Refine search
Actions for selected content:
60619 results in Classical studies (general)
Erasmus - Erasmus. Chapters by M. M. Phillips, A. E. Douglas, J. W. Binns, B. Hall, D. F. S. Thomson, and T. A. Dorey. Edited by T. A. Dorey. (Studies in Latin Literature and its Influence.) Pp. x+163. London: Routledge, 1970. Cloth, £2·50 net.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, pp. 401-403
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cicero and the Word Popularis
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Quarterly / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 328-338
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
Lennart Rydén: Bemerkungen zum Leben des heiligen Narren Symeon von Leontios von Neapolis. Pp. 155. Uppsala: Almqvist & Wiksell, 1970. Paper, Kr.36.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, pp. 416-417
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
Semitic Loanwords in Greek - Émilia Masson: Recherches sur les plus anciens emprunts sémitiques en grec. (Études et Commentaires, lxvii.) Pp. 128. Paris: Klincksieck, 1967. Paper.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, pp. 369-370
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
Giuseppe Brocgia: Tradizione ed esegesi: studi su Esiodo e sulla lirica greca arcaica. Pp. 151. Brescia: Paideia, 1969. Paper, L.2,500.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, p. 404
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
Detlev Fehling: Die Wiederholungsfiguren und ihr Gebrauch bei den Griechen vor Gorgias. Pp. xii+358. Berlin: de Gruyter, 1969. Cloth, DM.78.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, p. 418
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Language of the Later Books of Tacitus' Annals1
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Quarterly / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 350-373
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
In Caelvm Ivsseris Ibit - Alan Cameron: Claudian: Poetry and Propaganda at the Court of Honorius. Pp. xvi+508. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1970. Cloth, £4·20.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, pp. 351-353
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mycenaean Studies the Brno Symposium - Antonín Bartoněk (ed.): Stadia Mycenaea; Proceedings of the Mycenaean Symposium, Brno, April 1966. (Opera Universitatis Purkynianae Brunensis: Facultas Philosophica, 127.) Pp. 260. Brno: Universita, 1968. Cloth, kčs.30.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, pp. 380-381
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
Plato's Psychology - T. M. Robinson: Plato's Psychology. (Phoenix Supp. Vol. xiii.) Pp. x+202. Toronto: University Press (London: Oxford University Press), 1970. Cloth, £3·15.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, pp. 335-339
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
Atrox Fortvna
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, pp. 309-311
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
Karl Plepelits: Die Fragmente der Demen des Eupolis. (Dissertationen der Universität Wien, 46.) Pp. 170. Vienna: Notring, 1970. Stiff paper, ö.S.75.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, pp. 405-406
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
Figures of Speech in Pindar - Walter Stockert: Klang figuren und Wortresponsionen bei Pindar. (Dissertationen der Universität Wien, 26.) Pp. 117. Vienna: Notring, 1969. Paper, DM. 14.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, pp. 323-324
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hector's Hair-Style
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Quarterly / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, p. 1
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Date of the Death of Lucullus
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, p. 314
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
Where are You Going to, My Pretty Maids?
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, pp. 311-313
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
Porphyry Ad Marcellam - Walter Pötscher: Porphyris, Πρ⋯ς Μαρκ⋯λλαν. Griechischer Text herausgegeben, übersetzt, eingeleitet und erklärt. Pp. x+142. Leiden: Brill, 1969. Paper, fl.48.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, pp. 344-345
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
Juvenal 8.220
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, p. 313
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Politics - Alois Dreizehnter: Aristoteles' Politik. Eingeleitet, kritisch herausgegeben und mit Indices versehen. (Studia et Testimonia Antiqua, vii.) Pp. lii+242. Munich: Fink, 1970. Paper, DM.36.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2009, pp. 339-341
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tycho Von Wilamowitz-Moellendorff on the Dramatic technique of Sophocles
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Quarterly / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / December 1972
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2009, pp. 214-228
- Print publication:
- December 1972
-
- Article
- Export citation
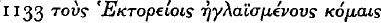 ), the source of the comment being provided by Eustathius 1276. 29, a scholion on
), the source of the comment being provided by Eustathius 1276. 29, a scholion on 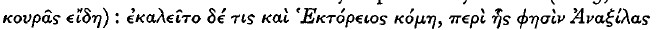
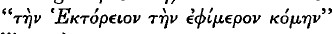 (Anaxilas,
(Anaxilas, 