We present a new radio continuum study of the Large Magellanic Cloud supernova remnant (SNR) MC SNR J0519–6902. With a diameter of 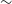 $\sim$8 pc, this SNR shows a radio ring-like morphology with three bright regions towards the north, east, and south. Its linear polarisation is prominent with average values of
$\sim$8 pc, this SNR shows a radio ring-like morphology with three bright regions towards the north, east, and south. Its linear polarisation is prominent with average values of 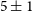 $5\pm1$% and
$5\pm1$% and 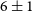 $6\pm1$% at 5 500 and 9 000 MHz, and we find a spectral index of
$6\pm1$% at 5 500 and 9 000 MHz, and we find a spectral index of 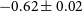 ${-0.62\pm0.02}$, typical of a young SNR. The average rotation measure is estimated at
${-0.62\pm0.02}$, typical of a young SNR. The average rotation measure is estimated at 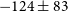 ${-124\pm83}$ rad m
${-124\pm83}$ rad m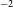 $^{-2}$ and the magnetic field strength at
$^{-2}$ and the magnetic field strength at 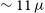 ${\sim11}\,\mu$G. We also estimate an equipartition magnetic field of
${\sim11}\,\mu$G. We also estimate an equipartition magnetic field of 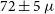 ${72\pm 5}\,\mu$G and minimum explosion energy of E
${72\pm 5}\,\mu$G and minimum explosion energy of E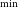 $_\textrm{ min}$ = 2.6
$_\textrm{ min}$ = 2.6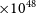 $\times10^{48}$ erg. Finally, we identified an H i cloud that may be associated with MC SNR J0519–6902, located in the southeastern part of the remnant, along with a potential wind-bubble cavity.
$\times10^{48}$ erg. Finally, we identified an H i cloud that may be associated with MC SNR J0519–6902, located in the southeastern part of the remnant, along with a potential wind-bubble cavity.