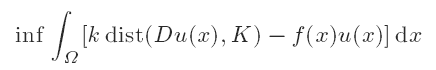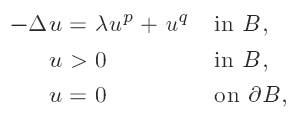Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25846 results in Abstract analysis
Existence of a solution to the line contact problem of elastohydrodynamic lubrication
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 14 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2003, pp. 279-290
-
- Article
- Export citation
Estimates for the low eigenfrequencies of a multi-structure including an elastic shell
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 14 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2003, pp. 313-342
-
- Article
- Export citation
The onset of superconductivity in long rectangles
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 14 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2003, pp. 257-277
-
- Article
- Export citation
GERMS OF CHARACTERS OF ADMISSIBLE REPRESENTATIONS OF p-ADIC GENERAL LINEAR GROUPS
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 2 / Issue 3 / July 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 July 2003, pp. 409-481
- Print publication:
- July 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Extinction and wavefront propagation in a reaction-diffusion model of a structured population with distributed maturation delay
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 527-548
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Relaxation in an L∞-optimization problem
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 599-615
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Constructing an operator from a complete and minimal set
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 653-663
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Relative normal modes for nonlinear Hamiltonian systems*
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 665-704
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the parallelizability of generalized complex projective Stiefel manifolds
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 497-504
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Interior Hölder estimates for non-parametric surfaces of prescribed mean curvature
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 625-638
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
On two functionals connected to the Laplacian in a class of doubly connected domains
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 617-624
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Constructing the symplectic Evans matrix using maximally analytic individual vectors
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 505-526
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Extensions of multilinear operators and Banach space properties
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 549-566
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exact multiplicity for semilinear elliptic Dirichlet problems involving concave and convex nonlinearities
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 705-717
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Non-existence of global smooth solutions to symmetrizable nonlinear hyperbolic systems
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 719-728
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Indefinite Sturm–Liouville problems
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 639-652
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Homogenized model for a laminar ferromagnetic medium
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 567-598
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Existence of renormalized solutions of degenerate elliptic-parabolic problems
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 477-496
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Corrigendum
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 133 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 729-730
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Oberwolfach Meeting on Combinatorics, Probability and Computing
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 12 / Issue 3 / May 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2003, p. 223
-
- Article
- Export citation