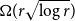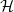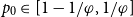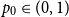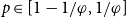Refine search
Actions for selected content:
6974 results in Algorithmics, Complexity, Computer Algebra, Computational Geometry
1 - Bridging Continuous and Discrete Optimization
-
- Book:
- Algorithms for Convex Optimization
- Published online:
- 24 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 October 2021, pp 1-16
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Acknowledgments
-
- Book:
- Algorithms for Convex Optimization
- Published online:
- 24 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 October 2021, pp xiv-xiv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Preface
-
- Book:
- Algorithms for Convex Optimization
- Published online:
- 24 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 October 2021, pp xi-xiii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- Algorithms for Convex Optimization
- Published online:
- 24 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 October 2021, pp vii-x
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
8 - Accelerated Gradient Descent
-
- Book:
- Algorithms for Convex Optimization
- Published online:
- 24 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 October 2021, pp 143-159
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
10 - An Interior Point Method for Linear Programming
-
- Book:
- Algorithms for Convex Optimization
- Published online:
- 24 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 October 2021, pp 185-214
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Index
-
- Book:
- Algorithms for Convex Optimization
- Published online:
- 24 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 October 2021, pp 319-324
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
7 - Mirror Descent and the MultiplicativeWeights Update
-
- Book:
- Algorithms for Convex Optimization
- Published online:
- 24 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 October 2021, pp 108-142
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
11 - Variants of Interior Point Method and Self-Concordance
-
- Book:
- Algorithms for Convex Optimization
- Published online:
- 24 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 October 2021, pp 215-247
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
5 - Duality and Optimality
-
- Book:
- Algorithms for Convex Optimization
- Published online:
- 24 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 October 2021, pp 69-83
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
3 - Convexity
-
- Book:
- Algorithms for Convex Optimization
- Published online:
- 24 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 October 2021, pp 35-48
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
12 - Ellipsoid Method for Linear Programming
-
- Book:
- Algorithms for Convex Optimization
- Published online:
- 24 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 October 2021, pp 248-278
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Expansion for the critical point of site percolation: the first three terms
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 31 / Issue 3 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2021, pp. 430-454
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On deficiency problems for graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 31 / Issue 3 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2021, pp. 478-488
-
- Article
- Export citation

Algorithms for Convex Optimization
-
- Published online:
- 24 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 October 2021
Strong complete minors in digraphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 31 / Issue 3 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 September 2021, pp. 489-506
-
- Article
- Export citation

An Invitation to Combinatorics
-
- Published online:
- 16 September 2021
- Print publication:
- 22 July 2021
-
- Textbook
- Export citation
On the number of Hadamard matrices via anti-concentration
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 31 / Issue 3 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 September 2021, pp. 455-477
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the edit distance function of the random graph
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 31 / Issue 2 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2021, pp. 345-367
-
- Article
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- The Discrete Mathematical Charms of Paul Erdos
- Published online:
- 05 August 2021
- Print publication:
- 26 August 2021, pp ix-xii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation