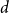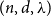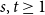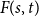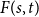Refine search
Actions for selected content:
52610 results in Statistics and Probability
8 - Multivariate Dependent Sequences
-
- Book:
- Dependence Models via Hierarchical Structures
- Published online:
- 20 March 2025
- Print publication:
- 27 March 2025, pp 118-124
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
A large language model based data generation framework to improve mild cognitive impairment detection sensitivity
-
- Journal:
- Data & Policy / Volume 7 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 March 2025, e33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hamiltonicity of sparse pseudorandom graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2025, pp. 596-620
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A central limit theorem for jump diffusion processes in the presence of round-off errors
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 57 / Issue 4 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2025, pp. 1242-1280
- Print publication:
- December 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Optimal inventory control with state-dependent jumps
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 57 / Issue 4 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 March 2025, pp. 1360-1391
- Print publication:
- December 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Global patterns and trends in deaths of influenza-associated lower respiratory infections from 1990 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 153 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 March 2025, e49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cyber risk capital
-
- Journal:
- British Actuarial Journal / Volume 30 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 March 2025, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Consideration of the proxy modelling validation framework by the proxy modelling working party
-
- Journal:
- British Actuarial Journal / Volume 30 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 March 2025, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The real-time growth rate of stochastic epidemics on random intersection graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 62 / Issue 3 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 March 2025, pp. 1132-1155
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Quantifying the direct and indirect components of COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness during the Delta variant era
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 153 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 March 2025, e59
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Robust mortality forecasting in the presence of outliers
-
- Journal:
- British Actuarial Journal / Volume 30 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 March 2025, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Moderate deviations of many–server queues via idempotent processes – Corrigendum
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 March 2025, pp. 743-747
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Antimicrobial susceptibility of gram-negative strains isolated from bloodstream infections in China: Results from the study for monitoring antimicrobial resistance trends (SMART) 2018–2020
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 153 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2025, e48
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A note on digraph splitting
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2025, pp. 559-564
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Joint mortality models based on subordinated linear hypercubes
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 55 / Issue 2 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2025, pp. 332-351
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
TIME-VARYING COMPLETE SUBSET AVERAGING IN A DATA-RICH ENVIRONMENT
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2025, pp. 1-56
-
- Article
- Export citation
Invasive group a streptococcal infection associated with community healthcare services delivered at home, South East England, December 2021–2023: Descriptive epidemiological study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 153 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2025, e56
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation

Quantitative Research Methods in Corporate Finance
- Exemplified by Stata, Python, and R
-
- Published online:
- 20 March 2025
- Print publication:
- 20 March 2025
-
- Textbook
- Export citation

Dependence Models via Hierarchical Structures
-
- Published online:
- 20 March 2025
- Print publication:
- 27 March 2025
2 - The Nature of Sampling, Non-parametric Analysis, and Hypothesis Testing
-
- Book:
- Quantitative Research Methods in Corporate Finance
- Published online:
- 20 March 2025
- Print publication:
- 20 March 2025, pp 8-20
-
- Chapter
- Export citation