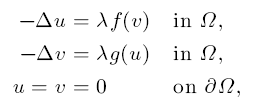Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25847 results in Abstract analysis
Bifurcation results for semilinear elliptic problems in RN
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 134 / Issue 1 / February 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 11-32
- Print publication:
- February 2004
-
- Article
- Export citation
Estimates for the energy of the solutions to elliptic Dirichlet problems on convex domains
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 134 / Issue 1 / February 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 89-107
- Print publication:
- February 2004
-
- Article
- Export citation
An existence result on positive solutions for a class of semilinear elliptic systems
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 134 / Issue 1 / February 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 137-141
- Print publication:
- February 2004
-
- Article
- Export citation
Topologically trivial holomorphic vector bundles on infinite-dimensional projective varieties
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 134 / Issue 1 / February 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 33-38
- Print publication:
- February 2004
-
- Article
- Export citation
Curvatures of complete hypersurfaces in space forms
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 134 / Issue 1 / February 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 55-68
- Print publication:
- February 2004
-
- Article
- Export citation
Uniqueness and exact multiplicity of solutions for a class of fourth-order semilinear problems
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 134 / Issue 1 / February 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 179-190
- Print publication:
- February 2004
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multiple solutions for a non-homogeneous elliptic equation at the critical exponent
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 134 / Issue 1 / February 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 69-87
- Print publication:
- February 2004
-
- Article
- Export citation
Existence of a positive solution of an elliptic equation on RN
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 134 / Issue 1 / February 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 191-200
- Print publication:
- February 2004
-
- Article
- Export citation
Closed characteristics of second-order Lagrangians
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 134 / Issue 1 / February 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 143-158
- Print publication:
- February 2004
-
- Article
- Export citation
Energy and pointwise bounds in some non-standard parabolic problems
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 134 / Issue 1 / February 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2007, pp. 1-9
- Print publication:
- February 2004
-
- Article
- Export citation
Thin film epitaxy with or without slope selection
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 14 / Issue 6 / December 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2004, pp. 713-743
-
- Article
- Export citation
Blow-up in a fourth-order semilinear parabolic equation from explosion-convection theory
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 14 / Issue 6 / December 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2004, pp. 745-764
-
- Article
- Export citation
Similarity solutions to an averaged model for superconducting vortex motion
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 14 / Issue 6 / December 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2004, pp. 639-675
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hopf bifurcation of spike solutions for the shadow Gierer–Meinhardt model
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 14 / Issue 6 / December 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2004, pp. 677-711
-
- Article
- Export citation
Influences in Product Spaces: KKL and BKKKL Revisited
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 13 / Issue 1 / January 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 January 2004, pp. 17-29
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Turán Theorem for Random Graphs
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 13 / Issue 1 / January 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 January 2004, pp. 61-91
-
- Article
- Export citation
Extremal Combinatorics: with Applications in Computer Science by Stasys Jukna, Springer, 2001, xvii + 375 pp. £32.50; $49.95, ISBN 3–540–66313–4
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 13 / Issue 1 / January 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 January 2004, pp. 119-121
-
- Article
- Export citation
Large Topological Cliques in Graphs Without a 4-Cycle
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 13 / Issue 1 / January 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 January 2004, pp. 93-102
-
- Article
- Export citation
On Generalized Random Railways
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 13 / Issue 1 / January 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 January 2004, pp. 31-35
-
- Article
- Export citation
Random Assignment with Integer Costs
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 13 / Issue 1 / January 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 January 2004, pp. 103-113
-
- Article
- Export citation