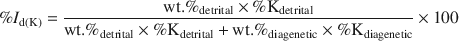Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418326 results in Open Access
Focused on the Frieze: Observations on the Soane Museum’s Adam Volume 53
-
- Journal:
- Architectural History / Volume 67 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 April 2025, pp. 1-14
- Print publication:
- 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Liquid-Phase Xylene Adsorption in Unary, Binary, and Ternary Solute Systems Using Raw and Ni2+ Ion-Exchanged Clinoptilolite: Experimental Study and Thermodynamic Assessment
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / February 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 38-49
-
- Article
- Export citation
Infrared Study of Reduced and Reduced-Reoxidized Ferruginous Smectite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 50 / Issue 4 / August 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 455-469
-
- Article
- Export citation
Extraction of diagenetic and detrital ages and of the 40Kdetrital/40Kdiagenetic ratio from K-Ar dates of clay fractions
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 57 / Issue 1 / February 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 93-103
-
- Article
- Export citation
Low-Temperature Synthesis of Micas under Conventional- and Microwave-Hydrothermal Conditions
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 51 / Issue 6 / December 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 693-700
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ni Enrichment and Stability of Al-Free Garnierite Solid-Solutions: A Thermodynamic Approach
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 60 / Issue 2 / April 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 121-135
-
- Article
- Export citation
Referees Volume 66
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 66 / Issue 6 / December 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, p. 529
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Comparison of Three Small-Scale Devices for the Investigation of the Electrical Conductivity/Resistivity of Swelling and Other Clays
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 62 / Issue 1 / February 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Modifying a Smectite using Organic Nutrients to Enhance its Efficacy at Removing Aflatoxin B1 from Corn Fermentation Solution
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 196-208
-
- Article
- Export citation
Differences in the Dehydration-Rehydration Behavior of Halloysites: New Evidence and Interpretations
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 54 / Issue 4 / August 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 473-484
-
- Article
- Export citation
An Integrated Methodological Approach for Source-Clay Determination of Ancient Ceramics: The Case of Aegina Island, Greece
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 62 / Issue 6 / December 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 447-469
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Surface Modification of Zeolite 4A and Its Effect on the Water-Absorption Capability of Starch-G-Poly (Acrylic Acid) Composite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 62 / Issue 3 / June 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 211-223
-
- Article
- Export citation
Maghemite Formation in Burnt Plant Litter at East Trinity, North Queensland, Australia
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 51 / Issue 4 / August 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 390-396
-
- Article
- Export citation
Influence of Silicate- and Magnesium-Specific Adsorption and Particle Shape on the Rheological Behavior of Mixed Serpentine-Goethite Suspensions
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 50 / Issue 3 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 342-347
-
- Article
- Export citation
Adsorptive Removal Of Ni2+ Ions From Aqueous Solutions by Nodular Sepiolite (Meerschaum) and Industrial Sepiolite Samples From Eskişehir, Turkey
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 68 / Issue 3 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 220-236
-
- Article
- Export citation
Preparation and Characterization of Ti-Pillared Clays Using Ti Alkoxides. Influence of the Synthesis Parameters
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 51 / Issue 1 / February 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 41-51
-
- Article
- Export citation
Novel method for transmission infrared analysis of clay minerals using silicon wafer substrates
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 55 / Issue 2 / April 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 213-219
-
- Article
- Export citation
ANK volume 74 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Anatolian Studies / Volume 74 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2024, pp. b1-b3
- Print publication:
- 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Role of Microbial Fe(III) Reduction and Solution Chemistry in Aggregation and Settling of Suspended Particles in the Mississippi River Delta Plain, Louisiana, USA
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 56 / Issue 4 / August 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 416-428
-
- Article
- Export citation
Halloysite-Based Nanosystems for Biomedical Applications
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 5 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 501-521
-
- Article
- Export citation