map. By base change we can write
 \begin{align*} &\mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{I}}}_i,\bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{I}}}_j \otimes L_k\bigg)\\ &\quad= \mathbf{L}\iota^{*}\mathbf{R}\pi'_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I} {{\mathcal{I}}}'_i(-(N_i-n_i)c_i),\bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{I}}}'_j(-(N_j-n_j)c_j) \otimes L_k\bigg), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &\mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{I}}}_i,\bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{I}}}_j \otimes L_k\bigg)\\ &\quad= \mathbf{L}\iota^{*}\mathbf{R}\pi'_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I} {{\mathcal{I}}}'_i(-(N_i-n_i)c_i),\bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{I}}}'_j(-(N_j-n_j)c_j) \otimes L_k\bigg), \end{align*}therefore
 \[ \int_{C^{(n_1)}\times \cdots\times C^{(n_s)}}f= \int_{C^{(N_1)}\times \cdots\times C^{(N_s)}} f'\cdot \prod_{i=1}^{s} e({{\mathcal{G}}}_i), \]
\[ \int_{C^{(n_1)}\times \cdots\times C^{(n_s)}}f= \int_{C^{(N_1)}\times \cdots\times C^{(N_s)}} f'\cdot \prod_{i=1}^{s} e({{\mathcal{G}}}_i), \]
where each ![]() ${{\mathcal {G}}}_i=\pi _*\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}({{\mathcal {W}}}_i)|_{C^{(N_i)}\times (N_i-n_i)c_i}$ and
${{\mathcal {G}}}_i=\pi _*\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}({{\mathcal {W}}}_i)|_{C^{(N_i)}\times (N_i-n_i)c_i}$ and ![]() $f'$ is a polynomial in the Chern classes of
$f'$ is a polynomial in the Chern classes of
 \[ \mathbf{R}\pi'_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{I}}}'_i,\bigotimes_{j\in J} {{\mathcal{I}}}'_j\otimes \bigotimes_{i\in I} \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}((N_i-n_i)c_i) \otimes\bigotimes_{j\in J}\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}(-(N_j-n_j)c_j) \otimes L_k\bigg) . \]
\[ \mathbf{R}\pi'_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{I}}}'_i,\bigotimes_{j\in J} {{\mathcal{I}}}'_j\otimes \bigotimes_{i\in I} \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}((N_i-n_i)c_i) \otimes\bigotimes_{j\in J}\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}(-(N_j-n_j)c_j) \otimes L_k\bigg) . \]The exact sequence
yields the identity in ![]() $K$-theory
$K$-theory
by which we conclude that we can apply the construction in § 5.3.1 to express
where ![]() $\tilde {f}$ is a polynomial in the classes
$\tilde {f}$ is a polynomial in the classes
Smooth projective curves of the same genus are diffeomorphic to each other, therefore ![]() $\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{n}(C)$ is diffeomorphic to a
$\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{n}(C)$ is diffeomorphic to a ![]() $g$-dimensional complex torus. By the intersection theory on
$g$-dimensional complex torus. By the intersection theory on ![]() $\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{n}(C)$ developed in [Reference Arbarello, Cornalba, Griffiths and HarrisACGH85, § VIII.2] we immediately obtain the following result.
$\mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits ^{n}(C)$ developed in [Reference Arbarello, Cornalba, Griffiths and HarrisACGH85, § VIII.2] we immediately obtain the following result.
Proposition 5.3 Let ![]() $f$ be a polynomial in the Chern classes of the
$f$ be a polynomial in the Chern classes of the ![]() $K$-theory classes
$K$-theory classes
 \[ \mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{I}}}_i, \bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{I}}}_j\otimes L_k\bigg), \]
\[ \mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{I}}}_i, \bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{I}}}_j\otimes L_k\bigg), \]
where ![]() $L_k$ are line bundles on
$L_k$ are line bundles on ![]() $C$ and
$C$ and ![]() $I,J$ are families of indices (possibly with repetitions). Then
$I,J$ are families of indices (possibly with repetitions). Then
where ![]() $\tilde {f}$ is a polynomial in the classes (5.5). In particular, the integral is a polynomial in the genus
$\tilde {f}$ is a polynomial in the classes (5.5). In particular, the integral is a polynomial in the genus ![]() $g=g(C)$ and the degrees of the line bundles
$g=g(C)$ and the degrees of the line bundles ![]() $\{L_k\}_k$.
$\{L_k\}_k$.
As a corollary, we obtain that the localized contributions on ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ only depend on the Chern numbers of
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ only depend on the Chern numbers of ![]() $(C, L_1, L_2)$.
$(C, L_1, L_2)$.
Corollary 5.4 Let ![]() $C$ be a genus
$C$ be a genus ![]() $g$ irreducible smooth projective curve and
$g$ irreducible smooth projective curve and ![]() $L_1, L_2$ line bundles on
$L_1, L_2$ line bundles on ![]() $C$. Then the intersection numbers (5.1) are polynomials in
$C$. Then the intersection numbers (5.1) are polynomials in ![]() $g, \deg L_1, \deg L_2$.
$g, \deg L_1, \deg L_2$.
Proof. Let ![]() $i:C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}\hookrightarrow A_{C, \mathbf {n}_\lambda }$ be the embedding of Theorem 2.8 and to ease the notation set
$i:C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}\hookrightarrow A_{C, \mathbf {n}_\lambda }$ be the embedding of Theorem 2.8 and to ease the notation set ![]() $A_{C, \mathbf {n}_\lambda }=C^{(n_1)}\times \cdots \times C^{(n_s)}$. We claim that
$A_{C, \mathbf {n}_\lambda }=C^{(n_1)}\times \cdots \times C^{(n_s)}$. We claim that
for a certain class ![]() $\tilde {N}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{C, L_1, L_2}\in K^{0}_\mathbf {T}(A_{C, \mathbf {n}_\lambda })$. In fact,
$\tilde {N}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{C, L_1, L_2}\in K^{0}_\mathbf {T}(A_{C, \mathbf {n}_\lambda })$. In fact, ![]() $N^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{C, L_1, L_2}$ is a linear combination of classes in
$N^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{C, L_1, L_2}$ is a linear combination of classes in ![]() $K$-theory of the form
$K$-theory of the form
where ![]() $\Delta$ is a
$\Delta$ is a ![]() ${{\mathbb {Z}}}$-linear combination of the universal divisors
${{\mathbb {Z}}}$-linear combination of the universal divisors ![]() ${{\mathcal {Z}}}_{ij}$ on
${{\mathcal {Z}}}_{ij}$ on ![]() $C\times C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$,
$C\times C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, ![]() $a,b\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$ and
$a,b\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$ and ![]() $\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu }$ is a
$\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu }$ is a ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-character. Each of such universal divisors
$\mathbf {T}$-character. Each of such universal divisors ![]() $\Delta$ can be expressed, in the Picard group of
$\Delta$ can be expressed, in the Picard group of ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, as a linear combination of the divisors
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, as a linear combination of the divisors ![]() $i^{*}{{\mathcal {Z}}}_{00}, i^{*}{{\mathcal {X}}}_{ij}, i^{*}{{\mathcal {Y}}}_{ij}$, with notation as in § 2.4; applying base change proves the claim. Therefore, the integral (5.1) can be expressed as an intersection number on the product of symmetric powers of curves
$i^{*}{{\mathcal {Z}}}_{00}, i^{*}{{\mathcal {X}}}_{ij}, i^{*}{{\mathcal {Y}}}_{ij}$, with notation as in § 2.4; applying base change proves the claim. Therefore, the integral (5.1) can be expressed as an intersection number on the product of symmetric powers of curves ![]() $A_{C, \mathbf {n}_\lambda }$
$A_{C, \mathbf {n}_\lambda }$
where ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is the vector bundle of Theorem 2.8. In particular, the
${{\mathcal {E}}}$ is the vector bundle of Theorem 2.8. In particular, the ![]() $K$-theory class of
$K$-theory class of ![]() ${{\mathcal {E}}}-\tilde {N}_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ is a linear combination of classes of the form
${{\mathcal {E}}}-\tilde {N}_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ is a linear combination of classes of the form
 \[ \mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{I}}}_i, \bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{I}}}_j\otimes L_k\bigg)\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{\mu}, \]
\[ \mathbf{R}\pi_*\mathbf{R}\mathscr{H}\!om\bigg(\bigotimes_{i\in I}{{\mathcal{I}}}_i, \bigotimes_{j\in J}{{\mathcal{I}}}_j\otimes L_k\bigg)\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{\mu}, \]
where ![]() $L_k$ are line bundles on
$L_k$ are line bundles on ![]() $C$ and
$C$ and ![]() $I,J$ are families of indices (possibly with repetitions). By Proposition 5.3 this integral is a polynomial in
$I,J$ are families of indices (possibly with repetitions). By Proposition 5.3 this integral is a polynomial in ![]() $g$ and the degrees of
$g$ and the degrees of ![]() $L_k$. We conclude the proof by noticing that all line bundles
$L_k$. We conclude the proof by noticing that all line bundles ![]() $L_k$ possibly occurring are a linear combination of
$L_k$ possibly occurring are a linear combination of ![]() $L_1, L_2, K_C$.
$L_1, L_2, K_C$.
6. The leading term
We compute the leading term of the generating series of the integrals (5.1), which is essential for the computation of the full generating series in Theorem 8.1.
Proposition 6.1 Let ![]() $C$ be a smooth projective curve of genus
$C$ be a smooth projective curve of genus ![]() $g$ and
$g$ and ![]() $L_1, L_2$ line bundles on
$L_1, L_2$ line bundles on ![]() $C$. Then under the anti-diagonal restriction
$C$. Then under the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$ we have
$s_1+s_2=0$ we have
 \begin{align*} &\int_{C^{[\mathbf{0}_{\lambda}]}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})\nonumber\\ &\quad =(-1)^{|\lambda|(g-1+\deg L_2)+n(\lambda)\deg L_1+n(\bar{\lambda})\deg L_2} \bigg(s_1^{|\lambda|}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)\bigg)^{2g-2 -\deg L_1-\deg L_2}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &\int_{C^{[\mathbf{0}_{\lambda}]}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})\nonumber\\ &\quad =(-1)^{|\lambda|(g-1+\deg L_2)+n(\lambda)\deg L_1+n(\bar{\lambda})\deg L_2} \bigg(s_1^{|\lambda|}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)\bigg)^{2g-2 -\deg L_1-\deg L_2}, \end{align*}
where ![]() $\mathbf {0}_{\lambda }$ is the unique reversed plane partition of size
$\mathbf {0}_{\lambda }$ is the unique reversed plane partition of size ![]() $0$ and underlying Young diagram
$0$ and underlying Young diagram ![]() $\lambda$.
$\lambda$.
Proof. We have that ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {0}_{\lambda }]}\cong {{\mathsf {pt}}}$ and
$C^{[\mathbf {0}_{\lambda }]}\cong {{\mathsf {pt}}}$ and ![]() $[C^{[\mathbf {0}_{\lambda }]}]^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}=[{{\mathsf {pt}}}]\in A_*({{\mathsf {pt}}})$, therefore
$[C^{[\mathbf {0}_{\lambda }]}]^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}=[{{\mathsf {pt}}}]\in A_*({{\mathsf {pt}}})$, therefore ![]() ${{\mathbb {E}}}^{\vee }$ is completely
${{\mathbb {E}}}^{\vee }$ is completely ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-movable and
$\mathbf {T}$-movable and
where by (4.1), (4.6) we express the class in ![]() $K$-theory of the virtual normal bundle as
$K$-theory of the virtual normal bundle as
 \begin{align*} N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}&=\sum_{(i,j)\in \lambda}(\mathbf{R} \Gamma(L_1^{-i}L_2^{-j}) \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{-j}-(\mathbf{R} \Gamma( K_C L_1^{-i-1}L_2^{-j-1}) \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{-j})^{\vee} \otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)\\ &\quad -\sum_{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda}(\mathbf{R}\Gamma((\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_C-L_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1) L_1^{i-l}L_2^{j-k})\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k}\\ &\quad -(\mathbf{R}\Gamma((\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_C- L_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1)K_CL_1^{i-l-1}L_2^{j-k-1})\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k})^{\vee} \otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}&=\sum_{(i,j)\in \lambda}(\mathbf{R} \Gamma(L_1^{-i}L_2^{-j}) \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{-j}-(\mathbf{R} \Gamma( K_C L_1^{-i-1}L_2^{-j-1}) \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{-j})^{\vee} \otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)\\ &\quad -\sum_{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda}(\mathbf{R}\Gamma((\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_C-L_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1) L_1^{i-l}L_2^{j-k})\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k}\\ &\quad -(\mathbf{R}\Gamma((\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_C- L_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1)K_CL_1^{i-l-1}L_2^{j-k-1})\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{i-l}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{j-k})^{\vee} \otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2). \end{align*}
Applying Riemann–Roch, every line bundle ![]() $L$ on
$L$ on ![]() $C$ satisfies
$C$ satisfies
therefore we can write the virtual normal bundle as
 \begin{align} N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}&=\sum_\mu({{\mathbb{C}}}^{m_{\mu}+1-g}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{\mu}- {{\mathbb{C}}}^{m_{\mu}+ g-1-\deg L_1-\deg L_2}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-\mu}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)\nonumber\\ &\quad -\sum_\nu({{\mathbb{C}}}^{m_{\nu}+1-g}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{\nu}-{{\mathbb{C}}}^{m_{\nu}+ g-1-\deg L_1-\deg L_2}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-\nu}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2), \end{align}
\begin{align} N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}&=\sum_\mu({{\mathbb{C}}}^{m_{\mu}+1-g}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{\mu}- {{\mathbb{C}}}^{m_{\mu}+ g-1-\deg L_1-\deg L_2}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-\mu}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)\nonumber\\ &\quad -\sum_\nu({{\mathbb{C}}}^{m_{\nu}+1-g}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{\nu}-{{\mathbb{C}}}^{m_{\nu}+ g-1-\deg L_1-\deg L_2}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-\nu}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2), \end{align}
where the weights ![]() $\mu$ range among
$\mu$ range among
 \begin{equation} \begin{aligned} & (-i,-j)\in{{\mathbb{Z}}}^{2} \text{ such that } (i,j)\in \lambda, (i,j)\neq (0,0), \\ & (i-l+1,j-k)\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}^{2} \text{ such that } ((i-j),(l-k))\in \lambda, (i,j)\neq ((l-1,k), (l,k+1)), \end{aligned} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \begin{aligned} & (-i,-j)\in{{\mathbb{Z}}}^{2} \text{ such that } (i,j)\in \lambda, (i,j)\neq (0,0), \\ & (i-l+1,j-k)\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}^{2} \text{ such that } ((i-j),(l-k))\in \lambda, (i,j)\neq ((l-1,k), (l,k+1)), \end{aligned} \end{equation}
the weights ![]() $\nu$ range among
$\nu$ range among
and, for a weight ![]() $\mu =(\mu _1,\mu _2)$, we set
$\mu =(\mu _1,\mu _2)$, we set ![]() $m_{\mu }=\mu _1 \deg L_1+\mu _2 \deg L_2$. In particular, the weights
$m_{\mu }=\mu _1 \deg L_1+\mu _2 \deg L_2$. In particular, the weights ![]() $1,\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2$ do not appear in (6.1), as the virtual tangent bundle of the
$1,\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2$ do not appear in (6.1), as the virtual tangent bundle of the ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus has rank zero and by the explicit description of the weight space of
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus has rank zero and by the explicit description of the weight space of ![]() $\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2$ in Example 4.2. For every weight
$\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2$ in Example 4.2. For every weight ![]() $\mu$, we compute
$\mu$, we compute
where ![]() $s=(s_1,s_2)$ and
$s=(s_1,s_2)$ and ![]() $\mu \cdot s$ is the standard inner product. With a simple manipulation we end up with
$\mu \cdot s$ is the standard inner product. With a simple manipulation we end up with
 \begin{align*} &e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})\\ &\quad=(-1)^{\sum_{\nu\neq (a,a)}m_{\nu} +\sum_{\mu\neq (b,b)}m_{\mu}+(1-g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2)(\#\{\nu \neq (a,a)\}-\#\{\mu\neq (b,b)\})}\\ &\qquad \cdot\frac{\prod_{\nu\neq (a,a)}(\nu\cdot s)^{m_\nu+ 1-g}(\nu \cdot s-s_1-s_2)^{-m_{\nu}+1-g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}}{\prod_{\mu \neq (b,b)}(\mu\cdot s)^{m_\mu+ 1-g}(\mu\cdot s-s_1-s_2)^{-m_{\mu} +1-g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}}\\ &\qquad \cdot\frac{\prod_{\nu= (a,a)} a^{a(\deg L_1+\deg L_2) +1-g}(1-a)^{(1-a)(\deg L_1+\deg L_2)+1-g}(s_1+s_2)^{2-2g+\deg L_1 +\deg L_2}}{\prod_{\mu= (b,b)} b^{b(\deg L_1+\deg L_2)+1-g}(1-b)^{(1 -b)(\deg L_1+\deg L_2)+1-g}(s_1+s_2)^{2-2g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}}. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})\\ &\quad=(-1)^{\sum_{\nu\neq (a,a)}m_{\nu} +\sum_{\mu\neq (b,b)}m_{\mu}+(1-g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2)(\#\{\nu \neq (a,a)\}-\#\{\mu\neq (b,b)\})}\\ &\qquad \cdot\frac{\prod_{\nu\neq (a,a)}(\nu\cdot s)^{m_\nu+ 1-g}(\nu \cdot s-s_1-s_2)^{-m_{\nu}+1-g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}}{\prod_{\mu \neq (b,b)}(\mu\cdot s)^{m_\mu+ 1-g}(\mu\cdot s-s_1-s_2)^{-m_{\mu} +1-g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}}\\ &\qquad \cdot\frac{\prod_{\nu= (a,a)} a^{a(\deg L_1+\deg L_2) +1-g}(1-a)^{(1-a)(\deg L_1+\deg L_2)+1-g}(s_1+s_2)^{2-2g+\deg L_1 +\deg L_2}}{\prod_{\mu= (b,b)} b^{b(\deg L_1+\deg L_2)+1-g}(1-b)^{(1 -b)(\deg L_1+\deg L_2)+1-g}(s_1+s_2)^{2-2g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}}. \end{align*}
Following the proof of Lemma A.1, we see that for any weight ![]() $\nu =(a,a)$ (with
$\nu =(a,a)$ (with ![]() $a\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$) there is either a weight
$a\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$) there is either a weight ![]() $\mu =(a,a)$ or
$\mu =(a,a)$ or ![]() $\mu =(1-a,1-a)$ (and vice versa). This implies that
$\mu =(1-a,1-a)$ (and vice versa). This implies that
and
 \[ \frac{\prod_{\nu= (a,a)} a^{a(\deg L_1+\deg L_2)+1-g}(1-a)^{(1-a)(\deg L_1+\deg L_2)+1-g}(s_1+s_2)^{2-2g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}}{\prod_{\mu= (b,b)} b^{b(\deg L_1+\deg L_2)+1-g}(1-b)^{(1-b)(\deg L_1+\deg L_2)+1-g}(s_1+s_2)^{2-2g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}}=1. \]
\[ \frac{\prod_{\nu= (a,a)} a^{a(\deg L_1+\deg L_2)+1-g}(1-a)^{(1-a)(\deg L_1+\deg L_2)+1-g}(s_1+s_2)^{2-2g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}}{\prod_{\mu= (b,b)} b^{b(\deg L_1+\deg L_2)+1-g}(1-b)^{(1-b)(\deg L_1+\deg L_2)+1-g}(s_1+s_2)^{2-2g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}}=1. \]
In particular, the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$ is well-defined; we obtain
$s_1+s_2=0$ is well-defined; we obtain
 \begin{align*} &\frac{\prod_{\nu\neq (a,a)}(\nu\cdot s)^{m_\nu+ 1-g}(\nu\cdot s-s_1-s_2)^{-m_{\nu}+1-g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}}{\prod_{\mu \neq (b,b)}(\mu\cdot s)^{m_\mu+ 1-g}(\mu\cdot s-s_1-s_2)^{-m_{\mu} +1-g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}}\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0}\\ &\quad =\bigg(s_1^{\#\nu-\#\mu}\cdot\frac{\prod_{\nu= (\nu_1, \nu_2)}(\nu_1-\nu_2)}{\prod_{\mu= (\mu_1,\mu_2)}(\mu_1 -\mu_2)}\bigg)^{2-2g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &\frac{\prod_{\nu\neq (a,a)}(\nu\cdot s)^{m_\nu+ 1-g}(\nu\cdot s-s_1-s_2)^{-m_{\nu}+1-g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}}{\prod_{\mu \neq (b,b)}(\mu\cdot s)^{m_\mu+ 1-g}(\mu\cdot s-s_1-s_2)^{-m_{\mu} +1-g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}}\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0}\\ &\quad =\bigg(s_1^{\#\nu-\#\mu}\cdot\frac{\prod_{\nu= (\nu_1, \nu_2)}(\nu_1-\nu_2)}{\prod_{\mu= (\mu_1,\mu_2)}(\mu_1 -\mu_2)}\bigg)^{2-2g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}, \end{align*}
where the product is over all ![]() $\mu,\nu \neq (a,a)$. Moreover, it is immediate to check that
$\mu,\nu \neq (a,a)$. Moreover, it is immediate to check that ![]() $\#\mu -\#\nu =|\lambda |$. By Lemma A.2, we conclude that the last expression is equal to
$\#\mu -\#\nu =|\lambda |$. By Lemma A.2, we conclude that the last expression is equal to
 \[ \sigma(\lambda)^{\deg L_1+\deg L_2}\cdot\bigg(s_1^{-|\lambda|} \cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{-1}\bigg)^{2-2g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}, \]
\[ \sigma(\lambda)^{\deg L_1+\deg L_2}\cdot\bigg(s_1^{-|\lambda|} \cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{-1}\bigg)^{2-2g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2}, \]
where ![]() $\sigma (\lambda )$ is defined in Lemma A.2. We are only left with a sign computation; we conclude by Lemma A.3
$\sigma (\lambda )$ is defined in Lemma A.2. We are only left with a sign computation; we conclude by Lemma A.3
 \begin{align*} &(-1)^{\sum_{\nu\neq (a,a)}m_{\nu}+\sum_{\mu\neq (b,b)}m_{\mu} +(1-g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2)|\lambda|}\sigma(\lambda)^{\deg L_1+\deg L_2}\\ &\quad = (-1)^{\rho(\lambda)+ |\lambda|(k_1+k_2+ g-1)}\sigma(\lambda)^{k_1+k_2}\\ &\quad =(-1)^{|\lambda|(k_2+g-1)+ n(\lambda)k_1+n(\bar{\lambda})k_2}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &(-1)^{\sum_{\nu\neq (a,a)}m_{\nu}+\sum_{\mu\neq (b,b)}m_{\mu} +(1-g+\deg L_1+\deg L_2)|\lambda|}\sigma(\lambda)^{\deg L_1+\deg L_2}\\ &\quad = (-1)^{\rho(\lambda)+ |\lambda|(k_1+k_2+ g-1)}\sigma(\lambda)^{k_1+k_2}\\ &\quad =(-1)^{|\lambda|(k_2+g-1)+ n(\lambda)k_1+n(\bar{\lambda})k_2}, \end{align*}
where ![]() $\rho (\lambda )$ was defined in Lemma A.3 and we set
$\rho (\lambda )$ was defined in Lemma A.3 and we set ![]() $k_i=\deg L_i$.
$k_i=\deg L_i$.
7. Toric computations
7.1 Torus action
Let ![]() $U_0, U_\infty$ be the standard open cover of
$U_0, U_\infty$ be the standard open cover of ![]() ${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$. The torus
${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$. The torus ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$ acts on the coordinate functions of
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$ acts on the coordinate functions of ![]() ${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ as
${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ as ![]() $t\cdot x=tx$ (respectively,
$t\cdot x=tx$ (respectively, ![]() $t\cdot x=t^{-1}x$) in the chart
$t\cdot x=t^{-1}x$) in the chart ![]() $U_0$ (respectively,
$U_0$ (respectively, ![]() $U_\infty$). The
$U_\infty$). The ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-representation of the tangent space at the
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-representation of the tangent space at the ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed points of
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed points of ![]() ${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ is
${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ is
 \begin{align*} T_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},0}&={{\mathbb{C}}}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1},\\ T_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},\infty}&={{\mathbb{C}}}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} T_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},0}&={{\mathbb{C}}}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1},\\ T_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},\infty}&={{\mathbb{C}}}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}. \end{align*}
We prove some identities of ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-representations that are useful later in this section.
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-representations that are useful later in this section.
Lemma 7.1 Let ![]() $Z=Z_0\sqcup Z_\infty \subset {{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ be a closed subscheme, where
$Z=Z_0\sqcup Z_\infty \subset {{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ be a closed subscheme, where ![]() $Z_0$ (respectively,
$Z_0$ (respectively, ![]() $Z_\infty$) is a closed subscheme of length
$Z_\infty$) is a closed subscheme of length ![]() $n_0$ (respectively,
$n_0$ (respectively, ![]() $n_\infty$) supported on
$n_\infty$) supported on ![]() $0$ (respectively,
$0$ (respectively, ![]() $\infty$). For any
$\infty$). For any ![]() $a\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$, we have the following identities in
$a\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$, we have the following identities in ![]() $K^{0}_{{{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$:
$K^{0}_{{{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$:
 \begin{align*} &\mathbf{R}\Gamma(K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a})=\begin{cases} \displaystyle\sum_{i=a}^{-a}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{i} & a\leq 0,\\ -\displaystyle\sum_{i=-a+1}^{a-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{i} & a\geq 1, \end{cases}\\ &\mathbf{R}\Gamma(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z(Z))= \sum_{i=1}^{n_0}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-i}+\sum_{i=1}^{n_\infty}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{i},\\ &\mathbf{R}\Gamma(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a} )= \sum_{i=0}^{n_0-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a+i}+\sum_{i=0}^{n_\infty-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-a-i},\\ &\mathbf{R}\operatorname{Hom}(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z,K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a} )=-\sum_{i=0}^{n_0-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a-i-1}-\sum_{i=0}^{n_\infty-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-a+i+1}. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &\mathbf{R}\Gamma(K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a})=\begin{cases} \displaystyle\sum_{i=a}^{-a}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{i} & a\leq 0,\\ -\displaystyle\sum_{i=-a+1}^{a-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{i} & a\geq 1, \end{cases}\\ &\mathbf{R}\Gamma(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z(Z))= \sum_{i=1}^{n_0}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-i}+\sum_{i=1}^{n_\infty}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{i},\\ &\mathbf{R}\Gamma(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a} )= \sum_{i=0}^{n_0-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a+i}+\sum_{i=0}^{n_\infty-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-a-i},\\ &\mathbf{R}\operatorname{Hom}(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z,K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a} )=-\sum_{i=0}^{n_0-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a-i-1}-\sum_{i=0}^{n_\infty-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-a+i+1}. \end{align*}Proof. We have that
 \begin{align*} \mathbf{R}\Gamma(K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a})&=\chi({{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a} )\\ &=\frac{\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a}}{1-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}}-\frac{\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-a}}{1-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}}\\ &=\begin{cases}\displaystyle\sum_{i=a}^{-a}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{i} & a\leq 0,\\ -\displaystyle\sum_{i=-a+1}^{a-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{i} & a\geq 1, \end{cases} \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \mathbf{R}\Gamma(K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a})&=\chi({{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a} )\\ &=\frac{\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a}}{1-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}}-\frac{\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-a}}{1-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}}\\ &=\begin{cases}\displaystyle\sum_{i=a}^{-a}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{i} & a\leq 0,\\ -\displaystyle\sum_{i=-a+1}^{a-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{i} & a\geq 1, \end{cases} \end{align*}
where in the second line we applied the classical ![]() $K$-theoretic localization [Reference ThomasonTho92] on
$K$-theoretic localization [Reference ThomasonTho92] on ![]() ${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$.
${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$.
Second, we have
 \begin{align*} \mathbf{R}\Gamma(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z(Z))&=H^{0}({{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z(Z))\\ &= H^{0}(U_0,\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_0}(Z_0)|_{U_0})+H^{0}(U_\infty,\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_{\infty}}(Z_\infty)|_{U_\infty})\\ &= H^{0}(U_0, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_0}\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}|_{U_0} )^{*}+H^{0}(U_\infty, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_\infty}\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}|_{U_\infty} )^{*}\\ &= \sum_{i=1}^{n_0}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-i}+\sum_{i=1}^{n_\infty}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{i}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \mathbf{R}\Gamma(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z(Z))&=H^{0}({{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z(Z))\\ &= H^{0}(U_0,\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_0}(Z_0)|_{U_0})+H^{0}(U_\infty,\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_{\infty}}(Z_\infty)|_{U_\infty})\\ &= H^{0}(U_0, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_0}\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}|_{U_0} )^{*}+H^{0}(U_\infty, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_\infty}\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}|_{U_\infty} )^{*}\\ &= \sum_{i=1}^{n_0}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-i}+\sum_{i=1}^{n_\infty}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{i}, \end{align*}where in the second line we used Čech cohomology and in the third line we used [Reference OkounkovOko17, Exercise 3.4.5].
Third, by applying Čech cohomology as before we have
 \begin{align*} \mathbf{R}\Gamma(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a})&= H^{0}(U_0, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_0}\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a}|_{U_0} )+H^{0}(U_\infty, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_\infty}\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a}|_{U_\infty} )\\ &= \sum_{i=0}^{n_0-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a+i}+\sum_{i=0}^{n_\infty-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-a-i}. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \mathbf{R}\Gamma(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a})&= H^{0}(U_0, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_0}\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a}|_{U_0} )+H^{0}(U_\infty, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_\infty}\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a}|_{U_\infty} )\\ &= \sum_{i=0}^{n_0-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a+i}+\sum_{i=0}^{n_\infty-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-a-i}. \end{align*}Finally, combining Serre duality and the previous result yields
 \begin{align*} \mathbf{R}\operatorname{Hom}(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z, K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a})&=-\mathbf{R}\Gamma(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{1-a})^{*}\\ &=-\sum_{i=0}^{n_0-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a-i-1}-\sum_{i=0}^{n_\infty-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-a+i+1}. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \mathbf{R}\operatorname{Hom}(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z, K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a})&=-\mathbf{R}\Gamma(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_Z\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{1-a})^{*}\\ &=-\sum_{i=0}^{n_0-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a-i-1}-\sum_{i=0}^{n_\infty-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-a+i+1}. \end{align*} The ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on ![]() ${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ naturally lifts to a
${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ naturally lifts to a ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on the Hilbert scheme of point
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on the Hilbert scheme of point ![]() ${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[n]}$, whose
${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[n]}$, whose ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed locus consists of length
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed locus consists of length ![]() $n$ closed subschemes
$n$ closed subschemes ![]() $Z\subset {{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ supported on
$Z\subset {{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ supported on ![]() $0, \infty$. Therefore, there is an induced
$0, \infty$. Therefore, there is an induced ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on ![]() $A_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}, \mathbf {n}_\lambda }$, whose
$A_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}, \mathbf {n}_\lambda }$, whose ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed locus is zero-dimensional and reduced. This
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed locus is zero-dimensional and reduced. This ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action restricts to a
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action restricts to a ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on ![]() ${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, whose
${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, whose ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed locus is necessarily zero-dimensional and reduced. Moreover, the perfect obstruction theory (2.2) is naturally
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed locus is necessarily zero-dimensional and reduced. Moreover, the perfect obstruction theory (2.2) is naturally ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-equivariant, as all the ingredients of Theorem 2.8 are.
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-equivariant, as all the ingredients of Theorem 2.8 are.
Proposition 7.2 Let ![]() $\underline {Z}\in {{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ], {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}$ be a
$\underline {Z}\in {{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ], {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}$ be a ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed point. Then
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed point. Then ![]() $T_{{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}, \underline {Z}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ is completely
$T_{{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}, \underline {Z}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ is completely ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-movable. In particular, the induced perfect obstruction theory on
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-movable. In particular, the induced perfect obstruction theory on ![]() ${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ], {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}$ is trivial.
${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ], {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}$ is trivial.
Proof. We need to show that the class in ![]() $K$-theory
$K$-theory
does not have ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed part. Recall that we have an identity in
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed part. Recall that we have an identity in ![]() $K^{0}_{{{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$
$K^{0}_{{{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$
 \begin{align*} T_{A_{C,\mathbf{n}_\lambda}}|_{\underline{Z}}=\mathbf{R}\Gamma({{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_{00}}(Z_{00}))+\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}} \mathbf{R}\Gamma({{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{X_{ij}}(X_{ij}))+\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq 1}}\mathbf{R}\Gamma({{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Y_{ij}}(Y_{ij})), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} T_{A_{C,\mathbf{n}_\lambda}}|_{\underline{Z}}=\mathbf{R}\Gamma({{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_{00}}(Z_{00}))+\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}} \mathbf{R}\Gamma({{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{X_{ij}}(X_{ij}))+\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq 1}}\mathbf{R}\Gamma({{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Y_{ij}}(Y_{ij})), \end{align*}
where, for simplicity, we denoted by ![]() $X_{ij}= Z_{ij}-Z_{i-1,j}$ and by
$X_{ij}= Z_{ij}-Z_{i-1,j}$ and by ![]() $Y_{ij}=Z_{ij}-Z_{i,j-1}$. Moreover, we have
$Y_{ij}=Z_{ij}-Z_{i,j-1}$. Moreover, we have
 \begin{align*} {{\mathcal{E}}}|_{\underline{Z}}=\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}\mathbf{R}\Gamma({{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{W_{ij} }(W_{ij}))\in K^{0}_{{{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}({{\mathsf{pt}}}), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} {{\mathcal{E}}}|_{\underline{Z}}=\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}\mathbf{R}\Gamma({{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{W_{ij} }(W_{ij}))\in K^{0}_{{{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}({{\mathsf{pt}}}), \end{align*}
where for simplicity we used the notation ![]() $W_{ij}= Z_{ij}-Z_{i-1,j-1}$. Therefore, the virtual tangent space is a sum of classes of the form
$W_{ij}= Z_{ij}-Z_{i-1,j-1}$. Therefore, the virtual tangent space is a sum of classes of the form ![]() $\mathbf {R}\Gamma ({{\mathbb {P}}}^{1},\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_Z(Z))$, with
$\mathbf {R}\Gamma ({{\mathbb {P}}}^{1},\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_Z(Z))$, with ![]() $Z\subset {{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ a closed subscheme, which is entirely
$Z\subset {{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ a closed subscheme, which is entirely ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-movable by the description in Lemma 7.1.
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-movable by the description in Lemma 7.1.
7.2 Case I: Calabi–Yau
We compute the integral (5.1) for ![]() $C={{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ in the case of
$C={{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ in the case of ![]() $L_1\otimes L_2=K_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$, showing that it coincides (up to a sign) with the topological Euler characteristic
$L_1\otimes L_2=K_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$, showing that it coincides (up to a sign) with the topological Euler characteristic ![]() $e({{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$.
$e({{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$.
Theorem 7.3 Let ![]() $L_1,L_2$ be line bundles on
$L_1,L_2$ be line bundles on ![]() ${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ such that
${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ such that ![]() $L_1\otimes L_2=K_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$. For any reversed plane partition
$L_1\otimes L_2=K_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$. For any reversed plane partition ![]() $\mathbf {n}_\lambda$, we have
$\mathbf {n}_\lambda$, we have
Proof. By Graber and Pandharipande [Reference Graber and PandharipandeGP99], there is an induced perfect obstruction theory and virtual fundamental class on the ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed locus
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed locus ![]() ${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ], {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}$, both trivial by Proposition 7.2. By Proposition 4.3
${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ], {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}$, both trivial by Proposition 7.2. By Proposition 4.3
and applying the virtual localization formula with respect to the ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action yields
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action yields
 \begin{align*} \int_{[{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}) &=\bigg(\sum_{\underline{Z}\in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda],{{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}} \frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(T_{{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \underline{Z}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}},\vee}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)}{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(T_{{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \underline{Z}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})}\cdot \frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\Omega|_{\underline{Z}}^{\vee}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)}{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\Omega|_{\underline{Z}})}\bigg) \bigg|_{s_3=0}\\ &=\bigg(\sum_{\underline{Z}\in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda],{{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}} \frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}^{\vee} \otimes\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2) }{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}})} \bigg)\bigg|_{s_3=0}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \int_{[{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}) &=\bigg(\sum_{\underline{Z}\in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda],{{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}} \frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(T_{{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \underline{Z}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}},\vee}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)}{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(T_{{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \underline{Z}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})}\cdot \frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\Omega|_{\underline{Z}}^{\vee}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)}{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\Omega|_{\underline{Z}})}\bigg) \bigg|_{s_3=0}\\ &=\bigg(\sum_{\underline{Z}\in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda],{{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}} \frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}^{\vee} \otimes\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2) }{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}})} \bigg)\bigg|_{s_3=0}, \end{align*}
where ![]() $s_3$ is the generator of the equivariant cohomology
$s_3$ is the generator of the equivariant cohomology ![]() $H^{*}_{{{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$ and we denoted by
$H^{*}_{{{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$ and we denoted by
the ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-equivariant lift of the
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-equivariant lift of the ![]() $K$-theoretic class
$K$-theoretic class ![]() $T_{{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}+ \underline {Z}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}, \Omega |_{\underline {Z}}\in K^{0}_{\mathbf {T}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$. Under the Calabi–Yau restriction
$T_{{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}+ \underline {Z}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}, \Omega |_{\underline {Z}}\in K^{0}_{\mathbf {T}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$. Under the Calabi–Yau restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$, we have by Lemma 7.6
$s_1+s_2=0$, we have by Lemma 7.6
 \[ \bigg(\frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}^{\vee} \otimes\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2) }{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}})} \bigg)\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0}=(-1)^{\operatorname{rk} \mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}}. \]
\[ \bigg(\frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}^{\vee} \otimes\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2) }{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}})} \bigg)\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0}=(-1)^{\operatorname{rk} \mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}}. \]Moreover, by Lemma 7.5
Therefore, we conclude that
 \begin{align*} \bigg(\sum_{\underline{Z}\in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda],{{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}} \frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}^{\vee}\otimes\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1 \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2) }{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}})}\bigg) \bigg|_{s_+s_2=0}&=\sum_{\underline{Z}\in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda], {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}} (-1)^{\operatorname{rk} \mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}}\\ &= (-1)^{\deg L_1(c_\lambda+|\lambda|)+ |\lambda|+|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|}\cdot e( {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \bigg(\sum_{\underline{Z}\in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda],{{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}} \frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}^{\vee}\otimes\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1 \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2) }{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}})}\bigg) \bigg|_{s_+s_2=0}&=\sum_{\underline{Z}\in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda], {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}} (-1)^{\operatorname{rk} \mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}}\\ &= (-1)^{\deg L_1(c_\lambda+|\lambda|)+ |\lambda|+|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|}\cdot e( {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}), \end{align*}
as the Euler characteristic of a ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-scheme coincides with the Euler characteristic of its
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-scheme coincides with the Euler characteristic of its ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed locus (in our case the number of fixed points).
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed locus (in our case the number of fixed points).
Exploiting the close formula for the generating series of the topological Euler characteristic proved in Theorem 2.11, we derive the following close expression in the Calabi–Yau case.
Corollary 7.4 Let ![]() $L_1,L_2$ be line bundles on
$L_1,L_2$ be line bundles on ![]() ${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ such that
${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ such that ![]() $L_1\otimes L_2=K_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$ and
$L_1\otimes L_2=K_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$ and ![]() $\lambda$ be a Young diagram. We have
$\lambda$ be a Young diagram. We have
 \[ \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|}\cdot \bigg( \int_{[{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C, L_1, L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})\bigg)\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0} =(-1)^{\deg L_1(c_\lambda+|\lambda|)+ |\lambda|}\cdot \prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-(-q)^{h(\Box)})^{-2}, \]
\[ \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|}\cdot \bigg( \int_{[{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C, L_1, L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})\bigg)\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0} =(-1)^{\deg L_1(c_\lambda+|\lambda|)+ |\lambda|}\cdot \prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-(-q)^{h(\Box)})^{-2}, \]
where the sum is over all reversed plane partition ![]() $\mathbf {n}_\lambda$.
$\mathbf {n}_\lambda$.
We devote the remainder of this section to prove the technical lemmas we used in Theorem 7.3.
Lemma 7.5 Let ![]() $C$ be a smooth projective curve of genus
$C$ be a smooth projective curve of genus ![]() $g$,
$g$, ![]() $L_1,L_2$ be line bundles on
$L_1,L_2$ be line bundles on ![]() $C$ such that
$C$ such that ![]() $L_1\otimes L_2=K_{C}$ and let
$L_1\otimes L_2=K_{C}$ and let ![]() $\Omega \in K^{0}_\mathbf {T}( {C}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$ be the
$\Omega \in K^{0}_\mathbf {T}( {C}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$ be the ![]() $K$-theory class of Remark 4.4. Then
$K$-theory class of Remark 4.4. Then
Proof. Let ![]() $\underline {Z}\in {C}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$. Then
$\underline {Z}\in {C}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$. Then
 \begin{align*} \operatorname{rk} T_{{C}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}&= \operatorname{rk} T_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}|_{\underline{Z}}\\ &= n_{00}+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}}(n_{ij} -n_{i-1,j})+\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq 1}}(n_{ij} -n_{i,j-1})-\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}(n_{ij} -n_{i-1,j-1}). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \operatorname{rk} T_{{C}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}&= \operatorname{rk} T_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}|_{\underline{Z}}\\ &= n_{00}+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}}(n_{ij} -n_{i-1,j})+\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq 1}}(n_{ij} -n_{i,j-1})-\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}(n_{ij} -n_{i-1,j-1}). \end{align*}
For any line bundle ![]() $L$ on
$L$ on ![]() $C$ and
$C$ and ![]() $\Delta$ a
$\Delta$ a ![]() ${{\mathbb {Z}}}$-linear combination of the universal divisors
${{\mathbb {Z}}}$-linear combination of the universal divisors ![]() ${{\mathcal {Z}}}_{ij}$ on
${{\mathcal {Z}}}_{ij}$ on ![]() $C\times C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, Riemann–Roch yields
$C\times C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$, Riemann–Roch yields
As ![]() $\Omega$ is a sum of
$\Omega$ is a sum of ![]() $K$-theoretic classes of the form
$K$-theoretic classes of the form ![]() $\mathbf {R}\pi _*(\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}(\Delta )\otimes L)$, for suitable
$\mathbf {R}\pi _*(\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}(\Delta )\otimes L)$, for suitable ![]() $L, \Delta$, we have
$L, \Delta$, we have
 \begin{align*} \operatorname{rk}\Omega&=\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (0,0)}}( n_{ij} -i\cdot\deg L_1-j\cdot(2g-2-\deg L_1)+1-g)\\ &\quad -\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (l,k)\\(i,j)\neq (l+1,k+1)}}(n_{lk}-n_{ij}-(i-l)\deg L_1-(j-k)(2g-2-\deg L_1)+1-g )\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (l-1,k)\\(i,j)\neq (l,k+1)}}(n_{lk}-n_{ij}-(i-l+1)\deg L_1-(j-k)(2g-2-\deg L_1)+1-g ). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \operatorname{rk}\Omega&=\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (0,0)}}( n_{ij} -i\cdot\deg L_1-j\cdot(2g-2-\deg L_1)+1-g)\\ &\quad -\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (l,k)\\(i,j)\neq (l+1,k+1)}}(n_{lk}-n_{ij}-(i-l)\deg L_1-(j-k)(2g-2-\deg L_1)+1-g )\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (l-1,k)\\(i,j)\neq (l,k+1)}}(n_{lk}-n_{ij}-(i-l+1)\deg L_1-(j-k)(2g-2-\deg L_1)+1-g ). \end{align*}
Denote by ![]() $\equiv$ the congruence modulo two. We have
$\equiv$ the congruence modulo two. We have
 \begin{align*} n_{00}-\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (0,0)}} n_{ij}\equiv|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} n_{00}-\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (0,0)}} n_{ij}\equiv|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|. \end{align*}
Denote by ![]() $V$,
$V$, ![]() $E$ and
$E$ and ![]() $Q$ the number of vertices, edges and squares of the graph, respectively, associated with
$Q$ the number of vertices, edges and squares of the graph, respectively, associated with ![]() $\lambda$ as in Lemma 2.1. We have
$\lambda$ as in Lemma 2.1. We have
 \begin{align*} \sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (0,0)}}1- \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (l,k)\\(i,j) \neq (l+1,k+1)}}1+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j) \neq (l-1,k)\\(i,j)\neq (l,k+1)}}1&= V-1-(|\lambda|^{2}-V-Q)+(|\lambda|^{2}-E)\\ &=|\lambda|, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (0,0)}}1- \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (l,k)\\(i,j) \neq (l+1,k+1)}}1+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j) \neq (l-1,k)\\(i,j)\neq (l,k+1)}}1&= V-1-(|\lambda|^{2}-V-Q)+(|\lambda|^{2}-E)\\ &=|\lambda|, \end{align*}
where in the last line we used Lemma 2.1. The coefficient of ![]() $\deg L_1$ in
$\deg L_1$ in ![]() $\operatorname {rk} \Omega$ is
$\operatorname {rk} \Omega$ is
 \begin{align*} &\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (0,0)}}(i-j)- \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l,k)\\ (i,j)\neq (l+1,k+1)}}(i-j-l+k)+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l-1,k)\\ (i,j)\neq (l,k+1)}}(i-j+l-k+1) \\ &\quad \equiv \sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda}}(i+j)+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)= (l,k)\\ (i,j)= (l+1,k+1)}}(i+j+l+k)+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)= (l-1,k)\\ (i,j)= (l,k+1)}}(i+j+l+k)+\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l-1,k)\\(i,j)\neq (l,k+1)}} 1\\ &\quad \equiv c_\lambda+ 2E+ |\lambda|\\ &\quad \equiv c_\lambda+|\lambda|. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (0,0)}}(i-j)- \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l,k)\\ (i,j)\neq (l+1,k+1)}}(i-j-l+k)+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l-1,k)\\ (i,j)\neq (l,k+1)}}(i-j+l-k+1) \\ &\quad \equiv \sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda}}(i+j)+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)= (l,k)\\ (i,j)= (l+1,k+1)}}(i+j+l+k)+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)= (l-1,k)\\ (i,j)= (l,k+1)}}(i+j+l+k)+\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l-1,k)\\(i,j)\neq (l,k+1)}} 1\\ &\quad \equiv c_\lambda+ 2E+ |\lambda|\\ &\quad \equiv c_\lambda+|\lambda|. \end{align*}Finally,
 \begin{align*} &\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l,k)\\ (i,j)\neq (l+1,k+1)}}(n_{lk}-n_{ij})+\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l-1,k)\\ (i,j)\neq (l,k+1)}}(n_{lk}-n_{ij})\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}}(n_{ij}-n_{i-1,j})+\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq 1}}(n_{ij}-n_{i,j-1})-\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}(n_{ij}-n_{i-1,j-1})\equiv 0. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l,k)\\ (i,j)\neq (l+1,k+1)}}(n_{lk}-n_{ij})+\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l-1,k)\\ (i,j)\neq (l,k+1)}}(n_{lk}-n_{ij})\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i\geq 1}}(n_{ij}-n_{i-1,j})+\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ j\geq 1}}(n_{ij}-n_{i,j-1})-\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ i,j\geq 1}}(n_{ij}-n_{i-1,j-1})\equiv 0. \end{align*}Combining all these identities together, we conclude that
Lemma 7.6 Let ![]() $\underline {Z}\in {{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ], {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}$ be a
$\underline {Z}\in {{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ], {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}$ be a ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed point and set
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed point and set
where ![]() $\Omega \in K^{0}_\mathbf {T}( {{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$ is as in Remark 4.4. Then we have
$\Omega \in K^{0}_\mathbf {T}( {{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]})$ is as in Remark 4.4. Then we have
 \[ \bigg(\frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}^{\vee} \otimes\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2) }{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}})} \bigg)\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0}=(-1)^{\operatorname{rk} \mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}}. \]
\[ \bigg(\frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}^{\vee} \otimes\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2) }{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}})} \bigg)\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0}=(-1)^{\operatorname{rk} \mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}}. \]Proof. Denote by ![]() $\mathsf {V}_{\underline {Z}}^{CY}$ the sub-representation of
$\mathsf {V}_{\underline {Z}}^{CY}$ the sub-representation of ![]() $\mathsf {V}_{\underline {Z}}$ consisting of weight spaces corresponding to the characters
$\mathsf {V}_{\underline {Z}}$ consisting of weight spaces corresponding to the characters ![]() $(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2)^{a}$, for all
$(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2)^{a}$, for all ![]() $a\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$, with respect to the
$a\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$, with respect to the ![]() $\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action. We claim that
$\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action. We claim that ![]() $\mathsf {V}_{\underline {Z}}^{CY}$ is of the form
$\mathsf {V}_{\underline {Z}}^{CY}$ is of the form
for a suitable ![]() $A_{\underline {Z}}\in K^{0}_{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$.
$A_{\underline {Z}}\in K^{0}_{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$.
Step I. Assuming the claim, set
and ![]() $\tilde {\mathsf {V}}_{\underline {Z}}=\sum _{\mu }\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu }-\sum _{\nu }\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\nu }\in K^{0}_{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$, where none of the characters
$\tilde {\mathsf {V}}_{\underline {Z}}=\sum _{\mu }\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu }-\sum _{\nu }\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\nu }\in K^{0}_{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$, where none of the characters ![]() $\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu }, \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\nu }$ is a power of
$\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu }, \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\nu }$ is a power of ![]() $\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2$. Write
$\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2$. Write ![]() $e^{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu })=\mu \cdot s$, where
$e^{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu })=\mu \cdot s$, where ![]() $s=(s_1,s_2,s_3)$. Then we conclude that
$s=(s_1,s_2,s_3)$. Then we conclude that
 \begin{align*} \bigg(\frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}^{\vee} \otimes\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2) }{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}})} \bigg)\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0}&= \bigg(\frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}} (\tilde{\mathsf{V}}_{\underline{Z}}^{\vee}\otimes\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2) }{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\tilde{\mathsf{V}}_{\underline{Z}})}\bigg)\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0}\\ &=\bigg(\prod_{\mu}\frac{-\mu\cdot s+s_1+s_2}{\mu\cdot s}\cdot \prod_{\nu}\frac{\nu\cdot s}{-\nu\cdot s+s_1+s_2}\bigg)\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0}\\ &=(-1)^{\operatorname{rk} \mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \bigg(\frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}^{\vee} \otimes\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2) }{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}})} \bigg)\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0}&= \bigg(\frac{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}} (\tilde{\mathsf{V}}_{\underline{Z}}^{\vee}\otimes\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2) }{e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(\tilde{\mathsf{V}}_{\underline{Z}})}\bigg)\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0}\\ &=\bigg(\prod_{\mu}\frac{-\mu\cdot s+s_1+s_2}{\mu\cdot s}\cdot \prod_{\nu}\frac{\nu\cdot s}{-\nu\cdot s+s_1+s_2}\bigg)\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0}\\ &=(-1)^{\operatorname{rk} \mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}}, \end{align*}
where we used that no ![]() $\mu \cdot s, \nu \cdot s$ is a multiple of
$\mu \cdot s, \nu \cdot s$ is a multiple of ![]() $s_1+s_2$ and that
$s_1+s_2$ and that ![]() $\operatorname {rk} \mathsf {V}_{\underline {Z}}=\operatorname {rk} \tilde {\mathsf {V}}_{\underline {Z}} \mod 2$.
$\operatorname {rk} \mathsf {V}_{\underline {Z}}=\operatorname {rk} \tilde {\mathsf {V}}_{\underline {Z}} \mod 2$.
Step II. We now prove our claim on ![]() $\mathsf {V}_{\underline {Z}}^{CY}$. First, by Proposition 7.2
$\mathsf {V}_{\underline {Z}}^{CY}$. First, by Proposition 7.2 ![]() $T_{{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}, \underline {Z}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ is
$T_{{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}, \underline {Z}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ is ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-movable, which implies that there are no weight spaces corresponding to a power of
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-movable, which implies that there are no weight spaces corresponding to a power of ![]() $\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2$.
$\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2$.
It is clear that the ![]() $\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-weight spaces of
$\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-weight spaces of ![]() $\Omega |_{\underline {Z}}$ relative to the characters
$\Omega |_{\underline {Z}}$ relative to the characters ![]() $(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2)^{a}$ are given by
$(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2)^{a}$ are given by ![]() $\Omega '|_{\underline {Z}}$, where
$\Omega '|_{\underline {Z}}$, where
 \begin{align*} \Omega'&=\sum_{\substack{(a,a)\in \lambda\\ a\neq 0}}\mathbf{R}\pi_* (\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}\times {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{aa}) \otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{-a}) (\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)^{-a} -\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)=(l+a,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1}} \mathbf{R}\pi_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}(\Delta_{ij;lk})\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a} ) (\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)^{a}\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)= (l+a-1,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1}}\mathbf{R}\pi_* (\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}(\Delta_{ij;lk}) \otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a} )(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)^{a}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \Omega'&=\sum_{\substack{(a,a)\in \lambda\\ a\neq 0}}\mathbf{R}\pi_* (\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}\times {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}({{\mathcal{Z}}}_{aa}) \otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{-a}) (\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)^{-a} -\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)=(l+a,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1}} \mathbf{R}\pi_*(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}(\Delta_{ij;lk})\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a} ) (\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)^{a}\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)= (l+a-1,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1}}\mathbf{R}\pi_* (\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}(\Delta_{ij;lk}) \otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a} )(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)^{a}, \end{align*}
as we just considered the weight spaces of ![]() $(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2)^{a}$ in
$(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2)^{a}$ in ![]() $\Omega$ of Remark 4.4. We note that
$\Omega$ of Remark 4.4. We note that ![]() $\Omega '|_{\underline {Z}}$ is a sum of
$\Omega '|_{\underline {Z}}$ is a sum of ![]() $\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-representations of the form
$\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-representations of the form
or
where ![]() $Z_a\subset {{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ are effective divisors. We have the following identities of
$Z_a\subset {{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$ are effective divisors. We have the following identities of ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-representations:
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-representations:
By Lemma 7.1, their ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed part is
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-fixed part is
 \begin{align*} (\mathbf{R}\Gamma(K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a}))^{\mathsf{fix}}&=\begin{cases}1 & a\leq -1,\\ -1 & a \geq 2,\end{cases}\\ (\mathbf{R}\operatorname{Hom}(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_a}, K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{-a}))^{\mathsf{fix}}&=0, \quad a\geq 1,\\ (\mathbf{R}\Gamma(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_a}\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a}))^{\mathsf{fix}}&=0, \quad a\geq 2. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} (\mathbf{R}\Gamma(K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a}))^{\mathsf{fix}}&=\begin{cases}1 & a\leq -1,\\ -1 & a \geq 2,\end{cases}\\ (\mathbf{R}\operatorname{Hom}(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_a}, K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{-a}))^{\mathsf{fix}}&=0, \quad a\geq 1,\\ (\mathbf{R}\Gamma(\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{Z_a}\otimes K_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{a}))^{\mathsf{fix}}&=0, \quad a\geq 2. \end{align*}Combining everything together, we conclude that
 \begin{align*} \mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}^{CY}=\sum_{\substack{(a,a)\in \lambda\\ a\neq 0}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)^{-a} +\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)=(l+a,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1}}{{\mathrm{sgn}}}(a)(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)^{a} - \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)= (l+a-1,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1}}{{\mathrm{sgn}}}(a) (\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)^{a}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \mathsf{V}_{\underline{Z}}^{CY}=\sum_{\substack{(a,a)\in \lambda\\ a\neq 0}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)^{-a} +\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)=(l+a,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1}}{{\mathrm{sgn}}}(a)(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)^{a} - \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)= (l+a-1,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1}}{{\mathrm{sgn}}}(a) (\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)^{a}, \end{align*}
where ![]() ${\rm sgn}$ is the usual sign function. Our claim follows by Lemma A.1.
${\rm sgn}$ is the usual sign function. Our claim follows by Lemma A.1.
7.3 Case II: trivial vector bundle
If ![]() $L_1=L_2=\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$, the integral (5.1) amounts to the leading term computation of § 6 and a vanishing result, which relies on a combinatorial fact about the topological vertex formalism for stable pairs developed in [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09b].
$L_1=L_2=\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$, the integral (5.1) amounts to the leading term computation of § 6 and a vanishing result, which relies on a combinatorial fact about the topological vertex formalism for stable pairs developed in [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09b].
Proposition 7.7 Under the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$ we have an identity
$s_1+s_2=0$ we have an identity
 \[ \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0} =(-s_1^{2})^{-|\lambda|}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{-2}. \]
\[ \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})\bigg|_{s_1+s_2=0} =(-s_1^{2})^{-|\lambda|}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{-2}. \]Proof. The leading term is computed in Proposition 6.1, therefore we just need to prove that the integral vanishes for ![]() $|\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }|>0$. We apply Graber–Pandharipande virtual localization [Reference Graber and PandharipandeGP99] with respect to the
$|\mathbf {n}_{\lambda }|>0$. We apply Graber–Pandharipande virtual localization [Reference Graber and PandharipandeGP99] with respect to the ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on ![]() ${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$
${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$
 \[ \int_{[{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})=\bigg(\sum_{\underline{Z}\in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda], {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}} } e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(-T^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \underline{Z}}-N_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}, \underline{Z}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})\bigg)\bigg|_{s_3=0}, \]
\[ \int_{[{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}, \operatorname{\mathcal{O}},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})=\bigg(\sum_{\underline{Z}\in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda], {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}} } e^{\mathbf{T}\times {{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}}(-T^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \underline{Z}}-N_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}},\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}, \underline{Z}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})\bigg)\bigg|_{s_3=0}, \]
where ![]() $s_3$ is the generator of
$s_3$ is the generator of ![]() $H^{*}_{{{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$. The
$H^{*}_{{{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$. The ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on ![]() ${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ is just the restriction of the natural
${{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ is just the restriction of the natural ![]() $\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on
$\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action on ![]() $P_n({{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{2}, d[{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}])$, where
$P_n({{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{2}, d[{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}])$, where ![]() $d=|\lambda |$ and
$d=|\lambda |$ and ![]() $n=|\lambda |+|\mathbf {n}_\lambda |$. This means that, as
$n=|\lambda |+|\mathbf {n}_\lambda |$. This means that, as ![]() $\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-representation,
$\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-representation,
can be described via the topological vertex formalism of Pandharipande and Thomas [Reference Pandharipande and ThomasPT09b, Theorem 3], which states
where ![]() $\mathsf {V}_{0,\underline {Z}},\mathsf {V}_{\infty,\underline {Z}}$ are the vertex terms corresponding to the two toric charts of
$\mathsf {V}_{0,\underline {Z}},\mathsf {V}_{\infty,\underline {Z}}$ are the vertex terms corresponding to the two toric charts of ![]() ${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{2}$ and
${{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{2}$ and ![]() ${\mathsf {E}_{\underline {Z}}}$ is the edge term. By [Reference Maulik, Pandharipande and ThomasMPT10, Lemma 22] we have that
${\mathsf {E}_{\underline {Z}}}$ is the edge term. By [Reference Maulik, Pandharipande and ThomasMPT10, Lemma 22] we have that ![]() $e^{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}(-\mathsf {V}_{0,\underline {Z}}-\mathsf {V}_{\infty,\underline {Z}})$ is divisible by
$e^{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}(-\mathsf {V}_{0,\underline {Z}}-\mathsf {V}_{\infty,\underline {Z}})$ is divisible by ![]() $(s_1+s_2)$ if
$(s_1+s_2)$ if ![]() $|\mathbf {n}_\lambda |>0$, whereas
$|\mathbf {n}_\lambda |>0$, whereas ![]() $e^{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}(-{\mathsf {E}_{\underline {Z}}})$ is easily seen to be coprime with
$e^{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}(-{\mathsf {E}_{\underline {Z}}})$ is easily seen to be coprime with ![]() $(s_1+s_2)$.Footnote 5 This implies that the anti-diagonal restriction
$(s_1+s_2)$.Footnote 5 This implies that the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$ is well-defined on every localized term and satisfies
$s_1+s_2=0$ is well-defined on every localized term and satisfies
by which we conclude the required vanishing.
8. Summing up the theory
8.1 Anti-diagonal restriction
We combine the computations in §§ 6 and 7 to prove the second part of Theorem 1.3 from the introduction.
Theorem 8.1 Under the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$ the three universal series are
$s_1+s_2=0$ the three universal series are
 \begin{align*} A_{\lambda}(q,s_1,-s_1)&=(-s_1^{2})^{|\lambda|}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{2},\\ B_{\lambda}(-q,s_1,-s_1)&=(-1)^{n(\lambda)}\cdot s_1^{-|\lambda|}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{-1}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)}),\\ C_{\lambda}(-q,s_1,-s_1)&=(-1)^{n(\bar{\lambda})}\cdot (-s_1)^{-|\lambda|}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{-1}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)}). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} A_{\lambda}(q,s_1,-s_1)&=(-s_1^{2})^{|\lambda|}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{2},\\ B_{\lambda}(-q,s_1,-s_1)&=(-1)^{n(\lambda)}\cdot s_1^{-|\lambda|}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{-1}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)}),\\ C_{\lambda}(-q,s_1,-s_1)&=(-1)^{n(\bar{\lambda})}\cdot (-s_1)^{-|\lambda|}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)^{-1}\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)}). \end{align*}Proof. Let ![]() $C_{g,\deg L_1\deg L_2}\in {{\mathbb {Q}}}(s_1,s_2)$ be the leading term of the generating series of Theorem 5.1. We can write
$C_{g,\deg L_1\deg L_2}\in {{\mathbb {Q}}}(s_1,s_2)$ be the leading term of the generating series of Theorem 5.1. We can write
 \begin{align*} &C_{g,\deg L_1\deg L_2}^{-1}\cdot \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})= \tilde{A}_{\lambda,1}^{g-1}\cdot \tilde{A}_{\lambda,2}^{\deg L_1}\cdot \tilde{A}_{\lambda,3}^{\deg L_2}\\ &\quad =\exp((g-1)\cdot\log\tilde{A}_{\lambda,1}+ \deg L_1\cdot \log\tilde{A}_{\lambda,2}+\deg L_2\cdot \log \tilde{A}_{\lambda,3}), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &C_{g,\deg L_1\deg L_2}^{-1}\cdot \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \int_{[C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}e^{\mathbf{T}}(-N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}})= \tilde{A}_{\lambda,1}^{g-1}\cdot \tilde{A}_{\lambda,2}^{\deg L_1}\cdot \tilde{A}_{\lambda,3}^{\deg L_2}\\ &\quad =\exp((g-1)\cdot\log\tilde{A}_{\lambda,1}+ \deg L_1\cdot \log\tilde{A}_{\lambda,2}+\deg L_2\cdot \log \tilde{A}_{\lambda,3}), \end{align*}
for suitable ![]() $\tilde {A}_{\lambda,i}\in 1+{{\mathbb {Q}}}(s_1,s_2)[\![ q ]\!]$, where
$\tilde {A}_{\lambda,i}\in 1+{{\mathbb {Q}}}(s_1,s_2)[\![ q ]\!]$, where ![]() $\log \tilde {A_i}$ are well-defined as
$\log \tilde {A_i}$ are well-defined as ![]() $\tilde {A_i}$ are power series starting with 1. The claim is therefore reduced to the computation of the leading term (under the anti-diagonal restriction
$\tilde {A_i}$ are power series starting with 1. The claim is therefore reduced to the computation of the leading term (under the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$) and to the solution of a linear system. The leading term is computed in Proposition 6.1, which also shows that it is invertible in
$s_1+s_2=0$) and to the solution of a linear system. The leading term is computed in Proposition 6.1, which also shows that it is invertible in ![]() ${{\mathbb {Q}}}(s_1,s_2)$. The linear system is solved by computing the generating series of the integrals (5.1), under the anti-diagonal restriction, on a basis of
${{\mathbb {Q}}}(s_1,s_2)$. The linear system is solved by computing the generating series of the integrals (5.1), under the anti-diagonal restriction, on a basis of ![]() ${{\mathbb {Q}}}^{3}$. The classes
${{\mathbb {Q}}}^{3}$. The classes
are linearly independent and we computed their generating series in Proposition 7.7 and Corollary 7.4.
8.2 degree 1
In degree 1, we consider the Young diagram consisting of a single box and the corresponding double nested Hilbert scheme is ![]() $C^{[n]}\cong C^{(n)}$, the symmetric power of a smooth projective curve
$C^{[n]}\cong C^{(n)}$, the symmetric power of a smooth projective curve ![]() $C$, with universal subscheme
$C$, with universal subscheme ![]() ${{\mathcal {Z}}}\subset C\times C^{(n)}$. Given line bundles
${{\mathcal {Z}}}\subset C\times C^{(n)}$. Given line bundles ![]() $L_1, L_2$ on
$L_1, L_2$ on ![]() $C$, the class (4.1) in
$C$, the class (4.1) in ![]() $K$-theory of the virtual normal bundle is
$K$-theory of the virtual normal bundle is
 \begin{align*} N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{C, L_1, L_2}&=-\mathbf{R}\pi_*(L_1L_2\otimes \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{\mathcal{Z}}})\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2+ \mathbf{R}\pi_*L_1\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1+\mathbf{R}\pi_*L_2\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2\\ &=-(L_1L_2)^{[n]}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2+ \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C^{(n)}}^{\deg L_1+ 1-g} \otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1+\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C^{(n)}}^{\deg L_2+ 1-g}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{C, L_1, L_2}&=-\mathbf{R}\pi_*(L_1L_2\otimes \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{{\mathcal{Z}}})\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2+ \mathbf{R}\pi_*L_1\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1+\mathbf{R}\pi_*L_2\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2\\ &=-(L_1L_2)^{[n]}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2+ \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C^{(n)}}^{\deg L_1+ 1-g} \otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1+\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C^{(n)}}^{\deg L_2+ 1-g}\otimes \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2, \end{align*}
where ![]() $(L_1L_2)^{[n]}$ is the tautological bundle with fibers
$(L_1L_2)^{[n]}$ is the tautological bundle with fibers ![]() $(L_1L_2)^{[n]}|_{Z}=H^{0}(C,L_1L_2\otimes \operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_Z)$. This yields
$(L_1L_2)^{[n]}|_{Z}=H^{0}(C,L_1L_2\otimes \operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_Z)$. This yields
By the universal structure of Theorem 5.1, we just need to compute the (generating series of the) last integral for ![]() $L_1=L_2=\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{C}$ and
$L_1=L_2=\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{C}$ and ![]() $L_1\otimes L_2\cong K_{C}$, which yields the explicit universal series
$L_1\otimes L_2\cong K_{C}$, which yields the explicit universal series
 \begin{align*} A_{\Box}(q,s_1,s_2)&=s_1 s_2,\\ B_{\Box}(q,s_1,s_2)&= s_1^{-1}(1+q),\\ C_{\Box}(q,s_1,s_2)&=s_2^{-1}(1+q). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} A_{\Box}(q,s_1,s_2)&=s_1 s_2,\\ B_{\Box}(q,s_1,s_2)&= s_1^{-1}(1+q),\\ C_{\Box}(q,s_1,s_2)&=s_2^{-1}(1+q). \end{align*}8.3 GW/PT correspondence
Let ![]() $X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ be a local curve. Combining Theorem 5.1, Theorem 8.1 and the description of the
$X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ be a local curve. Combining Theorem 5.1, Theorem 8.1 and the description of the ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus of
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus of ![]() $P_n(X, d[C])$ in Proposition 3.1, we obtain our main result.
$P_n(X, d[C])$ in Proposition 3.1, we obtain our main result.
Theorem 8.2 The generating series of stable pair invariants satisfies
where ![]() $A_{\lambda,i}$ are the universal series of Theorem 5.1. Moreover, under the anti-diagonal restriction
$A_{\lambda,i}$ are the universal series of Theorem 5.1. Moreover, under the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$
$s_1+s_2=0$
 \begin{align*} \mathsf{PT}_d(X;-q)|_{s_1+s_2=0}&= (-1)^{d\deg L_2}\sum_{\lambda\vdash d}q^{d(1-g)-\deg L_1 n(\lambda)- \deg L_2 n(\bar{\lambda})}\\ &\quad \cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(s_1h(\Box))^{2g-2- \deg L_1- \deg L_2}(1-q^{h(\Box)})^{\deg L_1+\deg L_2}. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \mathsf{PT}_d(X;-q)|_{s_1+s_2=0}&= (-1)^{d\deg L_2}\sum_{\lambda\vdash d}q^{d(1-g)-\deg L_1 n(\lambda)- \deg L_2 n(\bar{\lambda})}\\ &\quad \cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(s_1h(\Box))^{2g-2- \deg L_1- \deg L_2}(1-q^{h(\Box)})^{\deg L_1+\deg L_2}. \end{align*}Comparing with Bryan and Pandharipande's results (cf. Theorem 1.5 and [Reference Bryan and PandharipandeBP08, § 8] for the fully equivariant result in degree 1) we obtain a proof of the GW/stable pairs correspondence for local curves.
Corollary 8.3 Let ![]() $X$ be a local curve. Under the anti-diagonal restriction
$X$ be a local curve. Under the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $s_1+s_2=0$ the GW/stable pair correspondence holds
$s_1+s_2=0$ the GW/stable pair correspondence holds
after the change of variable ![]() $q=-e^{iu}$. Moreover, it holds fully equivariantly in degree 1.
$q=-e^{iu}$. Moreover, it holds fully equivariantly in degree 1.
8.4 Resolved conifold
In some cases, the moduli space ![]() $P_n(X, d[C])$ happens to be proper, for example whenever
$P_n(X, d[C])$ happens to be proper, for example whenever ![]() $H^{0}(C, L_i)=0$ for
$H^{0}(C, L_i)=0$ for ![]() $i=1,2$; see [Reference Cao, Kool and MonavariCKM22b, Proposition 3.1] for a similar setting for local surfaces. Under this assumption, the invariants are computed as
$i=1,2$; see [Reference Cao, Kool and MonavariCKM22b, Proposition 3.1] for a similar setting for local surfaces. Under this assumption, the invariants are computed as
and can be deduced from the anti-diagonal restriction. The resulting invariants are interesting, that is, non-zero, only in the Calabi–Yau case; in this case, they coincide with the virtual Euler characteristic and Behrend's weighted Euler characteristic of ![]() $P_n(X, d[C])$ [Reference BehrendBeh09]. Applying Riemann–Roch, this situation may appear only when
$P_n(X, d[C])$ [Reference BehrendBeh09]. Applying Riemann–Roch, this situation may appear only when ![]() $H^{l}(C,L_i)=0$ for
$H^{l}(C,L_i)=0$ for ![]() $l=0,1$ and
$l=0,1$ and ![]() $\deg L_i= g-1$ for
$\deg L_i= g-1$ for ![]() $i=1,2$.
$i=1,2$.
An interesting example is the resolved conifold ![]() $X=\operatorname {Tot}_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}(\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}(-1)\oplus \operatorname {\mathcal {O}}(-1))$; in this case, the invariants can be further packaged into a generating series
$X=\operatorname {Tot}_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}(\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}(-1)\oplus \operatorname {\mathcal {O}}(-1))$; in this case, the invariants can be further packaged into a generating series
 \begin{align*} 1+ \sum_{d\geq 1}Q^{d}\cdot\mathsf{PT}_d(X;-q)&=\sum_{d\geq 0}(-Qq)^{d}\sum_{\lambda\vdash d}q^{ n(\lambda)+ n(\bar{\lambda})}\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)})^{-2}\\ &= \sum_{\lambda}(-Qq)^{|\lambda|}\frac{q^{n(\lambda)}}{\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)})}\frac{q^{n(\bar{\lambda})}}{\prod_{\Box\in \bar{\lambda}}(1-q^{h(\Box)})}\\ &= \sum_{\lambda}(-Qq)^{|\lambda|} s_{\lambda}(q)s_{\bar{\lambda}}(q)\\ &=\prod_{ n\geq 1}(1-Qq^{n})^{n}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} 1+ \sum_{d\geq 1}Q^{d}\cdot\mathsf{PT}_d(X;-q)&=\sum_{d\geq 0}(-Qq)^{d}\sum_{\lambda\vdash d}q^{ n(\lambda)+ n(\bar{\lambda})}\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)})^{-2}\\ &= \sum_{\lambda}(-Qq)^{|\lambda|}\frac{q^{n(\lambda)}}{\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)})}\frac{q^{n(\bar{\lambda})}}{\prod_{\Box\in \bar{\lambda}}(1-q^{h(\Box)})}\\ &= \sum_{\lambda}(-Qq)^{|\lambda|} s_{\lambda}(q)s_{\bar{\lambda}}(q)\\ &=\prod_{ n\geq 1}(1-Qq^{n})^{n}, \end{align*}
where we used some classical identities involving the Schur function ![]() $s_\lambda$ (see, e.g., [Reference MacdonaldMac95, p. 45] and [Reference TakasakiTak14, § 2.3]). This last generating series is well-known as it agrees with the expression of the unrefined limit of the topological vertex of Iqbal, Kozçaz and Vafa [Reference Iqbal, Kozçaz and VafaIKV09] and can be seen as a specialization both of the motivic invariants of Morrison et al. [Reference Morrison, Mozgovoy, Nagao and SzendröiMMNS12] and of the
$s_\lambda$ (see, e.g., [Reference MacdonaldMac95, p. 45] and [Reference TakasakiTak14, § 2.3]). This last generating series is well-known as it agrees with the expression of the unrefined limit of the topological vertex of Iqbal, Kozçaz and Vafa [Reference Iqbal, Kozçaz and VafaIKV09] and can be seen as a specialization both of the motivic invariants of Morrison et al. [Reference Morrison, Mozgovoy, Nagao and SzendröiMMNS12] and of the ![]() $K$-theoretic invariants of Kononov, Okounkov and Osinenko [Reference Kononov, Okounkov and OsinenkoKOO21].
$K$-theoretic invariants of Kononov, Okounkov and Osinenko [Reference Kononov, Okounkov and OsinenkoKOO21].
9.  $K$-theoretic refinement
$K$-theoretic refinement
9.1  $K$-theoretic invariants
$K$-theoretic invariants
Let ![]() $X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ be a local curve. The perfect obstruction theory on
$X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ be a local curve. The perfect obstruction theory on ![]() $P_X:=P_n(X, d[C])$ induces a (
$P_X:=P_n(X, d[C])$ induces a (![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant) virtual structure sheaf
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant) virtual structure sheaf ![]() $\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{P_X}\in K^{\mathbf {T}}_0(P_X)$ [Reference Fantechi and GöttscheFG10] which depends only on the
$\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}^{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}_{P_X}\in K^{\mathbf {T}}_0(P_X)$ [Reference Fantechi and GöttscheFG10] which depends only on the ![]() $K$-theory class of the perfect obstruction theory [Reference ThomasTho22, Corollary 4.5]. The
$K$-theory class of the perfect obstruction theory [Reference ThomasTho22, Corollary 4.5]. The ![]() $K$-theoretic PT invariants are defined by virtual
$K$-theoretic PT invariants are defined by virtual ![]() $K$-theoretic localization [Reference Fantechi and GöttscheFG10] for any
$K$-theoretic localization [Reference Fantechi and GöttscheFG10] for any ![]() $V\in K_0^{\mathbf {T}}(P_X)$
$V\in K_0^{\mathbf {T}}(P_X)$
 \begin{align*} \mathsf{PT}^{K}_{d,n}(X, V)&:=\chi(P_n(X, d[C]), \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{P_X}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}\otimes V)\\ &:=\chi\bigg(P_n(X, d[C])^{\mathbf{T}}, \frac{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}\otimes V|_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}}{\Lambda^{\bullet} N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} \bigg)\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1, \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \mathsf{PT}^{K}_{d,n}(X, V)&:=\chi(P_n(X, d[C]), \operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{P_X}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}\otimes V)\\ &:=\chi\bigg(P_n(X, d[C])^{\mathbf{T}}, \frac{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}\otimes V|_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}}{\Lambda^{\bullet} N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} \bigg)\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1, \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2), \end{align*}
where ![]() $\Lambda ^{\bullet }(V):=\sum _{i=0}^{\operatorname {rk} V}(-1)^{i} \Lambda ^{i} V$ is defined for every locally free sheaf
$\Lambda ^{\bullet }(V):=\sum _{i=0}^{\operatorname {rk} V}(-1)^{i} \Lambda ^{i} V$ is defined for every locally free sheaf ![]() $V$ and then extended by linearity to any class in
$V$ and then extended by linearity to any class in ![]() $K$-theory.
$K$-theory.
Remark 9.1 Differently than the case of equivariant cohomology, ![]() $\chi (M, {{\mathcal {F}}})\in K_0^{\mathbf {T}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})_{\mathrm {loc}}$ is well-defined for any
$\chi (M, {{\mathcal {F}}})\in K_0^{\mathbf {T}}({{\mathsf {pt}}})_{\mathrm {loc}}$ is well-defined for any ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-equivariant coherent sheaf
$\mathbf {T}$-equivariant coherent sheaf ![]() ${{\mathcal {F}}}$ on a non-proper scheme
${{\mathcal {F}}}$ on a non-proper scheme ![]() $M$, as long as the weight spaces of
$M$, as long as the weight spaces of ![]() ${{\mathcal {F}}}$ are finite-dimensional; in this case, the virtual localization formula is an actual theorem, rather than an ad hoc definition of the invariants.
${{\mathcal {F}}}$ are finite-dimensional; in this case, the virtual localization formula is an actual theorem, rather than an ad hoc definition of the invariants.
Using the description of the ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus ![]() $(P_n(X, d[C))^{\mathbf {T}}$ of Proposition 3.1,
$(P_n(X, d[C))^{\mathbf {T}}$ of Proposition 3.1, ![]() $K$-theoretic stable pair invariants on
$K$-theoretic stable pair invariants on ![]() $X$ (with no insertions) are reduced to intersection numbers on
$X$ (with no insertions) are reduced to intersection numbers on ![]() $C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$. The same techniques of § 5 can be applied in this setting, yielding the following result.
$C^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$. The same techniques of § 5 can be applied in this setting, yielding the following result.
Proposition 9.2 Let ![]() $C$ be a genus
$C$ be a genus ![]() $g$ smooth irreducible projective curve and
$g$ smooth irreducible projective curve and ![]() $L_1, L_2$ line bundles over
$L_1, L_2$ line bundles over ![]() $C$. We have an identity
$C$. We have an identity
 \[ \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \chi \bigg(C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \frac{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}{\Lambda^{\bullet} N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} \bigg)=A_{K,\lambda}^{g-1}\cdot B_{K,\lambda}^{\deg L_1}\cdot C_{K,\lambda}^{\deg L_2}\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)[\![ q ]\!], \]
\[ \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \chi \bigg(C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \frac{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}{\Lambda^{\bullet} N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} \bigg)=A_{K,\lambda}^{g-1}\cdot B_{K,\lambda}^{\deg L_1}\cdot C_{K,\lambda}^{\deg L_2}\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)[\![ q ]\!], \]
where ![]() $A_{K,\lambda },B_{K,\lambda },C_{K,\lambda }\in {{\mathbb {Q}}}(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1,\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2)[\![ q ]\!]$ are fixed universal series for
$A_{K,\lambda },B_{K,\lambda },C_{K,\lambda }\in {{\mathbb {Q}}}(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1,\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2)[\![ q ]\!]$ are fixed universal series for ![]() $i=1,2,3$, only depending on
$i=1,2,3$, only depending on ![]() $\lambda$. Moreover,
$\lambda$. Moreover,
 \begin{align*} A_{K,\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)&=A_{K,\bar{\lambda}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1),\\ B_{K,\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)&=C_{K,\bar{\lambda}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} A_{K,\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)&=A_{K,\bar{\lambda}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1),\\ B_{K,\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)&=C_{K,\bar{\lambda}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1). \end{align*}Proof. The proof follows the same strategy as Theorem 5.1. We just need to notice that ![]() $\Lambda ^{\bullet }(\cdot )$ is multiplicative and that, via virtual Hirzebruch–Riemann–Roch [Reference Fantechi and GöttscheFG10], we can express
$\Lambda ^{\bullet }(\cdot )$ is multiplicative and that, via virtual Hirzebruch–Riemann–Roch [Reference Fantechi and GöttscheFG10], we can express
 \begin{align*} \chi\bigg(C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \frac{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}{\Lambda^{\bullet} N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} \bigg)&=\int_{[C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} {{\mathrm{ch}}}(-\Lambda^{\bullet} N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *})\cdot {{\mathrm{td}}}(T^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}})\\ &=\int_{A_{C, \mathbf{n}_\lambda}}f, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \chi\bigg(C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \frac{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}{\Lambda^{\bullet} N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} \bigg)&=\int_{[C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}]^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}} {{\mathrm{ch}}}(-\Lambda^{\bullet} N_{C,L_1,L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *})\cdot {{\mathrm{td}}}(T^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}})\\ &=\int_{A_{C, \mathbf{n}_\lambda}}f, \end{align*}
where ![]() $f$ is a polynomial expression of classes of the same form as in Proposition 5.3.
$f$ is a polynomial expression of classes of the same form as in Proposition 5.3.
Denote by ![]() $\mathsf {PT}^{K}_d(X;q)=\sum _{n\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}}q^{n}\mathsf {PT}^{K}_{d,n}(X)$ the generating series of
$\mathsf {PT}^{K}_d(X;q)=\sum _{n\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}}q^{n}\mathsf {PT}^{K}_{d,n}(X)$ the generating series of ![]() $K$-theoretic stable pair invariants.
$K$-theoretic stable pair invariants.
Corollary 9.3 Let ![]() $X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ be a local curve. We have
$X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ be a local curve. We have
9.2 Nekrasov–Okounkov
Let ![]() $M$ be a scheme with a perfect obstruction theory
$M$ be a scheme with a perfect obstruction theory ![]() ${{\mathbb {E}}}$. Define the virtual canonical bundle to be
${{\mathbb {E}}}$. Define the virtual canonical bundle to be ![]() $K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}=\det {{\mathbb {E}}}\in \mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits (M)$. Assume that
$K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}=\det {{\mathbb {E}}}\in \mathop {\rm Pic}\nolimits (M)$. Assume that ![]() $K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ admits a square root
$K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$ admits a square root ![]() $K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}^{1/2}$, that is a line bundle such that
$K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}^{1/2}$, that is a line bundle such that ![]() $(K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}^{1/2})^{\otimes 2}\cong K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$. Nekrasov and Okounkov [Reference Nekrasov and OkounkovNO16] teach us that it is much more natural to consider the twisted virtual structure sheaf
$(K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}^{1/2})^{\otimes 2}\cong K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}}$. Nekrasov and Okounkov [Reference Nekrasov and OkounkovNO16] teach us that it is much more natural to consider the twisted virtual structure sheaf
In [Reference Nekrasov and OkounkovNO16], Nekrasov and Okounkov showed the existence of square roots for ![]() $P_X$ (and uniqueness, up to 2-torsion). Nevertheless, even if square roots could not exists on
$P_X$ (and uniqueness, up to 2-torsion). Nevertheless, even if square roots could not exists on ![]() $P_X$ as line bundles, they exist as a class
$P_X$ as line bundles, they exist as a class ![]() $K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}, P_X}^{1/2}\in K^{0}(P_X, {{\mathbb {Z}}}[\frac {1}{2}])$ and are unique [Reference Oh and ThomasOT20, Lemma 5.1]. In our setting, we define Nekrasov–Okounkov
$K_{\operatorname {\mathrm {vir}}, P_X}^{1/2}\in K^{0}(P_X, {{\mathbb {Z}}}[\frac {1}{2}])$ and are unique [Reference Oh and ThomasOT20, Lemma 5.1]. In our setting, we define Nekrasov–Okounkov ![]() $K$-theoretic stable pair invariants asFootnote 6
$K$-theoretic stable pair invariants asFootnote 6
 \begin{align*} \mathsf{PT}^{\hat{K}}_{d,n}(X)&:= \mathsf{PT}^{K}_{d,n}(X, K_{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, P_X}^{1/2})\\ &=\chi(P_n(X, d[C])^{\mathbf{T}}, \frac{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}\otimes K_{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, P_X}^{1/2}|_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}}{\Lambda^{\bullet} N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} )\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{1/2}, \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{1/2}), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \mathsf{PT}^{\hat{K}}_{d,n}(X)&:= \mathsf{PT}^{K}_{d,n}(X, K_{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, P_X}^{1/2})\\ &=\chi(P_n(X, d[C])^{\mathbf{T}}, \frac{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}\otimes K_{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, P_X}^{1/2}|_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}}{\Lambda^{\bullet} N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} )\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{1/2}, \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{1/2}), \end{align*}
which are an algebro-geometric analogue of the ![]() $\widehat {A}$-genus of a spin manifold. On the
$\widehat {A}$-genus of a spin manifold. On the ![]() $\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus, we have an identity in
$\mathbf {T}$-fixed locus, we have an identity in ![]() $K^{0}_\mathbf {T}(P_X^{\mathbf {T}}, {{\mathbb {Z}}}[\frac {1}{2}])_{\mathrm {loc}}$
$K^{0}_\mathbf {T}(P_X^{\mathbf {T}}, {{\mathbb {Z}}}[\frac {1}{2}])_{\mathrm {loc}}$
 \begin{align*} \frac{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}\otimes K_{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, P_X}^{1/2} |_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}}{\Lambda^{\bullet} N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} &= \frac{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}} \otimes K_{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{1/2}\otimes (\det N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *})^{1/2}}{{\Lambda^{\bullet} N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}}}\\ &= \frac{\widehat{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}{\widehat{\Lambda}^{\bullet} N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \frac{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}\otimes K_{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, P_X}^{1/2} |_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}}{\Lambda^{\bullet} N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} &= \frac{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}} \otimes K_{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{1/2}\otimes (\det N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *})^{1/2}}{{\Lambda^{\bullet} N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}}}\\ &= \frac{\widehat{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}{\widehat{\Lambda}^{\bullet} N^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}}, \end{align*}
where we define ![]() $\widehat {\Lambda }^{\bullet }(\cdot )=\Lambda ^{\bullet }(\cdot )\otimes \det (\cdot )^{-1/2}$. Again, the same techniques of § 5 and Proposition 9.2 and can be applied in this setting, yielding the following result.
$\widehat {\Lambda }^{\bullet }(\cdot )=\Lambda ^{\bullet }(\cdot )\otimes \det (\cdot )^{-1/2}$. Again, the same techniques of § 5 and Proposition 9.2 and can be applied in this setting, yielding the following result.
Theorem 9.4 Let ![]() $C$ be a genus
$C$ be a genus ![]() $g$ smooth irreducible projective curve and
$g$ smooth irreducible projective curve and ![]() $L_1, L_2$ line bundles over
$L_1, L_2$ line bundles over ![]() $C$. We have an identity
$C$. We have an identity
 \[ \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \chi\bigg(C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \frac{\widehat{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}{\widehat{\Lambda}^{\bullet} N_{C, L_1, L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} \bigg)=A_{\hat{K},\lambda}^{g-1}\cdot B_{\hat{K},\lambda}^{\deg L_1}\cdot C_{\hat{K},\lambda}^{\deg L_2}\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{1/2}, \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{1/2})[\![ q ]\!], \]
\[ \sum_{\mathbf{n}_\lambda}q^{|\mathbf{n}_\lambda|} \chi\bigg(C^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \frac{\widehat{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}{\widehat{\Lambda}^{\bullet} N_{C, L_1, L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} \bigg)=A_{\hat{K},\lambda}^{g-1}\cdot B_{\hat{K},\lambda}^{\deg L_1}\cdot C_{\hat{K},\lambda}^{\deg L_2}\in {{\mathbb{Q}}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{1/2}, \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2^{1/2})[\![ q ]\!], \]
where ![]() $A_{\hat {K},\lambda },B_{\hat {K},\lambda },C_{\hat {K},\lambda }\in {{\mathbb {Q}}}(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1^{1/2}, \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2^{1/2})[\![ q ]\!]$ are fixed universal series for
$A_{\hat {K},\lambda },B_{\hat {K},\lambda },C_{\hat {K},\lambda }\in {{\mathbb {Q}}}(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1^{1/2}, \operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2^{1/2})[\![ q ]\!]$ are fixed universal series for ![]() $i=1,2,3$. Moreover
$i=1,2,3$. Moreover
 \begin{align*} A_{\hat{K},\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)&=A_{\hat{K},\bar{\lambda}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1),\\ B_{\hat{K},\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)&=C_{\hat{K},\bar{\lambda}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} A_{\hat{K},\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)&=A_{\hat{K},\bar{\lambda}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1),\\ B_{\hat{K},\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2)&=C_{\hat{K},\bar{\lambda}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_2,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1). \end{align*} Denote by ![]() $\mathsf {PT}^{\hat {K}}_d(X;q)=\sum _{n\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}}q^{n}\mathsf {PT}^{\hat {K}}_{d,n}(X)$ the generating series of Nekrasov–Okounkov
$\mathsf {PT}^{\hat {K}}_d(X;q)=\sum _{n\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}}q^{n}\mathsf {PT}^{\hat {K}}_{d,n}(X)$ the generating series of Nekrasov–Okounkov ![]() $K$-theoretic stable pair invariants.
$K$-theoretic stable pair invariants.
Corollary 9.5 Let ![]() $X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ be a local curve. We have
$X=\operatorname {Tot}_C(L_1\oplus L_2)$ be a local curve. We have
The techniques of § 6, 7 can be adapted to compute the generating series of Nekrasov– Okounkov ![]() $K$-theoretic invariants under the anti-diagonal restriction
$K$-theoretic invariants under the anti-diagonal restriction ![]() $\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2=1$. In fact, as in the proof of Theorem 8.1, we just need to compute the leading term of the generating series and the cases
$\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_1\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_2=1$. In fact, as in the proof of Theorem 8.1, we just need to compute the leading term of the generating series and the cases ![]() $g=0$,
$g=0$, ![]() $L_1\otimes L_2=K_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$ and
$L_1\otimes L_2=K_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$ and ![]() $L_1=L_2=\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$. Similarly to the proof of Theorem 7.3, as we work with
$L_1=L_2=\operatorname {\mathcal {O}}_{{{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}}$. Similarly to the proof of Theorem 7.3, as we work with ![]() $C\cong {{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$, applying the
$C\cong {{\mathbb {P}}}^{1}$, applying the ![]() $K$-theoretic virtual localization formula [Reference Fantechi and GöttscheFG10] on
$K$-theoretic virtual localization formula [Reference Fantechi and GöttscheFG10] on ![]() $({{\mathbb {P}}}^{1})^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ yields
$({{\mathbb {P}}}^{1})^{[\mathbf {n}_\lambda ]}$ yields
 \[ \chi\bigg({{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \frac{\widehat{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}{\widehat{\Lambda}^{\bullet} N_{C, L_1, L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} \bigg)=\bigg(\sum_{\underline{Z} \in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda],{{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}} }\chi \bigg(\underline{Z}, \frac{1}{\widehat{\Lambda}^{\bullet}(T^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}_{{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]},\underline{Z}} +N_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},L_1,L_2, \underline{Z}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *} )}\bigg)\bigg)\bigg|_{\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_3=1}, \]
\[ \chi\bigg({{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \frac{\widehat{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}{\widehat{\Lambda}^{\bullet} N_{C, L_1, L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} \bigg)=\bigg(\sum_{\underline{Z} \in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda],{{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}} }\chi \bigg(\underline{Z}, \frac{1}{\widehat{\Lambda}^{\bullet}(T^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}_{{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]},\underline{Z}} +N_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},L_1,L_2, \underline{Z}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *} )}\bigg)\bigg)\bigg|_{\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_3=1}, \]
where ![]() $\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_3$ is the equivariant parameter of the
$\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}_3$ is the equivariant parameter of the ![]() ${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action. For a character
${{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}$-action. For a character ![]() $\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu }\in K_{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}^{0}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$, define the operator
$\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu }\in K_{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}^{0}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$, define the operator ![]() $[\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu }]=\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{{\mu }/{2}}-\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{-{\mu }/{2}}$ and extend it by linearity to any
$[\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\mu }]=\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{{\mu }/{2}}-\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{-{\mu }/{2}}$ and extend it by linearity to any ![]() $V\in K_{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}^{0}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$. It is proven in [Reference Fasola, Monavari and RicolfiFMR21, § 6.1] that
$V\in K_{\mathbf {T}\times {{\mathbb {C}}}^{*}}^{0}({{\mathsf {pt}}})$. It is proven in [Reference Fasola, Monavari and RicolfiFMR21, § 6.1] that
which satisfies ![]() $[V^{*}]=(-1)^{\operatorname {rk} V}[V]$, therefore
$[V^{*}]=(-1)^{\operatorname {rk} V}[V]$, therefore
 \[ \chi\bigg({{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \frac{\widehat{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}{\widehat{\Lambda}^{\bullet} N_{C, L_1, L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} \bigg)=\bigg(\sum_{\underline{Z} \in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda],{{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}} } [-T^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \underline{Z}}-N_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},L_1,L_2, \underline{Z}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}] \bigg)\bigg|_{\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_3=1}. \]
\[ \chi\bigg({{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \frac{\widehat{\operatorname{\mathcal{O}}}_{P_X^{\mathbf{T}}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}}{\widehat{\Lambda}^{\bullet} N_{C, L_1, L_2}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}, *}} \bigg)=\bigg(\sum_{\underline{Z} \in {{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda],{{\mathbb{C}}}^{*}} } [-T^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}_{{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1}}^{[\mathbf{n}_\lambda]}, \underline{Z}}-N_{{{\mathbb{P}}}^{1},L_1,L_2, \underline{Z}}^{\operatorname{\mathrm{vir}}}] \bigg)\bigg|_{\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_3=1}. \]Explicit computations yields
 \begin{align*} A_{\hat{K},\lambda}(q,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}_1)&=(-1)^{|\lambda|}\cdot F_\lambda^{-2},\\ B_{\hat{K}, \lambda}(-q,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}_1)&=(-1)^{n(\lambda)}\cdot F_\lambda\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)}),\\ C_{\hat{K},\lambda}(-q,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}_1)&=(-1)^{|\lambda|+n(\bar{\lambda})}F_\lambda\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)}), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} A_{\hat{K},\lambda}(q,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}_1)&=(-1)^{|\lambda|}\cdot F_\lambda^{-2},\\ B_{\hat{K}, \lambda}(-q,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}_1)&=(-1)^{n(\lambda)}\cdot F_\lambda\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)}),\\ C_{\hat{K},\lambda}(-q,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1,\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}_1)&=(-1)^{|\lambda|+n(\bar{\lambda})}F_\lambda\cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}(1-q^{h(\Box)}), \end{align*}where
 \[ F_\lambda=\prod_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (a,a)}}\frac{1}{\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{{|j-i|}/{2}}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-{|j-i|}/{2}}}\cdot \frac{\prod_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l+a,k+a)}} (\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{{|i-j+k-l|}/{2}}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-{|i-j+k-l|}/{2}}) }{\prod_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l+a-1,k+a)}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{{|1+i-j+k-l|}/{2}}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-{|1+i-j+k-l|}/{2}})}. \]
\[ F_\lambda=\prod_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (a,a)}}\frac{1}{\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{{|j-i|}/{2}}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-{|j-i|}/{2}}}\cdot \frac{\prod_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l+a,k+a)}} (\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{{|i-j+k-l|}/{2}}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-{|i-j+k-l|}/{2}}) }{\prod_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l+a-1,k+a)}}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{{|1+i-j+k-l|}/{2}}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}_1^{-{|1+i-j+k-l|}/{2}})}. \]Acknowledgements
I am grateful to M. Kool for suggesting this problem and for many helpful discussions. I wish to thank J.-W. van Ittersum and A. Ricolfi for useful discussions. I also thank the anonymous referee for helpful comments which improved the exposition of the paper. S.M. is supported by NWO grant TOP2.17.004.
Appendix A. The combinatorial identities
In this appendix, we collect the proofs of some technical results on the combinatorics of Young diagrams we have used.
Lemma A.1 Let ![]() $\lambda$ be a Young diagram and consider the Laurent polynomials in
$\lambda$ be a Young diagram and consider the Laurent polynomials in ![]() ${{\mathbb {Z}}}[\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\pm 1}]$
${{\mathbb {Z}}}[\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\pm 1}]$
 \begin{align*} g_{\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}})&=\sum_{\substack{(a,a)\in \lambda\\ a\neq 0, a\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-a} +\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)=(l+a,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1, a\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}}{{\mathrm{sgn}}}(a)\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a} - \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)= (l+a-1,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1, a\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}}{{\mathrm{sgn}}}(a)\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a},\\ h_{\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}})&=\sum_{\substack{(a,a)\in \lambda\\ a\neq 0, a\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-a} -\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)=(l+a,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1, a\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a} + \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)= (l+a-1,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1, a\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a}. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} g_{\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}})&=\sum_{\substack{(a,a)\in \lambda\\ a\neq 0, a\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-a} +\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)=(l+a,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1, a\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}}{{\mathrm{sgn}}}(a)\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a} - \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)= (l+a-1,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1, a\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}}{{\mathrm{sgn}}}(a)\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a},\\ h_{\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}})&=\sum_{\substack{(a,a)\in \lambda\\ a\neq 0, a\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-a} -\sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)=(l+a,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1, a\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a} + \sum_{\substack{(i,j),(l,k)\in \lambda\\(i,j)= (l+a-1,k+a)\\a\neq 0,1, a\in {{\mathbb{Z}}}}}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{a}. \end{align*}Then we have
 \begin{align*} g_{\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}})&=A_\lambda(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}})+A_\lambda(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1})\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}},\\ h_{\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}})&=B_\lambda(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}})-B_\lambda(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1})\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} g_{\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}})&=A_\lambda(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}})+A_\lambda(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1})\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}},\\ h_{\lambda}(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}})&=B_\lambda(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}})-B_\lambda(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1})\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}, \end{align*}
where ![]() $A_{\lambda }(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}),B_{\lambda }(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}})\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}[\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\pm 1}]$.
$A_{\lambda }(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}),B_{\lambda }(\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}})\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}[\operatorname {\mathfrak {t}}^{\pm 1}]$.
Proof. We prove the first claim by induction on the size of ![]() $\lambda$. If
$\lambda$. If ![]() $|\lambda |=1$ this is clear. Now suppose that the claim holds for all Young diagrams of size
$|\lambda |=1$ this is clear. Now suppose that the claim holds for all Young diagrams of size ![]() $|\lambda |=n$ and consider a Young diagram of size
$|\lambda |=n$ and consider a Young diagram of size ![]() $|\tilde {\lambda }|=n+1$ obtained by adding to a Young diagram
$|\tilde {\lambda }|=n+1$ obtained by adding to a Young diagram ![]() $\lambda$ a box whose lattice coordinates are
$\lambda$ a box whose lattice coordinates are ![]() $(i,j)\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}^{2}$:
$(i,j)\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}^{2}$:
•
 $(i,j)=(i,0)$ or
$(i,j)=(i,0)$ or  $(i,j)=(0,j)$, with
$(i,j)=(0,j)$, with  $i,j\neq 0$, we have
$i,j\neq 0$, we have
 \[ g_{\tilde{\lambda}}=g_{\lambda}; \]
\[ g_{\tilde{\lambda}}=g_{\lambda}; \]•
 $(i,j)=(i,1)$,
$(i,j)=(i,1)$,  $i\geq 1$, we have
$i\geq 1$, we have
 \begin{align*} g_{\tilde{\lambda}}&=g_{\lambda}+\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}\\ &=g_{\lambda}; \end{align*}
\begin{align*} g_{\tilde{\lambda}}&=g_{\lambda}+\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}\\ &=g_{\lambda}; \end{align*}•
 $(i,j)=(1,j)$,
$(i,j)=(1,j)$,  $j\geq 2$, we have
$j\geq 2$, we have
 \begin{align*} g_{\tilde{\lambda}}&=g_{\lambda}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{2}\\ &=g_{\lambda}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}-(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1})^{-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}; \end{align*}
\begin{align*} g_{\tilde{\lambda}}&=g_{\lambda}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{2}\\ &=g_{\lambda}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1}-(\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-1})^{-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}; \end{align*}•
 $(i,j)=(i,i)$,
$(i,j)=(i,i)$,  $i\geq 2$, we have
$i\geq 2$, we have
 \begin{align*} g_{\tilde{\lambda}}&=g_{\lambda}+\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-i}- \sum_{l=1}^{i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-l}+\sum_{l=2}^{i} \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{l}- \bigg(\sum_{l=2}^{i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{l}-\sum_{l=1}^{i-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-l}\bigg)\\ &=g_{\lambda}; \end{align*}
\begin{align*} g_{\tilde{\lambda}}&=g_{\lambda}+\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-i}- \sum_{l=1}^{i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-l}+\sum_{l=2}^{i} \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{l}- \bigg(\sum_{l=2}^{i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{l}-\sum_{l=1}^{i-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-l}\bigg)\\ &=g_{\lambda}; \end{align*}•
 $(i,j)$,
$(i,j)$,  $i> j\geq 2$, we have
$i> j\geq 2$, we have
 \begin{align*} g_{\tilde{\lambda}}&=g_{\lambda}-\sum_{l=1}^{j}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-l}+ \sum_{l=2}^{j} \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{l}-\bigg(\sum_{l=2}^{j}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{l}-\sum_{l=1}^{j}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-l}\bigg)\\ &=g_{\lambda}; \end{align*}
\begin{align*} g_{\tilde{\lambda}}&=g_{\lambda}-\sum_{l=1}^{j}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-l}+ \sum_{l=2}^{j} \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{l}-\bigg(\sum_{l=2}^{j}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{l}-\sum_{l=1}^{j}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-l}\bigg)\\ &=g_{\lambda}; \end{align*}•
 $(i,j)$,
$(i,j)$,  $j> i\geq 2$, we have
$j> i\geq 2$, we have
 \begin{align*} g_{\tilde{\lambda}}&=g_{\lambda}-\sum_{l=1}^{i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-l}+ \sum_{l=2}^{i} \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{l}-\bigg(\sum_{l=2}^{i+1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{l}- \sum_{l=1}^{i-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-l}\bigg)\\ &=g_{\lambda}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-i}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{i+1}; \end{align*}
\begin{align*} g_{\tilde{\lambda}}&=g_{\lambda}-\sum_{l=1}^{i}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-l}+ \sum_{l=2}^{i} \operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{l}-\bigg(\sum_{l=2}^{i+1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{l}- \sum_{l=1}^{i-1}\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-l}\bigg)\\ &=g_{\lambda}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{-i}-\operatorname{\mathfrak{t}}^{i+1}; \end{align*}
Therefore, the induction step is proven in all possible cases and we conclude the proof.
With an analogous analysis one proves the second claim as well.
Lemma A.2 Let ![]() $\lambda$ be a Young diagram. Then the following identity holds:
$\lambda$ be a Young diagram. Then the following identity holds:
 \[ \prod_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (a,a)}}(j-i)\cdot \frac{\prod_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j) \neq (l+a-1,k+a)}} (1+i-j+k-l)}{\prod_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k) \in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l+a,k+a)}} (i-j+k-l)}=\sigma(\lambda) \cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box), \]
\[ \prod_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (a,a)}}(j-i)\cdot \frac{\prod_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j) \neq (l+a-1,k+a)}} (1+i-j+k-l)}{\prod_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k) \in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l+a,k+a)}} (i-j+k-l)}=\sigma(\lambda) \cdot\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box), \]where
 \begin{align*} \sigma(\lambda) & = \prod_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (a,a)}}{{\mathrm{sgn}}}(j-i)\cdot \prod_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l+a-1,k+a)}} {{\mathrm{sgn}}}(1\!+\!i\!-\!j\!+\!k\!-\!l) \cdot\prod_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l+a,k+a)}} {{\mathrm{sgn}}}(i\!-\!j\!+\!k\!-\!l). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \sigma(\lambda) & = \prod_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\(i,j)\neq (a,a)}}{{\mathrm{sgn}}}(j-i)\cdot \prod_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l+a-1,k+a)}} {{\mathrm{sgn}}}(1\!+\!i\!-\!j\!+\!k\!-\!l) \cdot\prod_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l+a,k+a)}} {{\mathrm{sgn}}}(i\!-\!j\!+\!k\!-\!l). \end{align*}Proof. The sign ![]() $\sigma (\lambda )$ is easily determined, so we just need to compute the absolute value. To ease the notation, we adopt the following convention for the remainder of the proof: we set
$\sigma (\lambda )$ is easily determined, so we just need to compute the absolute value. To ease the notation, we adopt the following convention for the remainder of the proof: we set ![]() $|0|=1$, which is merely a formal shortcut to include in the productory trivial factors we would have otherwise excluded. The claim therefore becomes
$|0|=1$, which is merely a formal shortcut to include in the productory trivial factors we would have otherwise excluded. The claim therefore becomes
 \begin{equation} \prod_{(i,j)\in \lambda}|i-j|\cdot \prod_{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda}\frac{ |1+i-j+k-l|}{|i-j+k-l|}=\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box). \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \prod_{(i,j)\in \lambda}|i-j|\cdot \prod_{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda}\frac{ |1+i-j+k-l|}{|i-j+k-l|}=\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box). \end{equation}
Denote the left-hand side of (A.1) by ![]() $H_\lambda$. We prove this claim on the induction on the size of
$H_\lambda$. We prove this claim on the induction on the size of ![]() $\lambda$. If
$\lambda$. If ![]() $|\lambda |=1$, the claim is trivially satisfied. Assume it holds for all Young diagrams of size
$|\lambda |=1$, the claim is trivially satisfied. Assume it holds for all Young diagrams of size ![]() $n$ and consider a Young diagram
$n$ and consider a Young diagram ![]() $\lambda '$ of size
$\lambda '$ of size ![]() $n+1$ obtained by a Young diagram of size
$n+1$ obtained by a Young diagram of size ![]() $\lambda$ by adding a box with lattice coordinates
$\lambda$ by adding a box with lattice coordinates ![]() $(i,j)\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}^{2}$. We have
$(i,j)\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}^{2}$. We have
 \[ H_{\lambda'}=H_\lambda\cdot |i-j|\cdot \prod_{(l,k)\in \lambda}\frac{|1+i-j+k-l|}{|i-j+k-l|}\cdot\frac{|-1+i-j+k-l|}{|i-j+k-l|}. \]
\[ H_{\lambda'}=H_\lambda\cdot |i-j|\cdot \prod_{(l,k)\in \lambda}\frac{|1+i-j+k-l|}{|i-j+k-l|}\cdot\frac{|-1+i-j+k-l|}{|i-j+k-l|}. \]
To avoid confusion, we denote by ![]() $h(\Box )$ (respectively,
$h(\Box )$ (respectively, ![]() $h'(\Box )$) the hooklength of
$h'(\Box )$) the hooklength of ![]() $\Box \in \lambda$ (respectively,
$\Box \in \lambda$ (respectively, ![]() $\Box \in \lambda '$). The strategy now is to divide the boxes of
$\Box \in \lambda '$). The strategy now is to divide the boxes of ![]() $\lambda '$ in sub-collections and compute separately each contribution of the product on the right-hand side.
$\lambda '$ in sub-collections and compute separately each contribution of the product on the right-hand side.
Step I. Fix a box ![]() $(\tilde {i}, j)\in \lambda$, with
$(\tilde {i}, j)\in \lambda$, with ![]() $\tilde {i}< i$. The contribution of all boxes on the right (on the same row) of
$\tilde {i}< i$. The contribution of all boxes on the right (on the same row) of ![]() $(\tilde {i},j)$ is
$(\tilde {i},j)$ is
 \begin{align*} &\prod_{k=j}^{\lambda_{\tilde{i}}-1} \frac{|i-j+k-\tilde{i}+1|\cdot|i-j+k-\tilde{i}-1|}{|i-j+k -\tilde{i}|\cdot|i-j+k-\tilde{i}|}\\ &\quad =\frac{|i-\tilde{i}+1|\cdot|i-\tilde{i}-1|}{|i- \tilde{i}|\cdot|i-\tilde{i}|}\cdot\frac{|i-\tilde{i}+2|\cdot|i- \tilde{i}|}{|i-\tilde{i}+1|\cdot|i-\tilde{i}+1|}\cdots\frac{|i- \tilde{i}+\lambda_{\tilde{i}}-j|\cdot|i-\tilde{i}+\lambda_{\tilde{i}}- j-2|}{|i-\tilde{i}+\lambda_{\tilde{i}}-j-1|\cdot|i-\tilde{i} +\lambda_{\tilde{i}}-j-1|}\\ &\quad =\frac{|i-\tilde{i}-1|\cdot|i-\tilde{i}+\lambda_{\tilde{i}}-j|}{|i- \tilde{i}|\cdot|i-\tilde{i}+\lambda_{\tilde{i}}-j-1|}\\ &\quad =\frac{|i-\tilde{i}-1|}{|i-\tilde{i}|}\cdot\frac{h'(\tilde{i}, j)}{h(\tilde{i},j)}. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &\prod_{k=j}^{\lambda_{\tilde{i}}-1} \frac{|i-j+k-\tilde{i}+1|\cdot|i-j+k-\tilde{i}-1|}{|i-j+k -\tilde{i}|\cdot|i-j+k-\tilde{i}|}\\ &\quad =\frac{|i-\tilde{i}+1|\cdot|i-\tilde{i}-1|}{|i- \tilde{i}|\cdot|i-\tilde{i}|}\cdot\frac{|i-\tilde{i}+2|\cdot|i- \tilde{i}|}{|i-\tilde{i}+1|\cdot|i-\tilde{i}+1|}\cdots\frac{|i- \tilde{i}+\lambda_{\tilde{i}}-j|\cdot|i-\tilde{i}+\lambda_{\tilde{i}}- j-2|}{|i-\tilde{i}+\lambda_{\tilde{i}}-j-1|\cdot|i-\tilde{i} +\lambda_{\tilde{i}}-j-1|}\\ &\quad =\frac{|i-\tilde{i}-1|\cdot|i-\tilde{i}+\lambda_{\tilde{i}}-j|}{|i- \tilde{i}|\cdot|i-\tilde{i}+\lambda_{\tilde{i}}-j-1|}\\ &\quad =\frac{|i-\tilde{i}-1|}{|i-\tilde{i}|}\cdot\frac{h'(\tilde{i}, j)}{h(\tilde{i},j)}. \end{align*}
We now multiply the last expression for all boxes ![]() $(\tilde {i}, j)$ with
$(\tilde {i}, j)$ with ![]() $\tilde {i}=0,\ldots, i-1$
$\tilde {i}=0,\ldots, i-1$
 \begin{align*} \prod_{\tilde{i}=0}^{i-1}\frac{|i-\tilde{i}-1|}{|i-\tilde{i}|}\cdot\frac{h'(\tilde{i},j)}{h(\tilde{i},j)}&= \frac{|i-1|}{|i|}\cdot \frac{|i-2|}{|i-1|}\cdots \frac{|0|}{|1|}\cdot\prod_{\tilde{i}=0}^{i-1}\frac{h'(\tilde{i},j)}{h(\tilde{i},j)}\\ &=\frac{1}{|i|}\cdot\prod_{\tilde{i}=0}^{i-1}\frac{h'(\tilde{i},j)}{h(\tilde{i},j)}. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \prod_{\tilde{i}=0}^{i-1}\frac{|i-\tilde{i}-1|}{|i-\tilde{i}|}\cdot\frac{h'(\tilde{i},j)}{h(\tilde{i},j)}&= \frac{|i-1|}{|i|}\cdot \frac{|i-2|}{|i-1|}\cdots \frac{|0|}{|1|}\cdot\prod_{\tilde{i}=0}^{i-1}\frac{h'(\tilde{i},j)}{h(\tilde{i},j)}\\ &=\frac{1}{|i|}\cdot\prod_{\tilde{i}=0}^{i-1}\frac{h'(\tilde{i},j)}{h(\tilde{i},j)}. \end{align*}
This is the contribution of all boxes ![]() $(l,k)\in \lambda$ such that
$(l,k)\in \lambda$ such that ![]() $k\geq j$. By symmetry, we obtain that the contribution of all boxes
$k\geq j$. By symmetry, we obtain that the contribution of all boxes ![]() $(l,k)\in \lambda$ such that
$(l,k)\in \lambda$ such that ![]() $l\geq i$ is given by
$l\geq i$ is given by
 \[ \frac{1}{|j|}\cdot\prod_{\tilde{j}=0}^{j-1}\frac{h'(i,\tilde{j})}{h(i,\tilde{j})}. \]
\[ \frac{1}{|j|}\cdot\prod_{\tilde{j}=0}^{j-1}\frac{h'(i,\tilde{j})}{h(i,\tilde{j})}. \]Step II. The contribution of the remaining boxes is given by
 \begin{align*} &|i-j|\cdot \prod_{\substack{(l,k)\in \lambda\\ l< i \\ k< j}} \frac{|1+i-j+k-l|}{|i-j+k-l|}\cdot\frac{|-1+i-j+k-l|}{|i-j+k-l|} \\ &\quad =|i-j|\cdot \prod_{l=0}^{i-1}\prod_{k=0}^{j-1}\frac{|1+i-j+k-l|}{|i-j+k-l|}\cdot\frac{ |-1+i-j+k-l|}{|i-j+k-l|} \\ &\quad =|i-j|\cdot \prod_{l=0}^{i-1}\frac{|i-l-j-1|\cdot |i-l|}{|i-l-j|\cdot |i-l-1|} =|i-j|\cdot\frac{|i|\cdot |j|}{|i-j|}=|i|\cdot |j|. \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &|i-j|\cdot \prod_{\substack{(l,k)\in \lambda\\ l< i \\ k< j}} \frac{|1+i-j+k-l|}{|i-j+k-l|}\cdot\frac{|-1+i-j+k-l|}{|i-j+k-l|} \\ &\quad =|i-j|\cdot \prod_{l=0}^{i-1}\prod_{k=0}^{j-1}\frac{|1+i-j+k-l|}{|i-j+k-l|}\cdot\frac{ |-1+i-j+k-l|}{|i-j+k-l|} \\ &\quad =|i-j|\cdot \prod_{l=0}^{i-1}\frac{|i-l-j-1|\cdot |i-l|}{|i-l-j|\cdot |i-l-1|} =|i-j|\cdot\frac{|i|\cdot |j|}{|i-j|}=|i|\cdot |j|. \end{align*}Step III. Using steps I and II and the induction step we have
 \begin{align*} H_{\lambda'}&=\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)\cdot \prod_{\tilde{i}=0}^{i-1} \frac{h'(\tilde{i},j)}{h(\tilde{i},j)}\cdot\prod_{\tilde{j}=0}^{j-1} \frac{h'(i,\tilde{j})}{h(i,\tilde{j})}\\ &=\prod_{\Box\in \lambda'}h'(\Box), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} H_{\lambda'}&=\prod_{\Box\in \lambda}h(\Box)\cdot \prod_{\tilde{i}=0}^{i-1} \frac{h'(\tilde{i},j)}{h(\tilde{i},j)}\cdot\prod_{\tilde{j}=0}^{j-1} \frac{h'(i,\tilde{j})}{h(i,\tilde{j})}\\ &=\prod_{\Box\in \lambda'}h'(\Box), \end{align*}which concludes the proof.
Lemma A.3 Let ![]() $\lambda$ be a Young diagram and
$\lambda$ be a Young diagram and ![]() $k_1, k_2\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$. Set
$k_1, k_2\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}$. Set
 \begin{align*} \rho(\lambda)&=\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\(i,j) \neq (a,a)}}(i k_1+jk_2)+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l+a-1,k+a)}} ((i-l+1)k_1+(j-k)k_2)\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j) \neq (l+a,k+a)}} ((i-l)k_1+(j-k)k_2). \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \rho(\lambda)&=\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\(i,j) \neq (a,a)}}(i k_1+jk_2)+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)\neq (l+a-1,k+a)}} ((i-l+1)k_1+(j-k)k_2)\\ &\quad +\sum_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j) \neq (l+a,k+a)}} ((i-l)k_1+(j-k)k_2). \end{align*}We have
where ![]() $\sigma (\lambda )$ was defined in Lemma A.2.
$\sigma (\lambda )$ was defined in Lemma A.2.
Proof. Let ![]() $\equiv$ denote congruence modulo two. We have
$\equiv$ denote congruence modulo two. We have
 \begin{align*} &\rho(\lambda)+ |\lambda|(k_1+k_2)\nonumber\\ &\quad \equiv\sum_{(i,j)\in \lambda}(i k_1+jk_2)+ (k_1+k_2)\bigg(\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)= (a,a)}}a+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)= (l+a-1,k+a)}} a+\sum_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)= (l+a,k+a)}} a\bigg)\\ &\qquad +k_1\sum_{(i,j), (l.k)\in \lambda}1+ |\lambda|(k_1+k_2)\\ &\quad\equiv n(\lambda)k_1+n(\bar{\lambda})k_2+ |\lambda|k_2 +(k_1+k_2)\bigg(\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\(i,j)= (a,a)}}a+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)= (l+a-1,k+a)}} a+\sum_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)= (l+a,k+a)}} a\bigg), \end{align*}
\begin{align*} &\rho(\lambda)+ |\lambda|(k_1+k_2)\nonumber\\ &\quad \equiv\sum_{(i,j)\in \lambda}(i k_1+jk_2)+ (k_1+k_2)\bigg(\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)= (a,a)}}a+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)= (l+a-1,k+a)}} a+\sum_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)= (l+a,k+a)}} a\bigg)\\ &\qquad +k_1\sum_{(i,j), (l.k)\in \lambda}1+ |\lambda|(k_1+k_2)\\ &\quad\equiv n(\lambda)k_1+n(\bar{\lambda})k_2+ |\lambda|k_2 +(k_1+k_2)\bigg(\sum_{\substack{(i,j)\in \lambda\\(i,j)= (a,a)}}a+ \sum_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)= (l+a-1,k+a)}} a+\sum_{\substack{(i,j), (l,k)\in \lambda\\ (i,j)= (l+a,k+a)}} a\bigg), \end{align*}therefore the statement of the lemma reduces to the following claim:
Given a lattice point ![]() $\mu =(\mu _1, \mu _2)\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}^{2}$ define
$\mu =(\mu _1, \mu _2)\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}^{2}$ define
 \begin{align*} \tau(\mu)=\begin{cases}(-1)^{\mu_1} & \mu_1=\mu_2,\\ {{\mathrm{sgn}}}(\mu_1-\mu_2) & \mu_1\neq \mu_2. \end{cases} \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \tau(\mu)=\begin{cases}(-1)^{\mu_1} & \mu_1=\mu_2,\\ {{\mathrm{sgn}}}(\mu_1-\mu_2) & \mu_1\neq \mu_2. \end{cases} \end{align*}Note that the left-hand side of (A.2) can be rewritten as
and denote this last expression by ![]() $F_\lambda$. We prove the claim (A.2) on induction on the size of
$F_\lambda$. We prove the claim (A.2) on induction on the size of ![]() $\lambda$. If
$\lambda$. If ![]() $|\lambda |=1$, the result is clear. Assume it holds for all Young diagrams of size
$|\lambda |=1$, the result is clear. Assume it holds for all Young diagrams of size ![]() $n$ and consider a Young diagram
$n$ and consider a Young diagram ![]() $\lambda '$ of size
$\lambda '$ of size ![]() $n+1$ obtained from a Young diagram of size
$n+1$ obtained from a Young diagram of size ![]() $\lambda$ by adding a box with lattice coordinates
$\lambda$ by adding a box with lattice coordinates ![]() $(i,j)\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}^{2}$; we have
$(i,j)\in {{\mathbb {Z}}}^{2}$; we have
We analyze the contribution of every box ![]() $(l,k)\in \lambda$ in the product above. We say that a box
$(l,k)\in \lambda$ in the product above. We say that a box ![]() $(l,k)$ is in the same diagonal as
$(l,k)$ is in the same diagonal as ![]() $(i,j)$ if it is of the form
$(i,j)$ if it is of the form
The contribution of the boxes on the same diagonal of ![]() $(i,j)$ is
$(i,j)$ is
We say that a box ![]() $(l,k)$ is in the lower diagonal of
$(l,k)$ is in the lower diagonal of ![]() $(i,j)$ if it is of the form
$(i,j)$ if it is of the form
The contribution of the boxes in the lower diagonal of ![]() $(i,j)$ is
$(i,j)$ is
We say that a box ![]() $(l,k)$ is in the upper diagonal of
$(l,k)$ is in the upper diagonal of ![]() $(i,j)$ if it is of the form
$(i,j)$ if it is of the form
The contribution of the boxes in the upper diagonal of ![]() $(i,j)$ is
$(i,j)$ is
A completely analogous analysis shows that all other boxes ![]() $(i,j)\in \lambda$ do not contribute to the product. Therefore, the contribution to the sign in the product is just given by the boxes in the upper or lower diagonal of
$(i,j)\in \lambda$ do not contribute to the product. Therefore, the contribution to the sign in the product is just given by the boxes in the upper or lower diagonal of ![]() $(i,j)$, as displayed in Figure A.1.
$(i,j)$, as displayed in Figure A.1.

Figure 3. The label ![]() $\pm 1$ in every box represents the contribution to the final sign, with
$\pm 1$ in every box represents the contribution to the final sign, with ![]() $(i,j)=(2,3)$.
$(i,j)=(2,3)$.
If we denote by ![]() $\delta _{+}$ and
$\delta _{+}$ and ![]() $\delta _{-}$ the number of boxes in the upper diagonal and lower diagonal, respectively, we conclude that
$\delta _{-}$ the number of boxes in the upper diagonal and lower diagonal, respectively, we conclude that
where ![]() $\lceil \cdot \rceil,\lfloor \cdot \rfloor$ denote the usual ceiling and floor functions. One readily proves that
$\lceil \cdot \rceil,\lfloor \cdot \rfloor$ denote the usual ceiling and floor functions. One readily proves that
 \begin{align*} (\delta_+, \delta_{-})= \begin{cases} (j+1,j) & i>j,\\ (i,i) & i=j,\\ (i,i+1) & i< j. \end{cases} \end{align*}
\begin{align*} (\delta_+, \delta_{-})= \begin{cases} (j+1,j) & i>j,\\ (i,i) & i=j,\\ (i,i+1) & i< j. \end{cases} \end{align*}With a direct analysis we can show that
in all the three cases, by which we conclude the inductive step.