Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
67 results in 65Fxx
ANALYSIS OF THE INEXACT UZAWA ALGORITHMS FOR NONLINEAR SADDLE-POINT PROBLEMS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 51 / Issue 3 / January 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 October 2010, pp. 369-382
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ANALYSIS OF BLOCK-SOR ITERATION FOR THE THREE-DIMENSIONAL LAPLACIAN
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 50 / Issue 4 / April 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 December 2009, pp. 501-512
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The generalized condition numbers of bounded linear operators in Banach spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 76 / Issue 2 / April 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 281-290
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
THE DRAZIN INVERSES OF PRODUCTS AND DIFFERENCES OF PROJECTIONS IN A C*-ALGEBRA
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 86 / Issue 2 / April 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2009, pp. 189-198
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PERTURBATION RESULTS RELATED TO PALINDROMIC EIGENVALUE PROBLEMS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 50 / Issue 1 / July 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2008, pp. 87-100
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PERTURBATION THEORY FOR THE LU AND QR FACTORIZATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 49 / Issue 4 / April 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2008, pp. 451-461
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Infinite- and finite-buffer Markov fluid queues: a unified analysis
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 41 / Issue 2 / June 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 557-569
- Print publication:
- June 2004
-
- Article
- Export citation
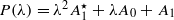 with
with 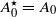 (where
(where 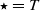 or
or 