Article contents
VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS TO THE INFINITY LAPLACIAN EQUATION WITH SINGULAR NONLINEAR TERMS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 March 2024
Abstract
In this paper, we study the singular boundary value problem 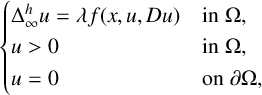 $$ \begin{align*} \begin{cases} \Delta_\infty^h u=\lambda f(x,u,Du) \quad &\mathrm{in}\; \Omega, \\ u>0\quad &\mathrm{in}\; \Omega,\\ u=0 \quad &\mathrm{on} \;\partial\Omega, \end{cases} \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \begin{cases} \Delta_\infty^h u=\lambda f(x,u,Du) \quad &\mathrm{in}\; \Omega, \\ u>0\quad &\mathrm{in}\; \Omega,\\ u=0 \quad &\mathrm{on} \;\partial\Omega, \end{cases} \end{align*} $$
where 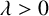 $\lambda>0$ is a parameter,
$\lambda>0$ is a parameter, 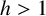 $h>1$ and
$h>1$ and 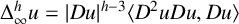 $\Delta _\infty ^h u=|Du|^{h-3} \langle D^2uDu,Du \rangle $ is the highly degenerate and h-homogeneous operator related to the infinity Laplacian. The nonlinear term
$\Delta _\infty ^h u=|Du|^{h-3} \langle D^2uDu,Du \rangle $ is the highly degenerate and h-homogeneous operator related to the infinity Laplacian. The nonlinear term 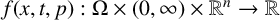 $f(x,t,p):\Omega \times (0,\infty )\times \mathbb {R}^{n}\rightarrow \mathbb {R}$ is a continuous function and may exhibit singularity at
$f(x,t,p):\Omega \times (0,\infty )\times \mathbb {R}^{n}\rightarrow \mathbb {R}$ is a continuous function and may exhibit singularity at 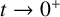 $t\rightarrow 0^{+}$. We establish the comparison principle by the double variables method for the general equation
$t\rightarrow 0^{+}$. We establish the comparison principle by the double variables method for the general equation 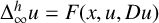 $\Delta _\infty ^h u=F(x,u,Du)$ under some conditions on the term
$\Delta _\infty ^h u=F(x,u,Du)$ under some conditions on the term 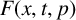 $F(x,t,p)$. Then, we establish the existence of viscosity solutions to the singular boundary value problem in a bounded domain based on Perron’s method and the comparison principle. Finally, we obtain the existence result in the entire Euclidean space by the approximation procedure. In this procedure, we also establish the local Lipschitz continuity of the viscosity solution.
$F(x,t,p)$. Then, we establish the existence of viscosity solutions to the singular boundary value problem in a bounded domain based on Perron’s method and the comparison principle. Finally, we obtain the existence result in the entire Euclidean space by the approximation procedure. In this procedure, we also establish the local Lipschitz continuity of the viscosity solution.
Keywords
MSC classification
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society , Volume 117 , Issue 3 , December 2024 , pp. 345 - 374
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of Australian Mathematical Publishing Association Inc.
Footnotes
Communicated by Florica C. Cîrstea
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 12141104)
References
- 1
- Cited by


