Article contents
Bulk scaling in wall-bounded and homogeneous vertical natural convection
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 March 2018
Abstract
Previous numerical studies on homogeneous Rayleigh–Bénard convection, which is Rayleigh–Bénard convection (RBC) without walls, and therefore without boundary layers, have revealed a scaling regime that is consistent with theoretical predictions of bulk-dominated thermal convection. In this so-called asymptotic regime, previous studies have predicted that the Nusselt number ( 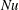 $\mathit{Nu}$ ) and the Reynolds number (
$\mathit{Nu}$ ) and the Reynolds number ( 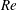 $\mathit{Re}$ ) vary with the Rayleigh number (
$\mathit{Re}$ ) vary with the Rayleigh number ( 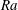 $\mathit{Ra}$ ) according to
$\mathit{Ra}$ ) according to 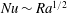 $\mathit{Nu}\sim \mathit{Ra}^{1/2}$ and
$\mathit{Nu}\sim \mathit{Ra}^{1/2}$ and 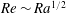 $\mathit{Re}\sim \mathit{Ra}^{1/2}$ at small Prandtl numbers (
$\mathit{Re}\sim \mathit{Ra}^{1/2}$ at small Prandtl numbers ( 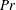 $\mathit{Pr}$ ). In this study, we consider a flow that is similar to RBC but with the direction of temperature gradient perpendicular to gravity instead of parallel to it; we refer to this configuration as vertical natural convection (VC). Since the direction of the temperature gradient is different in VC, there is no exact relation for the average kinetic dissipation rate, which makes it necessary to explore alternative definitions for
$\mathit{Pr}$ ). In this study, we consider a flow that is similar to RBC but with the direction of temperature gradient perpendicular to gravity instead of parallel to it; we refer to this configuration as vertical natural convection (VC). Since the direction of the temperature gradient is different in VC, there is no exact relation for the average kinetic dissipation rate, which makes it necessary to explore alternative definitions for 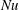 $\mathit{Nu}$ ,
$\mathit{Nu}$ , 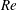 $\mathit{Re}$ and
$\mathit{Re}$ and 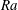 $\mathit{Ra}$ and to find physical arguments for closure, rather than making use of the exact relation between
$\mathit{Ra}$ and to find physical arguments for closure, rather than making use of the exact relation between 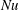 $\mathit{Nu}$ and the dissipation rates as in RBC. Once we remove the walls from VC to obtain the homogeneous set-up, we find that the aforementioned
$\mathit{Nu}$ and the dissipation rates as in RBC. Once we remove the walls from VC to obtain the homogeneous set-up, we find that the aforementioned 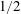 $1/2$ -power-law scaling is present, similar to the case of homogeneous RBC. When focusing on the bulk, we find that the Nusselt and Reynolds numbers in the bulk of VC too exhibit the
$1/2$ -power-law scaling is present, similar to the case of homogeneous RBC. When focusing on the bulk, we find that the Nusselt and Reynolds numbers in the bulk of VC too exhibit the 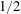 $1/2$ -power-law scaling. These results suggest that the
$1/2$ -power-law scaling. These results suggest that the 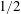 $1/2$ -power-law scaling may even be found at lower Rayleigh numbers if the appropriate quantities in the turbulent bulk flow are employed for the definitions of
$1/2$ -power-law scaling may even be found at lower Rayleigh numbers if the appropriate quantities in the turbulent bulk flow are employed for the definitions of 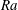 $\mathit{Ra}$ ,
$\mathit{Ra}$ , 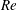 $\mathit{Re}$ and
$\mathit{Re}$ and 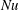 $\mathit{Nu}$ . From a stability perspective, at low- to moderate-
$\mathit{Nu}$ . From a stability perspective, at low- to moderate- 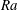 $\mathit{Ra}$ , we find that the time evolution of the Nusselt number for homogenous vertical natural convection is unsteady, which is consistent with the nature of the elevator modes reported in previous studies on homogeneous RBC.
$\mathit{Ra}$ , we find that the time evolution of the Nusselt number for homogenous vertical natural convection is unsteady, which is consistent with the nature of the elevator modes reported in previous studies on homogeneous RBC.
Information
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2018 Cambridge University Press
References
- 27
- Cited by


