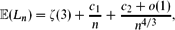Refine search
Actions for selected content:
48202 results in Computer Science
16 - Multimodal and Cross-Modal Perception: Audition
- from Part III - Perception and Modality
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Applied Perception Research
- Published online:
- 05 July 2015
- Print publication:
- 26 January 2015, pp 325-344
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
7 - Perception and Attention
- from Part II - Attention and Perceptual Processes
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Applied Perception Research
- Published online:
- 05 July 2015
- Print publication:
- 26 January 2015, pp 107-125
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part III - Perception and Modality
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Applied Perception Research
- Published online:
- 05 July 2015
- Print publication:
- 26 January 2015, pp 297-424
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
49 - Gender Differences in Time Perception
- from Part VII - Individual and Population Differences
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Applied Perception Research
- Published online:
- 05 July 2015
- Print publication:
- 26 January 2015, pp 1004-1028
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
23 - Attention in the Wild
- from Part IV - Perception in Context
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Applied Perception Research
- Published online:
- 05 July 2015
- Print publication:
- 26 January 2015, pp 466-487
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part VIII - Pedagogical and Professional Issues
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Applied Perception Research
- Published online:
- 05 July 2015
- Print publication:
- 26 January 2015, pp 1097-1128
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Dedication
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Applied Perception Research
- Published online:
- 05 July 2015
- Print publication:
- 26 January 2015, pp xix-xxiv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
About the Editors
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Applied Perception Research
- Published online:
- 05 July 2015
- Print publication:
- 26 January 2015, pp xv-xviii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
33 - Ecological Interface Design: A Selective Overview
- from Part V - Perception and Design
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Applied Perception Research
- Published online:
- 05 July 2015
- Print publication:
- 26 January 2015, pp 669-691
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
32 - Interface Design: A Control Theoretic Context for a Triadic Meaning Processing Approach
- from Part V - Perception and Design
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Applied Perception Research
- Published online:
- 05 July 2015
- Print publication:
- 26 January 2015, pp 647-668
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
17 - Haptic Perception
- from Part III - Perception and Modality
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Applied Perception Research
- Published online:
- 05 July 2015
- Print publication:
- 26 January 2015, pp 345-365
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Copyright page
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Applied Perception Research
- Published online:
- 05 July 2015
- Print publication:
- 26 January 2015, pp iv-iv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
10 - Visual Attention and Emotion: Studying Influence on a Two-Way Street
- from Part II - Attention and Perceptual Processes
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Applied Perception Research
- Published online:
- 05 July 2015
- Print publication:
- 26 January 2015, pp 175-198
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
On the Length of a Random Minimum Spanning Tree
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 25 / Issue 1 / January 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2015, pp. 89-107
-
- Article
- Export citation
ON THE ADAN–WEISS LOSS MODEL HAVING SKILL-BASED SERVERS AND LONGEST IDLE ASSIGNMENT RULE
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 29 / Issue 2 / April 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2015, pp. 181-189
-
- Article
- Export citation
HEAVY-TRAFFIC ANALYSIS OF A NON-PREEMPTIVE MULTI-CLASS QUEUE WITH RELATIVE PRIORITIES
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 29 / Issue 2 / April 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2015, pp. 153-180
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
EXTREME VALUE DISTRIBUTIONS FOR BIASED SAMPLES
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 29 / Issue 2 / April 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2015, pp. 277-290
-
- Article
- Export citation