Contents
Research Article
Algebraic and Geometric Theory of the Topological Ring of Colombeau Generalized Functions
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2008, pp. 545-564
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Generalized Prüfer Angle and Variational Methods for p-Laplacian Eigenvalue Problems on the Half-Line
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2008, pp. 565-579
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Spectral Multipliers for Laplacians Associated with some Dirichlet Forms
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2008, pp. 581-607
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Non-Terminating Basic Hypergeometric Series and the q-Zeilberger Algorithm
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2008, pp. 609-633
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Lamé Equation, Quantum Euler Top and Elliptic Bernoulli Polynomials
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2008, pp. 635-650
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Finitary Group Cohomology and Group Actions on Spheres
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2008, pp. 651-655
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Hecke C*-Algebras, Schlichting Completions and Morita Equivalence
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2008, pp. 657-695
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Distribution of Finite Values of Meromorphic Functions with Deficient Poles
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2008, pp. 697-709
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Spectral Theory of the Klein–Gordon Equation in Krein Spaces
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2008, pp. 711-750
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Spectrum of Periodic Jacobi Matrices with Slowly Oscillating Diagonal Terms
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2008, pp. 751-763
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Vector Fields Tangent to Foliations
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2008, pp. 765-778
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Sylow Normalizers with a Normal Sylow 2-Subgroup
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2008, pp. 779-783
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On the Critical Fujita Exponent for a Degenerate Parabolic System Coupled Via Nonlinear Boundary Flux
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2008, pp. 785-805
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Book Reviews
William Dunham The Genius of Euler: Reflections on His Life and Work (Mathematical Association of America, 2007), 309 pp, 0 883 85558 5/9 780 883 85558 4 (hardback), £25.99 - C. Edward Sandifer The Early Mathematics of Leonhard Euler (Mathematical Association of America, 2007), 391 pp, 0 883 85559 3/9 780 883 85559 1 (hardback), £25.99.
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2008, pp. 807-808
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Martin Nowak Evolutionary dynamics: exploring the equations of life (Belknap Press/Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA, 2006), 384 pp, 978 0 674 02338 3 (hardback), £21.80.
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2008, pp. 808-809
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
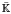 and introduce several invariants of the ideals of
and introduce several invariants of the ideals of 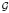 (Ω). The main tools we use are the algebraic results obtained by Aragona and Juriaans and the theory of differential calculus on generalized manifolds developed by Aragona and co-workers. The main achievement of the differential calculus is that all classical objects, such as distributions, become
(Ω). The main tools we use are the algebraic results obtained by Aragona and Juriaans and the theory of differential calculus on generalized manifolds developed by Aragona and co-workers. The main achievement of the differential calculus is that all classical objects, such as distributions, become 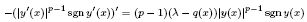
 anov. Topics include Sturmian results, connections between problems on finite intervals and the half-line, and variational principles.
anov. Topics include Sturmian results, connections between problems on finite intervals and the half-line, and variational principles.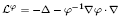 be the self-adjoint operator associated with the Dirichlet form
be the self-adjoint operator associated with the Dirichlet form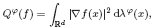
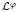 . We prove that if ϕ grows or decays at most exponentially at infinity and satisfies a suitable ‘curvature condition’, then functions which are bounded and holomorphic in the intersection of a parabolic region and a sector and satisfy Mihlin-type conditions at infinity are spectral multipliers of
. We prove that if ϕ grows or decays at most exponentially at infinity and satisfies a suitable ‘curvature condition’, then functions which are bounded and holomorphic in the intersection of a parabolic region and a sector and satisfy Mihlin-type conditions at infinity are spectral multipliers of 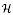 of a Hecke pair (
of a Hecke pair (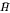 ), which is a Hecke pair whose Hecke algebra is isomorphic to
), which is a Hecke pair whose Hecke algebra is isomorphic to 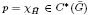 using both Fell's and Rieffel's imprimitivity theorems and the identity
using both Fell's and Rieffel's imprimitivity theorems and the identity 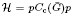 . An extended analysis of the case where
. An extended analysis of the case where